해당 단원의 내용이 너무 많아서 지치기도 하지만
공부하면 할 수록 드디어 나도 토이 프로젝트들을 시작 할 수 있을 것 같다는 생각이 들어 기대 된다. ><
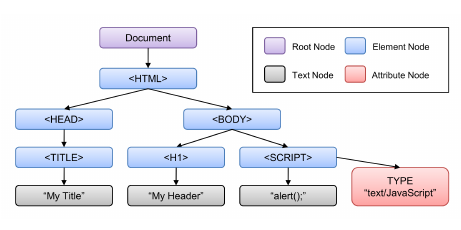
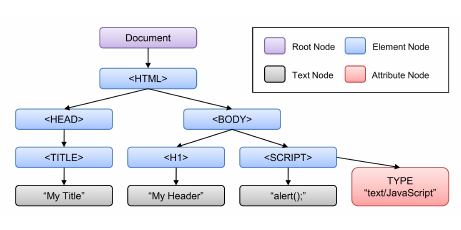
노드 정보 취득
노드 객체에 대한 정보를 취득하려면 다음과 같은 노드 정보 프로퍼티를 사용한다.
| 프로퍼티 | 설명 |
|---|---|
Node.prototype.nodeType |
노드 객체의 종류, 즉 노드 타입을 나타내는 상수를 반환한다. 노드 타입 상수는 Node 에 정이 되어 있다.
|
Node.prototype.nodeName |
노드의 이름을 문자열로 반환한다.
|
const $picknode = document.getElementById('Child2');
const textNode = $picknode.firstChild;
const elementNode = textNode.nextSibling;
console.log('NodeType에 대하여');
console.log(`textNode : ${textNode.nodeType}`);
console.log(`elementNode : ${elementNode.nodeType}`);
console.log(`document : ${document.nodeType}`);
console.log(`NodeName에 대하여`);
console.log(`textNode : ${textNode.nodeName}`);
console.log(`elementNode : ${elementNode.nodeName}`);
console.log(`document : ${document.nodeName}`);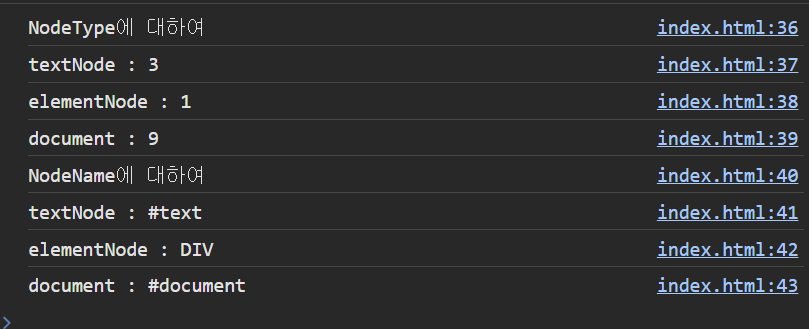
요소 노드의 텍스트 조작
nodeValue
nodeValue 는 접근자 프로퍼티로 setter / getter 모두 존재하는 접근자 프로퍼티이다.
nodeValue 는 텍스트 노드의 값을 참조하는 프로퍼티로서, 텍스트 노드가 아닌 노드에서 사용하게 되면 null 값을 반환한다.
그럼으로 어떤 노드의 텍스트를 변경하려면, 해당 요소 노드에 접근 한 후 텍스트 노드에 접근한 후 수정해야 한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li id="orange">orange</li>
<li id="apple">apple</li>
<li id="banana">banana</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $orange = document.querySelector('#orange');
// orange 노드의 nodeValue 를 확인
console.log($orange.nodeValue); // null
// orange 노드의 텍스트 노드에 접근
const $textNodeFromOrange = $orange.firstChild;
// 텍스트 요소의 값 확인
console.log($textNodeFromOrange.nodeValue); // orange
$textNodeFromOrange.nodeValue = 'grape'; // 값 변경
</script>
</body>
</html>textContent
Node.prototype.textContent 프로퍼티 또한 getter / setter 가 존재하는 접근자 프로퍼티로서 요소 노드의 텍스트와 모든 자손 노드의 텍스트를 모두 취득하거나 변경한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="foo">
Hello
<span>world</span>
</div>
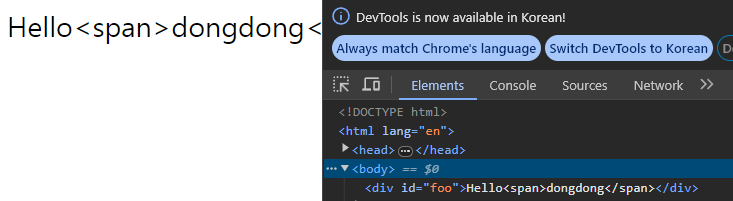
<script>
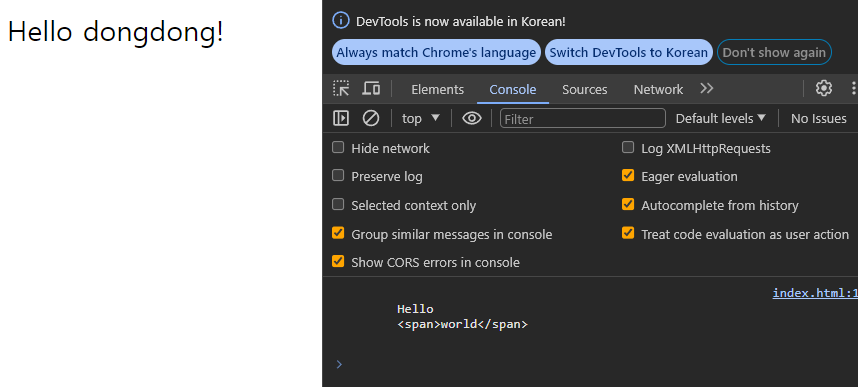
const parseSentance = document.getElementById('foo').textContent;
console.log(parseSentance);
document.getElementById('foo').textContent = 'Hello<span>dongdong</span>';
</script>
</body>
</html>
getElementID 로 가져온 노드의 textContent 프로퍼티를 이용하면 가져온 노드의 자식 노드들에 존재하는 textNode 를 모두 가져오는 것 처럼 보인다.
이는 요소 노드의 HTML 태그를 파싱해오지 않고 textNode 만 가져오는 것이라 그렇다.
textContent 는 접근자 프로퍼티로 getter / setter 모두 가지고 있다.
