상속
다형성
class Animal {
String name;
void love() {}
}
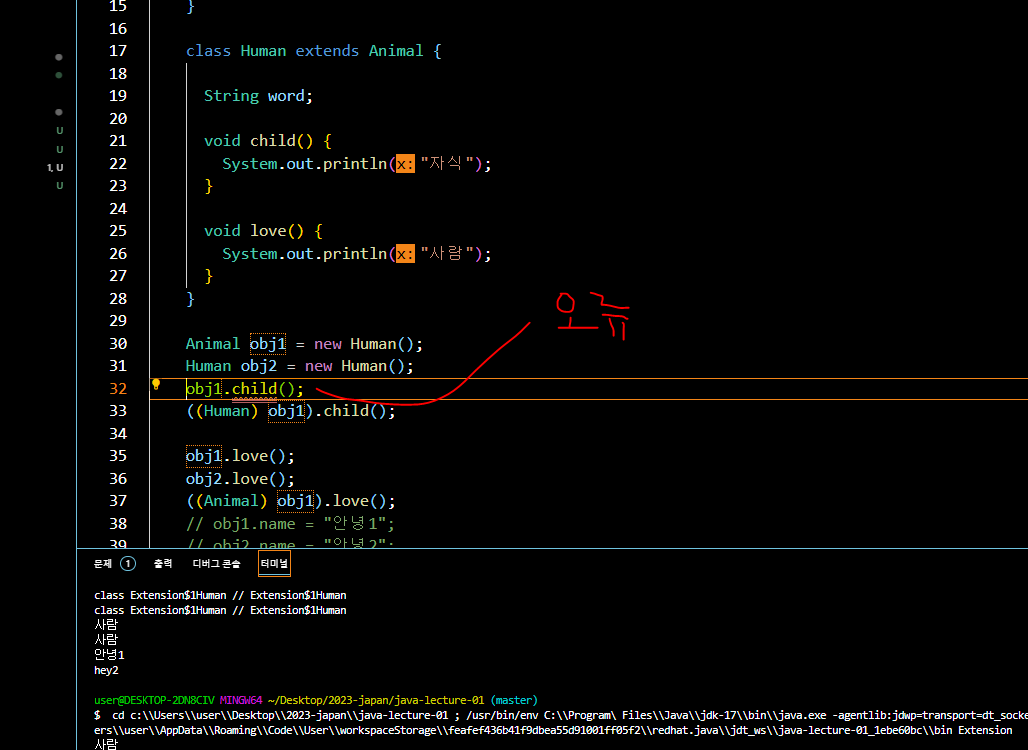
class Human extends Animal {
String word;
void child() {
System.out.println("자식");
}
void love() {
System.out.println("사람");
}
}
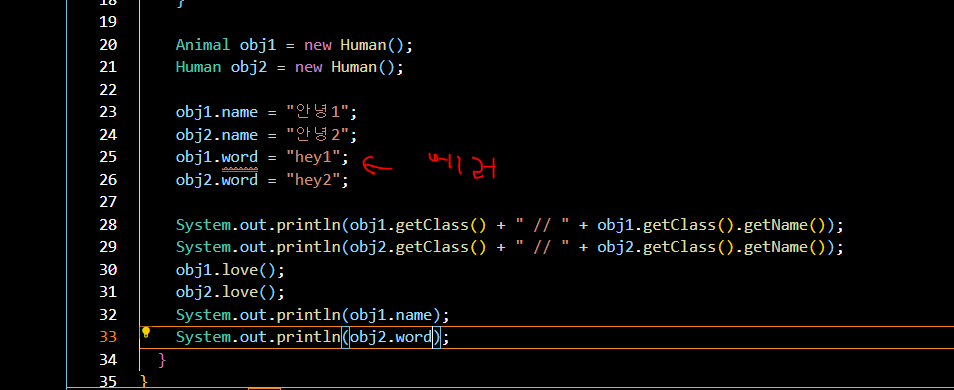
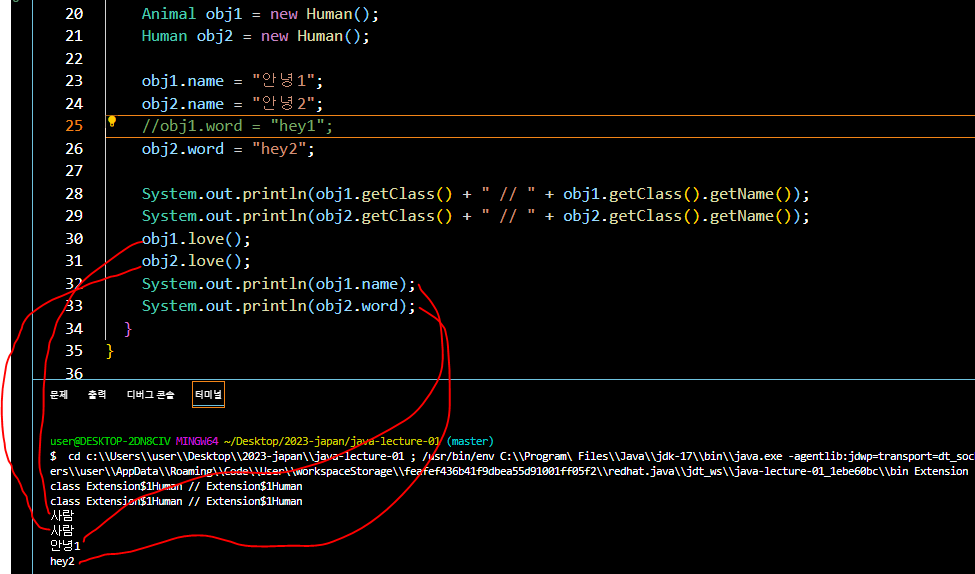
