Keyword
Virtual memory management
Paging
-
cpu 레지스터가 가지고 있는 가상메모리 주소로 어떻게 물리메모리에 접근 할 수 있을까? → os는 세그멘테이션, 페이징 기법을 섞어서 사용한다. 가상메모리는 paging 기법과 연관이 깊다
-
페이징은 프로세스를 일정 크기인 페이지로 잘라서 메모리에 적재하는 방식을 말한다. → 외부 단편화 해결
-
contiguous allocation(연속할당) 방식 → 치명적인 외부 단편화 문제 발생 → 문제 해결하기 위해 메모리를 동일한 크기로 쪼개는 paging 기법이 나옴 → 메모리 적재가 연속적이지가 않으니까 프로그램 수행에 문제가 있음 → 그 페이지들을 문제없이 수행하기 위해 (linear 하게) page table이라는게 있다는 것..
-
page table
- 페이지 테이블은 가상메모리의 페이지가 물리메모리의 몇 번째 프레임에 있냐라는 것을 알려주는 테이블이다..
- 테이블은 배열과 같은 것인데 페이지 테이블의 인덱스가 페이지 번호를 가르키고, 그 배열에 담고 있는 숫자가 매핑할 프레임 번호다.( 간단히 말해서)
- 사실 실제 페이지 테이블은 페이지 번호와, 프레임 번호 이외에도 여러 편리 기능을 위해 다양한 필드들로 구성(present/absent, protection, reference, cashing, dirty)
- page table은 프로세스마다 하나씩 있어야함. 프로세스가 바뀌면 page table도 해당 프로세스 page table로 바꿔서 관리해야함.
-
virtual page
-
logical memory에 나눠진 블럭
-
page크기는 보통 4kb → 4096byte
-
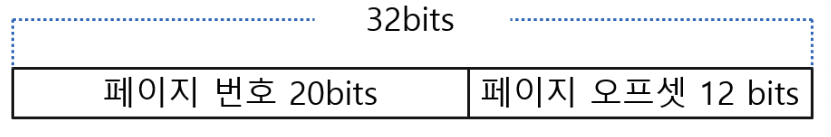
예를 들어 4kb인 ‘페이지0’이 있다 → ‘페이지 0’ 안에는 0번부터 2의 12승까지 번지가 있겠지 페이지자체 번호말고 페이지내의 번호를 offset이라 한다 이거야.
-
예를 들어 32비트체제에서는 2의 32승 즉 4GB, 페이지 4kb면 4GB를 4kb(2의 12승)로 나누면 2의 20승 즉 1M만큼 페이지가 있는거고, 32비트중 20비트는 페이지번호(p), 12비트는 페이지안의 오프셋(d)을 표현할 수 있음.
-
-
physical frame
- physical memory를 나눈 것을 frame이라 한다.
Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB)
- page table 문제
- page table을 어디에 저장해야 빠르게 참조해서 주소 변환을 시킬 수 있을까? → 당연히 CPU내에 있는 MMU에다가 넣으면 빠르겠지? 근데 page table을 표현하기 위해서는 대략적으로 프로세스 하나당 4MB(왜? 2의 20승만큼의 페이지(페이지 엔트리)가 있을 거고 페이지번호는 int형이니까 4MB) 가 필요해 이걸 MMU에 넣는다고? 비용이 어마어마해지지 → 그럼 RAM에 넣어야하네? 근데 RAM에 넣으면 몇번째 프레임이인지 알려면 결국 메모리를 두번 참조해야해 성능이 안좋아져 → 그래서 Cache memory를 쓰는 방식인 TLB가 나온것이야..
- TLB는 실제로 참조되는 페이지는 2의 20승개 중에서 몇개 안되다는 원리를 활용한것. → 자주 쓰는 페이지는 MMU안에다 캐시로 두겠다. → 그럼 MMU에서 바로 사용이 가능해지니까! 효율적인거지 → 이 MMU에다가 두는 캐시를 TLB라 하는 것이다 이거야..
- TLB 내의 각 항목(entry)는 키(key=Page number)와 값(value=Page number에 해당하는 frame number)로 구성 → Page Table은 배열 인덱스 와 값으로 구성
- TLB에 페이지 번호 검색한 후 존재하는 경우에는 프레임 번호를 빠르게 가져오고 없으면 Page Table 사용
계층적 페이징(Hierarchical Paging)
- 4MB의 연속된 메모리 공간은 생각보다 큼 → 심지어 프로세스 또한 그 주소 공간 중 아주 일부분만 사용함, 페이지 테이블의 아주 일부분에만 접근할 것 → 메모리 내에서 낭비되는 주소 공간을 페이징으로 해결한 것처럼, 페이지 테이블 내에서 낭비되는 공간 또한 페이징으로 해결할 수 있음.
Page type
Anonymous Page
- 익명 페이지는 커널로 부터 프로세스에게 할당된 일반적인 메모리 페이지이다.
- 여기서 익명이라는 뜻은 파일에 기반하고 있지 않은(파일로부터 매핑되지 않은) 페이지라는 뜻 (file-backed page의 반댓말)
swap in/out
Swapping
- 메모리에 최대 10개 프로세스를 올릴 수 있다고 가정해보자 이거야..
- 10개 다 올라가 있는데 11번째 프로세스가 실행되었네? 메모리가 다 차서 더 올릴 수 없어..
- 그래서 생각해낸 것이 10개 프로세스가 있는데 그 중 어떤 걸 잠깐 내리고 그 사이에 11번째를 실행시키는건 어떨까? 한거임.