다만 setter 프로퍼티로 사용하게 되면 할당한 문자열의 HTML 태그도 파싱되지 않아 문자열 그 자체로 파싱된다.
비슷한 동작을 하는 innerText 가 존재하나 이는 다음과 같은 이유로 사용하지 않을 것이 좋다.
innerText는CSS환경을 고려한다. (CSS에서visibility :hidden인 경우엔 나타나지 않음)CSS를 고려하기 때문에textContent에 비해 속도가 느리다.
DOM 조작
새로운 노드를 생성하여 이미 렌더링 된 DOM에 추가하거나, 기존 노드를 삭제, 교체하는 것을 말한다.
이 때 DOM 이 변경될 때 마다 리플로우, 리페인트가 발생하기 때문에
리플로우, 리페인트는 렌더링 속도를 낮춰 UX 에 영향을 미친다.
복잡한 콘텐츠를 다루는 DOM 조작은 성능 최적화에 주의해서 다뤄야 한다.
innerHTML
Element.prototype.innerHTML 은 취득한 노드의 자식 노드의 태그들을 문자열로 파싱해온다.
이 때 파싱해올 때 textContent 는 HTML 태그 는 파싱해오지 않았던 것과 별개로
HTML 태그도 모두 파싱해온다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="foo">
Hello
<span>world</span>
</div>
<script>
const $parseNode = document.getElementById('foo');
const $childNodes = $parseNode.innerHTML;
console.log($childNodes);
// 자식 노드 수정하기
$parseNode.innerHTML = 'Hello <span>dongdong!</span>';
</script>
</body>
</html>
이 때 innerHTML 또한 getter / setter 가 있는 접근자 프로퍼티로
setter 함수를 이용해서 HTML 태그가 담긴 문자열을 설정하면 DOM 조작이 가능하다.
innerHTML 의 단점
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
<li>orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
$fruitsFromDocument.innerHTML += '<li>grape</li>';
</script>
</body>
</html>innerHTML 은 자식 노드를 통째로 재작성하여 자식 노드로 설정한다.
위 코드의
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
$fruitsFromDocument.innerHTML += '<li>grape</li>';
</script>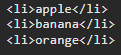
$fruitsFromDocument.innerHTML 자식 태그 문자열에 <li>grape</li> 태그를 더한 문자열을
$fruitsFromDocument의 자식 노드들로 설정하는 것과 같다.
그러니 이미 작성되어 있는 자식 태그를 다시 새로 작성 후 새로운 문자열 (태그)을 추가하는 것이기 때문에 효율적이지 않다.
또한 삽입될 위치를 지정해줄 수 없다는 단점이 존재한다.
맨 마지막에 추가되니 말이다.
innerHTML을 사용해서는aplle과banana사이에 태그를 추가하는 것이 불가능하다.
만약 그러기 위해선 새로 innerHTML 을 모두 재작성한 후 할당해야 한다.
insertAdjacentHTML
Element.prototype.insertAdjacentHTML 은 기존 요소를 제거하지 않으면서 위치를 지정해 새로운 요소를 삽입한다.

파라미터로는 삽입하고자 하는 위치를 가리키는 beforebegin , afterbegin , beforend , afterend 와 삽입하고자 하는 문자열이 존재한다.
이는 파싱된 태그의 위치에 삽입하고자 하는 문자열이 삽입된다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
<li>orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $appleTag = $fruitsFromDocument.firstElementChild;
$appleTag.insertAdjacentHTML('afterend', '<li>grape</li>');
</script>
</body>
</html>
노드 생성과 추가
노드를 그럼 불편하게 계속 문자열로 만들고 파싱 시켜야 하나 ?
걍 태그를 생성하면 안돼 ? 캬캬캭
됩니다
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
<li>orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $li = document.createElement('li');
const textNode = document.createTextNode('grape');
$li.appendChild(textNode);
$fruitsFromDocument.appendChild($li);
</script>
</body>
</html>createElement 로 element node 를 생성하고 거기에 text node 를 appendChild 시켜주면 된다.
const $li = document.createElement('li');
const textNode = document.createTextNode('grape');
$li.appendChild(textNode);까지 했을 때에는 기존 DOM 과 별개의 독립적인 노드이지만
$fruitsFromDocument.appendChild($li);를 통해 기존 DOM에 집어넣어줄 수 있다.
그럼 여러개를 넣고 싶으면 어떻게 할까 ?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
<li>orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
['grape', 'blueberry', 'lemon'].forEach((text) => {
const $li = document.createElement('li');
$li.textContent = text;
$fruitsFromDocument.appendChild($li);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>텍스트 노드가 하나밖에 없을 때에는
textContent로 접근하는게 훨씬 편하다.
배열 반복문을 이용하여 텍스트 노드가 담긴 $li 를 생성하고 지속적으로 DOM 트리에 추가해줬다.
하지만 이것은 치명적인 단점이 존재하는데
하나 하나 추가 될 때 마다 리페인트, 리렌더링이 된다는 점이며, 최대한 리페인트,리렌더링을 낮춰야 한다고 했다.
하나하나가 모두 코스트이며 UX 에 영향을 미친다.
그러면 머리 속에 드는 생각이 있다.
아.. 뭔가 추가 할 자식 노드들을 담을 가상의 컨테이너를 만들고, 가상의 컨테이너에다가 한 번에 담은 후에 담아버리고 싶은데 ..
있습니다
document.prototype.DocumentFragment 를 이용해주면 된다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
<li>orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $fragment = document.createDocumentFragment();
['grape', 'blueberry', 'lemon'].forEach((text) => {
const $li = document.createElement('li');
$li.textContent = text;
$fragment.appendChild($li);
});
$fruitsFromDocument.appendChild($fragment);
</script>
</body>
</html>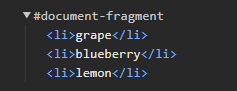
document.createDocumentFragment() 로 생성된 가상의 fragment 에 추가 된 자식 태그들을
기존 DOM tree 에 추가하면 한 번에 여러개의 태그들을 추가 할 수 있다.
이는 리렌더링, 리팩토리를 한 번만 일으키기 때문에 코스트도 절감하고 UX 도 향상 시킬 수 있다.
노드 이동
appendChild 를 이용한 노드 이동
appendChild 를 이용하게 되면 가장 마지막 자식 노드로 새로운 노드가 추가된다.
