다시 풀어 볼 때
동적 프로그래밍은 정말 잘 모르겠다.
- 이 문제를 완전탐색으로 풀려고 한다면 O(n^3)이 나오게 될 것이다.
- 다시 한 번 LCS 풀이를 정리한 것을 보았다.
- 이 문제가 단순 LCS문제와 다른 점은, traceback하면서, 실제 문자열을 구해야한다는 점이다.
- 일단 cache[r][c]는 항상, 최대 값을 갖는다. ( LCS 풀이 방법을 보면 이해할 수 있다 )
- 따라서 cache의 (r,c)위치에서부터 시작하여
- IF, r==0 또는 c ==0 이면 stop한다.
- 먼저, str[r]==str[c] 인 경우 이 글자를 출력한다.
- traceback한다. traceback하는 곳으로 r,c를 세팅한다.
- traceback 위치를 저장하는 배열을 따로 생성 해 둔다.
- 반복한다.
- 이 때 조금 고민이 되었던 부분은, str1[i]≠str2[j]인 경우, cache[i-1][j] 와 cache[i][j-1]이 같은 경우, 둘 중 아무거나를 선택해도 , 답을 도출할 때 영향이 없을까 라는 부분이었다.
-
영향 없다.
// [i-1][j]와 [i][j-1]중에 더 큰 값 // 만약 cache[i-1][j]와 cache[i][j-1]이 같다 해도 괜찮다. // 정답인 경우는 다양한 경우가 있을 수 있으며 // 글자를 출력하는 순간은 [i] == [j]인 순간만 출력하니까
-
고민 : StringBuilder
- StringBuilder를 사용한다면 , 지금 처럼, 끝에서부터 trace를 하는 경우, beginning쪽에 바로 append를 하는 식을 하려고 할 것이다.
- 근데 이것은 StringBuilder의 목적을 어기는 일.(왜냐하면, 매 번 새로 공간을 할당해야함... StringBuilder의 append는 내부 코드 상, 공간이 부족한 경우, 기존의 내용을 copy해 두고 뒤에 append하거든.. )
- 차라리, cache[r][c]에 있는 숫자의 길이로 integer array를 생성 한 후, 여기에는, index를 저장하고, 순차적으로, index의 character를 하나의 Stringbuilder에 append하는 식으로 하는게 좋을 것 같다.
package coding;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static int r,c;
public static int[] result;
public static int cnt =0;
public static int cache[][];
public static int[][][] trace;
public static String str1,str2;
// store
public static LinkedList<int[]> stack = new LinkedList<>();
public static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static StringTokenizer st;
public static void setting() throws IOException {
str1 = br.readLine();
str2 = br.readLine();
r = str1.length(); // str1을 row에 배치
c = str2.length(); // str2를 col에 배치
cache = new int[r+1][c+1];
trace = new int[r+1][c+1][2]; // trace[r][c][0]은 이전 위치의 row, trace[r][c][1]은 이전 위치의 column
// cache[0][0~c]는 0
// cache[0~r][0]는 0
}
public static void solve(){
for(int i=1;i<=r;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=c;j++){
// str1[i]==str2[j] --> [i-1][j-1] +1
if(str1.charAt(i-1)==str2.charAt(j-1)){
cache[i][j]=cache[i-1][j-1]+1;
trace[i][j][0]=i-1;
trace[i][j][1]=j-1;
}
else{
// [i-1][j]와 [i][j-1]중에 더 큰 값
// 만약 cache[i-1][j]와 cache[i][j-1]이 같다 해도 괜찮다.