- 어떤 프로세스가 이벤트 발생하기를 기다리고 있는지 1시간이 지난거지 → 그 프로세스를 쫓아내고 그 공간에다가 새로운 프로세스를 집어 넣는거지!
- 이걸 쫓아낼 때 없애버릴 순 없으니까 그 메모리 내용을 어딘가에 잠깐 저장 해야하는데 하드 디스크나 SSD같은 secondary storage에 저장을 하고 수행을 한다. → 이렇게 프로세스 단위로 쫓아내는 것을 Swap out이란 한다 이거야..
- 아까 저장해놨던 것을 다시 메모리에 올려서 이 프로세스를 그 다음부터 수행시켜주는데 이렇게 다시 로딩하는 것을 swap in이라 한다.. → 즉, in out 하는 과정을 swapping이라 함. → 하드디스크에 있던 것을 메모리에 다시 로딩하고 시켜야하는거니까 좀 느리긴해도 부족한 메모리에 더 많은 프로세스를 실행할 수 있다는 큰 장점이 있어.
Introduction(git book)
소스파일
템플릿 무조건 따르세요 안그러면 0점 받을거야. “DO NOT CHANGE” → 바꾸지말라면 마셈
include/vm/vm.h,vm/vm.c- 가상 메모리에 대한 일반 인터페이스를 제공한다. 가상 메모리 시스템이 지원해야 하는 다양한 vm_type에 대한 정의와 설명을 볼 수 있다.
include/vm/uninit.h,vm/uninit.c- 초기화되지 않은 페이지(vm_type =
VM_UNINIT)에 대한 작업을 제공 - 현재 디자인에서 모든 페이지는 초기에 초기화되지 않은 페이지로 설정된 다음 익명 페이지 또는 파일 지원 페이지로 변환됩니다.
- 초기화되지 않은 페이지(vm_type =
include/vm/anon.h,vm/anon.c- anonymous page에 대한 작업을 제공함. (vm_type =
VM_ANON)
- anonymous page에 대한 작업을 제공함. (vm_type =
include/vm/file.h,vm/file.c- file 지원 페이지에 대한 작업을 제공함. (vm_type =
VM_FILE)
- file 지원 페이지에 대한 작업을 제공함. (vm_type =
페이지
- 페이지 크기 → 4096 바이트 (4KB)
- 64비트 하위 12비트는 페이지 오프셋
- 상위 비트는 페이지 테이블 인덱스를 나타내는데 사용되는데, 64비트 시스템에서는 가상 주소를 4레벨 페이지 테이블을 사용한다
63 48 47 39 38 30 29 21 20 12 11 0
+-------------+----------------+----------------+----------------+-------------+------------+
| Sign Extend | Page-Map | Page-Directory | Page-directory | Page-Table | Page |
| | Level-4 Offset | Pointer | Offset | Offset | Offset |
+-------------+----------------+----------------+----------------+-------------+------------+
| | | | | |
+------- 9 ------+------- 9 ------+------- 9 ------+----- 9 -----+---- 12 ----+
Virtual Address- kernel은 user page와 kernel page 모두에 access할 수 있지만, user process는 자신만의 user page에만 접근할 수 있음.
프레임
- pintos는 커널 가상 메모리를 물리적 메모리에 직접 매핑한다. → 커널 가상 메모리를 통해 프레임에 접근할 수 있음
12 11 0
+-----------------------+-----------+
| Frame Number | Offset |
+-----------------------+-----------+
Physical Address페이지 테이블
- page table은 CPU가 가상주소를 물리주소로, 즉 page에서 frame으로 번역하기 위해 사용하는 자료구조다. page table 포맷은 x86-64 아키텍처에 따르게 되어 있음. Pintos 페이지 테이블 관리 코드 →
threads/mmu.c
+----------+
.--------------->|Page Table|-----------.
/ +----------+ |
| 12 11 0 V 12 11 0
+---------+----+ +---------+----+
| Page Nr | Ofs| |Frame Nr | Ofs|
+---------+----+ +---------+----+
Virt Addr | Phys Addr ^
\_______________________________________/스왑 슬롯
- swap slot은 swap partition에 있는 page-size(4,096bytes)의 디스크 공간. slot의 배치를 결정하는 것이 frame의 배치를 결정하는 것보다 하드웨어적인 제한이 유연하긴 하지만, swap slot에서 page-aligned를 하는 것에 대한 단점이 없기 때문에 그렇게 해야함.
자원 관리 개요
- supplemental page table
- supplemental page table로 페이지 폴트 핸들링을 가능하게 해.
- supplemental page table 관리는 밑에 참고..
- frame table
- physical frame의 제거 정책을 효율적으로 구현하여야함.
- 아래 프레임 테이블 관리 참조
- swap table
- 스왑 슬롯의 사용량을 추적
- 아래 스왑 테이블 관리 참조
managing the supplemental page table
- supplemental page table의 목적
- page fault 발생 시, 커널이 supplemental page table에서 fault가 발생한 가상 page를 찾아 그 곳에 있어야 하는 데이터를 찾는다.
