22.09.21 수요일
📝 useState 응용
✏️ 초기 상태 설정
import { useState } from 'react';
const IterationSample = () => {
const [names, setNames] = useState([
{ id: 1, text: '눈사람' },
{ id: 2, text: '얼음' },
{ id: 3, text: '눈' },
{ id: 4, text: '바람' },
]);
const [inputText, setInputText] = useState('');
const [nextId, setNextId] = useState(5); // 새로운 항목을 추가할 때 사용할 id
const nameList = names.map(name => <li key={name.id}>{name.text}</li>);
return (
<>
<ul>{nameList}</ul>;
</>
);
}
export default IterationSample;✏️ 데이터 추가 기능 구현
import { useState } from 'react';
const IterationSample = () => {
const [names, setNames] = useState([
{ id: 1, text: '눈사람' },
{ id: 2, text: '얼음' },
{ id: 3, text: '눈' },
{ id: 4, text: '바람' },
]);
const [inputText, setInputText] = useState('');
const [nextId, setNextId] = useState(5); // 새로운 항목을 추가할 때 사용할 id
const onChange = (e) => {
setInputText(e.target.value);
};
const onClick = () => {
const nextNames = names.concat({
id: nextId, // nextId 값을 id로 설정
text: inputText,
});
setNextId(nextId + 1); // nextId값에 1을 더해준다.
setNames(nextNames); // names 값을 업데이트한다.
setInputText(''); // inputText를 비운다.
// 값이 들어오면 그 값 이 inputText가 되겠다.
};
const nameList = names.map((name) => <li key={name.id}>{name.text}</li>);
return (
<>
<input value={inputText} onChange={onChange} />
<button onClick={onClick}>추가</button>
<ul>{nameList}</ul>
</>
);
};
export default IterationSample;✏️ 데이터 제거 기능 구현
import { useState } from 'react';
const IterationSample = () => {
const [names, setNames] = useState([
{ id: 1, text: '눈사람' },
{ id: 2, text: '얼음' },
{ id: 3, text: '눈' },
{ id: 4, text: '바람' },
]);
const [inputText, setInputText] = useState('');
const [nextId, setNextId] = useState(5); // 새로운 항목을 추가할 때 사용할 id
const onChange = (e) => {
setInputText(e.target.value);
};
const onClick = () => {
const nextNames = names.concat({
id: nextId, // nextId 값을 id로 설정
text: inputText,
});
setNextId(nextId + 1); // nextId값에 1을 더해준다.
setNames(nextNames); // names 값을 업데이트한다.
setInputText(''); // inputText를 비운다.
// 값이 들어오면 그 값 이 inputText가 되겠다.
};
const onRemove = (id) => {
const nextNames = names.filter((name) => name.id !== id);
setNames(nextNames);
};
const nameList = names.map((name) => (
<li key={name.id} onDoubleClick={() => onRemove(name.id)}>
{name.text}
</li>
));
return (
<>
<input value={inputText} onChange={onChange} />
<button onClick={onClick}>추가</button>
<ul>{nameList}</ul>
</>
);
};
export default IterationSample;
📝 javascript-37 : 화살표함수, 고차함수

📝 javascript-38 : 삼항연산자 (ternary operator)
if()문의 단점 : 영역(scope)이 깊어져 가독성이 매우 떨어지는 현상이 발생

복잡한 중첩처리도 가능하기때문에, 익숙해질수록 생산성이 매우 높아짐
📝 javascript-39 : 생성자함수 (constructor function)
두가지 방식의 생성자함수 생성법

