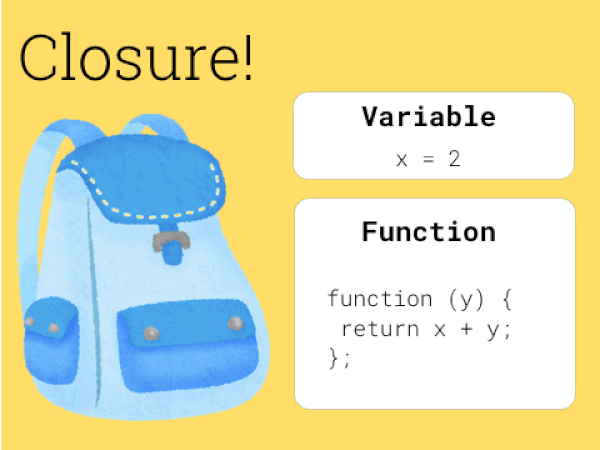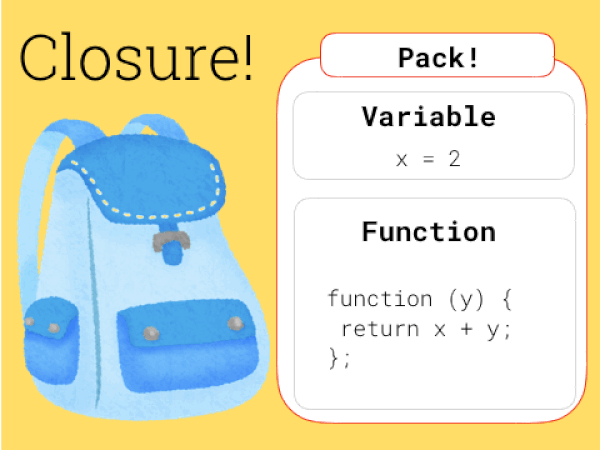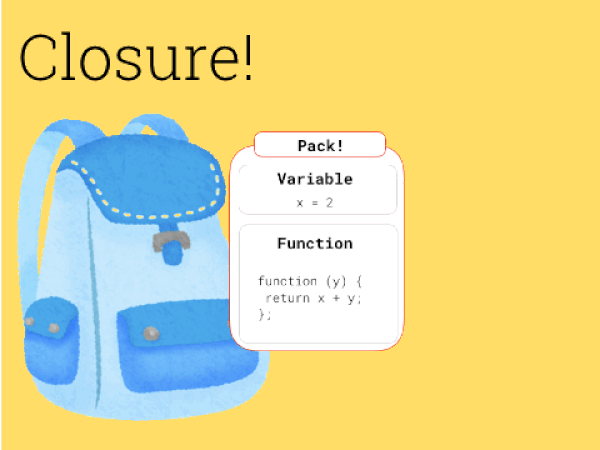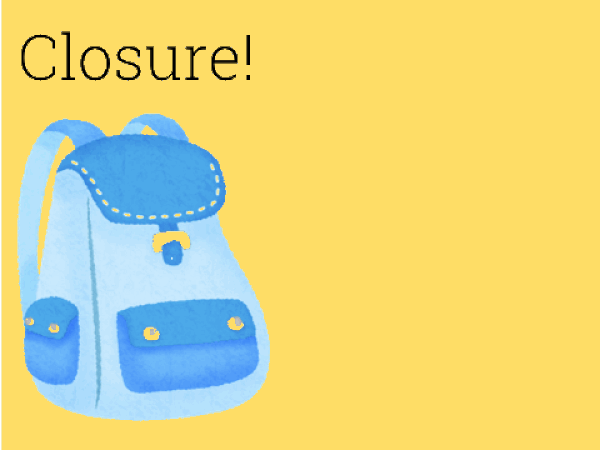
얼마전 throttle을 구현하려고 알아보다가 질문이 생겼다. '매번 throttle을 호출하면 throttle이 계속 새로 호출되게 되고 그럼 새로운 환경이 만들어질 것 같은데 어떻게 이전 환경을 유지할까?'