- 커널이 어떤 리소스를 free할 지 결정하기 위해 프로세스가 종료될 때 spt 참조
Memory Management
Implement Supplemental Page Table
현재 pintos에는 메모리의 가상 및 물리적 매핑을 관리할 수 있는 페이지테이블(pml4)가 있음. 하지만 pml4로만 충분하지 않다. 페이지 폴트와 리소스 관리를 처리하기 위해 각 페이지에 대한 추가 정보를 보관하기 위한 SPT가 필요.
supplemental_page_table에 있는 페이지들을 해쉬테이블 자료구조로 관리하기 위해struct hash ht를 만들어줌.
struct supplemental_page_table {
/* prj3-memory management, yeopto */
struct hash ht;
};- 페이지를 spt로 관리하기 위해서
page구조체 안에hash_elem추가
struct page {
const struct page_operations *operations;
void *va; /* Address in terms of user space */
struct frame *frame; /* Back reference for frame */
/* Your implementation */
/* prj3-memory management, yeopto */
struct hash_elem hash_elem;
/* prj3-memory mapped files, jack */
uint64_t *pml4;
/* eleshock */
bool writable;
/* Per-type data are binded into the union.
* Each function automatically detects the current union */
union {
struct uninit_page uninit;
struct anon_page anon;
struct file_page file;
#ifdef EFILESYS
struct page_cache page_cache;
#endif
};
};supplemental_page_table_init은 process가 시작될 때와 fork()될 때 호출된다.
// 프로세스 시작 될 때
static void
initd (void *f_name) {
#ifdef VM
supplemental_page_table_init (&thread_current ()->spt);
#endif
process_init ();
if (process_exec (f_name) < 0)
PANIC("Fail to launch initd\n");
NOT_REACHED ();
}// fork()할 때
static void
__do_fork (void *aux)
.
.
.
#ifdef VM
curr_thread->running_file = file_duplicate(parent->running_file); // Jack
supplemental_page_table_init (&curr_thread->spt);
if (!supplemental_page_table_copy (&curr_thread->spt, &parent->spt))
goto error;
#else
if (!pml4_for_each (parent->pml4, duplicate_pte, parent))
goto error;
#endif
.
.
.
}supplemental_page_table_init에서 hash를 init 해주자. (hash.c에 hash를 관리할 수 있도록 함수들이 제공되어있음. hash func, less func은 gitbook에 있음)
void
supplemental_page_table_init (struct supplemental_page_table *spt UNUSED) {
/* prj3-memory management, yeopto */
ASSERT(spt != NULL);
hash_init(&spt->ht, page_hash, page_less, NULL);
return;
}spt_find_page: spt에서 page를 찾는 함수 → 해쉬로 구현했으니까 해쉬에서 찾을 수 있게 구현
struct page *
spt_find_page (struct supplemental_page_table *spt UNUSED, void *va UNUSED) {
struct page *page = NULL;
/* TODO: Fill this function. */
if (spt == NULL || va == NULL) return NULL;
/* prj3-memory management, yeopto */
struct page local_page;
struct hash_elem *found_elem;
local_page.va = pg_round_down(va);
found_elem = hash_find(&spt->ht, &local_page.hash_elem);
if (found_elem == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
page = hash_entry(found_elem, struct page, hash_elem);
return page;
}spt_insert_page: page를 찾으려면 page를 spt에 넣어줘야지. 넣어 주기 위한 함수 spt에 만들어놓은ht에 page에 만들어 놓은hash_elem을 넣어주어야함.
bool
spt_insert_page (struct supplemental_page_table *spt UNUSED,
struct page *page UNUSED) {
if (spt == NULL || page == NULL) return false;
int succ = false;
/* TODO: Fill this function. */
/* Jack */
page->va = pg_round_down(page->va); // page의 va를 page 첫주소로 갱신
succ = hash_insert(&spt->ht, &page->hash_elem)? false: true; // spt의 hash table에 page hash_elem삽입 후 성공여부 저장
return succ;
}spt_remove_page: spt에서 페이지 지워주는 함수.
/* eleshock */
void
spt_remove_page (struct supplemental_page_table *spt, struct page *page) {
ASSERT(spt != NULL);
ASSERT(page != NULL);
struct hash *h = &spt->ht;
struct hash_elem *e = &page->hash_elem;
hash_delete(h, e);
vm_dealloc_page (page);
return true;
}Frame Mangement
pintos는 커널 가상주소와 물리메모리와 1대1로 매핑되어있다. 그래서 frame 구조체에는 커널 가상 메모리(kva), 매핑된 page가 있다. page 관리를 spt로 하기에 page안에 hash_elem을 넣어주었듯이, frame 관리는 frame table로 해주고 frame table은 리스트로 관리. 그래서 frame 안에 멤버로 list_elem을 추가.
struct frame_table
struct frame_table {
struct list table; // 리스트로 관리
struct lock lock; // 실제 물리메모리 공간에 대한 테이블이기에 공유자원이다. 그래서 lock 추가
};struct frame
struct frame {
void *kva;
struct page *page;
// Jack
struct list_elem f_elem; // frame_table을 리스트로 관리하기에 elem 추가
};vm_get_frame
static struct frame *
vm_get_frame (void) {
struct frame *frame = NULL;
/* eleshock */
void *pp = palloc_get_page(PAL_USER); // 유저 풀에서 물리 페이지(껍데기)를 얻음
if (pp == NULL)
PANIC("todo");
frame = malloc(sizeof(struct frame));
frame->kva = pp; // 프레임구조체에 있는 kva를 할당받은 pp로(이 프레임은 이제 페이지와 맵핑될 준비가 되어있음)
frame->page = NULL;
ASSERT (frame != NULL);
ASSERT (frame->page == NULL);
/* eleshock */
ft_insert(frame); // 프레임 테이블에 넣어줘
return frame;
}vm_do_claim_page→ 물리 프레임 할당받고, 그 물리 프레임이랑 인자로 들어온 페이지의 가상주소와 맵핑 시켜줌 그리고pml4_set_page로 가상주소에 대한 pte가 물리메모리를 가리키게 해줌.
