1. 리플렉션이란
- 자바의 리플렉션(Reflection)은 클래스, 인터페이스, 메소드들을 찾을 수 있고, 객체를 생성하거나 변수를 변경할 수 있고 메소드를 호출할 수도 있습니다.
- Reflection은 자바에서 기본적으로 제공하는 API입니다.
- 테스트 코드 작성을 위해 private 변수를 변경할 때 리플렉션을 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 3rd party 라이브러리를 사용하고 이것의 private 변수를 변경하고 싶을 때 리플렉션을 사용하면 라이브러리 코드 변경없이 값을 변경할 수 있습니다.
- Reflection은 다음과 같은 정보를 가져올 수 있습니다. 이 정보를 가져와서 객체를 생성하거나 메소드를 호출하거나 변수의 값을 변경할 수 있습니다.
- Class
- Constructor
- Method
- Field
2. 리플렉션 사용법
사전 준비 클래스
- 상속되는 클래스에서의 리플렉션을 확인하기 위해 Parent 클래스를 만든다.
- str1 변수와 method1, 3 가 private 임을 주의하자.
package reflectiontest;
public class Parent {
private String str1 = "1";
public String str2 = "2";
public Parent() {
}
private void method1() {
System.out.println("method1");
}
public void method2(int n) {
System.out.println("method2: " + n);
}
private void method3() {
System.out.println("method3");
}
}
- 상속되는 클래스에서의 리플렉션을 확인하기 위해 Child 클래스를 만든다.
- cstr2 변수와 method5가 private 임을 주의하자.
package reflectiontest;
public class Child extends Parent{
public String cstr1 = "1";
private String cstr2 = "2";
public Child() {
}
private Child(String str) {
cstr1 = str;
}
public int method4(int n) {
System.out.println("method4: " + n);
return n;
}
private int method5(int n) {
System.out.println("method5: " + n);
return n;
}
}
- static 변수와 메소드에서 어떻게 사용되는지 확인하기 위해 StaticExample 클래스를 만든다.
package reflectiontest;
public class StaticExample {
public static String EXAMPLE = "Example";
public static int getSquare(int num) {
System.out.println("Get square: " + num * num);
return num * num;
}
}
사용법
package reflectiontest;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws
ClassNotFoundException,
NoSuchMethodException,
NoSuchFieldException,
InvocationTargetException,
IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Class<Child> clazz = Child.class;
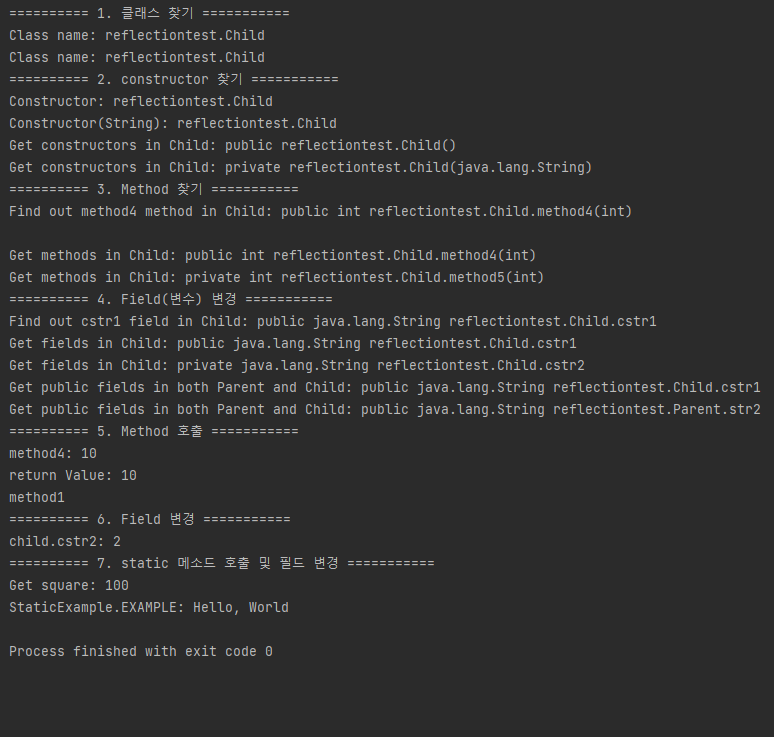
System.out.println("Class name: " + clazz.getName());
Class<?> clazz2 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
System.out.println("Class name: " + clazz2.getName());
Class<?> clazz3 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Constructor<?> constructor = clazz3.getDeclaredConstructor();
System.out.println("Constructor: " + constructor.getName());
Constructor<?> constructor2 = clazz3.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println("Constructor(String): " + constructor2.getName());
Class<?> clazz4 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz4.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> cons : constructors) {
System.out.println("Get constructors in Child: " + cons);
}
Class<?> clazz5 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Method method1 = clazz5.getDeclaredMethod("method4", int.class);
System.out.println("Find out method4 method in Child: " + method1);
System.out.println();
Class<?> clazz6 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Class partypes[] = new Class[1];
partypes[0] = int.class;
Method method2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("method4", partypes);
Class<?> clazz7 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Method methods[] = clazz7.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("Get methods in Child: " + method);
}
Class<?> clazz8 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Field field = clazz8.getDeclaredField("cstr1");
System.out.println("Find out cstr1 field in Child: " + field);
Class<?> clazz9 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Field fields[] = clazz9.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field fi : fields) {
System.out.println("Get fields in Child: " + fi);
}
Class<?> clazz10 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Field fields2[] = clazz10.getFields();
for (Field fi : fields2) {
System.out.println("Get public fields in both Parent and Child: " + fi);
}
Child child = new Child();
Class<?> clazz11 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Method method3 = clazz11.getDeclaredMethod("method4", int.class);
