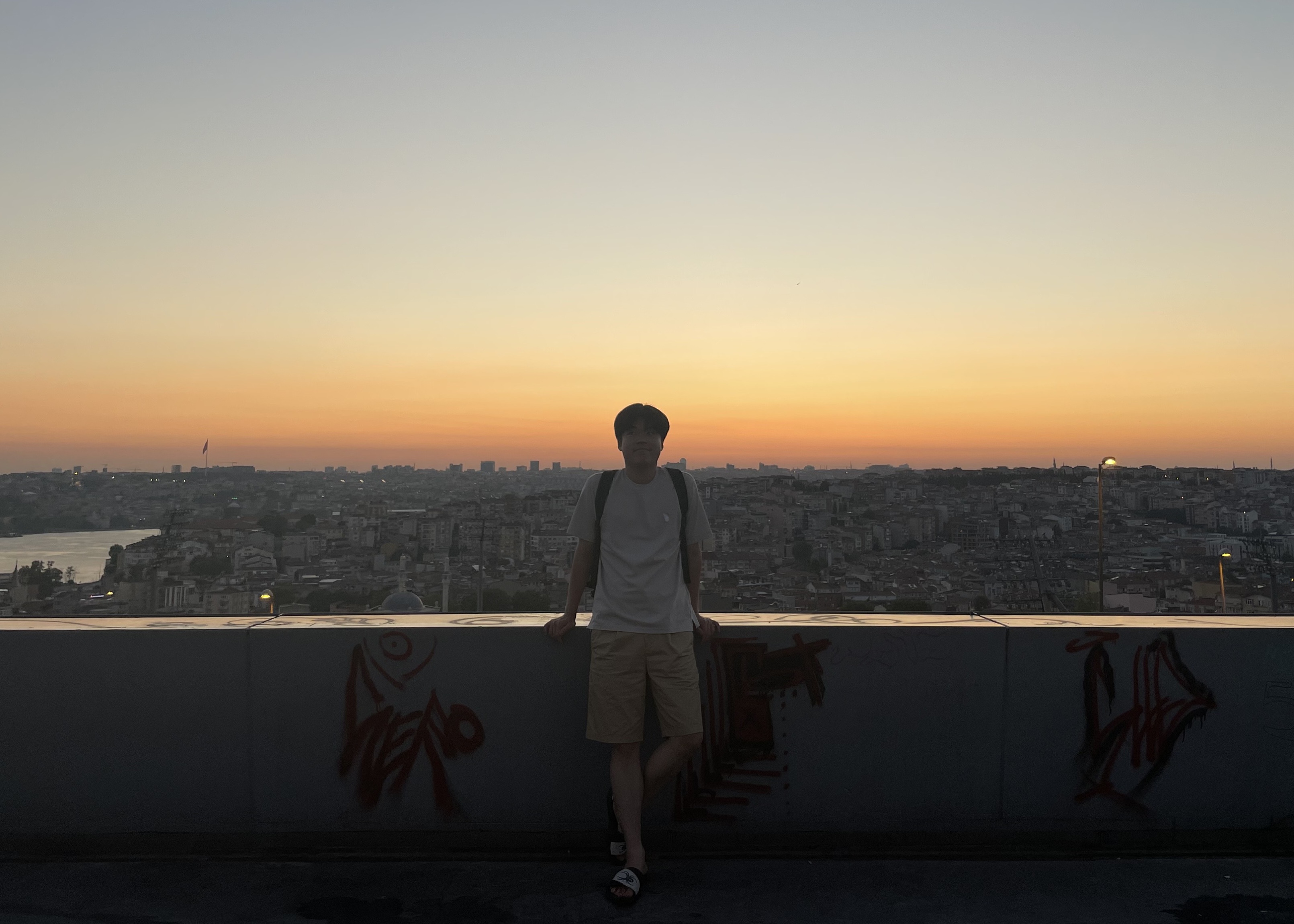
힙(heap)
- 완전 이진 트리에 있는 노드 중에서 키 값이 "가장 큰 노드"(max heap)나 키 값이 "가장 작은 노드"(min heap)를 찾기 위해서 만든 자료구조
개요
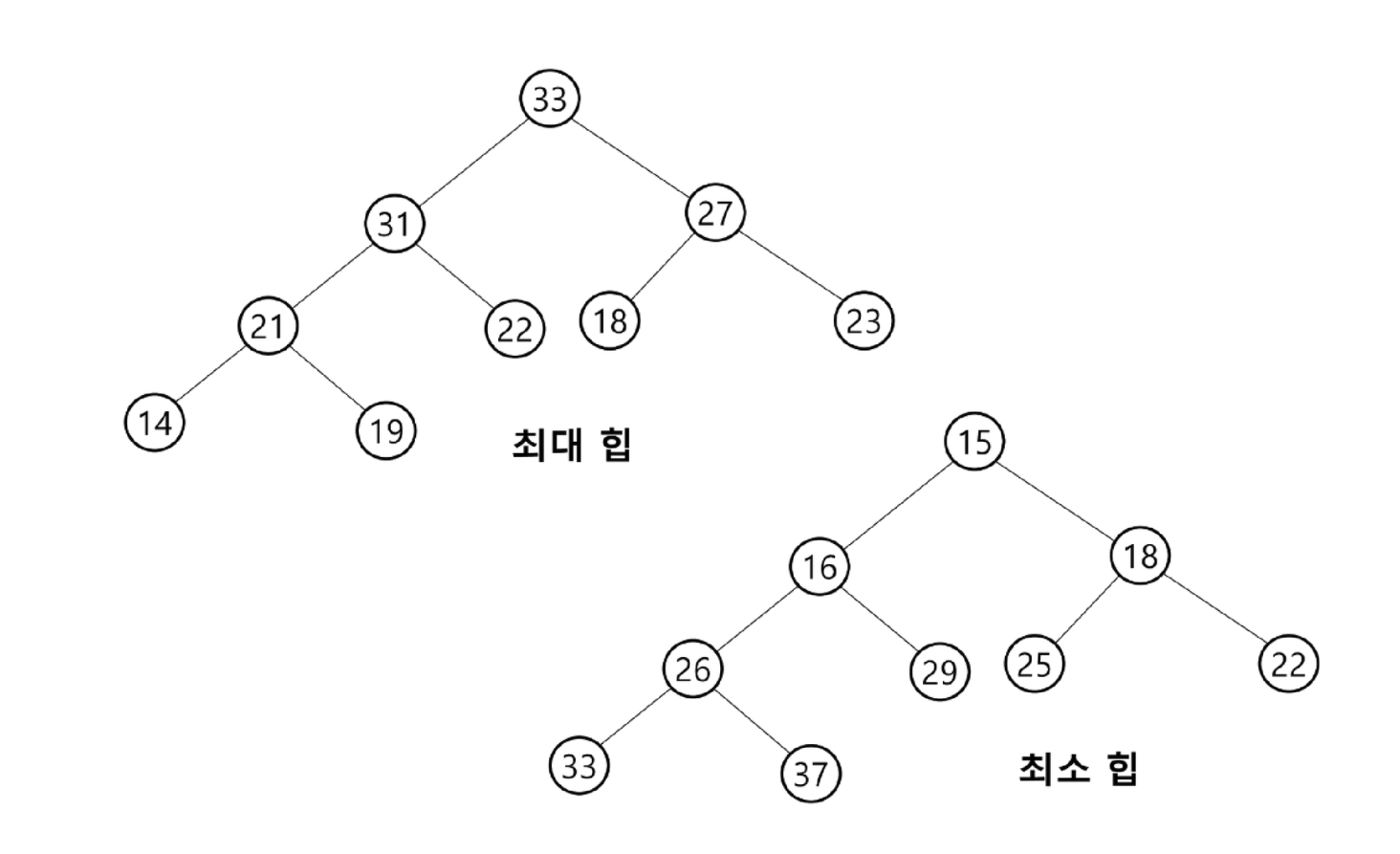
최대 힙(max heap)
- 키 값이 가장 큰 노드를 찾기 위한 완전 이진 트리
- 부모 노드의 키 값 > 자식 노드의 키 값
- 루트 노드: 키 값이 가장 큰 노드
최소 힙(min heap)