/* Claim the PAGE and set up the mmu. */
static bool
vm_do_claim_page (struct page *page) {
if (page == NULL) return false;
struct frame *frame = vm_get_frame ();
uint64_t *pml4 = thread_current()->pml4;
/* Set links */
frame->page = page;
page->frame = frame;
/* TODO: Insert page table entry to map page's VA to frame's PA. */
pml4_set_page(pml4, page->va, frame->kva, 1); // Jack
return swap_in (page, frame->kva);
}vm_claim_page→ 지금은 page는 만들어져서 spt에 있다는 가정하에! 없으면 false!
bool
vm_claim_page (void *va UNUSED) {
if (va == NULL) return false;
struct page *page = NULL;
struct supplemental_page_table *spt = &thread_current()->spt;
/* TODO: Fill this function */
page = spt_find_page(spt, va);
return page != NULL? vm_do_claim_page (page): false;Anonymous Page
anonymous mapping은 백업 파일이나 장치가 없음. file-backed 페이지와 달리 명명된 파일 소스가 없기 때문에 anonymous임. 익명 페이지는 스택 및 힙과 같은 실행 파일에 사용된다.
Page Initialization with Lazy Loading
Lazy Loading은 메모리 로딩이 필요한 시점까지 지연되는 설계. 페이지가 할당되지만 전용 Physical frame이 없고 페이지의 실제 내용이 아직 로드되지 않음.→ Page fault로 인해 신호가 전달되서 필요한 경우에만 로드가 되어야함.
페이지의 유형이 3개고, 초기화 루틴이 페이지마다 다름. 첫번째로, 커널이 새 페이지 요청을 받으면 vm_alloc_page_with_initializer가 호출됨.
initializer는 페이지 구조체를 할당하고 페이지 타입에 따라 적절한 initializer를 세팅하여 새 페이지를 초기화하고, 제어권을 유저 프로그램으로 되돌릴 것. 유저프로그램이 실행될 때, 어느 시점에서, 프로그램이 소유하고 있다고 생각하는 페이지에 액세스하려고 하지만 페이지에 아직 내용이 없기에 page fault가 발생함. fault 처리 절차중에 uninit_initialize 가 호출 되고, 이전에 설정한 initializer를 호출 함. anonymous 타입이면 anon_initializer , file-backed인 경우는 file_backed_initializer
정리 → load_segment 등에서 vm_alloc_page_with_initializer 가 호출되는데 load_sement에서 실제로 load가 되는것이 아님. load_segment에서 file 내용들을 페이지(uninit으로 만들면서 타입 셋팅, initializer 설정등 하고 spt에 삽입)로 만들어 놓음. 페이지 폴트가 일어나면 vm_do_claim 에서 frame이 만들어지면서 swap in 을 통해 이전에 설정해놓은 initializer가 실행되고, lazy load가 되도록 함.
Lazy Loading for Executable
Lazy loading에서 프로세스가 실행을 시작하면, 즉시 필요한 메모리 부분만 메인 메모리에 로드됨. 이는 모든 바이너리 이미지를 한 번에 메모리에 로드하는 eager loading(빠른 로딩)에 비해 오버헤드를 줄일 수 있다. → lazy-load 하는 이유
Lazy loading을 지원하기 위해 include/vm/vm.h에 VM_UNINIT라는 페이지 유형을 도입. 모든 페이지는 처음에 VM_INIT 페이지로 생성됨. 또한 초기화되지 않은 페이지에 대한 페이지 구조체를 제공. (include/vm/uninit.h의 uninit_page 구조체).
페이지 폴트가 발생하면, 페이지 폴트 핸들러(userprog/exception.c의 page_fault)는 vm/vm.c의 vm_try_handle_fault로 제어권을 전송하고, vm_try_handle_fault가 먼저 유효한 페이지 폴트인지 확인함.
유효한 페이지 폴트라는 것은, 유효하지 않은 주소에 액세스하는 것을 의미함. 가짜(bogus) 폴트(우리가 해결할 수 있는 폴트)인 경우 일부 콘텐츠를 페이지에 로드하고 제어 권한을 사용자 프로그램으로 되돌림. (bogus가 아닌 진짜 fault라면 false 반환 → 밑에 코드주석 참고)
3가지 케이스의 가짜 폴트가 있다 : lazy-loaded, swaped-out page, 그리고 write-protected page(extra 과제 참고). 이제부터 첫 번째 케이스인 lazy-loaded page만 고려하면 됨. lazy loading으로 인한 페이지 폴트라면, 커널은 세그먼트를 lazy load하기 위해 이전에 vm_alloc_page_with_initializer에 세팅해둔 initializer 중 하나를 호출함. userprog/process.c에 있는 lazy_load_segment를 구현해야 된다.
vm_alloc_page_with_initializer()→ 주어진 type(vm_type)으로 uninitialized page를 생성. uninit 페이지의 swap_in 핸들러(uninit_initialize)는 타입에 따라 자동적으로 페이지를 초기화하고, 주어진 AUX와 함께 INIT(lazy-load)을 호출.