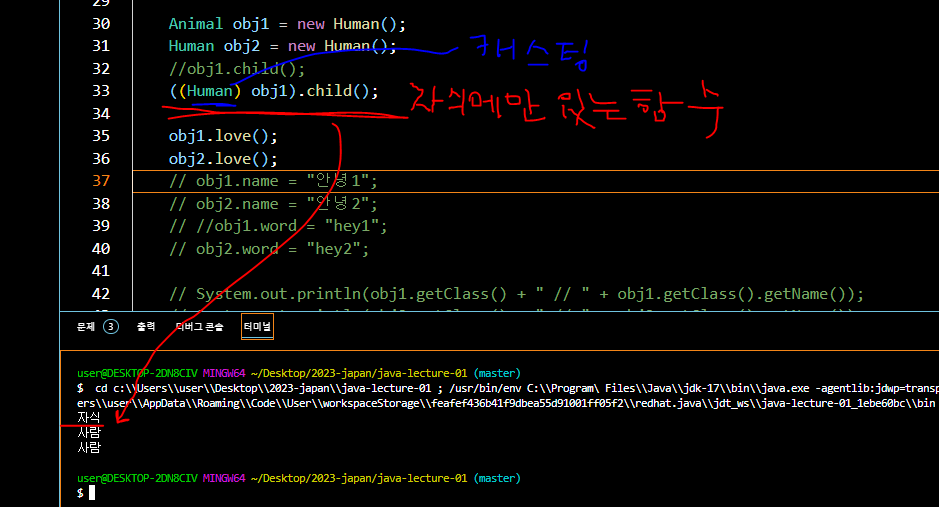
Animal obj1 = new Human();
Human obj2 = new Human();- 이 경우 obj1 객체는 age 변수에 접근할 수 없음
- 하지만 obj1 객체는 자식 클래스에서 새롭게 정의 된 love 함수를 출력함.
- 즉 부모 클래스를 참조해 만든 자식 클래스의 인스턴스는, 자식 클래스에서 새로이 만들어진 변수나 함수에 대해 접근할 수 없음.
뜯어보기
- new Human() : 자식 클래스를 메모리에 띄운다
- Animal obj1 : 그런데 그 메모리에 띄운 클래스의 타입은 Animal에 해당한다.