그럼 이 때 이미 존재하는 노드를 추가하면 어떻게 될까 ?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
<li>orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $firstChildElement = $fruitsFromDocument.firstElementChild; // 첫 번째 자식 노드 (apple)
$fruitsFromDocument.appendChild($firstChildElement);
</script>
</body>
</html>
이미 존재하는 노드를 명시적으로 선택하여 추가하면 노드가 이동한다.
...
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $newApple = document.createElement('li');
$newApple.textContent = 'apple';
$fruitsFromDocument.appendChild($newApple);
</script>
...
같은 내용을 새롭게 생성하면 이동하지 않는다
inertBrfore 를 이용한 노드 이동
document.prototype.insertBefore 를 이용하면 (이동 시키거나 삽입할 노드, 기존 노드) 를 매개변수로 받아 이동시키거나 삽입 할 수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
<li>orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruitsFromDocument = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $firstElement = $fruitsFromDocument.firstElementChild;
const $lastElement = $fruitsFromDocument.lastElementChild;
$fruitsFromDocument.insertBefore($firstElement, $lastElement);
document.inset
</script>
</body>
</html>
이 때 첫번째 매개변수에 기존에 존재하는 노드를 넣으면 이동이 되고
새로운 노드를 넣으면 새로운 노드가 해당 위치에 삽입된다. :)
노드를 이동시키고자 할 때 두 노드의 부모 노드가 다를 경우엔
DOMException에러가 발생한다.
노드 복사
Node.prototype.cloneNode([deep:true | false]) 를 이용하면 노드를 복사 할 수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruits = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $apple = $fruits.firstElementChild;
// 얕은 복사
const shallowCopy = $apple.cloneNode(false);
// 깊은 복사
const deepCopy = $apple.cloneNode(true);
console.log(shallowCopy);
console.log(deepCopy);
</script>
</body>
</html>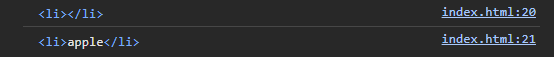
얕은 복사는 노드 자신만의 사본만을 생성한다.
이로 인해 자식 노드들이 복사되지 않으며 text Node 도 자식 노드이기 때문에 textNode 가 존재하지 않는다.
하지만 깊은 복사는 자식 노드까지 모두 복사하기에 text Node 를 포함하여 하위 자식 태그들도 복사한다.
<script>
const $fruits = document.getElementById('fruits');
// 깊은 복사
const deepCopy = $fruits.cloneNode(true);
console.log(deepCopy);
</script>
$fruits.appendChild(deepCopy);
복사본을 추가하는 행위도 가능하다.
노드 교체
Node.prototype.replaceChild(newChild , oldChild) 는 자신을 호출한 노드의 자식 노드를 새로운 노드로 교체한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruits = document.getElementById('fruits');
// 교체할 노드 생성
const newNode = document.createElement('li');
newNode.textContent = 'super banana';
$fruits.replaceChild(newNode, $fruits.lastElementChild);
</script>
</body>
</html>
노드 삭제
Node.prototype.removeChild(child) 는 인수로 전달 받은 노드를 DOM 에서 삭제하며
인수로 전달한 child 는 해당 노드의 자식 노드여야 한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li>apple</li>
<li>banana</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruits = document.getElementById('fruits');
// 마지막 자식 노드 삭제하기
$fruits.removeChild($fruits.lastElementChild);
</script>
</body>
</html>
어트리뷰트
이 부분 내용이 이해가 잘 안가서 이틀씩이나 고민했다.
여태껏 DOM 에 대해서 공부할 때 Element node 와 Text node 에 대해서만 이야기 하였지만
사실은 Attributes Node 도 존재한다.
class 나 id 등이 대표적인 Attribute Node 이며 종류에 따라 value , type .. 등 다양한 것들이 존재한다.
이런 Attrivbutes Node 는 Element Node 와 병렬적으로 배치된다.
병렬적이라고 애매하게 표현한 이유는 형제 노드라고 표현하기에는 부모 노드가 같지 않기 때문이다.
class 나 id 같이 모든 Element Node들이 가질 수 있는 어트리뷰트들을 글로벌 어트리뷰트라고 하며
아직 배우지 않았지만 이벤트와 관련된 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트들 또한 모든 Element Node 들이 가질 수 있다.
어떤 어트리뷰트들은 특정 엘레멘트 노드들만 가질 수 있는 어트리뷰트 노드들도 존재한다.
예를 들어
input태그같은 경우엔type , value , checked등이 존재한다.
그럼 Element Node들은 어떻게 Attributes node 들을 관리하고 DOM 에서는 어떻게 관리할까 ?
Element Node 에서의 Attribute Node 관리
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input id="user" type="text" value="dongdong" />
</body>
</html>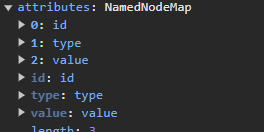
input 노드에는 수 많은 프로퍼티들이 존재하는데 이 중 attributes 라는 프로퍼티에는
NamedNodeMap 이란 자료 구조 (유사배열 객체)에서 프로퍼티와 value 형태로 관리하고 있는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
즉 Element node 를 생성하면 Element Node 객체의 프로퍼티에서 Attribute node 들을 저장하고 있다.
Attributes 조작
요소의 Attribute 들은 프로퍼티로 접근 할 수 있다.
<script>
const $input = document.getElementById('user');
const { attributes } = $input;
console.log(attributes);
console.log(attributes.id);
console.log(attributes.type);
console.log(attributes.value);
</script>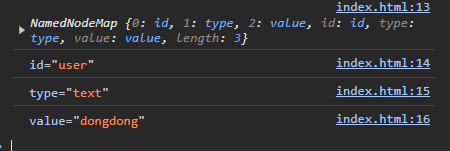
이렇게 프로퍼티로 직접적으로 접근하는 방법도 존재하며
Element.prototype.getAttribute / setAttribute 로 접근 , 조작 하는 방법도 가능하다.
<script>
const $input = document.getElementById('user');
// Attribute 접근
console.log($input.getAttribute('id')); // user
console.log($input.getAttribute('type')); // text
console.log($input.getAttribute('value')); // dongdong
// Attribute 설정
$input.setAttribute('value', 'kingkong');
</script>
setAttribute (property , 바꿀 value) 로 설정해주니 input 태그의 value 값이 변경되어 초기 값이 설정되어 있는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
특정 어트리뷰트가 존재하는지를 확인하고 싶다면 Node.prototype.hasAttribute 를 사용하면 된다.