bool
vm_alloc_page_with_initializer (enum vm_type type, void *upage, bool writable,
vm_initializer *init, void *aux) {
ASSERT (VM_TYPE(type) != VM_UNINIT)
struct supplemental_page_table *spt = &thread_current ()->spt;
/* Check wheter the upage is already occupied or not. */
if (spt_find_page (spt, upage) == NULL) {
/* TODO: Create the page, fetch the initialier according to the VM type,
* TODO: and then create "uninit" page struct by calling uninit_new. You
* TODO: should modify the field after calling the uninit_new. */
bool (*initializer)(struct page *, enum vm_type, void *);
switch (VM_TYPE(type))
{
case VM_ANON:
initializer = anon_initializer;
break;
case VM_FILE:
initializer = file_backed_initializer;
break;
default:
goto err;
}
struct page *new_page = malloc(sizeof(struct page));
upage = pg_round_down(upage);
uninit_new(new_page, upage, init, type, aux, initializer); // uninit page를 초기화하는 함수
new_page->writable = writable;
new_page->pml4 = thread_current()->pml4;
/* TODO: Insert the page into the spt. */
spt_insert_page(spt, new_page);
return true;
}
err:
return false;
}uninit_initialize→ 타입에 따라 자동적으로 페이지를 초기화하고, 주어진 AUX와 함께 INIT(lazy-load)을 호출.
/* Initalize the page on first fault */
static bool
uninit_initialize (struct page *page, void *kva) {
struct uninit_page *uninit = &page->uninit;
/* Fetch first, page_initialize may overwrite the values */
vm_initializer *init = uninit->init;
void *aux = uninit->aux;
/* TODO: You may need to fix this function. */
return uninit->page_initializer (page, uninit->type, kva) &&
(init ? init (page, aux) : true);
}vm_anon_init→ 커널이 부팅될 때 vm_init에서 실행됨.anon_page와 관련된 초기화를 해야한다면 이 함수에서.
/* Initialize the data for anonymous pages */
void
vm_anon_init (void) {
/* TODO: Set up the swap_disk. */
swapdisk_init(); // swap In/Out에서
}anon_initializer→ 실제로 페이지를 anon으로 만들어주는 함수
bool
anon_initializer (struct page *page, enum vm_type type, void *kva) {
if (page == NULL || kva == NULL) return false;
struct uninit_page *uninit = &page->uninit;
memset(uninit, 0, sizeof(struct uninit_page));
/* Set up the handler */
page->operations = &anon_ops;
struct anon_page *anon_page = &page->anon;
anon_page->sub_type = VM_SUBTYPE(type);
anon_page->swap_slot = -1;
return true;
}load_segment→ 루프를 돌 때마다vm_alloc_page_with_initializer를 호출하여 페이지를 생성함.vm_alloc_page_with_initializer에 제공할 aux인수를 설정해야함.(lazy_load_segment가 실행될 때 aux 필요), 이전엔 실제로 load가 되는 함수 였으나 이제는 아님.
static bool
load_segment (struct file *file, off_t ofs, uint8_t *upage,
uint32_t read_bytes, uint32_t zero_bytes, bool writable) {
ASSERT ((read_bytes + zero_bytes) % PGSIZE == 0);
ASSERT (pg_ofs (upage) == 0);
ASSERT (ofs % PGSIZE == 0);
while (read_bytes > 0 || zero_bytes > 0) {
/* Do calculate how to fill this page.
* We will read PAGE_READ_BYTES bytes from FILE
* and zero the final PAGE_ZERO_BYTES bytes. */
size_t page_read_bytes = read_bytes < PGSIZE ? read_bytes : PGSIZE;
size_t page_zero_bytes = PGSIZE - page_read_bytes;
/* TODO: Set up aux to pass information to the lazy_load_segment. */
/* prj3 - Anonymous Page, yeopto */
struct segment *segment = malloc(sizeof(struct segment));
segment->ofs = ofs;
segment->read_bytes = page_read_bytes;
segment->zero_bytes = page_zero_bytes;
/* prj3 - Anonymous Page, yeopto */
void *aux = segment;
if (!vm_alloc_page_with_initializer (VM_ANON | VM_SEGMENT, upage,
writable, lazy_load_segment, aux))
return false;
/* prj3 - Anonymous Page, yeopto */
ofs += page_read_bytes;
/* Advance. */
read_bytes -= page_read_bytes;
zero_bytes -= page_zero_bytes;
upage += PGSIZE;
}
return true;
}struct segment→ aux때문에 필요함 세그먼트에 올릴 정보들이 필요해서 →load_segment에서 aux에 담아주고,lazy_load_segment에서 꺼내서 실제로 적재 해주게 될 것.
/* prj3 - Anonymous Page, yeopto */
struct segment {
off_t ofs;
uint32_t read_bytes;
uint32_t zero_bytes;
};lazy_load_segment→ 페이지 폴트 시 uninit page가 initialize 되는 시점에 실행되는 함수. 실제 메모리에 적재되는 함수다. file에 대한 정보는 aux에서가아닌thread_current()에서running_file을 뽑아줌.
static bool
lazy_load_segment (struct page *page, void *aux) {
/* TODO: Load the segment from the file */
/* TODO: This called when the first page fault occurs on address VA. */
/* TODO: VA is available when calling this function. */
/* Jack */
struct segment *load_src = aux;
struct file *file = thread_current()->running_file;
off_t ofs = load_src->ofs;
uint32_t read_bytes = load_src->read_bytes;
uint32_t zero_bytes = load_src->zero_bytes;
void *kva = page->frame->kva;
if (file_read_at(file, kva, read_bytes, ofs) != (int) read_bytes)
return false;
memset (kva + read_bytes, 0, zero_bytes);
free(load_src);
return true;
}setup_stack→ 새 메모리 관리 시스템에 맞게setup_stack을 스택 할당을 조정해야함. 첫 번째 스택 페이지는 lazy-load 될 필요가 없음 fault 발생 기다릴 필요 없이 로드시 command line 인자를 사용하여 이를 할당하고 초기화할 수 있음. → 지금은 stack growth 까지는 고민 할 필요 없음. 그리고 메모리에 정보를 올리는 것이 아니기에 추가 함수를 인자로 전달할 필요는 없다.vm_alloc_page로 anon이면서 stack type으로 uninit page를 만들어주고 바로vm_claim_page함수를 호출해서 바로 frame 할당받고 사용가능하도록만 해줌(page fault로 initialize가 되는 것이 아닌거지).
