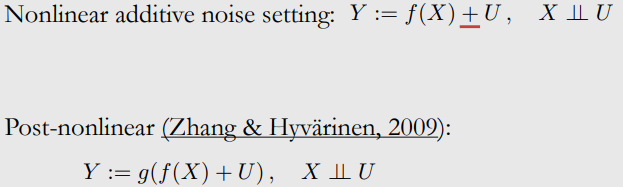https://www.bradyneal.com/causal-inference-course
Introduction to Causal Inference라는 강의를 듣고 정리했습니다.
10. Causal Discovery from Observational Data
Independence-Based Causal Discovery
casual discovery : data → causal graph
structure identification : causal graph를 identify
10-1. Assumptions
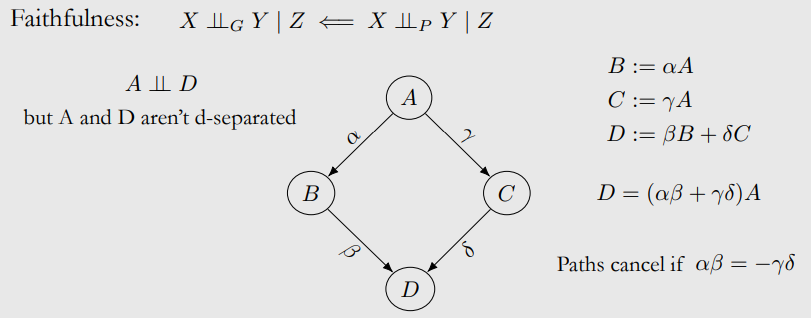
Faithfulness Assumption

- Markov assumption은 causal graph로 data의 distribution을 추론
- faithfulness : data의 independent로 graph 상의 d-seperation을 추론
Violation of Faithfulness
Causal Sufficiency and Acyclicity
-
Causal Sufficiency: no unobserved confounders
-
Acyclicity: no cycles in the graph
-
All assumptions:
- Markov assumption
- Faithfulness
- Causal sufficiency
- Acyclicity
10-2. Markov Equivalence and Main Theorem
Chains and Forks Encode Same Independencies
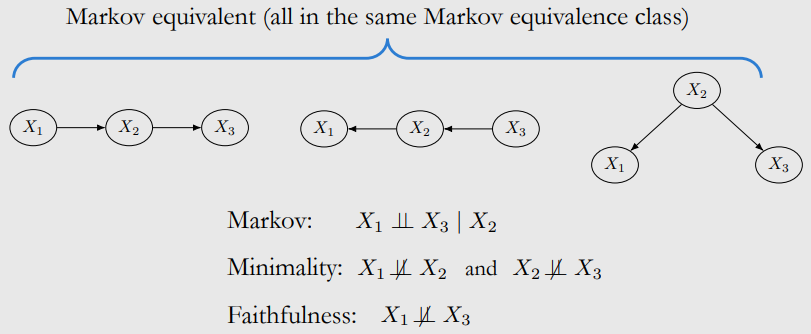
- same conditional independency
Immoralities are Special
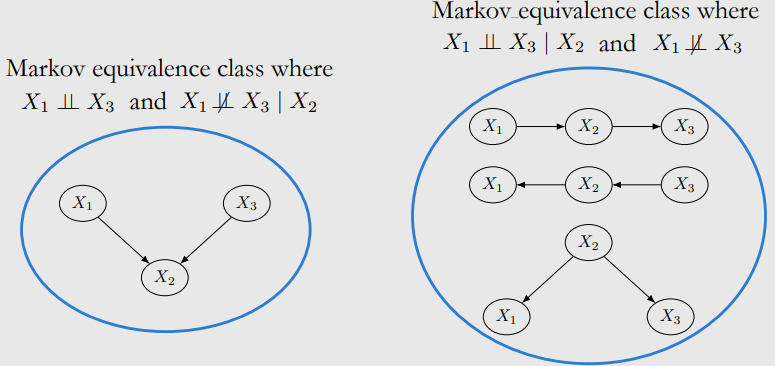
Skeletons
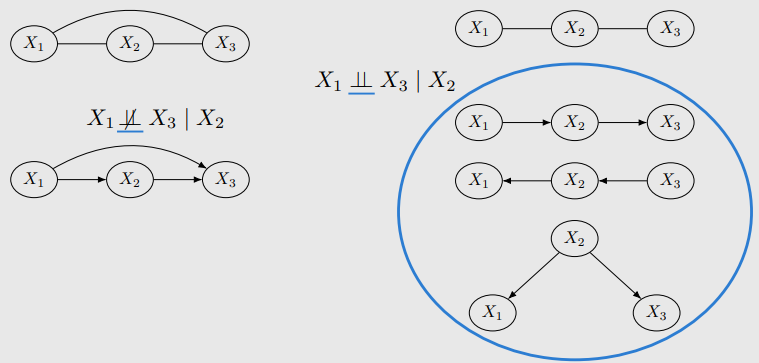
- skeleton으로 markov equivalence class에 대한 정보를 알 수 있다.