특정 어트리뷰트를 삭제하려면 Node.prototype.removeAttribute 를 사용하면 된다.
HTML어트리뷰트 VS DOM 프로퍼티
input 태그의 어트리뷰트인 value 의 역할은 사용자가 입력 하기 전 들어가 있을 초기 값을 설정한다.
그러니
<input id="user" type="text" value="dongdong" />에서는 초기값으로는 dongdong 이 들어가있다는 것이다.
이 때 만약 사용자가 input 값에 새로운 값을 넣는다면 어떻게 될까 ?
두 가지 변화가 있을 것이라고 예상 할 수 있다.
input태그 내에 존재하는attributes프로퍼티의value값이 변경된다.- 페이지를 구성하는
DOM트리 내에 존재하는value값이 변경 된다.
그럼 어떤 값이 변경될까 ?
어떤 값이 변경 되기 전, 페이지를 구성하는 DOM 트리의 attribute 값엔 어떻게 접근하는지 확인해보자
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input id="user" type="text" value="dongdong" />
<script>
const $input = document.getElementById('user');
console.log('현재 DOM 내부 input 태그의 value');
console.log($input.value);
console.log('현재 input 태그의 Attribute 의 value');
console.log($input.getAttribute('value'));
</script>
</body>
</html>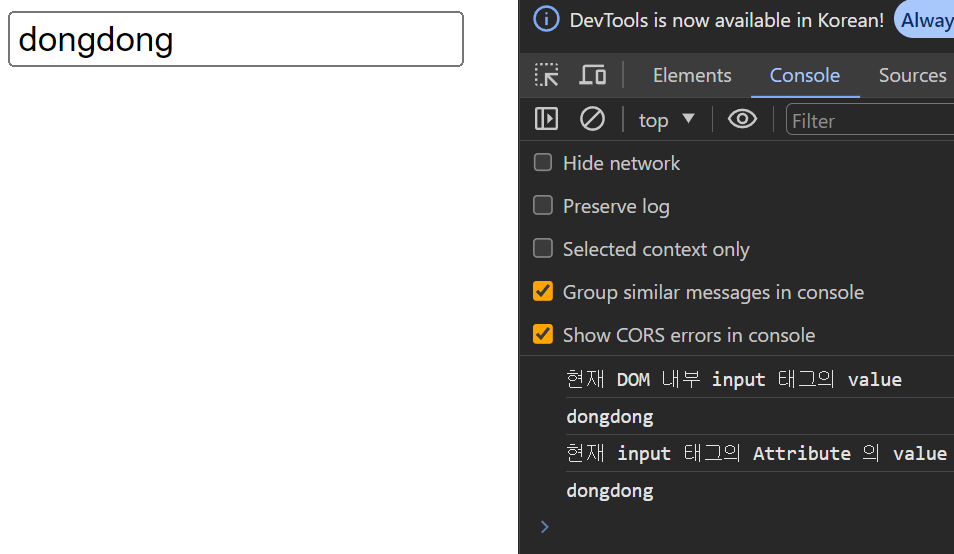
DOM 내부에 존재하는 input 태그의 value 값은 해당 태그의 .value 를 통해 접근 할 수 있다.
이러한 접근은 $input.getAttribute('value') 로 접근하는 것과는 다른 의미를 갖는다.
노드.value 로 접근하는 것은 현재 해당 노드에 들어가있는 value 를 반영하는 것이고
getAttribute 로 접근하는 것은 해당 노드의 초기값 value 를 반영하는 것이다.
브라우저에서 input 태그 내에 값을 변경하면서 value 값을 변경해보자
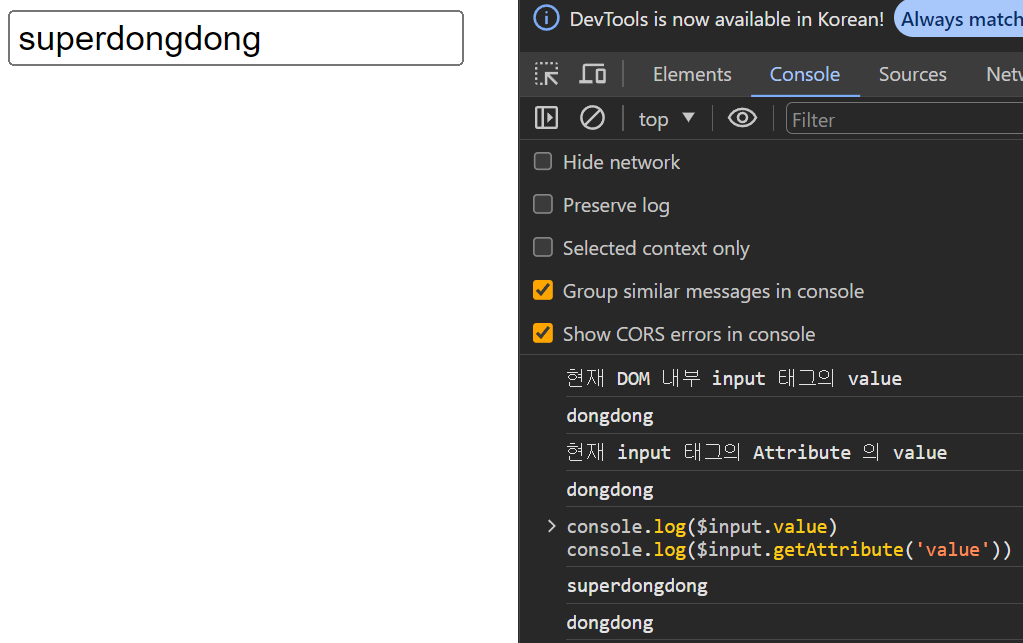
input 태그 내에 value 값을 dongdong => superdongdong 으로 변경했을 때 DOM 내부에서 관리하는 value 값은 변화가 이뤄졌지만 기존 attribute.value 값은 변경이 되지 않은 모습을 볼 수 있다.
이처럼 HTML태그를 작성 할 때 <input id = .. type = .. value = ..> 로 설정한 것은 요소에 지정된 초기 속성 을 의미한다. 이러한 어트리뷰트를 HTML 어트리뷰트 라고 하며 이는 DOM 을 생성 할 때 어트리뷰트 노드에 들어가는 초기 값이다.
