|| 문제설명 ||
-
인쇄 대기목록의 가장 앞에 있는 문서(J)를 대기목록에서 꺼낸다.
-
나머지 인쇄 대기목록에서 J보다 중요도가 높은 문서가 한 개라도 존재하면 J를 대기목록의 가장 마지막에 넣는다.
-
그렇지 않으면 J를 인쇄한다.
-
내가 인쇄를 요청한 문서가 몇 번째로 인쇄되는지 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성하라.
- priorities : 현재 대기목록에 있는 문서의 중요도가 순서대로 담긴 배열
- location : 내가 인쇄를 요청한 문서의 현재 대기목록에서의 위치
_ 현재 대기목록 : 1개 이상 100개 이하의 문서
_ 인쇄 작업의 중요도 : 1~9 (숫자가 클수록 중요)
_ 0 <= location <= (현재 대기목록에 있는 작업 수 - 1)|| 문제해결과정 ||
- size : priorities의 길이
- l : 변경될 location의 값
- 운선순위가 낮으면 priorities에 추가하여....|| 코드 ||
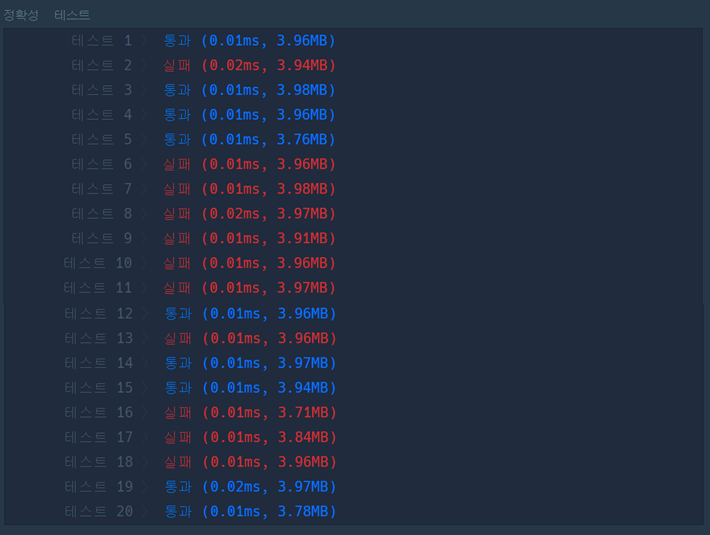
[2020.07.27] 실패
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> priorities, int location) {
int answer = 0, size = priorities.size(), l = location;
for(int i = 0; i < priorities.size() - 1; i++) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < priorities.size(); j++) {
if (priorities[i] < priorities[j]) {
priorities.push_back(priorities[i]);
if (i < location) l--;
else if (i == location) {
location += size;
l += size;
}
break;
}
}
}
answer = l % size + 1;
return answer;
}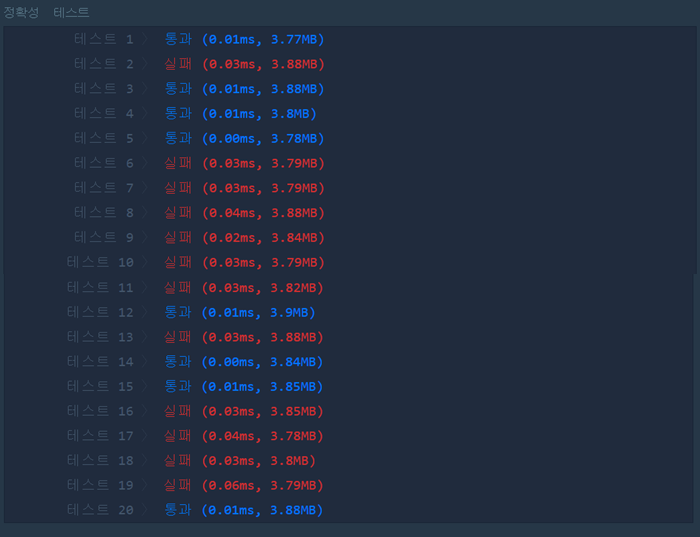
[2020.08.03] 실패
- 우선순위 큐의 사용#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> priorities, int location) {
int answer = 0;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for(int i = 0; i < priorities.size(); i++) {
q.push({priorities[i],i});
}
