1.이중 연결 리스트
사실 단일 연결이랑 코드는 크게 차이 나지는 않는다. 다만 포인터가 앞으로도 , 뒤로도 연결된다는 차이가 있을뿐. 그래서 이중 연결 리스트를 만들 때 양쪽 다 연결되도록 하는것이 중요하다.
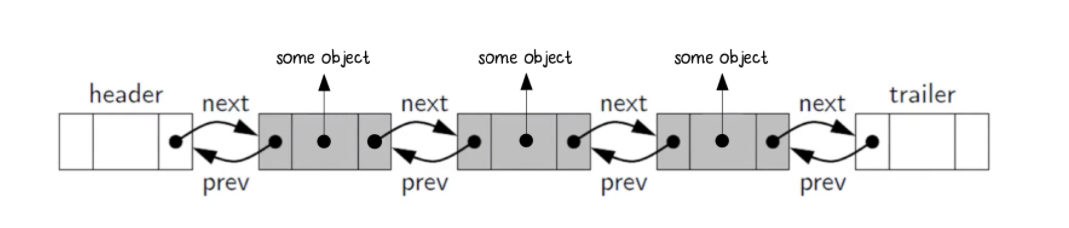
Almost identical to Singly linked list, except every node has another pointer , to the previous node!
And when you modify Doubly Linked list, make sure you have every node connected correctly back and forth
-
More Flexible === More memory.
-
It’s almost always a tradeoff!
그럼 제일 기본적인 push 메소드 부터 만들어 보자.
2. Push
차이점은 앞서 설명드렸듯이 Node에 prev 가 추가되었다. 이제는 뒤의 노드 뿐만 아니라 이전의 노드로도 이동가능 하다. 그래서 prev와 next를 잘 연결하는 것이 이중 연결 리스트의 기본이다.
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
push(val) {
var newNode = new Node(val);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// 새로운 노드를 tail과 연결하고
this.tail.next = newNode;
// 새로운 노드의 앞도 tail과 연결해준다.
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
쉽게 그림으로 설명하면 아래와 같다.
그럼 다음으로 pop 메소드를 알아보자
3. Pop
pop은 tail을 잘라내어 리스트의 길이를 하나씩 줄여나가는 작업이다. 그리고 잘라낸 node를 return한다. 이때 잘라낸 node가 깔끔하게 잘려있어야 한다. linkage가 있으면 안된다는 뜻. 따라서 prev/next를 null 해줘야하는 작업이 중요하다.
사실 이중 연결 리스트는 잘라 낼때도 앞과 뒤를 고려해야한다는 것을 말해주고 싶었다.
pop() {
var oldTail = this.tail;
if (!this.head) return undefined;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
// completely isolate and cut the linerging connection of the oldTail
oldTail.prev = null;
}
this.length--;
return oldTail;
}마지막으로 get 메소드를 알아보자
4. Get
이중 연결 리스트의 장점은 search 의 경우 O(N/2) 라는 것이다. 사실 grand scheme의 관점에서는 O(N)이지만 그래도 차이가 있다. 왜냐면, 앞뒤로 왔다갔다 할 수 있기 때문이다. 따라서 중간을 기점으로 head와 가까울 때는 head에서 중간까지만 찾으면 되고 tail이랑 가까울 경우 중간에서 tail까지만 찾으면 된다.
PseudoCode를 보도록 하자.
-- If the index is less than or equal to half the length of the list
-
Loop through the list starting from the head and loop towards the middle
-
Return the node once it is found
-- If the index is greater than half the length of the list
-
Loop through the list starting from the tail and loop towards the middle
-
Return the node once it is found
get(idx) {
if (idx < 0 || idx >= this.length) return null;
if (idx < Math.ceil(this.length / 2)) {
var current = this.head;
var countForSmallIdx = 0;
while (countForSmallIdx < idx) {
current = current.next;
countForSmallIdx++;
}
} else {
var current = this.tail;
var countForbigIdx = this.length - 1;
while (countForbigIdx > idx) {
current = current.prev;
countForbigIdx--;
}
}
return current;
}이렇게 리스트 데이터 구조에 대해서 대략 배워봤다. 그럼 다음으로 STACK 과 QUQUE에 대해서 배워보도록 하자.