이후 브라우저에서 input 태그 내에 값을 집어넣으면 value 값이 변경되게 되는데 변경 됨에 따라 DOM에 들어가있는 input 노드의 attribute node 중 value node 의 값이 변경되게 된다.
이는 모두 DOM 의 프로퍼티 (input 노드도 프로퍼티, input node 의 attribute node 도 프로퍼티, 모두 DOM 의 프로퍼티이다.) 값이 실시간으로 변경되는 것을 의미한다.
HTML 어트리뷰트 는 DOM 프로퍼티 내의 값이 변경 되어도 변경되지 않는다. 그 이유는 HTML 어트리뷰트 는 페이지의 불변하는 초기 설정이기 때문이다.
예를 들어 다른 사용자가 input 태그에 다른 값을 넣었다고 해서, 다른 사용자의 초기 페이지에서 해당 값이 들어가있거나 영향을 미치면 안되기 때문이다.
하지만 DOM 프로퍼티 는 변화에 따라 동적으로 조절된다. 동적으로 조절되는 DOM 프로퍼티 를 이용해서 더욱 다양한 로직을 구현 할 수 있기 때문이다.
DOM 프로퍼티값이 수정되면 페이지가 리페인트 되거나 리플로우 되나 ?특별한 애니메이션 효과나 레이아웃 변경이 없다면 리플로우 , 리페인트 되지 않는다 .그저 값만 변경 될 뿐
조금 복잡한 내용이기 때문에 정리를 한 번 하고 가자
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input id="user" type="text" value="dongdong" />
<script>
const $input = document.getElementById('user');
$input.oninput = () => {
console.log(`DOM 프로퍼티의 value : ${$input.value}`);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>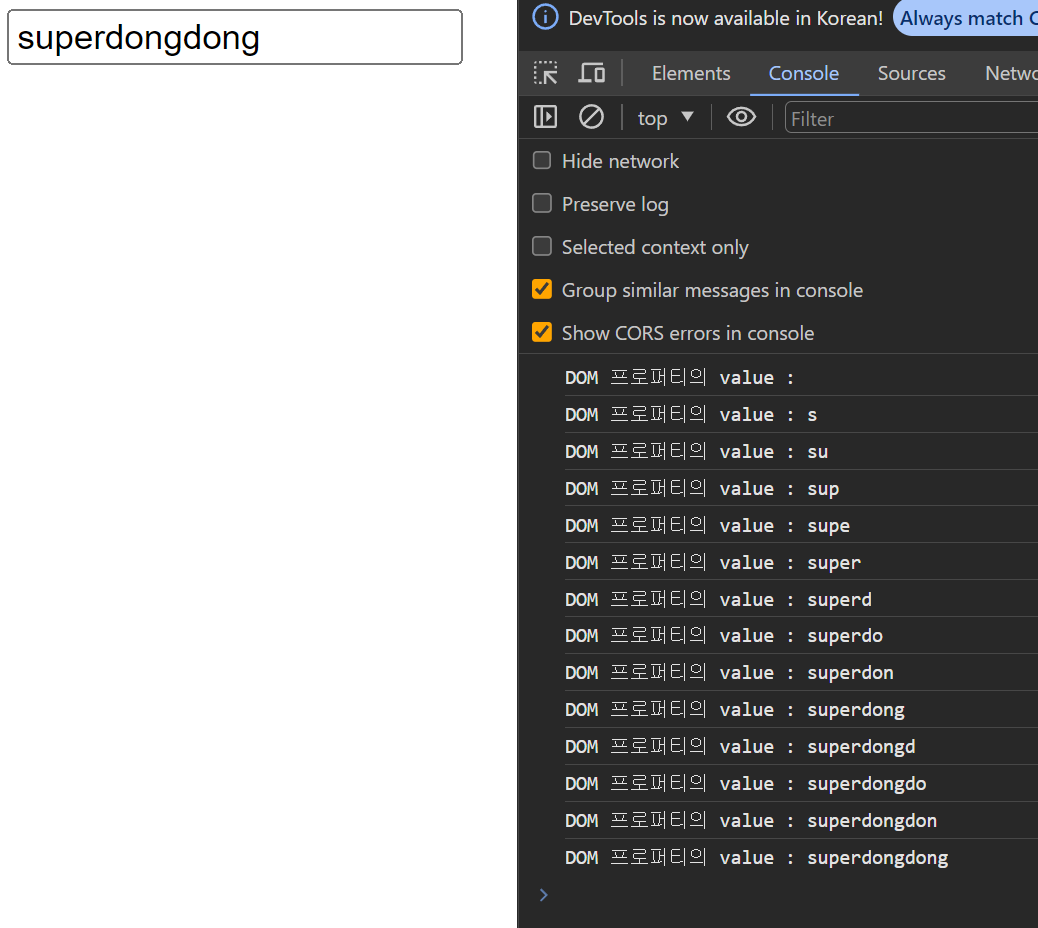
정리
태그 (
DOM에서는element node)의 어트리뷰트는 두 가지 방법으로 관리 된다.
하나는 초기값을 결정하는HTML 프로퍼티, 하나는 동적으로 값이 변경되는DOM 프로퍼티
HTML 프로퍼티는 태그에 지정된 초기 속성으로, 페이지가 로드 될 때의 기본 값을 제공한다.
값이 변경되어도HTML 프로퍼티는 변경되지 않는다.
HTML 프로퍼티는Node.prototype.getAttribute를 통해 접근 할 수 있다.
DOM 프로퍼티는 해당 노드의 현재 상태를 나타낸다.
그로 인해 사용자 상호작용, 스크립트 실행, 다른 이벤트에 따라 값이 동적으로 변경된다.
이 때 페이지 렌더링에는 영향을 미치지 않고 페이지의 현재 상태만 반영한다.
DOM 프로퍼티는Node.prototype.프로퍼티명을 통해 접근 할 수 있다.
HTML 어트리뷰트 와 DOM 프로퍼티 의 대응 관계
대부분의 HTML 어트리뷰트 와 DOM 프로퍼티 는 1:1 대응 관계를 맺는다.
경우에 따라 대응 관계를 맺지 않는 어트리뷰트들도 존재한다.
어트리뷰트 이름은 대소문자를 구별하지 않지만 대응하는 DOM 프로퍼티 는 카멜케이스를 따른다.
