문제 정보
- 난이도: 실버 2
- 알고리즘: 다이나믹 프로그래밍
코멘트
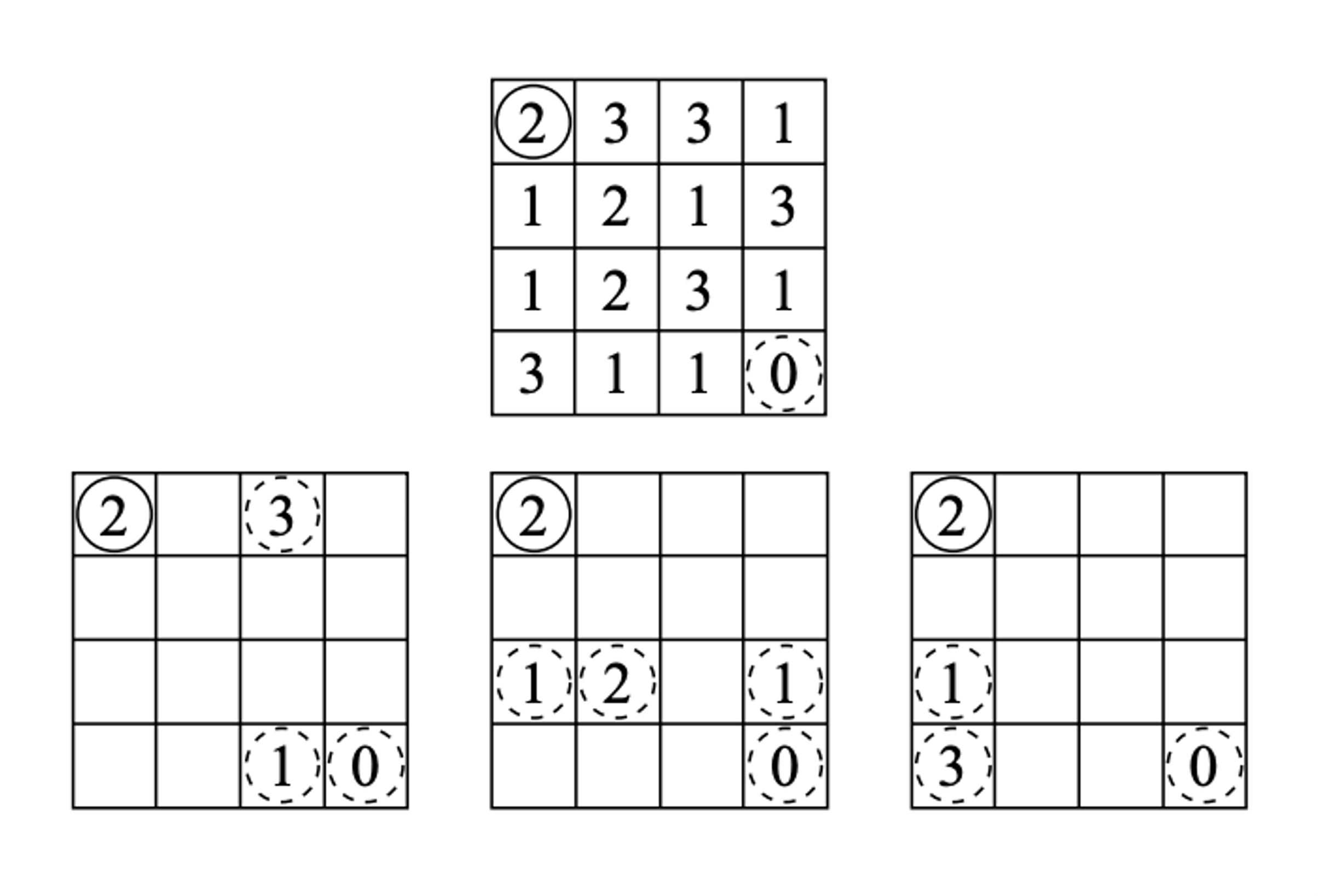
이 문제도 Moo 게임과 같이 수개월간 틀렸었던 문제다. 예전에 풀었을 때는 DP의 개념을 몰라서 메모이제이션을 하지 않아 시간 초과가 계속 떴었다.
- [Parameters]
- r: 행 좌표 (row)
- c: 열 좌표 (col)
- n: 해당 좌표에 적힌 숫자- [base case]
- 목적지에 도착하면 1 리턴
- n이 0이거나 좌표가 맵을 벗어날 경우 0 리턴- [Logic]
- 매 좌표에 적힌 숫자마다 오른쪽으로 간 경우와 아래쪽으로 간 경우의 함수를 호출한다.
- 재귀적으로 좌표가 이동하다가 목적지를 만나면 1을 리턴하므로 최종적으로는 모든 목적지의 수가 더해져서 리턴된다.
주의사항!!
- 경로의 개수는 보다 작거나 같다.
→ 출력 조건 함정에 조심!!8 byte크기의 자료형이 필요하다.
소스 코드
<탑다운 방식>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAX 101
using namespace std;
int maps[MAX][MAX];
long long int dp[MAX][MAX];
int N;
// r, c는 좌표 / n은 적힌 숫자
long long int jump(int r, int c, int n) {
// cout << "(" << r << "," << c << ") n: " << n << endl;
// base case
if (r == N - 1 && c == N - 1) return 1;
if (n == 0 || r > N - 1 || c > N - 1) return 0;
// memoization
if (dp[r][c] != -1) return dp[r][c];
long long int result = jump(r + n, c, maps[r + n][c]) + jump(r, c + n, maps[r][c + n]);
dp[r][c] = result;
return result;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N;
fill(&dp[0][0], &dp[MAX - 1][MAX], -1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
maps[i][j] = x;
}
}
dp[N - 1][N - 1] = 1;
// 스타트: jump(0, 0, map[0][0]);
cout << jump(0, 0, maps[0][0]);
}
<바텀업 방식> - by zzoni
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int map[101][101];
long long int dp[101][101]; // dp에 경로개수 저장!
int N;
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
dp[0][0] = 1; // 시작점은 무조건 1번 거치니까
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (map[i][j] != 0 ){ // 종착지가 아니라면
//아래로
if (i + map[i][j] < N) {
dp[i + map[i][j]][j] += dp[i][j];
}
//오른쪽으로
if (map[i][j] != 0 && j + map[i][j] < N) {
dp[i][j + map[i][j]] += dp[i][j];
}
}
}
}
cout << dp[N - 1][N - 1];
return 0;
}