아래 코드를 보면 shouldWait, waitingArgs같은 변수가 저장되었다가 나중에 적재적소에 사용되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
throttle 로직은 핵심만 설명하자면, 함수가 호출될때 받은 인자를 모아놨다가 delay시간이 지나면 받은 인자를 callback함수로 넘겨주어 실행하는 방식이다.
timoutOutFuc이 실행 되기 전까지 shouldWait=true인 상태이고 그 상태동안은 waitingArgs에 전달받은 인자가 쌓이게 된다. 그리고 delay 시간이 지나면서 timoutFunc가 실행되고, waitingArgs가 callback으로 넘어가고 shouldWait가 false가 된다.
일단 코드부터 보자.
function throttle(cb, delay = 1000) {
let count = 0
let shouldWait = false
let waitingArgs
const timeoutFunc = () => {
if (waitingArgs == null) {
shouldWait = false
} else {
cb(...waitingArgs)
waitingArgs = null
setTimeout(timeoutFunc, delay)
}
}
return (...args) => {
if (shouldWait) {
waitingArgs = args
return
}
cb(...args)
console.log(count++)
shouldWait = true
setTimeout(timeoutFunc, delay)
}
}
const updateThrottle = throttle(() => {}, 100)
document.addEventListener("mousemove", e=>{
throttle(() => {}, 100)() // => 매번 새로운 함수가 호출. 그래서 다른 환경이 매번 만들어짐
updateThrottle() // 매번 같은 함수 호출. closure된 변수가 같다.
})
console.log(updateThrottle === updateThrottle) // true
// 변수안에 함수를 가두는 것이다. 그래서 함수가 새로 호출되지 않는다.
// 그래서 closure가 새로 생성되지 않는것이다.
console.log(throttle(()=>{}) === throttle(()=>{})) // false주석에도 나와있듯이. updateThrottle에 throttle함수를 가둬놓으면 closure에 의해서 환경이 유지가 된다.
그게 아니면 계속 새로운 환경이 생성된다
.updateThrottle() throttle(() => {}, 100)() 을 비교해보면 throttle안에 있는 count 변수가 하나씩 증가하는지 아님 계속 0을 출력하는지 볼 수 있다.
이로써 클로져에 한발짝 더 가까워 졌다.
react에서 구현하려면??
간단하다. 위의 js코드를 react hook을 사용해서 옮기면 된다.
// useThrottle.ts
import { useCallback, useRef } from "react";
interface IUseThrottle {
callback: (arg: any) => void;
interval?: number;
}
export const useThrottle = ({ callback, interval = 500 }: IUseThrottle) => {
const lastArgs = useRef(null);
const shouldWait = useRef(false);
const timerId = useRef<NodeJS.Timeout>();
const timeoutFunc = useCallback(() => {
if (!lastArgs.current) {
shouldWait.current = false;
} else {
// 3. 두번째 콜백 호출
callback(lastArgs.current);
lastArgs.current = null;
// 4. 다음 interval에서 shouldWait 풀리면서 throttle밖에 있는 것이 몰려올것임.
timerId.current = setTimeout(timeoutFunc, interval);
}
}, []);
const throttle = useCallback(
function (arg: any) {
if (shouldWait.current) {
// 0. 일단 lastArgs를 갱신
lastArgs.current = arg;
return;
}
// 1. 첫번째 콜백 호출
callback(arg);
// 1-1. throttle 잠그기
shouldWait.current = true;
// 2. 두번째 콜백 예약(리턴문에서 막아줌)
timerId.current = setTimeout(timeoutFunc, interval);
},
[callback, interval],
);
return [throttle];
};
// usage
const [throttle] = useThrottle({
callback:()=>{
console.log('throttle')
}
})
return <input onChange={throttle}/>