다형성과 캐스팅
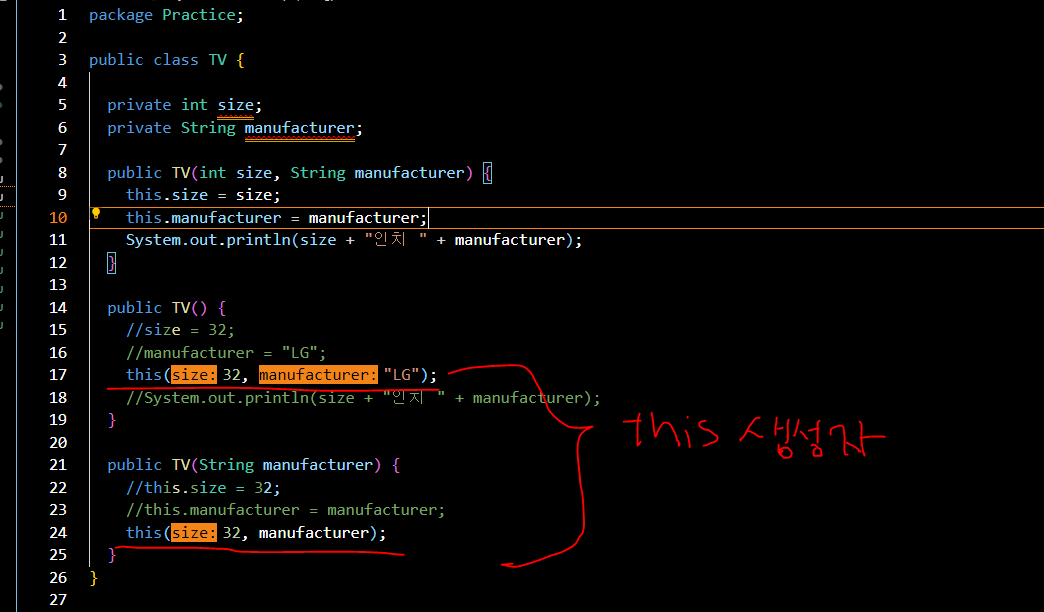
this()를 이용한 생성자
Super
class Point {
private int x, y;
public Point(String parent) {
System.out.println("생성자." + parent);
}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void set(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void showPoint() {
System.out.println("(" + x + ", " + y + ")");
}
public void superFunc() {
System.out.println("superTest");
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point {
private String color;
public ColorPoint(String child) {
super(child);
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public void showColorPoint() {
System.out.println(color);
showPoint();
}
public void colorSuperFunc() {
super.superFunc();
}
}
public class ColorPointEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point("parent");
p.set(1, 2);
p.showPoint();
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint("child");
cp.set(3, 4);
cp.setColor("red");
cp.showColorPoint();
Point pp = new ColorPoint("child"); // 자식 클래스의 객체를 만드는데 부모 타입을 참조
pp.set(1, 2);
System.out.println(pp.getClass() + ", " + pp.getClass().getSimpleName());
// p.showColorPoint(); : 자식클래스에서 새롭게 만든 함수는 접근 x
}
}
- 접근제어자가 private을 갖는 필드나 메소드는 상속할 수 없고 패키지가 다를 경우 접근제어자가 default인 경우도 상속할 수 없다.
업캐스팅 / 다운캐스팅
public class Person {
public String name;
public String id;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}public class Student extends Person {
String grade;
String department;
public Student(String name) {
super(name);
}
}public class UpcastingEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person;
Student student = new Student("티모시 샬라메");
person = student; // Upcasting : 자녀 클래스의 객체가 부모의 타입을 가짐 (상향)
person.id = "statistics";
System.out.println(person.name);
System.out.println(person.id);
// System.out.println(person.grade);
// 부모의 타입을 가진 자식 객체로는 자식에서 새로이 생성된 변수나 함수에 접근할 수 없다.
Person person02 = new Student("니콜라스 홀트");
// Student student02 = person02; // 에러 남
Student student02 = (Student) person02; // 이렇게 명시적으로 캐스팅해야 함
// Downcasting : 부모 클래스가 자녀의 타입으로 캐스팅됨
student02.department = "Philosophy";
System.out.println(student02.department);
}
}instanceof / getClassName
System.out.println(student instanceof Student);
System.out.println(person instanceof Person);
System.out.println(student instanceof Person);
System.out.println(person instanceof Student);
System.out.println(student02 instanceof Student);
System.out.println(person02 instanceof Person);
System.out.println(student02 instanceof Person);
System.out.println(person02 instanceof Student);
System.out.println("student / " + student.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("student02 / " + student02.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("person / " + person.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("person02 / " + person02.getClass().getSimpleName());<출력>
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
student / Student
student02 / Student
person / Student
person02 / Student추상 클래스 / 인터페이스
- 추상 클래스와 인터페이스 모두 미완성된 설계도에 가깝지만(둘 다 객체화시킬 수 없음, new 연산자 사용 못함)
- 인터페이스가 추상화의 정도가 높다. 추상 클래스와 달리 인터페이스는 바디가 있는 일반 메서드나 멤버 변수를 가질 수 없다.