Markov Equivalence via Immoral Skeletons
Two important graph qualities that we can use to distinguish graphs:
1. Immoralities
2. Skeleton
Theorem: Two graphs are Markov equivalent if and only if they have the same
skeleton and same immoralities
Essential graph : skeleton + immoralities
- CPDAG : completed partially direct acyclic graph
10-3. The PC Algorithm
PC algorithm
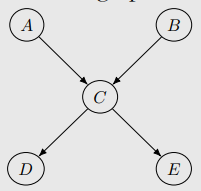
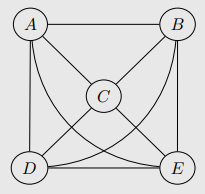
Start with complete undirected graph
Three steps:
1. Identify the skeleton
2. Identify immoralities and orient them
3. Orient qualifying edges that are incident on colliders
Identifying the Skeleton
- undirected graph로 시작
- conditioning set Z(empty도 가능)에 대하여 이면 X - Y edge를 삭제
- empty conditioning set로 시작하여 size를 키움
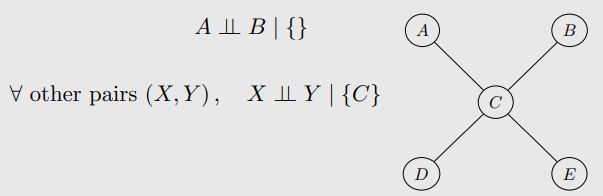
Identifying the Immoralities
X – Z – Y 일 때
1. no edge between X and Y
2. Z 가 X와 Y를 conditionally independent하게 만드는 conditioning set가 아닐 때
(Z를 conditioning 할 때, X랑 Y가 dependent)
X – Z – Y 는 immortality
Orienting Qualifying Edges Incident on Colliders
모든 immoralities를 찾은 상태에서
Z - Y가 X → Z - Y이고, X - Y에 no edge일 때,
Z → Y
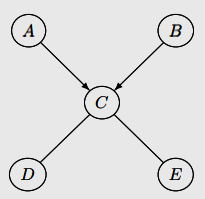
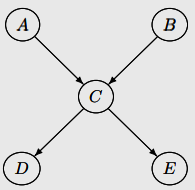
Markov equivalence class를 identify
essential graph에 가끔 undirected edge가 있기도 함
Removing Assumptions
- No assumed causal sufficiency: FCI algorithm
- No assumed acyclicity: CCD algorithm
- Neither causal sufficiency nor acyclicity: SAT-based causal discovery
Hardness of Conditional Independence Testing
- Independence-based causal discovery algorithms은 conditional independence testing으로 함.
- Conditional independence testing은 infinite data면 단순하다.
- finite data면 어렵다.
10-4. Can We Do Better?
