Problem
LeetCode - The World's Leading Online Programming Learning Platform

Solution
Priority Queue 사용
# Definition for singly-linked list.
from typing import Optional, List
from queue import PriorityQueue
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if len(lists) == 0 or all(node is None for node in lists):
return
values = PriorityQueue()
for node in lists:
while node is not None:
values.put(node.val)
node = node.next
new = ListNode()
node = new
while not values.empty():
node.next = ListNode(val=values.get())
node = node.next
return new.next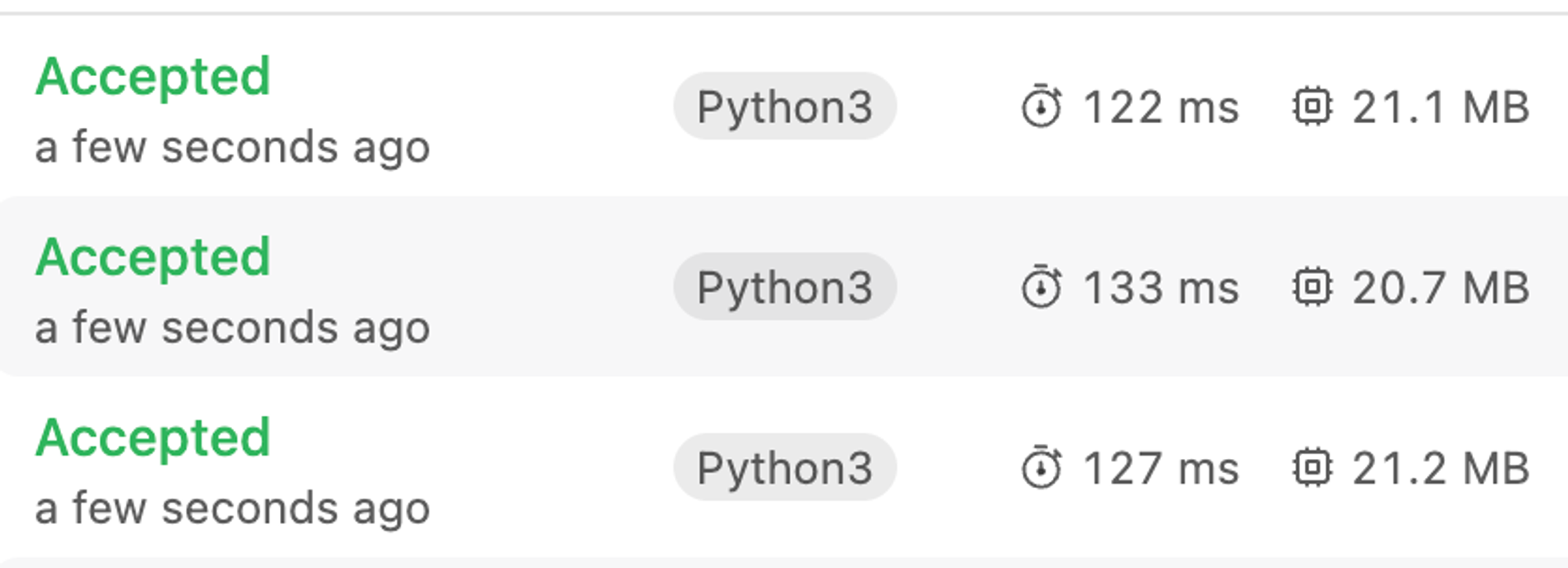
Heapq 사용
# Definition for singly-linked list.
from typing import Optional, List
import heapq
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if len(lists) == 0 or all(node is None for node in lists):
return
values = []
for node in lists:
while node is not None:
heapq.heappush(values, node.val)
node = node.next
new = ListNode()
node = new
while values:
node.next = ListNode(val=heapq.heappop(values))
node = node.next
return new.next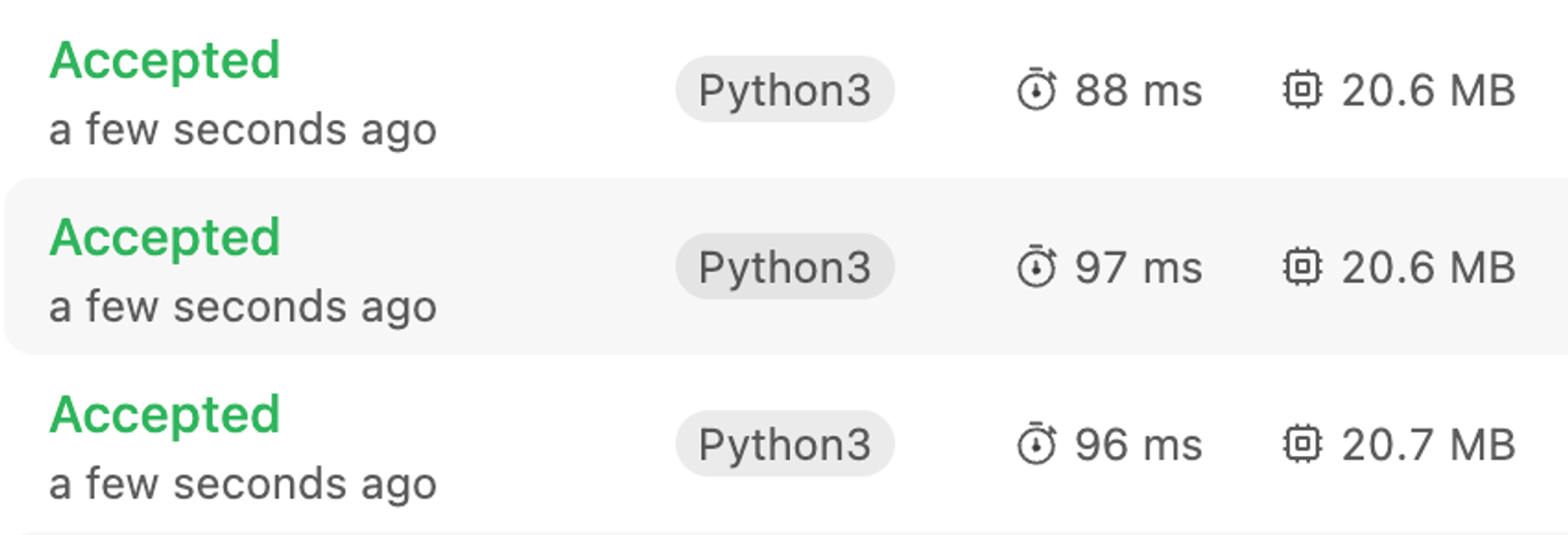
모든 연결리스트의 값을 heapq에 넣어 정렬 하였고, 이를 하나씩 pop하면서 새로운 정렬 리스트를 생성하였다.
heapq 모듈을 사용한 것이 PriorityQueue 모듈을 사용한 것보다 빠른 것을 확인할 수 있다.
PriorityQueue는 내부적으로 heapq를 이용하여 구현되어 있고 스레드 세이프를 보장한다. 즉, 멀티 스레딩을 지원하는 것인데 파이썬의 GIL으로 인해 멀티 스레딩이 거의 의미가 없다. 오히려 Locking Overhead가 발생하여 더 느려진 것으로 예상된다.
Reference
파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰 27번
