✨KB IT's Your Life✨ 5기 TIL 기자단 활동
KB IT's Your Life 5기에서 학습한 내용을 복습하고자 정리한 글
기간: 7/18 ~ 7/26
학습 내용: JDBC & MongoDB
MongoDB 내용은 곧 추가 예정
JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)란?
JAVA로 데이터베이스에 접속하여 각종 SQL문을 수행할 수 있는 기능을 제공하는 API
JDBC API는 JAVA에서 제공하며, 인터페이스가 이미 정의되어있어 DB 종류 상관없이 같은 방법으로 사용 가능
JAVA의 철학: “Write Once, Run Anywhere”
자바의 철학을 데이터베이스 연동에서도 실현하기 위해 만들어진 것이 JDBC
JDBC를 통해 특정 DBMS에 종속되지 않는 코드 작성 가능!
JDBC의 사용 목적
- 데이터베이스 연동
JDBC를 통해 JAVA 애플리케이션에서 데이터베이스에 저장된 데이터 조회, 삽입, 수정, 삭제가 가능
- DBMS 독립성 제공
다양한 DBMS(Oracle, MySQL 등)에 대해 동일한 API 사용 가능
- 유연성 제공
다양한 데이터베이스 드라이버를 통해 여러 종류의 데이터베이스에 접근 가능
- 표준화된 SQL 실행
JDBC 사용을 통해 표준화된 SQL문을 사용하여 데이터베이스 작업 수행 가능
- 트랜잭션 관리
JDBC는 데이터베이스 트랜잭션을 지원하여 트랜잭션을 통해 여러 개의 데이터베이스 작업을 하나의 논리적 작업 단위로 묶어 원자성 보장 가능원자성(Atomcity)이란?
트랜잭션은 더 이상 분해 불가능한 업무의 최소단위이므로 전부 처리되거나 아예 하나도 처리되지 않아야하는 ALL OR NOTHING 특성을 원자성이라고 한다!
JDBC의 주요 구성요소
- JDBC 드라이버
특정 DBMS와 JAVA 애플리케이션 사이에서 데이터 주고받는 통신을 담당
각 DBMS에서 자체 JDBC 드라이버 제공
- DriverManager
적절한 JDBC 드라이버를 불러오고 데이터베이스 연결을 관리하는 클래스
- Connection
데이터베이스와의 연결을 나타내는 인터페이스
Connection 인터페이스를 통해 SQL 명령문 실행 가능
SQL 쿼리 실행을 위한 Statement, PrepareStatement 등을 생성하는데 사용
- Statement
SQL 쿼리를 실행하기 위한 인터페이스
Connection 객체를 통해 생성
- ResultSet
SQL 쿼리의 결과 집합을 나타내는 인터페이스
결과를 반복하고 구조화된 형식으로 데이터베이스에서 데이터를 검색하는 방법 제공
JDBC 어플리케이션 구조
클라이언트(UI) ↔ JAVA 프로그램(DB관련 처리, DAO) ↔ DB 서버의 3-tier 구조
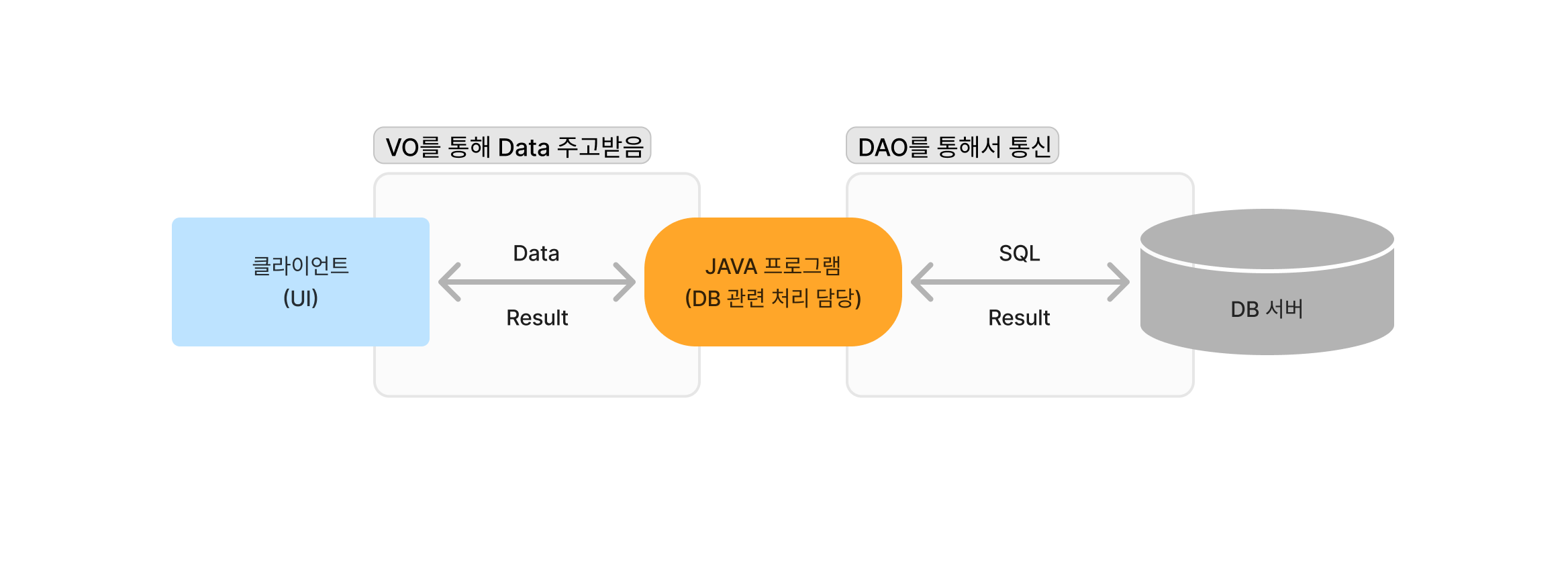
클라이언트가 보낸 데이터 받아서 JDBC API(자바 프로그램)가 아래와 같은 작업 처리하여 DB서버로 전달
- 사용할 드라이버 설정
- DB 연결
- SQL문 생성
- Oracle 서버로 SQL 전송
2-tier 구조와 3-tier 구조란?
2-tier 구조
웹 서버가 DB에 직접 연결되는 형태
하나의 클라이언트에 서버 프로세스가 하나씩 생성되는 방식
클라이언트가 직접 서버의 DB에 접속하여 자원을 활용
보안에 취약하고 유지보수가 어려운 방식
3-tier 구조
