
Practice 1-1
문제 설명
입력된 정수 자료형의 숫자를 거꾸로 변환하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
- 예를들어 12345가 입력되면 54321로 변환하여 출력하면 된다.
- 100의 경우 001이 되는데 이 경우 1만 출력하도록 한다.
입출력 예시
| 입력 | 결과 |
|---|---|
| 12345 | 54321 |
| -12345 | -54321 |
| 100 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 |
public class Practice1 {
public static void solution(int num) {
int numReverse = 0; // 숫자를 뒤집은 결과
boolean isMinus = false; // 음수인지 체크
if (num < 0) { // 음수일 경우
isMinus = true; // 음수인 조건을 변수에 저장.
num *= -1; // 우선 양수로 바꿔준다.
}
while (num > 0) {
int r = num % 10; // 맨 뒤의 숫자를 변수 r에 저장
num /= 10; // 뒷자리 숫자 없애기
numReverse = numReverse * 10 + r; // 숫자 뒤집어줌
}
System.out.println(isMinus ? numReverse * -1 : numReverse); // 음수일 경우 - 붙여서 출력
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
solution(12345);
solution(-12345);
solution(100);
solution(0);
}
}
Practice 2-2
문제 설명
아스키 코드는 미국정보교환표준부호를 의미한다.
영어로 American Standard Code for Information Interchange 이며, 줄여서 ASCII 라고 한다.
문자를 사용하는 대부분의 장치에서 사용하며 문자 인코딩 방식에 아스키를 기초로 두고 있다.
다음은 아스키의 특징이다.
- 7비트로 구성
- 총 128개의 문자로 구성 (출력 불가능한 제어문자 33개, 출력 가능한 문자 95개)
- 출력 가능한 문자들은 52개의 영문 알파벳 대소문자와, 10개의 숫자, 32개의 특수 문자, 1개의 공백 문자로 이루어진다.
이번 문제에서는 아스키 코드 중 알파벳에 대해서,
사용자가 입력한 알파벳의 대소문자를 변경하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입출력 예시
| 입력 | 결과 |
|---|---|
| a | A |
| b | B |
| C | c |
| D | d |
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Practice2 {
public static void solution() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("알파벳 입력: ");
char alphabet = sc.nextLine().charAt(0);
// string으로 저장된 문자열 중에서 0번째 인덱스를 선택해 char타입으로 변환!
if(alphabet >= 'a' && alphabet <= 'z') {
alphabet = (char) (alphabet - 'a' + 'A');
} else if(alphabet >= 'A' && alphabet <= 'Z') {
alphabet = (char) (alphabet - 'A' + 'a');
} else {
System.out.println("입력하신 값이 알파벳이 아닙니다.");
}
System.out.println("변환: " + alphabet);
}
public static void reference() {
int a = (int)'a';
System.out.println("a = " + a);
int z = (int)'z';
System.out.println("z = " + z);
int A = (int)'A';
System.out.println("A = " + A);
int Z = (int)'Z';
System.out.println("Z = " + Z);
int etc = (int)'%';
System.out.println("etc = " + etc);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
reference(); // 아스키 코드 참고
solution();
}
}Practice 1-3
문제 설명
자바의 String 자료형에는 많은 연산자 기능들이 있다.
프로그래밍의 기본기를 익히기 위해 일부 연산자들을 제한하고 다음의 기능을 구현하려 한다.
- String 의 replace 기능 구현
- String의 replace, indexOf, contains를 사용하지 않고 구현한다.
입출력 예시
| 입력 문자열 | from | to | 출력 |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Hello Java, Nice to meet you! Java is fun!" | "Java" | "자바" | "Hello 자바, Nice to meet you! 자바 is fun!" |
| POP | P | W | WOW |
public class Practice3 {
public static String solution(char[] str, char[] find, char[] to) {
int idx = 0;
String replaceStr = "";
char[] replaceBucket = str.clone(); // 중간에 변경하면서 임시로 사용할 배열
do {
idx = findIndex(replaceBucket, find);
if (idx != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i++) {
replaceStr += replaceBucket[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < to.length; i++) {
replaceStr += to[i];
}
for (int i = idx + find.length; i < replaceBucket.length; i++) {
replaceStr += replaceBucket[i];
}
replaceBucket = replaceStr.toCharArray();
replaceStr = "";
}
} while (idx != -1); // 매칭되는 문자를 찾을 때까지
replaceStr = new String(replaceBucket);
return replaceStr;
}
public static int findIndex(char[] str, char[] find) {
int idx = -1;
boolean isMatch = false;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (str[i] == find[0] && str.length - i >= find.length) {
isMatch = true;
for (int j = 0; j < find.length; j++) {
if (str[i + j] != find[j]) {
isMatch = false; // 한글자만이라도 같지 않으면 false!
break;
}
}
}
if (isMatch) {
idx = i;
break;
}
}
return idx;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
String str = "Hello Java, Nice to meet you! Java is fun!";
String find = "Java";
String to = "자바";
// 기존 String replace
System.out.println(str.replace(find, to));
// 자체 구현 replace
char[] strExArr = str.toCharArray();
char[] findArr = find.toCharArray();
char[] toArr = to.toCharArray();
System.out.println(solution(strExArr, findArr, toArr));
strExArr = "POP".toCharArray();
findArr = "P".toCharArray();
toArr = "W".toCharArray();
System.out.println(solution(strExArr, findArr, toArr));
}
}Practice 1-4
문제 설명
여러가지 별찍기 연습을 해보자.