📝 javascript-40 : 생성자함수 extends문법
기존 생성자함수의 기능들을 그대로 상속받아 다른 생성자 함수를 만드려면
extends 문법을 사용
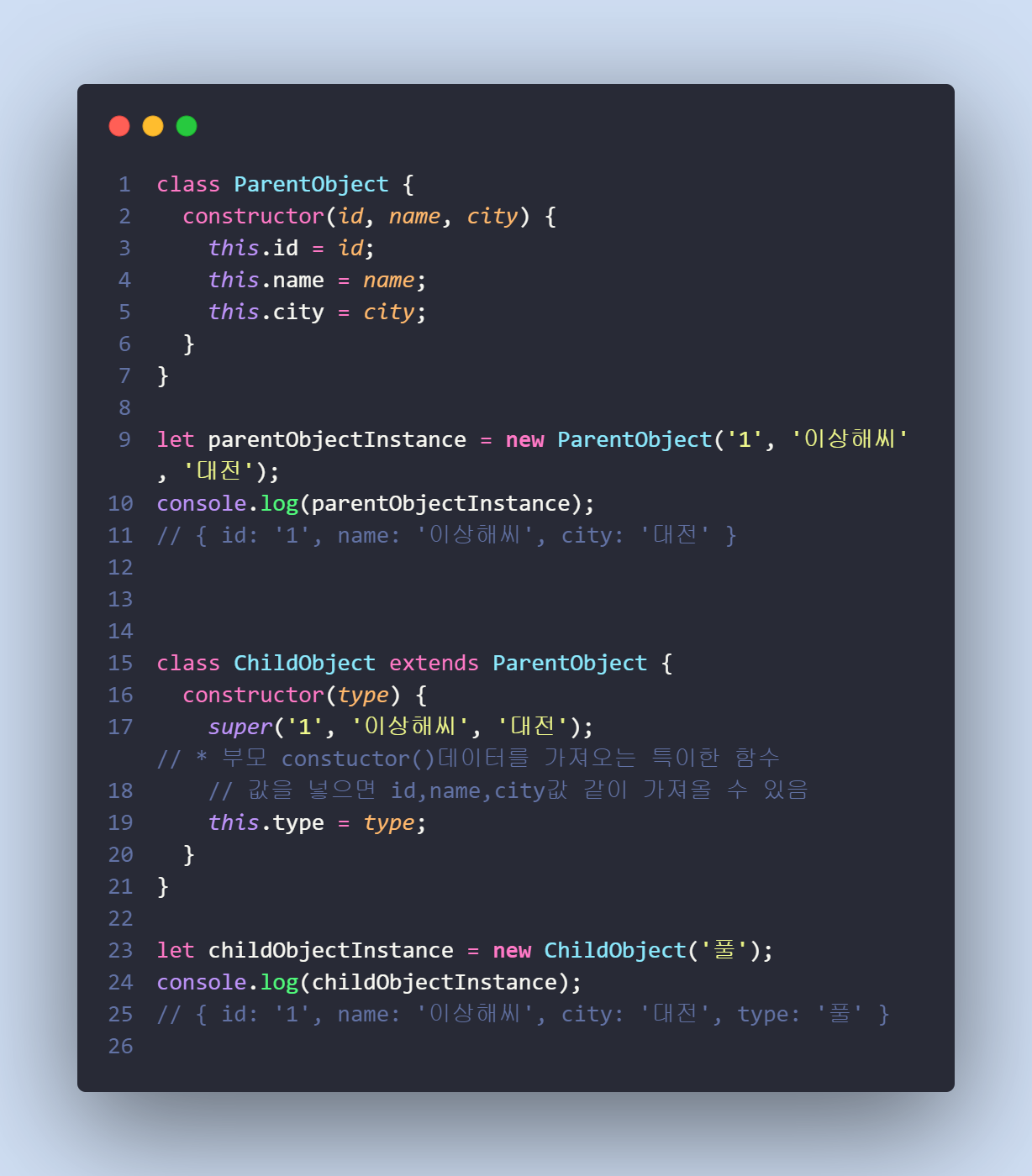
📝 javascript-41 : 심오한 데이터타입
✏️ 원시타입 vs 객체(참조타입)
- 원시타입
원시값 : 불변하는값, 값이 바뀌지 않는다
원시값은 바뀔 구 없지만, 원시값을 할당한 변수는 바뀔 수 있다.
let score = 80;
let copy = score;
console.log(score); // 80
console.log(copy); // 80
score = 100;
console.log(score); // 100
console.log(copy); // 80
console.log(score === copy); // falsescore 에 '80'이라는 값을 어떤 메모리공간에 할당
변수라는건 메모리 공간을 식별하기위한 이름
copy는 변수 score가 갖는 '80'이라는 값을 copy라는 메모리 공간에 할당
결국, score와 copy는 값 80을 공통으로 갖고 있지만, 80이 가지고 있는 메모리의 공간은 다르다.
score의 값을 100으로 재할당
score는 새로운 메모리공간에 100을 할당했다.
socore는 100 / copy는 여전히 80
그래서 socore와 copy는 같지 않다.
- 객체(참조)타입
객체는 변경 가능한 값
변수에 객체를 할당하면, 그 참조값은 생상된 객체가 저장된 메모리공간의 주소, 그 자체
객체는 변경 가능한 값이므로, 메모리에 저장된 객체를 직접 수정이 가능하다.
변수에 재할당을 하지 않았으므로 객체를 할당한 변수의 참조값은 변경되지 않는다.
💬 부족한 부분
화살표함수, 고차함수 부분
원시타입과 객체(참조)타입