- faithfulness로 essential graph를 identify할 수 있다.(Markov equivalence class)
- 더 assumption을 추가해서 narrow down
- multinomial distributions 이나 linear gaussian structual equations로 markov equivalence class의 graph를 identify할 수 있다.(best)
- non-gaussian structual equation, nonlinear structural equation은? Semi-parametric causal discovery
Semi-Parametric Causal Discovery
Independence-Based Causal Discovery 문제점
(Semi-Parametric Causal Discovery에는 없는 문제점)
- faithfulness assumption 요구
- conditional independence tests를 위해 large sample 필요
- markov equivalence class만 identify 할 수 있음. → Semi-Parametric Causal Discovery 는 true causal graph 찾을 수 있다
10-5. No Identifiability Without Parametric Assumptions
Two Variable Case: Markov Equivalence

Two Variable Case: SCMs Perspective
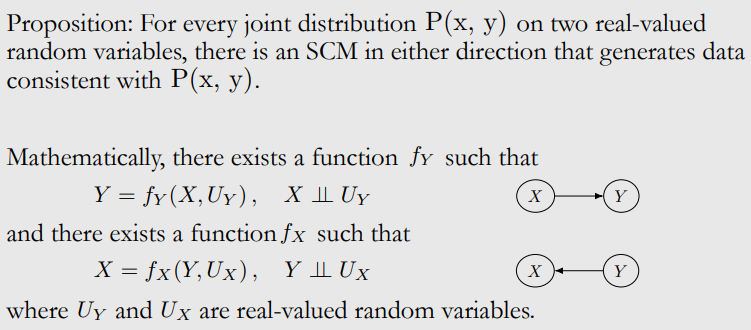
뭐가 맞는지 알 수 없다.
parametric form에 대하여 assumption을 만들어야 함
10-6. Linear Non-Gaussian Setting
Linear Non-Gaussian Assumption
- noise가 non-gaussian일 때

Identifiability in Linear Non-Gaussian Setting
- U가 non-gaussian일 때

- SCM의 reverse direction이 없다.
- Y랑 dependent
Identifiability in Linear Non-Gaussian Setting: Linear Fit
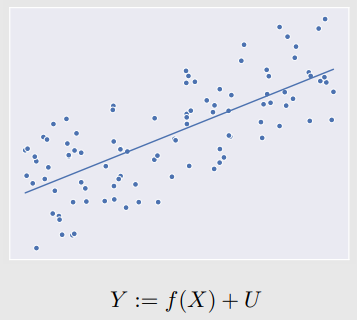
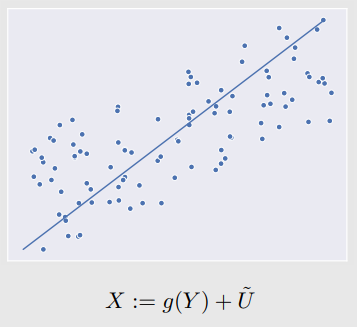
- anti-causal direction을 하면 regression한 것과 결과가 다르다.
- noise term이 non-gaussian이여서 생김.
Identifiability in Linear Non-Gaussian Setting: Residuals
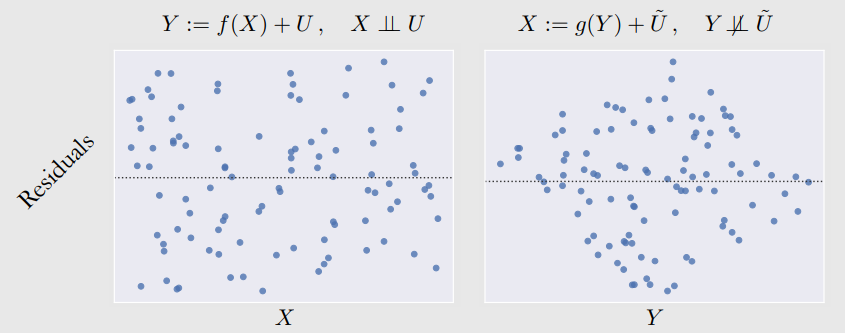
- anti-causal scm을 제대로 구하지 못함. 와 Y가 dependent
Linear Non-Gaussian Identifiability Extensions
• Multivariate: Shimizu et al., (2006)
• Drop causal sufficiency assumption: Hoyer et al. (2008)
• Drop acyclicity assumption: Lacerda et al. (2008)
10-7. Nonlinear Additive Noise Setting
Identifiability in Nonlinear Additive Noise Setting
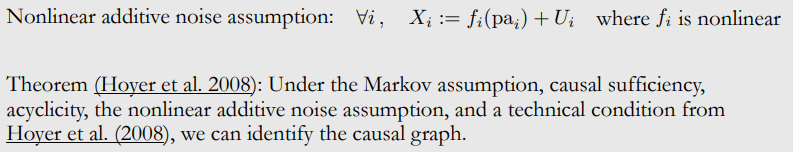
Post-Nonlinear Setting