대표적인 대응관계 테이블은 다음과 같다.
| HTML 어트리뷰트 | DOM 프로퍼티 | `getAttribute` 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | element.id | element.getAttribute('id') | 요소의 고유 식별자 |
| class | element.className | element.getAttribute('class') | 요소의 클래스 |
| src | element.src | element.getAttribute('src') | 이미지, 스크립트 등의 요소의 소스 경로 |
| href | element.href | element.getAttribute('href') | 링크 요소의 목적지 경로 |
| alt | element.alt | element.getAttribute('alt') | 이미지 요소의 대체 텍스트 |
| value | input.value | input.getAttribute('value') | 입력 필드 요소의 값 |
DOM 프로퍼티 의 값의 타입은 문자열이 아닌 다른 타입일 수도 있다.
예를 들어 checkbox 의 경우 체크 여부에 따라 boolean 값이 들어오기도 한다.
data 어트리뷰트와 dataset 프로퍼티
html 어트리뷰트 와 DOM 프로퍼티 는 서로 1:1 대응 된다고 하였다.
이런 대응 관계를 통해 html 어트리뷰트 값에 따라 DOM 에서 동적으로 쉽게 조회하고 삭제 및 변경이 가능하다.
이런 대응 관계를 효율적으로 이용 할 수 있는게 data 어트리뷰트이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="users">
<li data-id="1" data-Role="admin">Lee</li>
<li data-id="2" data-Role="user">kim</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
어떤 태그를 작성 할 때 data- 를 접두사로 갖는 html 어트리뷰트 를 설정해줄 수 있다.
다음과 같이 설정된 html 어트리뷰트 는 DOM 객체 내 해당 노드에서 dataset 이란 프로퍼티로 관리되며 DOMStringMap 이란 자료구조로 관리된다.
이 때 data-프로퍼티명 = value 로 저장한 HTML 어트리뷰트 가 data- 를 제외한 프로퍼티 명이 프로퍼티로, value 값이 값으로 들어가있다는게 포인트이다.
HTML어트리뷰트에서 지정한 이름을 카멜 케이스 형태로 변환해서 저장한다는게 포인트이다.data-에서 하이픈은 무시된다.
접두사 data- 를 붙인 모든 프로퍼티들은 dataset 이라는 프로퍼티에서 관리된다고 하였기 때문에 해당 프로퍼티에 접근해서 HTML어트리뷰트 에서 지정한 값들을 쉽고 빠르게 조회 및 수정이 가능하다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="users">
<li data-id="1" data-Role="admin">Lee</li>
<li data-id="2" data-Role="user">kim</li>
</ul>
<script>
// role 이 admin 인 사람을 찾아 id 를 변경하기
const $users = document.querySelector('#users');
const $admin = [...$users.children].find(
(user) => (user.dataset.role = 'admin'),
);
// 찾은 사람의 id 를 변경하기
$admin.dataset.id = 999;
console.log($admin.dataset);
</script>
</body>
</html>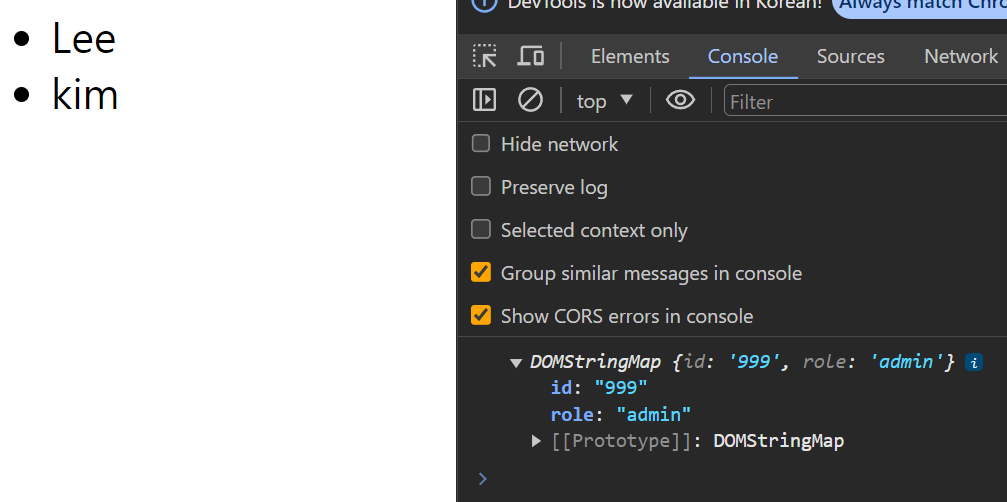
이 때 존재하지 않는 HTML 어트리뷰트 를 추가하게 되면 CamelCase 에서 케밥 케이스 로 변경되어 저장된다. (data-) 가 자동으로 붙는다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="users">
<li data-id="1" data-Role="admin">Lee</li>
<li data-id="2" data-Role="user">kim</li>
</ul>
<script>
// role 이 admin 인 사람을 찾아 id 를 변경하기
const $users = document.querySelector('#users');
const $admin = [...$users.children].find(
(user) => (user.dataset.role = 'admin'),
);
// 해당 태그에 AdminType 을 설정해줘보자
$admin.dataset.AdminType = 'SuperAdmin';
console.log($admin.dataset);
</script>
</body>
</html>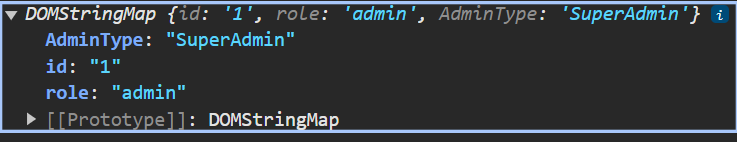
보면 DOM 프로퍼티 에서는 설정한 그대로 붙어있지만
HTML 어트리뷰트 를 확인하면
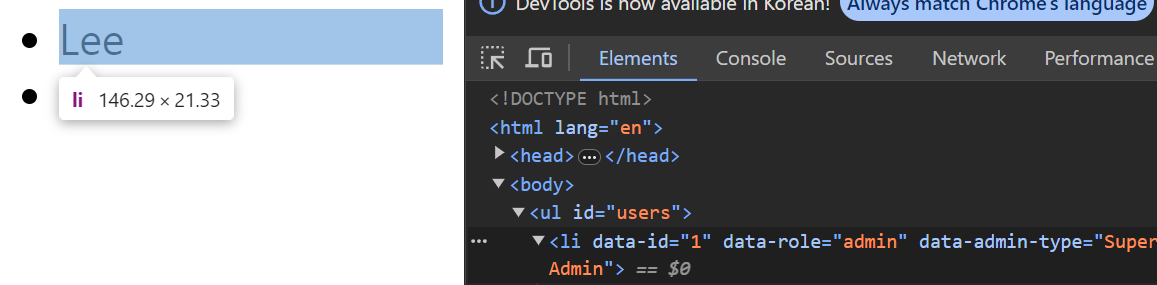
케밥 케이스 형태로 붙어있다. (data-admin-type)
스타일
인라인 스타일 조작
HTMLElement.prototype.style 프로퍼티는 setter / getter 모두 존재하는 접근자 프로퍼티로 요소 노드의 인라인 스타일 을 취득하거나 추가 또는 변경한다.