static bool
setup_stack (struct intr_frame *if_) {
bool success = false;
void *stack_bottom = (void *) (((uint8_t *) USER_STACK) - PGSIZE);
/* TODO: Map the stack on stack_bottom and claim the page immediately.
* TODO: If success, set the rsp accordingly.
* TODO: You should mark the page is stack. */
/* TODO: Your code goes here */
/* prj3 - Anonymous Page, yeopto */
vm_alloc_page(VM_ANON | VM_STACK, stack_bottom, 1);
success = vm_claim_page(stack_bottom);
/* prj3 - Anonymous Page, yeopto */
if (success) {
if_->rsp = USER_STACK;
}
return success;
}Supplemental Page Table - Revisit
fork() 로 하위 프로세스를 생성하거나, 프로세스를 폐기할 때 spt를 복사하고 정리하는 작업이 필요하다. 그 상황을 위해 supplemental_page_table_copy 와 supplemental_page_table_kill 를 구현해야함.
supplemental_page_table_copy→ spt를 복사하는 함수. fork()의 실행 컨텍스트를 상속받아야할 때 사용됨. → do_fork에서 호출함
/* Jack */
/* Copy page function for spt copy */
bool
page_copy (struct page *page, void *aux)
{
struct page *parent_page = aux;
void *parent_kva = parent_page->frame->kva;
void *child_kva = page->frame->kva;
return memcpy(child_kva, parent_kva, PGSIZE)!=NULL? true: false; // debugging sanori - kva로 접근해야할까 uva로 접근해야할까?
}
/* Copy supplemental page table from src to dst */
bool
supplemental_page_table_copy (struct supplemental_page_table *dst UNUSED,
struct supplemental_page_table *src UNUSED) {
/* Jack */
struct hash_iterator i;
hash_first(&i, &src->ht);
while (hash_next(&i))
{
struct page *src_p = hash_entry(hash_cur(&i), struct page, hash_elem);
switch (src_p->operations->type)
{
case VM_UNINIT:
if (!vm_alloc_page_with_initializer(src_p->uninit.type, src_p->va, src_p->writable, src_p->uninit.init, src_p->uninit.aux))
return false;
break;
case VM_ANON:
if (!vm_alloc_page_with_initializer(src_p->operations->type | src_p->anon.sub_type, src_p->va, src_p->writable, page_copy, src_p) && \
!vm_claim_page(src_p->va))
return false;
break;
case VM_FILE:
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}supplemental_page_table_kill→ spt가 보유한 모든 리소스를 해제하는 함수. 프로세스가 종료될 때 호출됨.
void
supplemental_page_table_kill (struct supplemental_page_table *spt UNUSED) {
/* TODO: Destroy all the supplemental_page_table hold by thread and
* TODO: writeback all the modified contents to the storage. */
/* eleshock */
hash_destroy(&spt->ht, spt_destructor);
}Page Cleanup
uninit_destroy in vm/uninit.c 와 anon_destroy in vm/anon.c 를 구현하라. uninitialized page에서 destroy 작업을 위한 핸들러임. uninitialized page가 다른 페이지 개체로 변환되더라도 프로세스가 종료될 때 초기화되지 않은 페이지가 있을 수 있음.
uninit_destroy- 페이지에 보관된 리소스를 free함. vm type을 확인하고 그에 따라 처리
static void
uninit_destroy (struct page *page) {
struct uninit_page *uninit UNUSED = &page->uninit;
/* TODO: Fill this function.
* TODO: If you don't have anything to do, just return. */
/* prj3 - Anonymous Page, yeopto */
if (page->frame != NULL) {
// palloc_free_page(page->frame->kva); // pml4 destroy에서 알아서 해줌
ft_delete(page->frame);
free(page->frame);
}anon_destroy- 익명 페이지에 보관된 리소스를 free함.
static void
anon_destroy (struct page *page) {
struct anon_page *anon_page = &page->anon;
/* eleshock */
struct frame *fr = page->frame;
ft_delete(fr);
~~//palloc_free_page(fr->kva);~~
free(fr);
}Stack Growth
X86-64에서의 ‘PUSH’ instruction (stack을 쓰려고 할 때 사용되는 instruction)은 바로 rsp를 아래로 내리는게 아니라 그 전에 8바이트 아래가 접근 가능한지 확인하도록 되어있다. → rsp - faulting addr 이 8바이트 차이가 나면 stack growth가 필요하다 판단할 수 있다.
vm_try_handle_fault 에서 차이가 8바이트인지 확인해주고 or 이때 테스트케이스중에 크기가 큰 배열이 스택에 할당되지않은채로 자리만 잡고있는 경우가 있는데 이 경우를 위해서 fault 주소가 스택범위에서 일어났다면 vm_stack_growth를 호출해서 스택영역을 만들어줌(setup_stack 과 같은 원리로 vm_alloc_page 호출해서 만들어주기만하고 내용을 Load하는게 아님. 그 후 vm_do_claim_page 로 frame 할당 받아서 사용가능하게만 해줌. setup_stack 과 차이라면 setup_stack은 첫 스택할당할때하는 것이고 stack_growth 는 필요할때 마다 page-fault가 일어나서 스택을 할당해주는 것.)