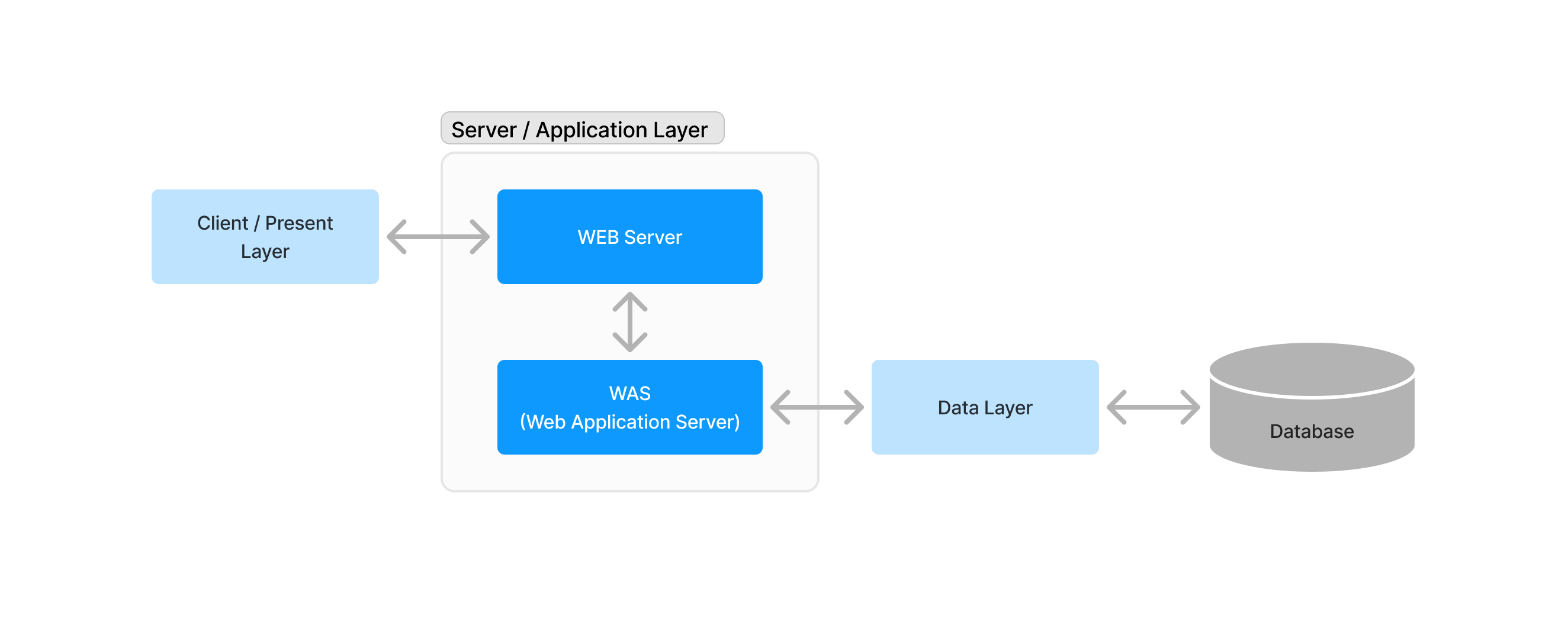
웹 서버와 DB 서버를 논리적 혹은 물리적으로 분리한 형태
서버를 통해서만 DB 서버에 접속 가능한 방식
- WEB Server
보통 사용자(클라이언트)가 마주하는 GUI, 인터페이스, 웹 화면을 제공하는 서버
HTTP 통신을 통해 브라우저 화면 및 기능 요소들을 보여주는 계층
- WAS(Web Application Server)
다양한 기능들의 동작을 실질적으로 처리하는 계층
- Database Server
WAS에서 사용자의 요청 처리 시 데이터의 추가 및 변경 등의 작업과 사용자들의 데이터를 보관하는 계층
DAO & VO(DTO)
DAO(Data Access Object)
DB에 접근하여 DB 관련 처리를 담당하는 클래스
각 기능별로 메서드를 구현
VO(Value Object) = DTO(Data Transfer Object)
많은 양의 데이터를 전달할 목적으로 사용한는 데이터 전달 담당 클래스
값들을 넣어서 전달하고, 전달된 값들을 꺼내서 사용하는 역할
JDBC 프로그래밍
IntelliJ에서 JDBC 연결하기
- MVN Repository에서 설치된 mysql 버전과 호환되는 mysql-connector-j 다운로드 후 프로젝트 설정에서 라이브러리 추가
- IntelliJ에서 직접 다운로드하여 설정(프로젝트 구조 > 라이브러리 > 설치된 mysql 버전과 호환되는 mysql-connector-j 선택하여 추가)
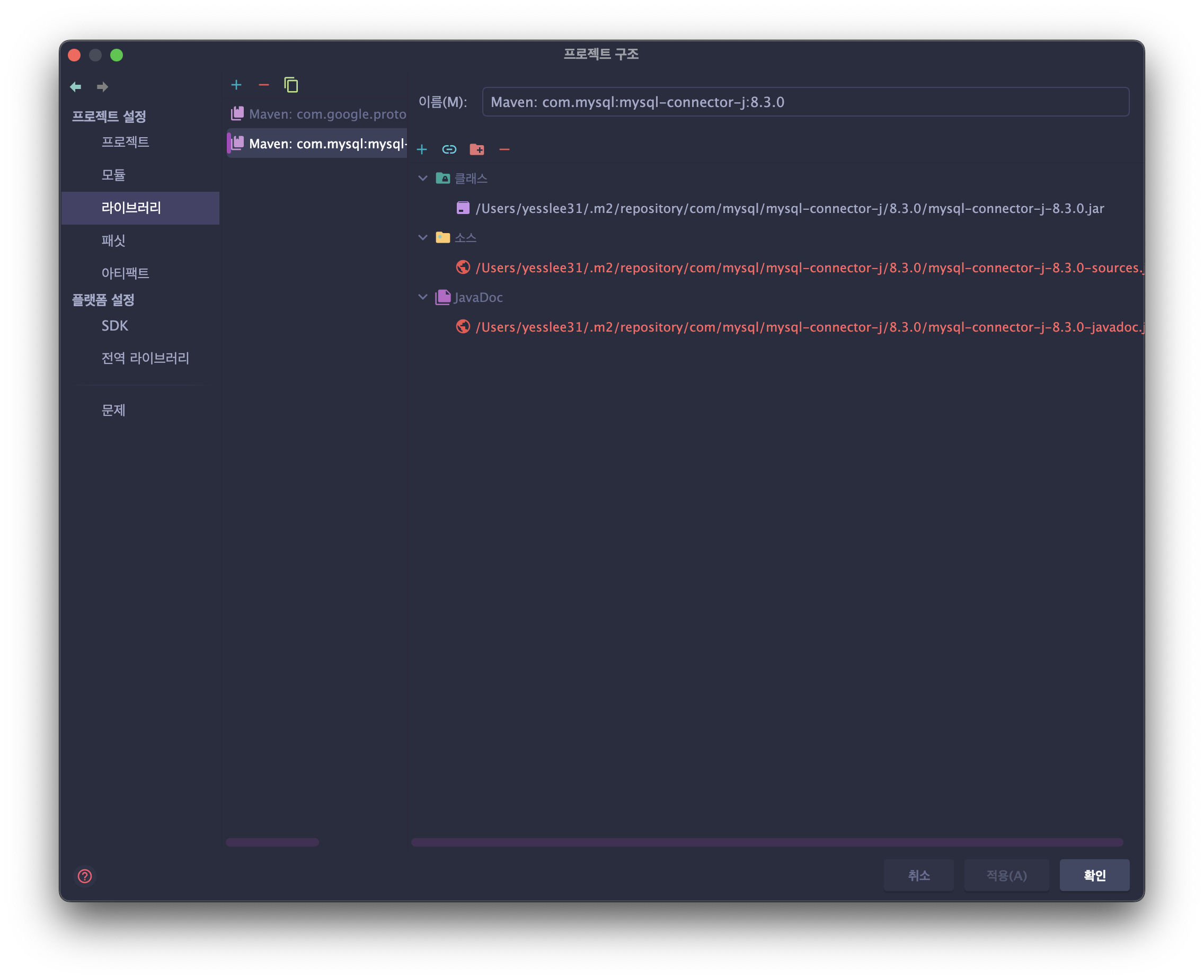
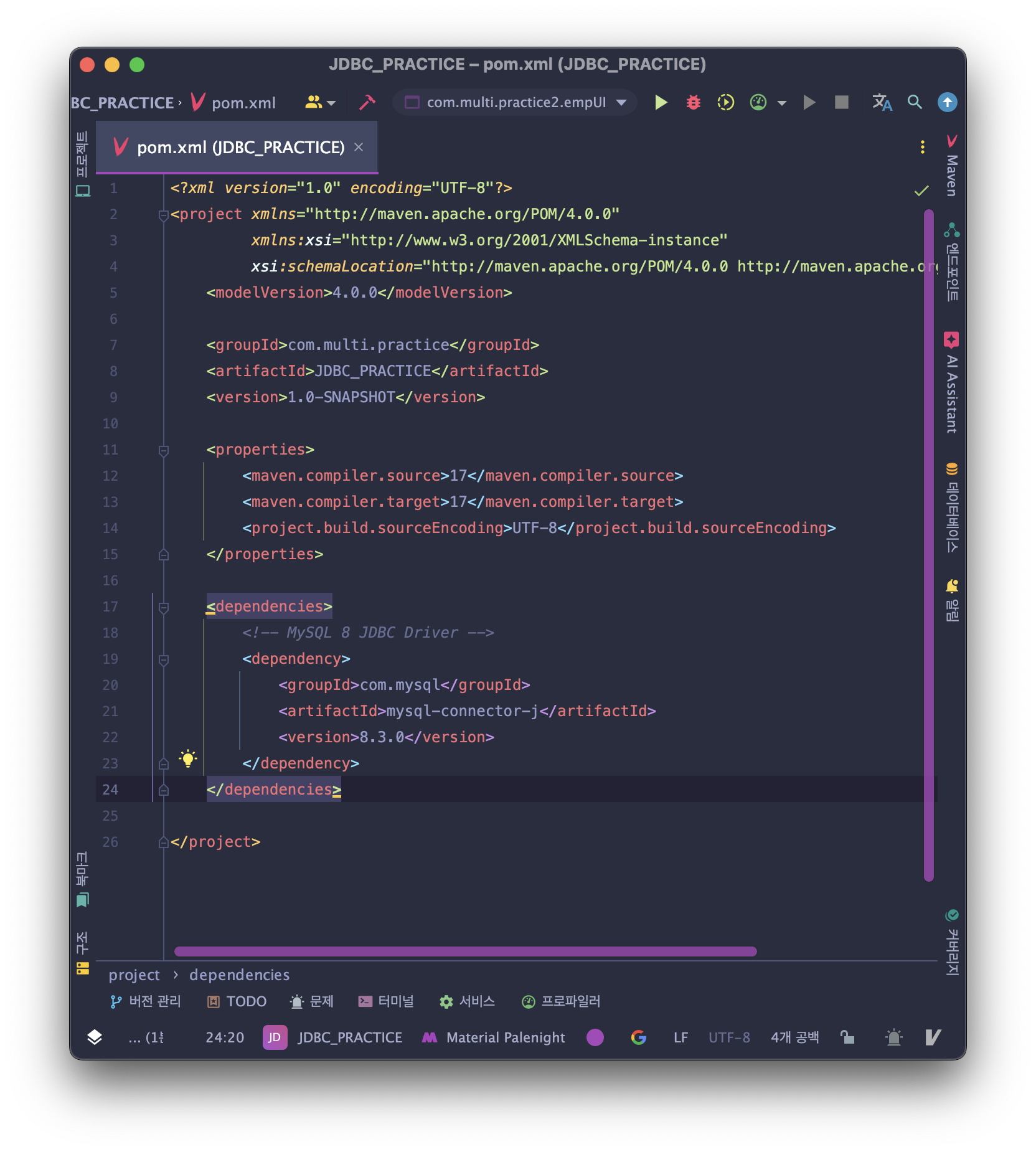
- Maven 프로젝트 생성 후 pom.xml에 dependencies 설정 추가 후 동기화
→ MVN Repository에서 dependencies code 제공
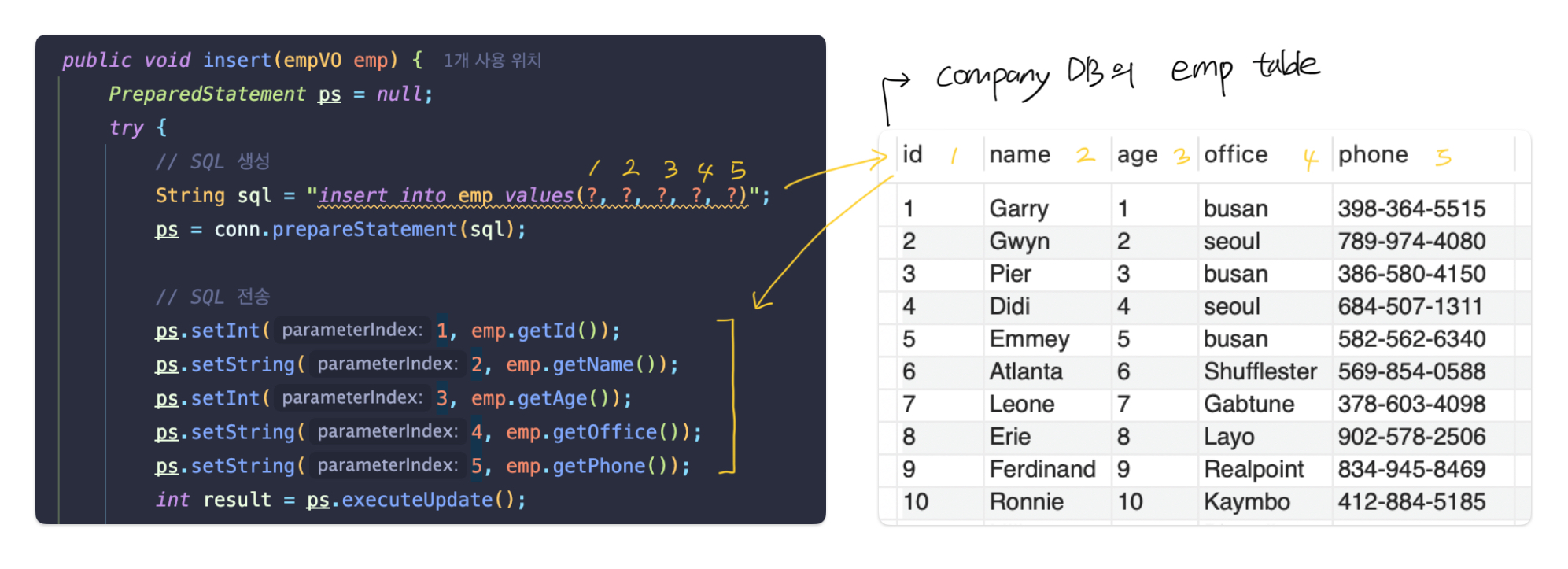
company DB의 emp 테이블 사용
CREATE DATABASE company;
CREATE TABLE emp (
id INT NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
age INT DEFAULT NULL,
office VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
phone VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);생성된 emp 테이블에 해당 데이터 import하여 JDBC 프로그래밍 진행
VO Code
// columns: id, name, age, office, phone
public class empVO {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String office;
private String phone;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getOffice() {
return office;
}
public void setOffice(String office) {
this.office = office;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "empVO { " +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", office='" + office + '\'' +
