who
- 현재 로그인된 사용자들의 목록 및 시간, 접속 터미널 등의 정보를 출력
man who
- man(manual) 명령어로 특정 명령어의 manual 확인 가능
$ who man- /var/run/utmp 파일에 현재 로그인한 사용자 상태 정보가 저장됨을 알 수 있음
man -k
- option -k: keyword 관련 매뉴얼 검색 및 간단한 설명 출력
utmp
- 현재 로그인한 사용자의 정보를 저장하고 있는 log 파일
find
- 파일 위치 검색 명령어
$ find /usr/include/ -name utmp.h
> /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/utmp.hvi
- 파일 내용 확인 명령어
$ vi /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/utmp.hstruct
struct utmp
{
short int ut_type; /* Type of login. */
pid_t ut_pid; /* Process ID of login process. */
char ut_line[UT_LINESIZE] /* Devicename. */
char ut_id[4] /* Inittab ID. */
char ut_user[UT_NAMESIZE] /* Username. */
char ut_host[UT_HOSTSIZE /* Hostname for remote login. */
struct exit_status ut_exit; /* Exit status of a process marked as DEAD_PROCESS. */
#if __WORDSIZE_TIME64_COMPAT32
int32_t ut_session; /* Session ID, used for windowing. */
struct
{
int32_t tv_sec; /* Seconds. */
int32_t tv_usec; /* Microseconds. */
} ut_tv; /* Time entry was made. */
#else
long int ut_session; /* Session ID, used for windowing. */
struct timeval ut_tv; /* Time entry was made. */
#endif
int32_t ut_addr_v6[4]; /* Internet address of remote host. */
char
__glibc_reserved[20]; /* Reserved for future use. */
};- char ut_user[UT_NAMESIZE]: Username
- int32_t tv_sec: 어느 한 시점에서 현재까지의 sec
How who works
- utmp 파일에서 각 사용자별 로그인 정보를 struct utmp 형태로 읽어옴
File open/close/read
-
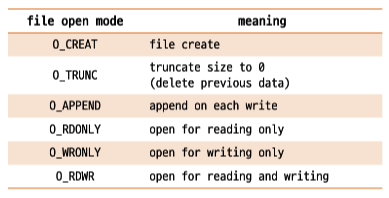
open
#include <sys/types.h> #include <fcntl.h> int open(const char *path, int flag); -> return a file descriptor if success, -1 if error
- sys/types.h: 시스템 소스 코드에서 사용되는 데이터 유형 정의
- fnctl.h: open의 flag에 지정할 수 있는 값 정의
- path: 파일 경로 + 파일명
- flag: open mode
-
close
#include <unistd.h> int close(int fd); -> return 0 if success, -1 if error- unistd.h: POSIX 표준과의 호환성을 위해 필요한 정의를 포함하는 파일을 포함
- fd: file descriptor
-
read
#include <unistd.h> ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t nbytes); -> 실제 읽은 byte 수를 리턴 -> EOF면 0 리턴, 읽기 실패하면 1 리턴- nbytes: 읽을 수 있는 최대 바이트 수
time
-
기본형
#include <time.h> char *ctime(const time_t *timer);
- time.h: 시간 및 날짜 함수 선언
- ctime: time_t 형식으로 주어진 시간 값을 사람이 읽기 쉽게 변환
-
who에서 응용
#include <time.h> #include <utmp.h> struct utmp buf; time_t sec = (time_t) buf.ut_tv.tv_sec; char *ctime_str = ctime(&sec);
- utmp 구조체의 ut_tv.tv_sec에서 초 단위를 가져와서 time_t 형태로 변환 (time_t는 실제로 long이나 int로 구현되어 있어 그대로 사용하는 경우도 있음)
- 출력 형식 변경
void show_time(long seconds){ time_t sec = (time_t)secondsl char *cp = ctime(&sec); printf("%12.12s", cp+4) }- "%12.12s", cp+4: index 4번부터 총 12개 출력