Memory Mapped Files
파일을 메모리에 매핑 → mmap() , munmap() 즉, 파일이 backing store가 된다. 이 형식도 동일하게 lazy loading 방식이다. uninit page를 만들어놓고 page fault가 일어나면 file-backed로 initialize를 해준다. user가 보내준 fd의 파일은 원상태 그대로 유지되어야 한다. 즉 file을 reopen 해서 들고 있어야함. 왜냐면 munmap() 시 file을 close 해버리기 때문.
file-backed 를 메모리에 적재하는 것은 lazy_load_segment 와 거의 같다. 차이는 vm_alloc_page_with_initializer 에서 type을 VM_FILE , lazy_load_file 를 호출하여 메모리에 적재한다.
munmap 될 때 dirty 인 페이지들은 모두 파일에 write 해야하고 not dirty인 페이지들은 그냥 버리면된다.
이번주는 구현하는데 시간을 쏟아서 개인적으로 정리하지 못했다. 팀 노션을 참고하며 나중에 복습하려 했지만 그래도 혼자 정리해보려고 했다. 하루만에 정리를 다 하려하니 굉장히 버겁다.. prj3의 나머지 내용들은 중간 중간 팀원과 큰 그림을 그렸던 사진과 팀 노션 링크로 대체하겠다.
-
stack growth 까지의 큰 흐름
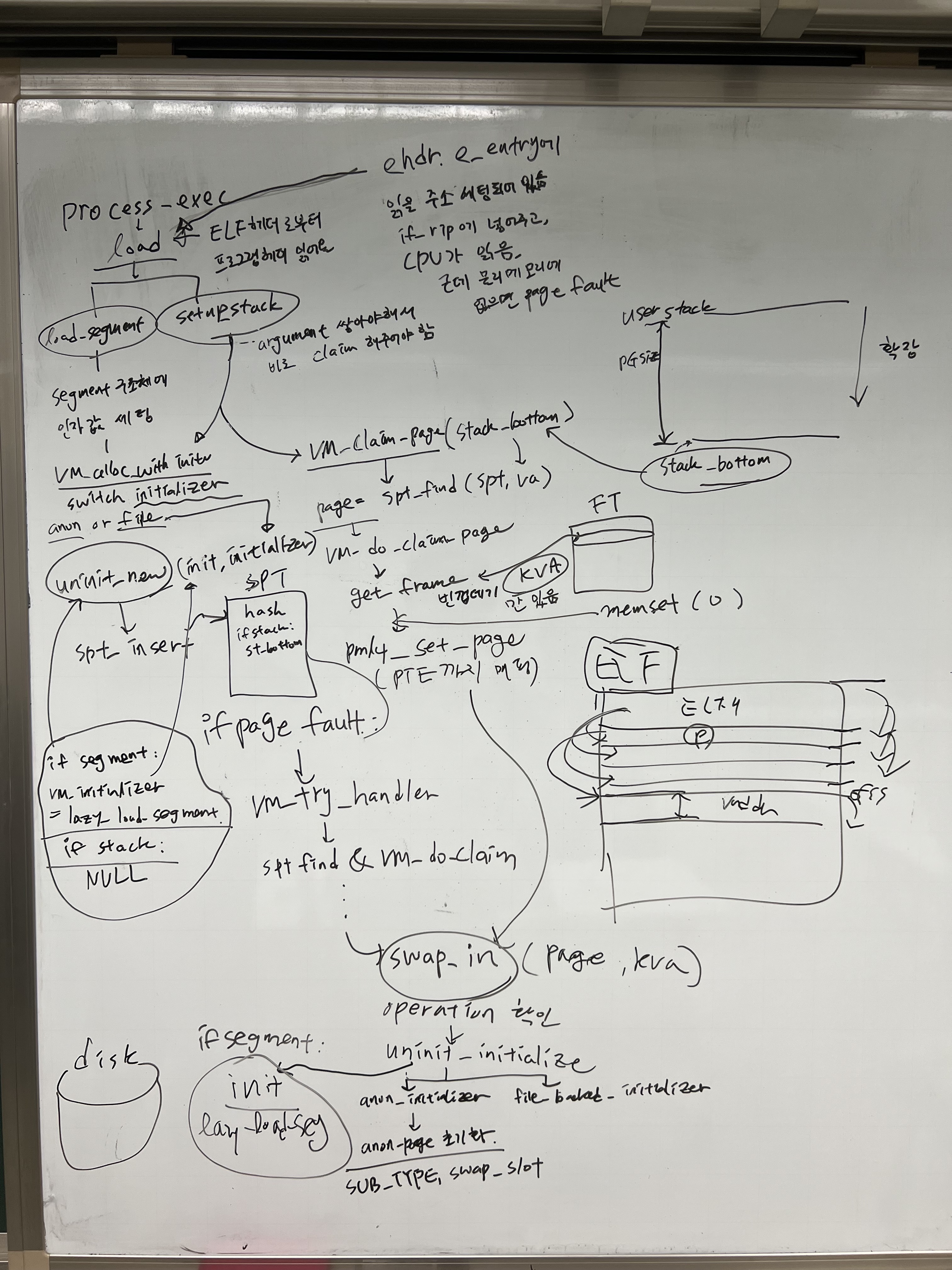