", phone='" + phone + '\'' +
" }";
}
}IDE에서 getter/setter 생성 기능을 이용하면 간단하게 작성 가능!
변수 작성한 뒤 코드 > 생성 > getter 및 setter 실행
DAO Code
JDBC 프로그래밍 4단계
- 드라이버 로딩(리플렉션)
- DB 연결
- SQL문 객체화 → DBCP등의 라이브러리가 처리
- SQL문 실행 요청 → Spring, myBatis, JPA 등의 라이브러리가 처리
각 단계별로 처리해주는 라이브러리 많이 존재함!
드라이버 로딩 & DB 연결 생성자
private Connection conn;
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/company";
private static String user = "root";
private static String pw = "1234";
public empDAO() {
try {
// 드라이버 설정
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
// DB 연결
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pw);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}INSERT
public void insert(empVO emp) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "insert into emp values(?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
ps.setInt(1, emp.getId());
ps.setString(2, emp.getName());
ps.setInt(3, emp.getAge());
ps.setString(4, emp.getOffice());
ps.setString(5, emp.getPhone());
int result = ps.executeUpdate();
if (result == 1) {
System.out.println("삽입 성공");
} else {
System.out.println("삽입 실패");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}DELETE
public void delete(int id) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "delete from emp where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
ps.setInt(1, id);
int result = ps.executeUpdate();
if (result == 1) {
System.out.println("삭제 성공");
} else {
System.out.println("삭제 실패");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}UPDATE
public void update(empVO emp) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "update emp set name = ?, age = ?, office = ?, phone = ? where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
