전위순회 : root → left → right
후위순회 : left → right → root
이진 검색트리를 [ 전위 순회한 결과 ] 가 주어졌을 때, 이 트리를 [ 후위 순회한 결과 ] 를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하라
-
같은 키를 가지는 경우는 없다고 한다.
-
순서대로, pre, cur을 두고, if( pre > cur ) 이면 pre의 left node로 cur을 등록 . cur의 parent로 pre를 등록
-
순서대로, pre, cur을 두고, if( pre < cur ) 이면 ? → 누구의 right node인지 알아야 한다. pre보다 parent인 노드의 right node일 수가 있기 때문이다.
-
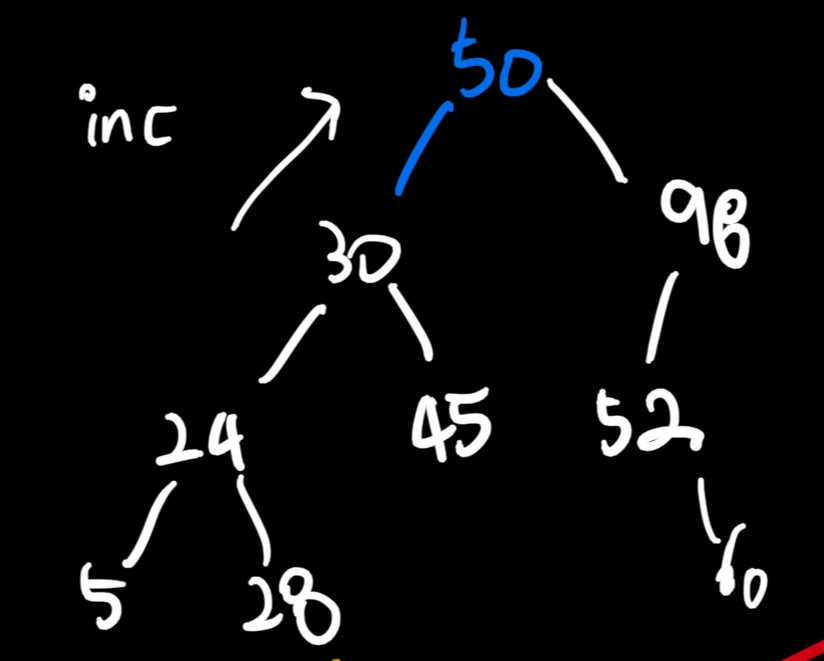
전위 순회 특성상, [ 맨 앞 ] 의 노드는 [ 트리의 root ] 노드이다.
package coding;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static StringTokenizer st;
public static node root;
public static void setting() throws IOException {
String temp = null;
int cur =0,pre =0;
node curn=null,pren=null;// next is for searching parent node when cur>pre
// 첫 번째 줄 -> root node
temp = br.readLine();
cur = Integer.parseInt(temp);
root = new node(cur);
pre = cur; pren =root;
// 다음 줄
while((temp = br.readLine())!=null){
if(temp.equals(""))break;
// System.out.println("TEMp : "+temp);
cur = Integer.parseInt(temp);
curn = new node(cur);
// cur < pre 인 경우
if(cur<pre){
// curn의 parent로 pren을 설정
curn.parent = pren;
// pren의 left child로 curn을 설정
pren.left = curn;
}
else if(cur>pre){
node nextn=null,findn=null;
// parent로 탐색하며 찾는다.
// nextn가 null인 경우 -> nextn의 right child
// nextn.key > cur 인 경우 -> 이제까지의 findn의 right child
findn = pren;
while(true){
nextn = findn.parent;
if(nextn==null)break;
else if (nextn.key>cur)break;
findn = nextn;
}
//curn의 parent로 findn을 설정
curn.parent = findn;
// findn의 right node로 curn을 설정
findn.right = curn;
}
pre = cur;
pren = curn;
}
}
// rootn에서 시작해서 후위순회 : left -> right -> 자기자신
public static void traverse(node rootn){
// System.out.println("CUR : "+rootn.key);
if(rootn.hasLeft()){
// System.out.println("CUR : "+rootn.key +" LEFT child : "+rootn.left.key);
traverse(rootn.left);
}
if(rootn.hasRight()){
// System.out.println("CUR : "+rootn.key +" RIGHT child : "+rootn.right.key);
traverse(rootn.right);
}
System.out.println(rootn.key);
}
public static void solve(){
}
// pre < cur 인 경우 탐색과정 세팅
public void findPar(){
}
public static class node{
node parent;
node left,right;
int key;