- 최대 힙의 반대 개념
예시
<힙 구조 O>
<힙 구조 X>

힙(heap) 연산
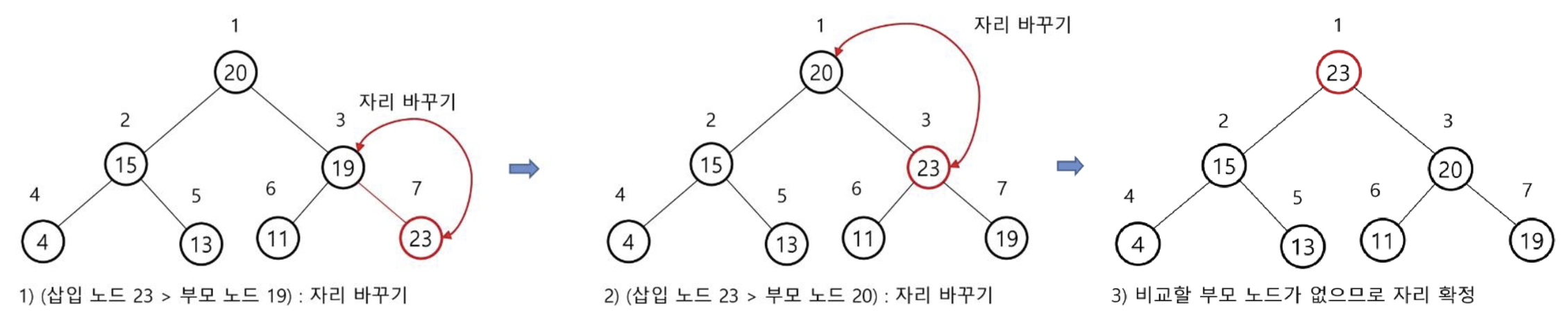
1. 삽입

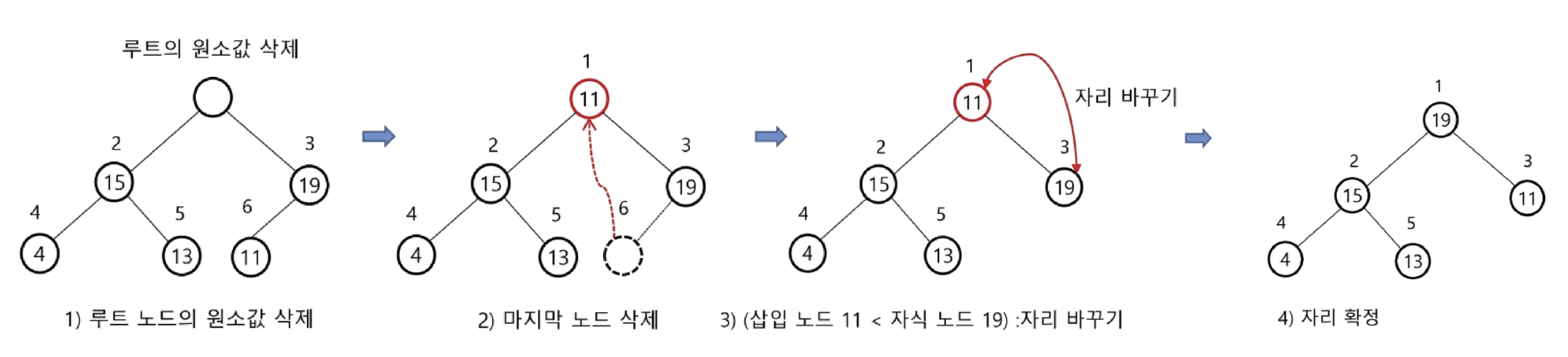
2. 삭제
구현
class MaxHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = []
def heappush(self, item):
self.heap.append(item)
self._siftup(len(self.heap) - 1)
def _siftup(self, idx):
parent = (idx - 1) // 2
while idx > 0 and self.heap[idx] > self.heap[parent]:
self.heap[idx], self.heap[parent] = self.heap[parent], self.heap[idx]
idx = parent
parent = (idx - 1) // 2
def heappop(self):
if len(self.heap) == 0
raise IndexError("힙이 비었습니다.")