- 또한 추상 클래스(extends)와 달리 인터페이스(implements)는 다중 상속이 가능하다.
- 따라서 추상 클래스 : 기능의 확장 / 인터페이스 : 기능 구현의 강제
- 인터페이스가 인터페이스를 상속 할 수 있다 (이 때는 implements가 아니라 extends).
- 추상클래스가 인터페이스를 implements 할 수 있다. (다른 클래스와 마찬가지로 추상 클래스도 인터페이스를 구현할 수 있습니다. 유일한 차이점은 추상 클래스이기 때문에 인터페이스의 모든 추상 메서드를 구현하도록 강제되지 않는다는 것입니다. 그러나 추상 클래스를 확장하는 클래스는 추상 클래스에 의해 구현되는 인터페이스뿐만 아니라 추상 클래스의 모든 추상 메서드를 구현해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 자신도 추상으로 선언해야 합니다.)
추상 클래스
abstract class Calculator { // 추상클래스
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
// 추상 클래스는 구체화 된 바디를 가질 수 있다.
}
public abstract int subtract(int a, int b);
// 추상 메서드
public abstract double average(int a[]);
// 추상 메서드
}
class RealCalc extends Calculator {
@Override
public int subtract(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
@Override
public double average(int[] a) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
sum += a[i];
}
return sum / a.length;
}
}
public class GoodCalc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RealCalc rc = new RealCalc();
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
System.out.println(rc.average(a)); // 3.0
System.out.println(rc.add(1, 2)); // 3
System.out.println(rc.subtract(10, 2)); // 8
}
}인터페이스
public interface CalcInterface {
int add(int a, int b);
int subtract(int a, int b);
double average(int a[]);
}
class Impl implements CalcInterface {
@Override
public int add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
@Override
public int subtract(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
@Override
public double average(int a[]) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
sum += a[i];
}
return sum / a.length;
}
}
public class CalcInterfaceSpec {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Impl ip = new Impl();
int[] arr = { 3, 5, 6, 7, 1 };
System.out.println(ip.add(1, 2));
System.out.println(ip.subtract(arr[4], arr[2]));
System.out.println(ip.average(arr));
}
}스택
인터페이스
public interface Stack {
int length();
int capacity();
String pop();
boolean push(String val);
}인터페이스 구현
end = 0
import java.util.Scanner;
class StringStack implements Stack {
private String element[];
private int end;
public StringStack(int capacity) {
element = new String[capacity];
//end = -1;
end = 0;
}
public int length() {
return end + 1;
}
public int capacity() {
return element.length;
}
public String pop() {
if (end == -1) {
return null;
} else {
String pop = element[end];
end--;
return pop;
}
}
public boolean push(String val) {
if (end == element.length - 1) {
// Stack이 가득 찼으면
element[end] = val;
return false;
} else {
// System.out.println("end : " + end);
element[end] = val;
end++;
}
return true;
}
}
public class StackApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("몇 개를 넣는 스택을 만들겠습니까 (자연수) >> ");
int capacity = sc.nextInt();
StringStack ss = new StringStack(capacity);
while (true) {
System.out.print("문자열 입력 >> ");
String str = sc.next();
if (str.equals("그만")) {
System.out.println("종료합니다.");
break;
}
boolean response = ss.push(str);
if (response == false) {
System.out.println("***스택이 이미 가득 차서 종료합니다.***");
break;
}
// System.out.println(
// "capacity : " + ss.capacity() + "// length : " + ss.length()
// );
}
int total = ss.length();
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
System.out.println("위에서부터 stack 출력 : " + ss.pop());
//System.out.println(i);
}
sc.close();
}
}end = -1
public class StringStack implements Stack {
private String element[];
private int end;
public StringStack(int capacity) {
element = new String[capacity];
end = -1;
}
public int length() {
return end + 1;
}
public int capacity() {
return element.length;
}
public String pop() {
if (end == -1) {
return null;
} else {
String popStr = element[end];
end--;
return popStr;
}
}
public boolean push(String val) {
if (end == element.length - 1) {