public node(int key ) {
this.key = key;
}
public boolean hasLeft(){
return left!=null;
}
public boolean hasRight(){
return right!=null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
setting();
traverse(root);
}
}틀렸다 틀린 이유
위와 같은 코드는
pre > cur 인 경우에는 잘 작동하고,
pre < cur인 경우 중에서도 다음과 같은 경우까지는 잘 동작하나
이렇게 29만 추가되어도 잘못된 결과를 발생 시킨다 : 29의 parent를 찾는 과정에서, 29보다 작은 28을 지나치고 24까지 간 후, 30은 29보다 작기에 24를 parent로 지정함으로서 28을 없애버리게 된다
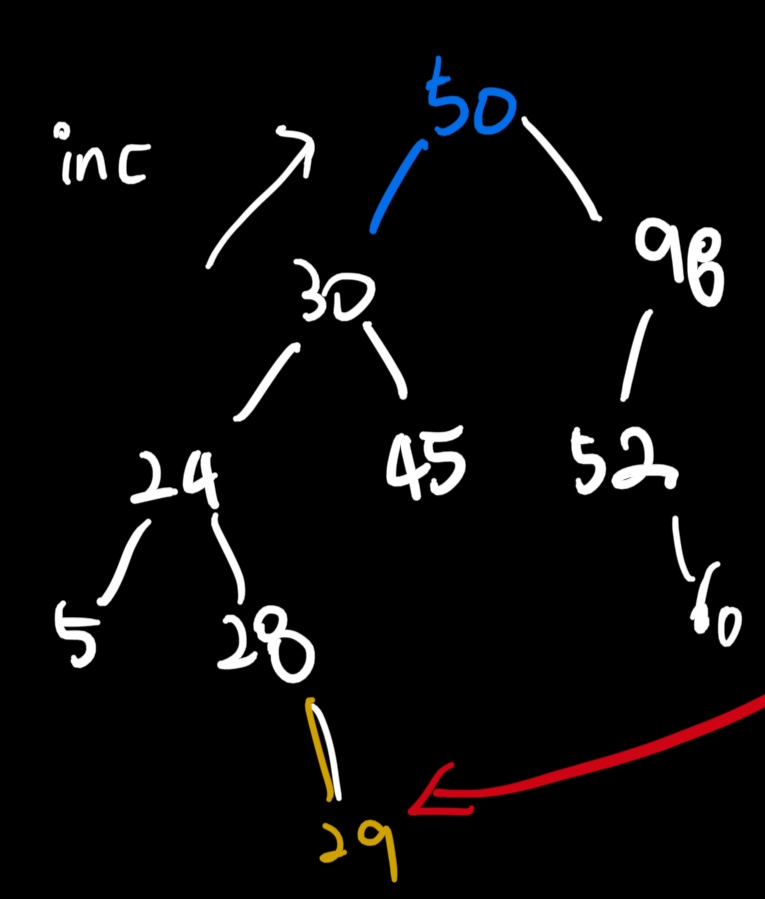
즉, Right에 위치하는 노드를 추가할 때, 이것의 parent를 탐색하는 과정이 제대로 되고 있지 않다.
어떤 노드의 바로 한 단계 right 만 있는 경우에는 잘 동작 ( 백준의 예시 ) 하나,
sekewed right subtree로 이루어져있으면, 가장 leaf node까지의 path의 intermediate 노드들을 다 없애버리고 가장 상위의 노드에 leaf node만 붙어버리면서 모두를 대체시켜버리게 된다.
다른 사람의 풀이를 보았다.
어떤 노드를 insert할 때, 이전 노드에 기반하지 않고
매 번, root로부터 시작하여, 위치를 탐색해 나가는 방법을 사용할 수도 있다.
그리고 이 때, parent를 굳이 저장할 필요가 없다
- root부터 시작하여, 현재 insert하려는 int k 를 인자로 넘긴다.
- 매 번 root부터 시작하여, insert 위치를 찾아나간다 . balanced 이진트리가 아닌 그냥 이진트리이기 때문에, insert 부분을 구현을 하는 것이 어렵지는 않다. → O(logn)의 시간복잡도를 갖는다. n의 개수가 최대 10^6 이기 때문에 괜찮다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static StringTokenizer st;
public static node root;
public static void setting() throws IOException {
String temp = null;
int cur = 0;
// 첫 번째 줄 -> root node
temp = br.readLine();
cur = Integer.parseInt(temp);
root = new node(cur);
// 다음 줄
while ((temp = br.readLine()) != null) {
if (temp.equals("")) break;
cur = Integer.parseInt(temp);
// root를 기준으로 이 새로운 노드를 추가한다.
insert(root,cur);
}
}
public static void traverse(node n ){
if(n.left !=null){
traverse(n.left);
}
if(n.right !=null){
traverse(n.right);
}
System.out.println(n.key);
}
public static class node{
node left,right;
int key;
public node(int key ) {
this.key = key;
}
}
// target : k
// 현재 cur 이라는 node에 추가를 하려고 한다.
public static void insert(node cur, int k){
// root를 입력으로 받고 시작 --> NullPointerException 방지
// cur는 항상 non-NULL
if(cur.key>k){
// left
if(cur.left == null){
cur.left = new node(k);
}
else insert(cur.left,k);
}else{
// Right
if(cur.right == null){
cur.right = new node(k);
}
else insert(cur.right,k);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
setting();
traverse(root);
}
}