// 정답인 경우는 다양한 경우가 있을 수 있으며
// 글자를 출력하는 순간은 [i] == [j]인 순간만 출력하니까
if(cache[i-1][j]>cache[i][j-1]){
trace[i][j][0] = i-1;
trace[i][j][1] = j;
cache[i][j]=cache[i-1][j];
}else{
trace[i][j][0] = i;
trace[i][j][1] = j-1;
cache[i][j]=cache[i][j-1];
}
}
}
}
}
//
public static void printResult(int cr, int cc){
// 먼저 cache[r][c]를 확인한다
cnt = cache[r][c];
if( cnt ==0){
System.out.println(cnt);
return;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
// result는 정답 문자열에 들어갈 str1상에서의 character를 담은 index를 저장한다.
result = new int[cnt];
recur(r,c);
// 생성된 result에서 String생성
int len = result.length;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
sb.append(str1.charAt(result[i]));
}
System.out.println(cache[r][c]);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
public static void recur(int cr, int cc){
if(cr ==0 || cc==0 )return;
// str1[cr] == str2[cc]인 경우, 출력해야한다
if(str1.charAt(cr-1) == str2.charAt(cc-1)){
result[--cnt]=cr-1;
}
// trace를 조회
recur(trace[cr][cc][0],trace[cr][cc][1]);
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
setting();
solve();
printResult(r,c);
}
}문제
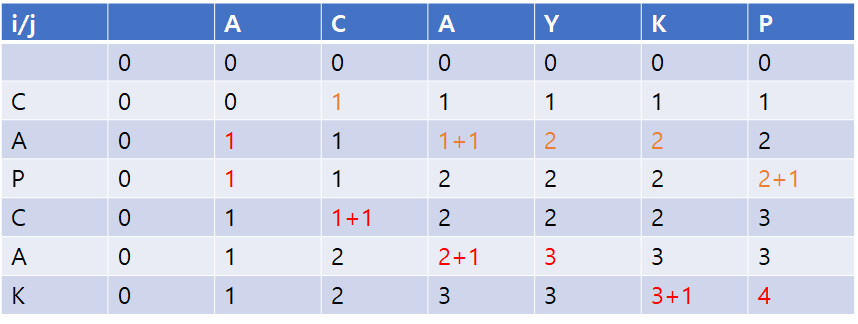
LCS(Longest Common Subsequence, 최장 공통 부분 수열)문제는 두 수열이 주어졌을 때, 모두의 부분 수열이 되는 수열 중 가장 긴 것을 찾는 문제이다.
예를 들어, ACAYKP와 CAPCAK의 LCS는 ACAK가 된다.
입력
첫째 줄과 둘째 줄에 두 문자열이 주어진다. 문자열은 알파벳 대문자로만 이루어져 있으며, 최대 1000글자로 이루어져 있다.
출력
첫째 줄에 입력으로 주어진 두 문자열의 LCS의 길이를, 둘째 줄에 LCS를 출력한다.
LCS가 여러 가지인 경우에는 아무거나 출력하고, LCS의 길이가 0인 경우에는 둘째 줄을 출력하지 않는다.
풀이 생각
기존의 것에 더불어, 백트랙킹 하며, 실제 LCS 수열까지 구하도록 해야 한다.
- LCS 수열은, str2(i)==str1(j) 인 것들만이 사용된다.
- 백트랙킹 한 지점마다, str2(i) == str1(j)인지를 다시 또 확인 해야 할 듯..
- 그리고 나는 백트랙킹을 하기 위해서, 각 좌표마다, 이전 좌표를 저장하는 방식을 사용했다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static String str1,str2;
public static int[][] dp = new int[1001][1001];
public static int[][][] cache = new int[1001][1001][3];
// 0은 이전 칸의 i, 1은 이전 칸의 j, 2는 LCS의 길이.
// i는 str2를 위해 사용, j는 str1을 위해 사용한다.