return false;
} else {
end++; //-1
element[end] = val;
System.out.println("end===" + end);
return true;
}
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Practice09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(" 스택 공간을 정수로 입력하시오 ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int total = scanner.nextInt();
StringStack ss = new StringStack(total);
while (true) {
System.out.print("문자열 입력 >>");
String str = scanner.next();
if (str.equals("그만")) {
break;
}
boolean response = ss.push(str);
if (response == false) {
System.out.println("스택이 가득 찼습니");
}
}
System.out.println("capacity===" + ss.capacity());
System.out.println("length===" + ss.length());
int total02 = ss.length();
for (int i = 0; i < total02; i++) {
System.out.println(ss.length());
System.out.print(ss.pop());
}
}
}
Map, 딕셔너리
추상 클래스
public abstract class Maps {
protected String keyArray[];
protected String valueArray[];
abstract String get(String key);
abstract void put(String key, String value);
abstract String delete(String key);
abstract int length();
}구현
package Practice;
class MapDict extends Maps {
protected String keyArray[];
protected String valueArray[];
//int length = 0;
public MapDict(int length) {
keyArray = new String[length];
valueArray = new String[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
keyArray[i] = null;
valueArray[i] = null;
}
}
String get(String key) {
for (int i = 0; i < keyArray.length; i++) {
if (key.equals(keyArray[i])) {
return valueArray[i];
}
}
return null;
}
void put(String key, String value) {
for (int i = 0; i < keyArray.length; i++) {
if (keyArray[i] == null) {
keyArray[i] = key;
valueArray[i] = value;
break;
}
if (keyArray[i].equals(key)) {
keyArray[i] = key;
valueArray[i] = value;
break;
}
}
}
String delete(String key) {
String delResult = "";
for (int i = 0; i < keyArray.length; i++) {
if (key.equals(keyArray[i])) {
delResult = valueArray[i];
keyArray[i] = null;
valueArray[i] = null;
break;
}
}
return delResult;
}
int length() {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < valueArray.length; i++) {
if (valueArray[i] != null) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
public class Practice10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MapDict md = new MapDict(10);
/*md.put("황기태", "자바");
md.put("이재문", "파이썬");
md.put("이재문", "C++");
for (int i = 0; i < md.keyArray.length; i++) {
if (md.keyArray[i] != null) {
System.out.print(md.keyArray[i] + ":" + md.valueArray[i] + "\t");
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("이재문의 값은 " + md.get("이재문"));
System.out.println("황기태의 값은 " + md.get("황기태"));
System.out.println("삭제한 값은 " + md.delete("황기태"));
System.out.println("황기태의 값은 " + md.get("황기태"));
md.put("황기태", "자바");
md.put("이재문", "파이썬");
md.put("이재문1", "C++");
for (int i = 0; i < md.keyArray.length; i++) {
if (md.keyArray[i] != null) {
System.out.print(md.keyArray[i] + ":" + md.valueArray[i] + "\t");
}
}
System.out.println();*/
md.put("1", "one");
md.put("2", "two");
md.put("3", "three");
md.put("4", "four");
for (int i = 0; i < md.keyArray.length; i++) {
if (md.keyArray[i] != null) {
System.out.print(md.keyArray[i] + ":" + md.valueArray[i] + "\t");
}
}
System.out.println();
md.put("1", "일");
md.put("2", "이");
md.put("3", "삼");
md.put("4", "사");
for (int i = 0; i < md.keyArray.length; i++) {
if (md.keyArray[i] != null) {
System.out.print(md.keyArray[i] + ":" + md.valueArray[i] + "\t");
}
}
System.out.println("\n삭제한 값 : " + md.delete("4"));
md.put("3", "three");
md.put("5", "five");
md.put("6", "six");
md.put("7", "seven");
for (int i = 0; i < md.keyArray.length; i++) {
if (md.keyArray[i] != null) {
System.out.print(md.keyArray[i] + ":" + md.valueArray[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
}결과
1:one 2:two 3:three 4:four
1:일 2:이 3:삼 4:사
삭제한 값 : 사
1:일 2:이 3:three 5:five 6:six 7:seven