스택(Stack)과 큐(Queue)
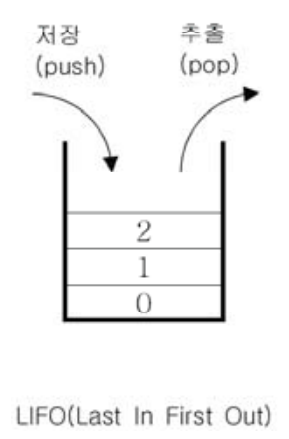
Last in First out 구조이다. 마지막에 저장된 것을 제일 먼저 꺼낸다.
//배열 사용
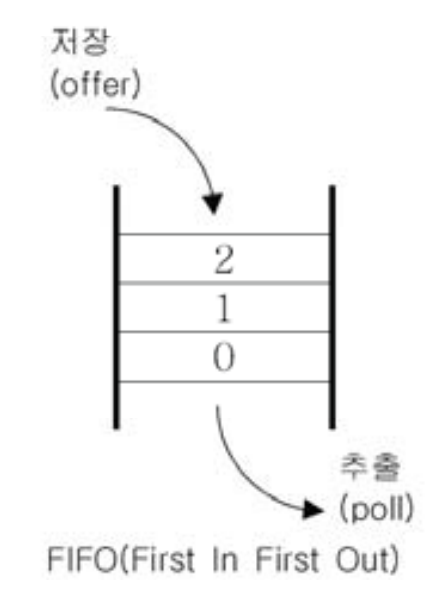
First in First out 구조이다. 제일 먼저 저장한 것을 제일 먼저 꺼낸다.
//LinkedList 사용
Stack 메서드
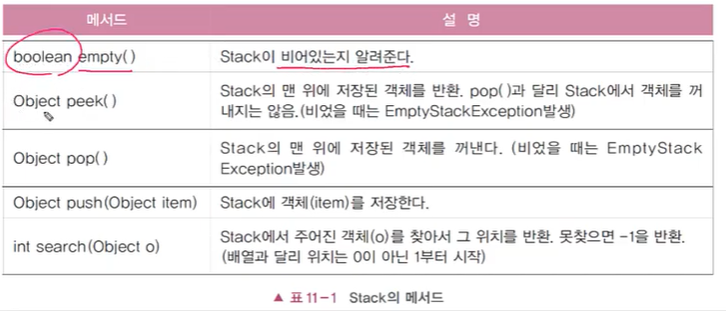
참고로 boolean add(Object o), Object remove(), Object element()는 예외가 발생하지만, boolean offer(Object o), Object poll(), Object peek()는 예외가 발생하지 않는다.
큐는 스택과 달리 인터페이스이기 때문에, 객체 생성이 불가능하다.(Queue queue = new Queue();-> X)
따라서, Queue를 구현할 클래스를 사용해야 한다.
**Queue(or LinkedList) q = new LinkedList();
q.offer("0");와 같이 써준다.
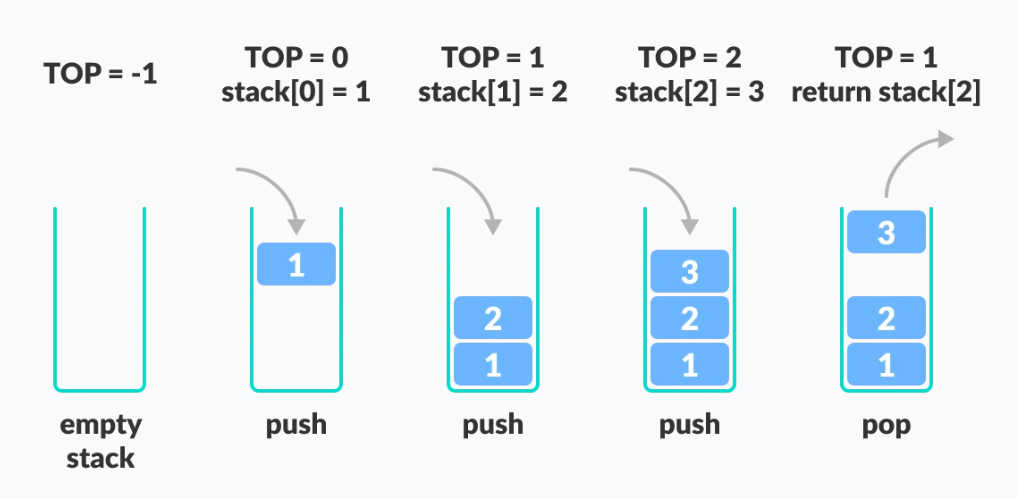
다음은 스택에 관한 예시이다.
package javaplus.Collection;
public class Stack {
private int arr[];
private int top;
private int capacity;
// Creating a stack
Stack(int size) {
arr = new int[size];
capacity = size;
top = -1;
}
// Add elements into stack
public void push(int x) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("OverFlow\nProgram Terminated\n");
System.exit(1);
}
System.out.println("Inserting " + x);
arr[++top] = x;
}
// Remove element from stack
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("STACK EMPTY");
System.exit(1);
}
return arr[top--];
}
// Utility function to return the size of the stack
public int size() {
return top + 1;
}
// Check if the stack is empty
public Boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
// Check if the stack is full
public Boolean isFull() {
return top == capacity - 1;
}
public void printStack() {
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack(5);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.pop();
System.out.println("\nAfter popping out");
stack.printStack();
}
}