// 0인 row,. column이 하나씩 추가되어있기 때문에, str에서 i,j 사용시, -1씩 해줘야함.
public static char[] res = new char[1000];
public static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public static void Setting() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
str1 = br.readLine();
str2 = br.readLine();
}
public static void solve(){
char cur1=0,cur2=0;
for (int i=0;i<str2.length();i++){
cur1 = str2.charAt(i);
for(int j=0;j<str1.length();j++){
cur2 = str1.charAt(j);
if(cur1==cur2) {
cache[i+1][j+1][2] = cache[i][j][2]+1;
cache[i+1][j+1][0] = i; // 여기에 값을 생성하는데 도움 준 이전 칸 정보
cache[i+1][j+1][1] = j; // 여기에 값을 생성하는데 도움 준 이전 칸 정보
}
else {
max(i,j);
}
}
}
int curi=str2.length(),curj= str1.length();
int nexi=0,nexj=0;
// 답은 항상, dp[str2.length()][str1.length()] 에 있다.
System.out.println(cache[curi][curj][2]);
if(cache[curi][curj][2]==0) return;
// 추적해 나간다.
while(curi>0 && curj>0) {
// 두 글자가 같은 경우,
if (str2.charAt(curi - 1) == str1.charAt(curj - 1)) {
sb.insert(0, str2.charAt(curi - 1));
}
// 같던, 같지 않은 경우
nexi = cache[curi][curj][0];
nexj = cache[curi][curj][1];
curi=nexi;
curj=nexj;
}
if(sb.length()==0) return;
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
public static void max(int i, int j){
int prei=0,prej=0;
if(cache[i+1][j][2]>cache[i][j+1][2]) {
prei=i+1;
prej=j;
}else{
prei = i;
prej = j+1;
}
cache[i+1][j+1][2] = cache[prei][prej][2];
cache[i+1][j+1][0] = prei;
cache[i+1][j+1][1] = prej;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Setting();
solve();
}
}개선된 방법 (메모리 개선 + 속도 향상)

- 앞서 알았듯이, 어차피, 실제 lcs 수열은 str2(i) == str1(j) 인 것으로만 이루어져있음을 이용한다면, 각 좌표마다, 이전 좌표를 저장하지 않아도 된다.
-
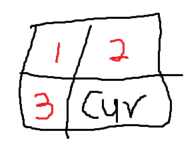
어차피 이전 좌표 지점은 세 칸 중 하나 이기 때문이다
-
이전의 좌표지점은 이 세칸 중 하나다. 이 중 1번의 경우는 , str1(j) == str2(i) 인 곳이기에, 정답 수열에 들어가야 할 부분이다.
-
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static String str1,str2;
public static int[][] dp = new int[1001][1001];
public static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public static void Setting() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
str1 = br.readLine();
str2 = br.readLine();
}
public static void solve(){
char cur1=0,cur2=0;
for (int i=0;i<str2.length();i++){
cur1 = str2.charAt(i);
for(int j=0;j<str1.length();j++){
cur2 = str1.charAt(j);
// 두 글자가 같은 경우
if(cur1==cur2) {
dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j]+1;
}
else {
dp[i+1][j+1] = Math.max(dp[i+1][j],dp[i][j+1]);
}
}
}
int curi=str2.length(),curj= str1.length();
int nexi=0,nexj=0;
// 답은 항상, dp[str2.length()][str1.length()] 에 있다.
System.out.println(dp[curi][curj]);
if(dp[curi][curj]==0) return;
// 추적해 나간다.
while(curi>0 && curj>0) {
// 두 글자가 같은 경우, 대각선으로 왼쪽 위칸으로 backtrack한다.
if (str2.charAt(curi - 1) == str1.charAt(curj - 1)) {
sb.insert(0, str2.charAt(curi - 1));
curi -=1;
curj -=1;
}
// 같지 않은 경우 1. 바로 왼쪽 칸과 같은 경우
else if(dp[curi-1][curj]==dp[curi][curj]) curi -=1;
// 같지 않은 경우 2. 바로 윗 칸 과 같은 경우
else if(dp[curi][curj-1]==dp[curi][curj]) curj -=1;
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Setting();
solve();
}
}