ps.setString(1, emp.getName());
ps.setInt(2, emp.getAge());
ps.setString(3, emp.getOffice());
ps.setString(4, emp.getPhone());
ps.setInt(5, emp.getId());
int result = ps.executeUpdate();
if (result == 1) {
System.out.println("갱신 성공");
} else {
System.out.println("갱신 실패");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}SELECT (One)
public void selectOne(int id) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "select * from emp where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
ps.setInt(1, id);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
empVO emp = new empVO();
emp.setId(rs.getInt(1));
emp.setName(rs.getString(2));
emp.setAge(rs.getInt(3));
emp.setOffice(rs.getString(4));
emp.setPhone(rs.getString(5));
System.out.println(emp);
} else {
System.out.println("검색 결과 없음");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 자원 해제
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}SELECT (All)
public ArrayList<empVO> selectAll() {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
ArrayList<empVO> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "select * from emp";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
empVO emp = new empVO();
emp.setId(rs.getInt(1));
emp.setName(rs.getString(2));
emp.setAge(rs.getInt(3));
emp.setOffice(rs.getString(4));
emp.setPhone(rs.getString(5));
list.add(emp);
}
for (empVO vo : list) {
System.out.println(vo.toString());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 자원 해제
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}DAO 전체 코드
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
// insert, delete, update, selectOne, selectALL
public class empDAO {
private Connection conn;
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/company";
private static String user = "root";
private static String pw = "1234";
public empDAO() {
try {
// 드라이버 설정
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
// DB 연결
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pw);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void insert(empVO emp) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "insert into emp values(?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
ps.setInt(1, emp.getId());
ps.setString(2, emp.getName());
ps.setInt(3, emp.getAge());
ps.setString(4, emp.getOffice());
ps.setString(5, emp.getPhone());
int result = ps.executeUpdate();
if (result == 1) {
System.out.println("삽입 성공");
} else {
System.out.println("삽입 실패");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void delete(int id) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "delete from emp where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
ps.setInt(1, id);
int result = ps.executeUpdate();
if (result == 1) {
System.out.println("삭제 성공");
} else {
System.out.println("삭제 실패");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void update(empVO emp) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "update emp set name = ?, age = ?, office = ?, phone = ? where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
ps.setString(1, emp.getName());
ps.setInt(2, emp.getAge());
ps.setString(3, emp.getOffice());
ps.setString(4, emp.getPhone());
ps.setInt(5, emp.getId());
int result = ps.executeUpdate();
if (result == 1) {
