프록시 생성 방식
MainAspect 클래스의 코드를 변경했다. 코드 수정 후 MainAspect 클래스를 실행하면 익셉션이 발생한다.
//before
Calculator cal = ctx.getBean("calculator",Calculator.class);
//after
RecCalculator cal = ctx.getBean("calculator",RecCalculator.class)...
Bean named 'calcuator' is expected to be of type 'chap07.RecCalculator'
but was actually of type 'com.sun.$proxy17' getBean() 메서드에 사용한 타입이 RecCalculator인데 반해 실제 타입은 $Proxy17이라는 메세지가 나온다. 스프링이 런타임에 생성한 프록시 객체의 클래스 이름이다. $Proxy 클래스는 RecCalculator 클래스가 상속바은 Calculator 인터페이스를 상속받게 된다. 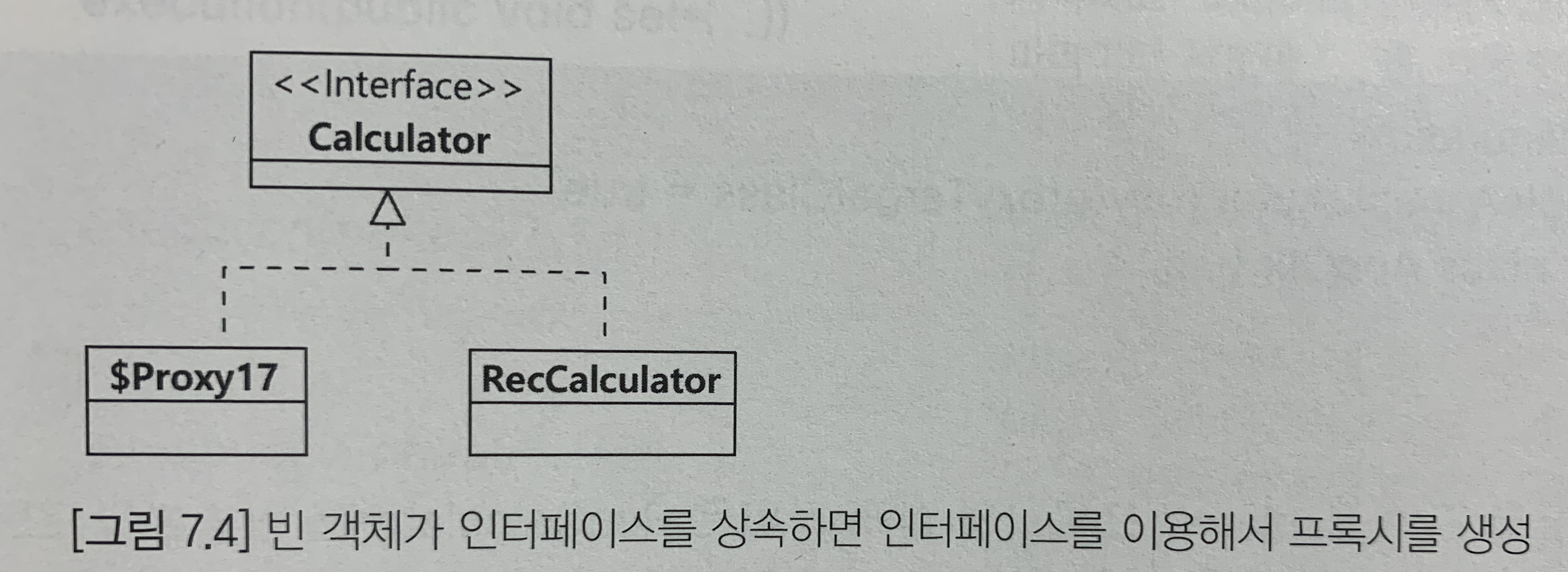
빈 객체가 인터페이스를 상속할 때 인터페이스가 아닌 클래스를 이용해서 프록시를 생성하고 싶으면 아래와 같이 설정할 수 있다.
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass=true)
public class AppCtx{...}@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass=true)로 지정하면 인터페이스가 아닌 자바 클래스를 상속받아 프록시를 생성한다. 스프링이 프록시를 이용해 생성한 빈 객체를 구할 때 다음과 같이 getBean() 메서드에 실제 클래스를 이용해서 빈 객체를 구할 수 있다.
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass=true)
public class AppCtx{...}
RecCalculator cal = ctx.getBean("calculator", RecCalculator.class);execution 명시자 표현식
Aspect를 적용할 위치를 지정할 때 사용한 Pointcut 설정을 보면 execution 명시자를 사용했다.
@Pointcut("execution(public * chap07..*(..))")
private void publicTarget(){}execution 명시자는 Advice를 적용할 메서드를 지정할 때 사용한다.
execution(수식어패턴? 리턴타입패턴 클래스이름패턴?메서드이름패턴(파라미터패턴))Advice 적용 순서
한 Pointcut에 여러 Advice를 적용할 수 있다.
@Aspect
public class ChacheAspect{
private Map<Long, Objec> cache = new HashMap<>();
@Pointcut("execution(public * chap07..*(long))")
public void cacheTarget(){}
@Around("cacheTarget())
public Object execute(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
...
}
} @Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppCtxWithCache{
@Bean
public CacheAspect cacheAspect(){
return new CacheAspect();
}
@Bean
public ExeTimeAspect exeTimeAspect(){
return new ExeTimeAspect();
}
@Bean
public Calculator calculator(){
return new RecCalculator();
}
}@Around의 Pointcut 설정과 Pointcut 재사용
@Pointcut 어노테이션이 아닌 @Around 어노테이션에 execution 명시자를 지정할 수 있다.
@Aspect
public class CacheAspect{
@Around("execution(public * Chap07..(..))")
public Object execute(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
...
}
}같은 Pointcut을 여러 Advice가 함께 사용한다면 공통 Pointcut을 재사용할 수도 있다.
다른 클래스에 위치한 @Around 어노테이션에서 publicTarget() 메서드의 Pointcut을 사용하고 싶으면 public으로 바꾸면 된다.
@Aspect
public class ExeTimeAspect{
@Pointcut("execution(public * Chap07..(..))")
public void publicTarget(){
}
}그리고 Pointcut의 완전한 클래스 이름을 포함한 메서드 이름을 @Around 어노테이션에서 사용하면 된다. CacheAspect 클래스의 @Around 메서드에서 ExeTimeAspect 클래스의 publicTarget()에 정의된 Ponintcut을 사용하는 예시다.
@Aspect
public class CacheAspect{
@Around("aspect.ExeTimeAspect.publicTarget()")
public Object execute(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
...
}
}여러 Aspect에서 공통으로 사용하는 Pointcut이 있다면 별도 클래스에 Pointcut을 정의하고 각 Aspect 클래스에서 해당 Pointcut을 사용하도록 구성하면 관리가 편해진다. 
@Pointcut을 설정한 CommonPointcut은 빈으로 등록할 필요가 없다. @Around 어노테이션에서 해당 클래스에 접근 가능하면 해당 Pointccut을 사용할 수 있다.