if len(self.heap) == 1:
return self.heap.pop()
root = self.heap[0]
self.heap[0] = self.heap.pop()
self._siftdown(0)
return root
def heapify(self, array):
self.heap = array[:]
n = len(array)
for i in range(n // 2 - 1, -1, -1):
self._siftdown(i)
def _siftdown(self, idx):
n = len(self.heap)
largest = idx
left = 2 * idx + 1
right = 2 * idx + 2
if left < n and self.heap[left] > self.heap[largest]:
largest = left
if right < n and self.heap[right] > self.heap[largest]:
largest = right
if largest != idx:
self.heap[idx], self.heap[largest] = self.heap[largest], self.heap[idx]
self._siftdown(largest)heapq 모듈
- 최소 힙을 구현한 라이브러리
- 힙 함수 활용
- heapq.heappush(heap, item) : item을 heap에 추가
- heapq.heappop(heap) : heap에서 가장 왼쪽 원소를 pop
- Heapq.heapify(x) : 리스트 x를 heap으로 변환 ( O(N) )
그러면 최대 힙은 어떻게? -> 값들을 모두 음수로 바꾸면 최소 힙으로 최대 힙처럼 사용 가능. 결과의 부호만 잘 처리하면 됨
우선순위 큐 (Priority Queue)
- 우선순위를 가진 항목들을 저장하는 큐
- FIFO 순서가 아니라 우선순위가 높은 순서대로 먼저 나가게 된다.
- 우선순위 큐를 구현하는 가장 효율적인 방법은 힙을 사용하는 것이다.
- 노드 하나 추가/삭제의 시간 복잡도가 O(logN) 이며, 최대값/최소값을 O(1)에 구할 수 있다.
예시
import heapq
priority_queue = []
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (3, "3순위 작업"))
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (1, "1순위 작업"))
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (2, "2순위 작업"))
print(priority_queue)
# [(1, "1순위 작업"), (3, "3순위 작업"), (2, "2순위 작업")]
while priority_queue:
task = heapq.heappop(priority_queue):
print(task)
# (1, "1순위 작업")
# (2, "2순위 작업")
# (3, "3순위 작업")백트래킹
개요
백트래킹 기법
- 어떤 노드의 유망성(promising)을 점검하여 유망하지 않다면 그 부모의 노드로 돌아가고(backtracking) 다음 자식 노드를 살핀다.
- 유망하다. = 해답이 될 가능성이 있다.
- 가지치기(pruning) = 유망하지 않다면 해당 노드를 가지 않는다. 나무(Tree)의 쓸모없는 가지를 치는 것.
백트래킹 절차
- 상태 공간 트리의 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)를 실시한다.
- 각 노드가 유망한지 점검한다.
- 만일 해당 노드가 유망하지 않으면, 그 노드의 부모 노드로 돌아가서 다른 노드 검색을 계속 진행한다.
백트래킹과 DFS 차이점
- DFS는 완전 탐색이다. 백트래킹은 가지치기를 통해 필요한 요소만 탐색한다. -> DFS를 pruning으로 최적화 하면 그게 백트래킹이다.
일반적인 코드 형태
def backtracking(node v):
if promising(v):
if there is a solution at v:
find the solution
else:
for child of v:
backtracking(child)