Array APIs
유용한 배열 함수들!
API 정의 읽어보고, 파라미터와 리턴값이 무엇인지 확인하는 연습하기!
API가 Object 자체를 변형(상태 변경)시키는지 확인하는 것 중요!★
1. join (Array API)
구분자(separator/옵션)를 이용해 배열의 아이템들을 문자열로 변환
const animals = ['fox', 'rabbit', 'dog'];
const strAnimals = animals.join();
console.log(strAnimals); // fox,rabbit,dog
const strAnimals2 = animals.join(', ');
console.log(strAnimals2); // fox, rabbit, dog

2. split (String API)
문자열을 구분자 단위로 문자를 나누어 배열로 변환
(구분자는 보통 콤마 단위로 문자를 나누기 때문에 필수로 작성!
필수 인자인 구분자가 없으면 문자열 전체가 하나의 배열(["□, □, □, □"])로 묶임)
또한, 리턴받을 배열의 사이즈 지정 가능(옵션)
const expressions = '😁, 🤣, 😍, 😉';
const arrExpressions = expressions.split(', ');
console.log(arrExpressions); // ["😁", "🤣", "😍", "😉"]
const arrExpressions = expressions.split(', ', 2);
console.log(arrExpressions); // ["😁", "🤣"]

3. reverse (Array API)
배열 안에 데이터의 순서를 거꾸로 만들고, 변형된 배열 자체를 리턴
(★중요 포인트! 함수를 호출한 원래 배열도 변형됨!✨)
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const revArray = array.reverse();
console.log(revArray); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
console.log(array); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]

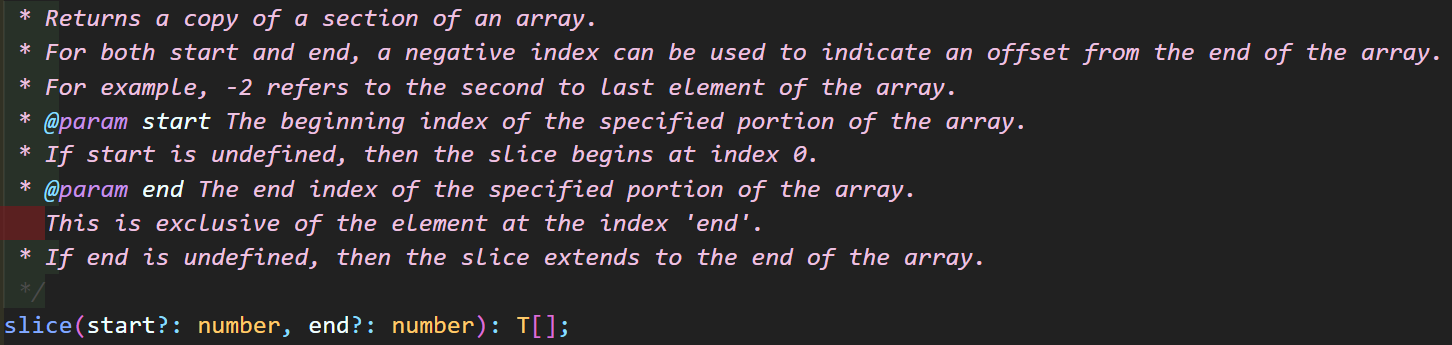
4. slice (시작 인덱스와 '마지막 인덱스'-1 까지의 데이터 추출!)
배열의 '시작 인덱스'와 '추출하고자 하는 마지막 인덱스+1'를 지정하여 특정한 데이터들을 리턴
'배열에서 원하는 부분만' 리턴해서 받아올 수 있음
index를 기준으로 추출하기 때문에 start index는 0부터 시작함을 기억하기!
두번째 인자인 end index는 추출하는데 포함되지 않고, 직전 index까지 추출됨
(★중요 포인트! 원래 배열은 변형되지 않고 새로운 배열을 생성!✨)
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const sliceArray = array.slice(2, 5); // 인덱스 4인 데이터를 받아오기 위해 추출 마지막 인덱스+1 처리
console.log(sliceArray); // [3, 4, 5]
console.log(array); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
※ vs. splice (시작 인덱스 부터 원하는 데이터 '갯수' 삭제!✂)
삭제하려는 'start index'와 삭제할 데이터 갯수를 인자로 갖고, 삭제된 요소들을 리턴
원형 배열에서는 데이터가 삭제되고 '남은 데이터'로만 이루어짐
만약, 두번째 인자인 deleteCount를 작성하지 않으면 start index 이후의 모든 요소들이 삭제됨
(★중요 포인트! 함수를 호출한 원래 배열도 변형됨!✨)
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const spliceArray = array.splice(0, 2);
console.log(spliceArray); // [1, 2] ← (새 배열)삭제된 데이터
console.log(array); // [3, 4, 5] ← (원형 배열)남은 데이터
const array2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const spliceArray2 = array.splice(2); // deleteCount 인자 없는 경우
console.log(spliceArray2); // [3, 4, 5] ← (새 배열)삭제된 데이터
console.log(array2); // [1, 2] ← (원형 배열)남은 데이터