int returnValue = (int)method3.invoke(child, 10);
System.out.println("return Value: " + returnValue);
Child child2 = new Child();
Class clazz12 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Parent");
Method method4 = clazz12.getDeclaredMethod("method1");
method4.setAccessible(true);
method4.invoke(child2);
Child child3 = new Child();
Class clazz13 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Field fld2 = clazz13.getDeclaredField("cstr2");
fld2.setAccessible(true);
fld2.set(child3, "cstr2");
System.out.println("child.cstr2: " + fld2.get(child));
Class clazz14 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.StaticExample");
Method method = clazz14.getDeclaredMethod("getSquare", int.class);
method.invoke(null, 10);
Class clazz15 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.StaticExample");
Field fld = clazz15.getDeclaredField("EXAMPLE");
fld.set(null, "Hello, World");
System.out.println("StaticExample.EXAMPLE: " + fld.get(null));
}
}
3. 리플렉션의 단점
- 컴파일타임 타입 검사가 주는 이점을 하나도 누릴 수 없다.
- 예외검사도 마찬가지며 존재하지 않는 혹은 접근할 수 없는 메서드 호출시 런타임 오류가 발생한다.
- 리플렉션을 이용하면 코드가 지저분하고 장황해진다.
- 성능이 떨어진다.
package reflectiontest;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("====== Normal ======");
long beforeTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Child child = new Child();
System.out.println(child.method4(4));
long afterTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long secDiffTime = (afterTime - beforeTime);
System.out.println("시간차이(ms) : "+secDiffTime);
}
}

package reflectiontest;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws
ClassNotFoundException,
NoSuchMethodException,
InvocationTargetException,
IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
System.out.println("====== reflection ======");
long beforeTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Child");
Constructor<?> cons = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
Child child2 = (Child) cons.newInstance();
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("method4", int.class);
System.out.println((int)method.invoke(child2, 4));
long afterTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long secDiffTime2 = (afterTime2 - beforeTime2);
System.out.println("시간차이(ms) : " + secDiffTime2);
}
}

- 굉장히는 아니고 좀 느리다.
- 확실히 코드가 지저분하다
- 코드 분석 도구나 외존관계 주입 프레임워크는 리플렉션을 써야하지만 명백한 단점으로 인해 사용을 줄이고 있다고 한다.
- 리플렉션은 아주 제한된 형태로만 사용해야 그 단점을 피하고 이점만 취할 수 있다.
4. 리플렉션의 제한된 사용
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<? extends Set<String>> cl = null;
try {
cl = (Class<? extends Set<String>>)
Class.forName(treeSet);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
fatalError("클래스를 찾을 수 없습니다.");
}
Constructor<? extends Set<String>> cons = null;
try {
cons = cl.getDeclaredConstructor();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
fatalError("매개변수 없는 생성자를 찾을 수 없습니다.");
}
Set<String> s = null;
try {
s = cons.newInstance();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
fatalError("생성자에 접근할 수 없습니다.");
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
fatalError("클래스를 인스턴스화 할 수 없습니다.");
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
fatalError("생성자가 예외를 던졌습니다." + e.getCause());
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
fatalError("Set을 구현하지 않은 클래스입니다.");
}
s.addAll(Arrays.asList(strings));
System.out.println(s);
}
private static void fatalError(String msg) {
System.err.println(msg);
System.exit(1);
}
- 이펙티브 자바에 있는 예시이다.
- 리플렉션은 인스턴스 생성에만 쓰고, 이렇게 만든 인스턴스는 인터페이스나 상위 클래스로 참조해 사용하라고 한다.
- 해당 코드에서 2가지 단점이 보인다.
- 런타임에 총 6가지 에러를 던진다. 물론 ReflectiveOperationException 으로 상위로 1번에 잡을 수도 있다.
- 생성자 1줄이면 되는게 리플렉션 쓸려고 하니 25줄로 늘어났다.
- 비검사 형변환 경고가 뜨지만 Class<? extends Set> 의 사용을 통해 Set 을 구현하지 않더라고 성공을 하게 된다.
5. 정리
- 리플렉션은 런타임에 존재하지 않을 수도 있는다른 클래스, 메서드, 필드와의 의존성을 관리할 때 적합하다.
- 버전이 여러개 존재하는 외부 패키지를 다룰 때 유용하다.
- 단 런타임 시 접근하려는 클래스나 메서드가 존재하지 않을 수 있음을 감안해야한다.
- 하지만 단점도 많기에 되도록 객체 생성에만 사용하고, 적절한 인터페이스나 상위 클래스로 형변환해 사용하자.
참고 사이트
https://codechacha.com/ko/reflection/