for(int i=0; i < priorities.size(); i++) {
if(q.top().second == location) {
answer = i;
break;
}
q.pop();
}
answer++;
return answer;
}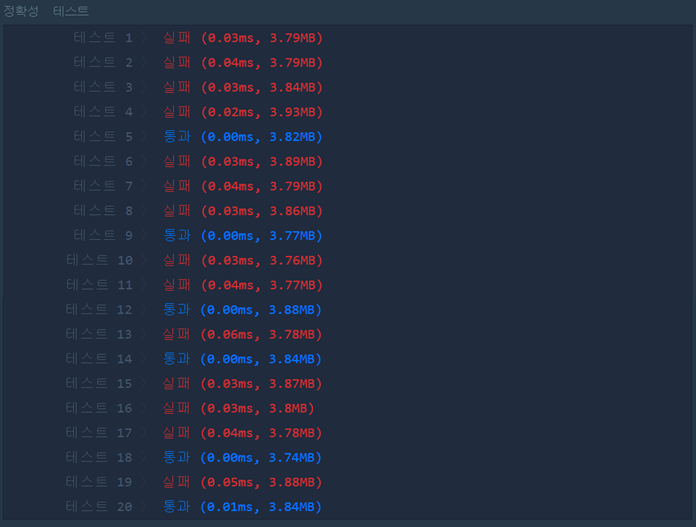
[2020.09.30] 성공
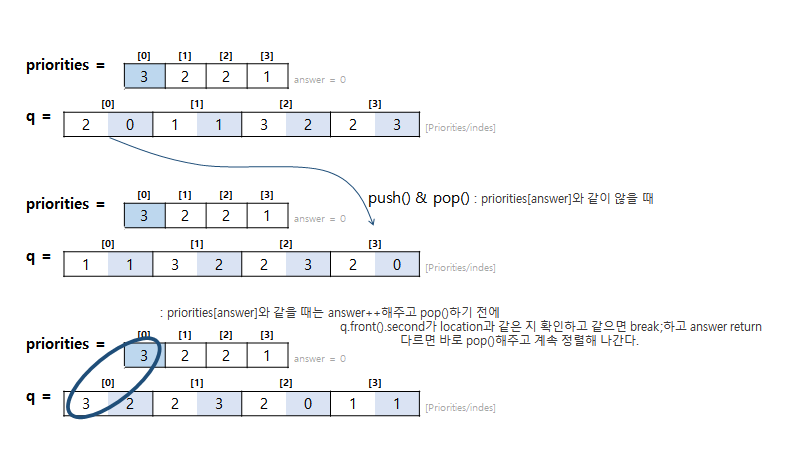
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <utility>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool compare(int a, int b) {
return a > b;
}
int solution(vector<int> priorities, int location) {
int answer = 0;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for(int i = 0; i < priorities.size(); i++) {
q.push({priorities[i], i});
}
sort(priorities.begin(), priorities.end(), compare);
while(!q.empty()) {
if(q.front().first == priorities[answer]) {
answer++;
if(q.front().second == location) break;
q.pop();
}
else {
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
}
}
return answer;
}
[2021.01.16]
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool compare(int a, int b) {
return a > b;
}
int solution(vector<int> priorities, int location) {
int out = 0, size = priorities.size();
queue<int> q;
for(int i : priorities)
q.push(i);
sort(priorities.begin(), priorities.end(), compare);
while(1) {
if(q.front() == priorities[out]) {
out++;
if(location == 0) break;
}
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
(location == 0) ? location += size-out-1 : location--;
}
return out;
}