반복문과 조건문의 연습에는 과연 별찍기 만한 것이 없다.
아래 5가지 별 찍기 타입이 있다.
- 아래 모양은 N (별 출력 행의 수)이 3일 떄의 출력 결과 들이다.
| 타입 | 모양 |
|---|---|
| 1 | *** *** *** |
| 2 | * ** *** |
| 3 | * ** *** |
| 4 | * *** ***** |
| 5 | * *** * |
별 출력 행의 수 N과 별 타입 T가 주어질 때 해당 별 모양을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
(N은 홀수)
입출력 예시
| N | T | 출력 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1 | *** *** *** |
| 3 | 2 | * ** *** |
| 3 | 3 | * ** *** |
| 3 | 4 | * *** ***** |
| 7 | 5 | * *** ***** ******* ***** *** * |
public class Practice4 {
public static void solution(int n, int type) {
if (type == 1) {
type1(n);
} else if (type == 2) {
type2(n);
} else if (type == 3) {
type3(n);
} else if (type == 4) {
type4(n);
} else if (type == 5) {
type5(n);
}
}
public static void type1(int n) {
System.out.println("== Type1 ==");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void type2(int n) {
System.out.println("== Type2 ==");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i + 1; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void type3(int n) {
System.out.println("== Type3 ==");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (j < n - i - 1) {
System.out.print(" ");
} else {
System.out.print("*");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void type4(int n) {
System.out.println("== Type4 ==");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int j = 0; j < i * 2 + 1; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void type5(int n) {
System.out.println("== Type5 ==");
// 상단부
for (int i = 0; i <= n / 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n / 2 - i; j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int j = 0; j < i * 2 + 1; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 하단부
for (int i = n / 2; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < n / 2 + 1 - i; j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int j = 0; j < i * 2 - 1; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
solution(3, 1);
solution(3, 2);
solution(3, 3);
solution(3, 4);
solution(7, 5);
}
}Practice 1-5
문제 설명
n개의 데이터가 height 배열에 주어졌다.
height 배열의 각각의 원소는 아래 그림과 같이 각 벽에 대한 높이를 의미한다.
이와 같이 높이 값들이 주어졌을 때,
이 중에서 어떤 두 벽을 고르면 가장 많은 물을 담을 수 있는지를 확인하고
그 때의 면적을 출력하세요.
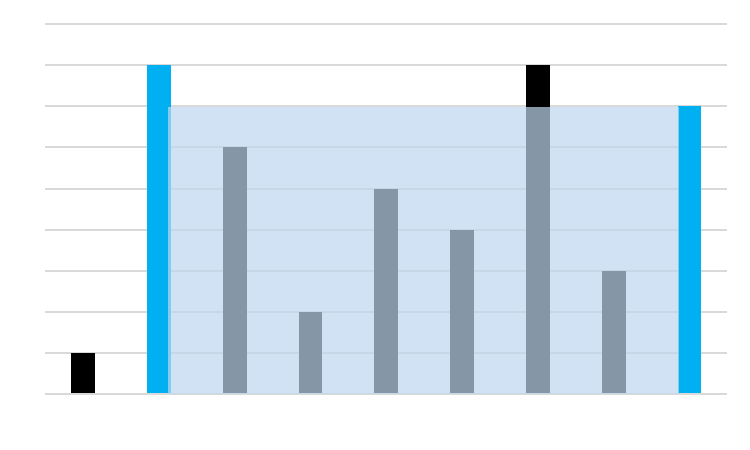
입출력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7 | 49 |
| 5, 3, 9, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2 | 26 |
public class Practice5 {
public static int solution(int[] height) {
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
int maxArea = 0;
while (left < right) {
// sol1
int x = (right - left);
int y = height[left] < height[right] ? height[left] : height[right];
int curArea = x * y;
maxArea = maxArea > curArea ? maxArea : curArea;
// sol2
curArea = x * Math.min(height[left], height[right]);
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, curArea);
// 더 작은 쪽의 높이를 가운데쪽으로 옮겨주기
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
left++; // left 오른쪽으로 한 칸 이동
} else {
right--; // right 왼쪽으로 한 칸 이동
}
}
return maxArea;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] height = {1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7};
System.out.println(solution(height));
height = new int[]{5, 3, 9, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2};
System.out.println(solution(height));
}
}