System.out.println("갱신 성공");
} else {
System.out.println("갱신 실패");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void selectOne(int id) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "select * from emp where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
ps.setInt(1, id);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
empVO emp = new empVO();
emp.setId(rs.getInt(1));
emp.setName(rs.getString(2));
emp.setAge(rs.getInt(3));
emp.setOffice(rs.getString(4));
emp.setPhone(rs.getString(5));
System.out.println(emp);
} else {
System.out.println("검색 결과 없음");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 자원 해제
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public ArrayList<empVO> selectAll() {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
ArrayList<empVO> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// SQL 생성
String sql = "select * from emp";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL 전송
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
empVO emp = new empVO();
emp.setId(rs.getInt(1));
emp.setName(rs.getString(2));
emp.setAge(rs.getInt(3));
emp.setOffice(rs.getString(4));
emp.setPhone(rs.getString(5));
list.add(emp);
}
for (empVO vo : list) {
System.out.println(vo.toString());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 자원 해제
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}
}SQL문에서 사용된 ? 는 어떤 의미?
매개변수 값 부분의 위치를 물음표로 표시한 것!
index는 물음표 순서대로 1부터 부여되는 점에 유의할 것
(시작 index가 0이 아님!)
Main Code
import java.util.Scanner;
public class empUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
empDAO dao = new empDAO();
empVO emp;
while (true) {
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("1. insert | 2. delete | 3. update | 4. select One | 5. select All | 0. exit");
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------");
int flag = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
if (flag == 0) break;
switch (flag) {
case 1:
emp = new empVO();
System.out.println("INSERT");
System.out.print("insert id: ");
emp.setId(sc.nextInt());
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("insert name: ");
emp.setName(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("insert age: ");
emp.setAge(sc.nextInt());
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("insert office: ");
emp.setOffice(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("insert phone: ");
emp.setPhone(sc.nextLine());
dao.insert(emp);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("DELETE");
System.out.print("delete id: ");
dao.delete(sc.nextInt());
sc.nextLine();
break;
case 3:
emp = new empVO();
System.out.println("UPDATE");
System.out.print("update id: ");
emp.setId(sc.nextInt());
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("update name: ");
emp.setName(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("update age: ");
emp.setAge(sc.nextInt());
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("update office: ");
emp.setOffice(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("update phone: ");
emp.setPhone(sc.nextLine());
dao.update(emp);
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("SELECT ONE");
System.out.print("select id: ");
dao.selectOne(sc.nextInt());
sc.nextLine();
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("SELECT ALL");
dao.selectAll();
break;
}
}
}
}