다음 예제를 참고해서 아래 설명하는 APIs 이해하기!!
class Student {
constructor(name, age, enrolled, score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.enrolled = enrolled;
this.score = score;
}
}
const students = [
new Student('A', 29, true, 45),
new Student('B', 28, false, 80),
new Student('C', 30, true, 90),
new Student('D', 40, false, 66),
new Student('E', 18, true, 88),
];5. find
전달되는 콜백 함수가 true인 첫 번째 요소를 리턴(찾지 못하면 undefined 리턴)
내가 만드는 predicate라는 콜백 함수는 배열의 모든 요소마다 호출 되며, 콜백 함수가 true를 리턴하면 함수를 바로 멈춤
아래 해당 API 정의 내용 중 '=> value is S'은 boolean 값으로 정의되는 함수를 리턴한다는 것을 의미함
const ninetyScore = students.find((student) => student.score === 90); // arrow function 이용
console.log(ninetyScore); // Student {name: "C", age: 30, enrolled: true, score: 90}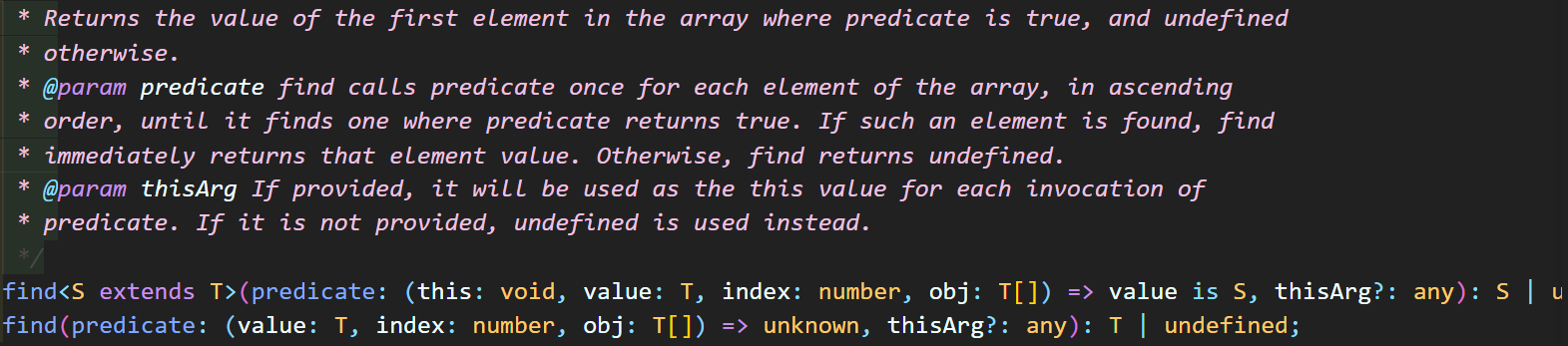
6. filter
true 값을 가지는 모든 요소들 추출
콜백 함수를 전달해서 콜백 함수가 true인 데이터들로 이루어진 새로운 배열을 리턴
const enrolledStudents = students.filter((student) => student.enrolled);
console.log(enrolledStudents); // ▼(3) [Student, Student, Student]🤔여기서 잠깐! 차이점?!
filter는 find처럼(예. student.score === 90) return문에 조건문 형식으로 작성하지 않았다는 것을 이해하자! (예. ❌student.enrolled === true❌)
(내 생각에는 Student 객체의 enrolled 속성처럼 'true/false'로 속성값을 가지는 경우에만 filter API를 사용하는 것 같다.)