인라인 스타일
인라인 스타일이란 태그의 스타일을 지정하는 여러가지 방법 중 태그 내에서 선언된 스타일을 의미한다.
예를 들어
<p style = 'color : red'>룰루뿅!</p>
처럼 태그 내에서 지정된style을 인라인 스타일이라고 한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="color: red">나는 p 태그 내의 text 라네</p>
<script>
const $p = document.querySelector('p');
console.log($p.style);
</script>
</body>
</html>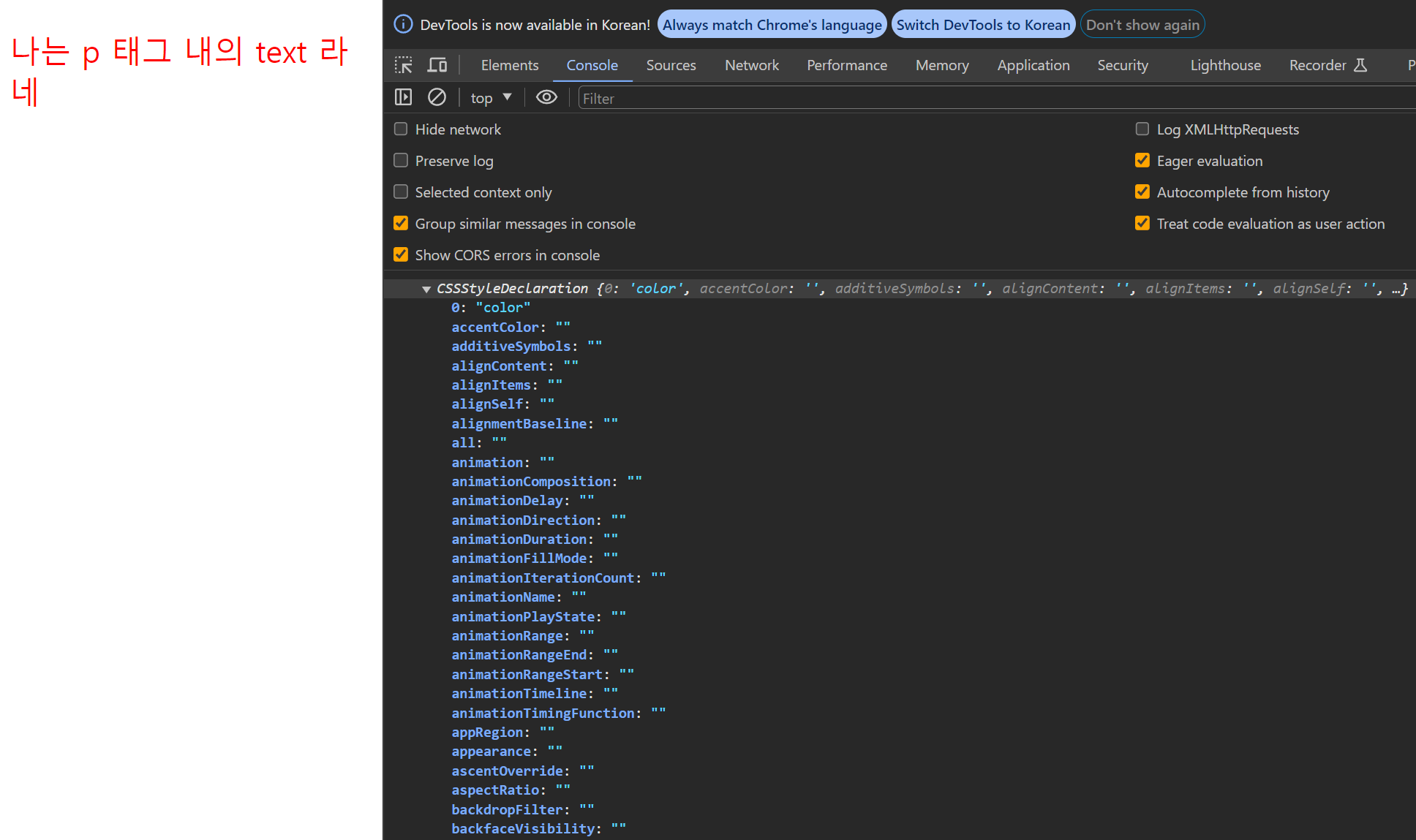
.style 을 통해 해당 태그의 스타일을 담은 프로퍼티인 CSSStyleDeclaration 에 접근 할 수 있다.
접근 한 후 프로퍼티들을 수정하거나 변경 할 수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="color: red">나는 p 태그 내의 text 라네</p>
<script>
const $p = document.querySelector('p');
$p.style.width = '400px';
$p.style.height = '100px';
$p.style.background = 'yellow';
</script>
</body>
</html>
클래스 조작
HTML 어트리뷰트 중 class 와 1:1 대응하는 DOM 프로퍼티 는 className 과 classList 이다.
자바스크립트에서
class는 예약어이기 때문이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px;
color: white;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.red {
background-color: red;
}
.blue {
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box red">div1</div>
<div class="box blue">div2</div>
</body>
</html>
다음과 같이 div1 , div2 는 다중 클래스를 가진 태그로 box 와 red , blue 클래스를 가지고 있다.
class 이름을 가지고 태그를 가져온 후 해당 노드의 클래스를 변경해보자
<script>
// class 명이 blue 인 div 태그 선택
const $blueDiv = document.querySelector('.blue');
// class 명 변경하기
$blueDiv.className = 'box red';
</script>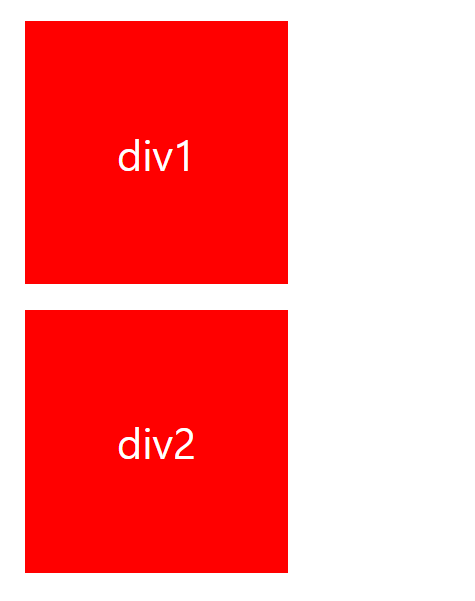
클래스 변경이 잘 된 모습을 볼 수 있다.