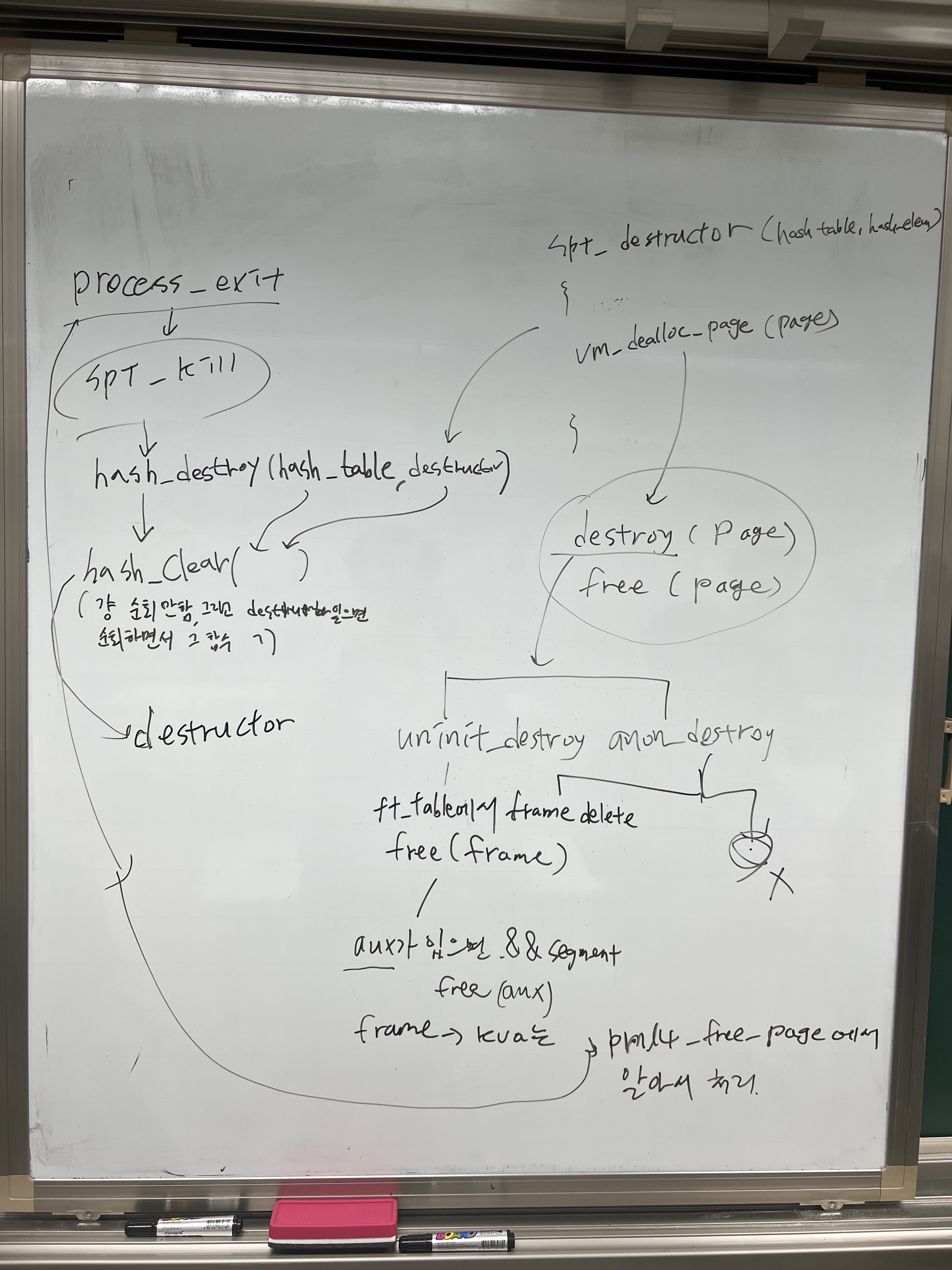
-
anon_page swap in/swap out 흐름

팀 노션 - https://www.notion.so/eleshock/Team-4-Project-3-Virtual-Memory-53ee57e6daf14aad954a210b2a40f6c6
나의 회고
회고 1
굉장히 어려웠음. 지금 돌이켜보니 pintos 코드를 분석하다보면 운영체제 지식이 자연스레 들어오는데, 코드를 파보기가 어렵다고 생각되어서 이론 위주로 외부 자료들을 많이 참고하여 공부를 하다보니, 실제 코드를 짤 때는 적용이 어려웠던 것 같다. 시간도 오래걸렸고. 이전에 왜.. ‘답안처럼 보이는 코드를 많이 봤을까?’에 대한 후회가 남는다. 팀원들과 같이 코드를 타고 들어가보면서 루틴을 정리했을 때 엄청 효과적으로 이해되었던 모먼트가 너무 좋았음
회고 2
마지막 swap in/out을 하면서, 계속하면 하게되어있고, 겁만 먹지 않고 내 의지만 잃지 않으면 할 수 있다고 느꼈음. 마지막에는 팀원들의 도움도 많이 안받고, 그 며칠 사이에 지식이 쌓였다고 혼자서 잘 짜볼 수 있었다. 다음 프로젝트인 file system에서도 이 자신감을 가지고 이 방향대로 정진해야겠다. 그리고 내가 맡은 구현 부분에 대해서 나의 의견을 적극적으로 제시해 볼 필요가 있다고 느꼈다. 잘 이끌어준 나머지 팀원 두분께 감사하다.