7. map
배열 안에 있는 요소들을 우리가 원하는 함수를 이용해 다른 데이터를 생성
콜백 함수의 내용에 따라서 배열 안에 모든 요소들이 다른 값으로 매핑(변환)되어 리턴됨
원하는 데이터(예. age, score)들로만 이루어진 새로운 배열 생성 가능
// 받은 값(Students라는 Object)을 그대로 리턴
const students = students.map((student) => student);
// 주어진 Students라는 Object를 score로 변환
const scores = students.map((student) => student.score);
console.log(scores); // [45, 80, 90, 66, 88]
// 주어진 Students라는 Object를 score*2로 변환
const scores = students.map((student) => student.score * 2);
console.log(scores); // [90, 160, 180, 132, 176]
8. some
배열의 요소 중에서 하나라도 콜백 함수가 true로 리턴 (조건에 충족)되면 true가 리턴됨
const lowScore = students.some((student) => student.score <= 50);
console.log(lowScore); // true
※ vs. every
배열 안에 모든 요소들이 true이면(조건이 충족) true가 리턴됨
즉, 하나라도 false인 요소가 있으면 false가 리턴됨
const stupidStudents = students.every((student) => student.score < 50);
console.log(stupidStudents); // false- 배열 중에 조건에 만족하는 요소가 하나라도 있는지 확인 => some
- 배열 안에 모든 요소가 만족되는지 확인 => every
9. reduce
우리가 원하는 시작점부터 배열의 모든 요소를 돌면서 특정 값을 누적할 때 사용
아래 해당 API 정의 내용 중 '=> T'는 리턴 값이 필요하다는 것을 의미함
콜백 함수 내용으로 인해 누적된 결과값을 리턴함
(이전값, 현재값을 인자로 하는)콜백 함수와 [최초값(첫번째 이전값이 지정한 값으로 설정)]을 전달
콜백 함수의 이전의 리턴값이 순차적으로 콜백 함수가 다음에 호출될 때 다음 요소의 'previousValue' 인자로 전달됨
'currentValue'는 배열의 아이템을 순차적으로 전달받음
'다음의 pre ↩ 이전의 curr' 같은 방식으로 pre가 계속 대체되며,
'curr ← 배열의 특정 요소를 가진 객체의 속성값' 연속해서 curr이 새로운 값으로 채워지면서 함수가 실행됨
const sumScore = students.reduce((pre, curr) => pre + curr.score, 0);
const avgScore = sumScore / students.length;
console.log(sumScore); // 369
console.log(avgScore); // 73.8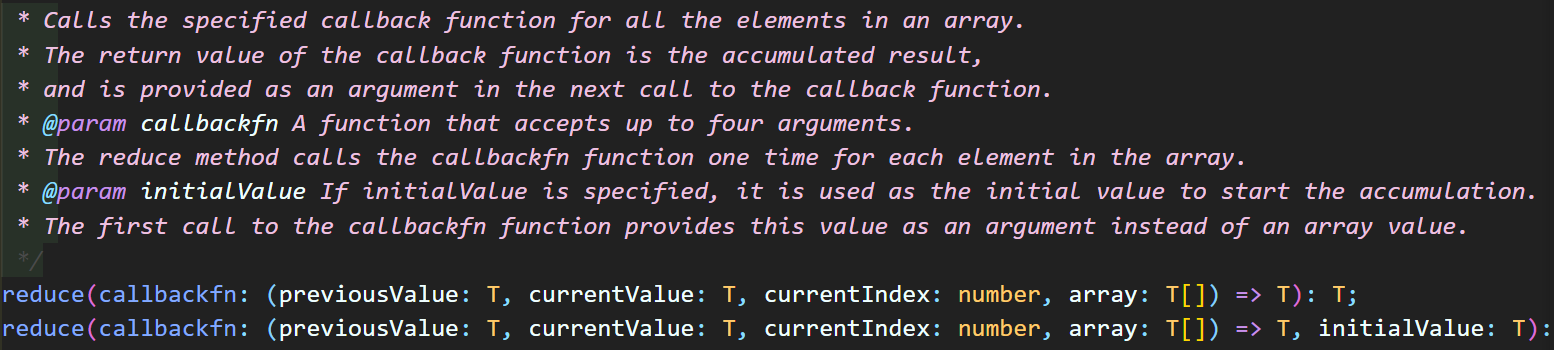
10. API 조합
특정 요소의 데이터들을 추출하여 변환한 배열을 문자열로 변환한다면?
- map: student 객체에서 score 데이터 추출 (새로운 배열 리턴)
- join: 배열을 문자열로 변환, 합침
const strScores = students
.map((student) => student.score)
.join(', ');
console.log(strScores); // 45, 80, 90, 66, 88
const strScores2 = students
.map((student) => student.score)
.filter((score) => score >= 80)
.join(', ');
console.log(strScores2); // 80, 90, 88Operation을 섞어서 호출 가능하며, 간편하고 유용함(함수형 프로그래밍)
한 눈에 파악하여 이해하기 쉽고, 가독성이 좋아짐
11. sort
오름차순으로 정렬하여 문자열로 변환
인자 a는 이전값, b는 현재값 으로 전달됨
오름차순(ascending) 정렬일 때, a - b (a < b이므로 음수(-))
내림차순(descending) 정렬일 때, b - a (양수(+))
(생략하면 요소가 기본적으로 ASCII 문자 순서로 오름차순 정렬)
const strScores = students
.map((student) => student.score)
.sort((a, b) => a - b) // 오름차순 정렬
.join(', ');
console.log(strScores); // 45, 66, 80, 88, 90
const strScores = students
.map((student) => student.score)
.sort((a, b) => b - a) // 내림차순 정렬
.join(', ');
console.log(strScores); // 90, 88, 80, 66, 45
📌원형 배열에 영향을 주는 메서드들 (꼭꼭 기억해두기로 약속!!)
=> reverse, splice, map, sort
참고! MDN Array