하지만 해당 태그에서 불편한 점이 있다.
나는 $bludDiv 노드의 blue 클래스를 red 로만 변경해주고 싶었지만 className 은 box blue 였기 때문에 box red 로 모두 변경해줬어야 했다.
다중 클래스를 가진 노드들이 있을 때 클래스들의 명을 관리하는 프로퍼티는 없을까 ?
있습니다
const classList = $blueDiv.classList;
console.log(classList);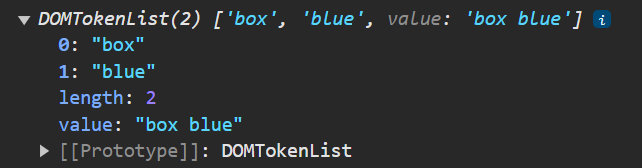
DomTokenList 라는 자료구조로 구성되어 클래스들을 유사 배열 객체 형태로 관리하고 있는 프로퍼티가 존재한다.
이는 classList 라는 프로퍼티를 통해 접근 가능하다.
DomTokenList 는 사용하기 편한 메소드들을 제공한다.
| 메소드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| add(token1, token2, ...) | 하나 이상의 클래스 이름 또는 토큰을 요소의 클래스 리스트에 추가합니다. |
| remove(token1, token2, ...) | 하나 이상의 클래스 이름 또는 토큰을 요소의 클래스 리스트에서 제거합니다. |
| contains(token) | 주어진 클래스 이름 또는 토큰이 요소의 클래스 리스트에 포함되어 있는지 여부를 확인합니다. |
| toggle(token, force) | 클래스 이름이나 토큰이 요소의 클래스 리스트에 있으면 제거하고 없으면 추가합니다. `force` 매개변수를 통해 강제로 추가하거나 제거할 수 있습니다. |
| item(index) | 주어진 인덱스에 해당하는 클래스 이름 또는 토큰을 반환합니다. 인덱스가 범위를 벗어나면 `null`을 반환합니다. |
| replace(oldToken, newToken) | 클래스 리스트에서 주어진 `oldToken`을 찾아 `newToken`으로 교체합니다. |
| entries() | 클래스 리스트의 각 항목에 대한 [인덱스, 값] 쌍을 포함하는 반복 가능한 객체를 반환합니다. |
| keys() | 클래스 리스트의 각 항목의 키(인덱스)를 포함하는 반복 가능한 객체를 반환합니다. |
| values() | 클래스 리스트의 각 항목의 값을 포함하는 반복 가능한 객체를 반환합니다. |
그러니 나는 해당 classList 에서 값을 변경해주기만 하면 된다.
const classList = $blueDiv.classList;
classList.replace('blue', 'red');
구우우웃 ~~
요소에 적용되어 있는 CSS 스타일 참조
.style 은 인라인 스타일 요소만 참조한다.
HTML 요소에 적용되어 있는 모든 CSS 스타일을 적용해야 하는 경우 getComputedStyle 을 사용 할 수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="box red">div1</div>
<div class="box blue">div2</div>
<script>
const $div1 = document.querySelector('.blue');
console.log($div1.style['background-color']); // 결과값이 나오지 않음
</script>
</body>
</html>이전과 동일한 CSS 와 class 이지만 인라인 스타일이 아닌 외부 스타일 요소로 적용해뒀더니 나오지 않는다.
이는 HTML 어트리뷰트 가 CSS 프로퍼티 로 1:1 대응 되지 않았기 때문이다.
inline style요소 일 때는 1:1 대응이 되었다.
이는 window.getComputedStyle(element [,pseudo]) 을 통해 가져올 수 있다.
평가된 스타일이라는 말과 동일하게 어떤 노드를 넣으면, 해당 노드에 계산되어 씌워진 스타일을 확인 할 수 있다.
<script>
const $div2 = document.querySelector('.blue');
const div2Style = getComputedStyle($div2);
console.log(div2Style);
</script>
불러와진 객체인 CSSStyleDeclaration 은 읽기 전용 프로퍼티로 값만 불러올 수 있고
해당 객체에서의 재할당은 불가능하다.
<script>
const $div2 = document.querySelector('.blue');
const div2Style = getComputedStyle($div2);
console.log(div2Style);
console.log(div2Style['background-color']); // rgb(0,0,255)
div2Style['background-color'] = 'hotpink';
//index.html:17 Uncaught DOMException: ... therefore the 'background-color' property is read-only.
</script>하지만 걱정하지말자, CSS 선택자의 우선 순위는 inline style 이 가장 높다.
$div2.style['background-color'] = 'hotpink';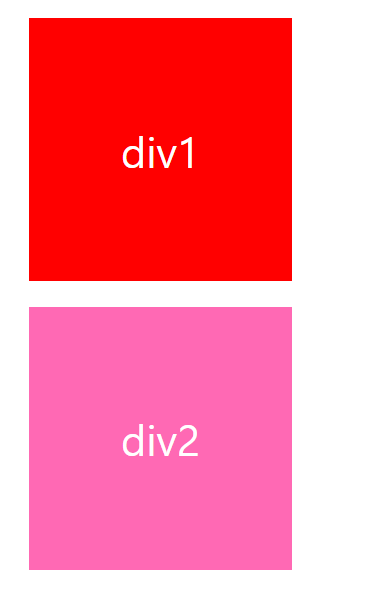
그러니 값을 수정 할 때에는 다음처럼 하자
길고도 긴
DOM관련 챕터가 끝났다.하지만 책을 읽고, 읽은 내용을 복습한다고 해서 습득 할 수 있을 거라고는 생각하지 않는다.
이벤트 관련을 읽고 매우 매우 조그만 사이드 프로젝트나 실습을 해봐야겠다.