- origin: Sat Oct 12 02:25:20 2024
- convert: Oct 12 02:25
buffering
- utmp 파일에서 하나의 record를 읽고 한 record씩 화면에 출력하는 방식 대신 system call의 횟수를 줄이기 위해 buffering 기법을 사용
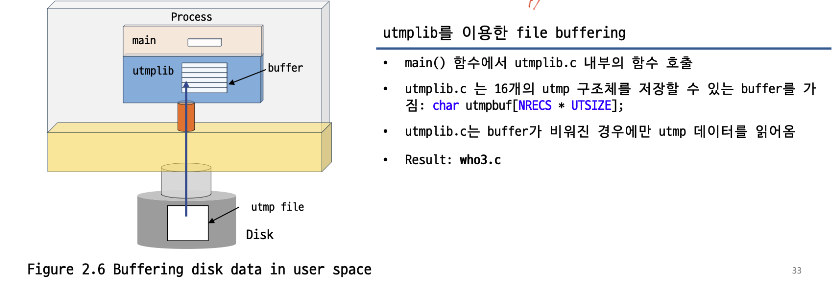
code
utmplib.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <utmp.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define NRECS 16
#define NULLUT ((struct utmp *)NULL)
#define UTSIZE (sizeof(struct utmp))
static char utmpbuf[NRECS * UTSIZE]; // storage(buffer)
static int num_recs; // num stored
static int cur_rec; // next to go
static int fd_utmp = -1;
int utmp_open(char *filename) {
fd_utmp = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
cur_rec = 0;
num_recs = 0;
return fd_utmp;
}
int utmp_reload(){
int amt_read = read(fd_utmp, &utmpbuf, NRECS * UTSIZE);
if (amt_read == -1){
fprintf(stderr, "Error: can not read from the utmp file");
perror("");
exit(-1);
}
num_recs = amt_read / UTSIZE;
cur_rec = 0; // reset to 0
return num_recs;
}
struct utmp *utmp_next(){
struct utmp *recp = NULLUT;
if (fd_utmp == -1){
return recp;
}
if ((cur_rec == num_recs) && (utmp_reload() == 0)){
return recp;
}
recp = (struct utmp *)(&utmpbuf[cur_rec * UTSIZE]);
cur_rec += 1; // increment the pointer by one
return recp;
}
void utmp_close(){
if (fd_utmp != -1){
close(fd_utmp);
}
}utmplib.c 함수 설명
- utmp_open: utmp 파일을 읽기 전용으로 열고, 파일 디스크립터를 fd_utmp에 저장
- utmp_reload: utmp 파일로부터 데이터를 읽어와 utmpbuf에 저장, 레코드의 수 갱신
- utmp_next: utmp 파일에서 다음 레코드 반환
- utmp_close: utmp 파일을 닫고 파일 디스크립터 초기화
who.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <utmp.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
extern int utmp_open(char *filename);
extern struct utmp *utmp_next();
extern void utmp_close();
void show_time(long seconds){
time_t sec = (time_t)seconds;
char *cp = ctime(&sec);
printf("%12.12s", cp+4);
}
void show_info(struct utmp *ut_buf_p){
if (ut_buf_p->ut_type != USER_PROCESS)
return;
printf("%-8.8s", ut_buf_p->ut_user);
printf(" ");
printf("%-8.8s", ut_buf_p->ut_line);
printf(" ");
show_time(ut_buf_p->ut_tv.tv_sec);
if (ut_buf_p->ut_host[0] != '\0'){
printf("(%s)", ut_buf_p->ut_host);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
struct utmp *utbufp = NULL;
if (utmp_open("/var/run/utmp") == -1){
perror("/var/run/utmp");
exit(-1);
} // file open
while ((utbufp = utmp_next()) != NULL){
show_info(utbufp);
} // file read
utmp_close();
return 0;
}who.c 함수 설명
- extern: 외부 함수 사용
- main: utmp 파일 읽기 -> next 함수로 버퍼에서 1개씩 꺼내오면서 출력-> 완료되면 파일 닫기
- show_time: 사용자가 로그인한 시간을 출력(사용자 친화 12자리)
- show_info: user_name, device_name, time, host를 차례로 출력
