1. SWEA1219 길찾기 BFS문제 풀이 중..
알고리즘 및 자료구조에서
어떤 정점 사이의 경로를 벡터로 표현하고,
그 벡터를 초기화하는 것에 부족함을 느끼게 되었당
왜 vector <pair<int,int>> v로 선언하면 안 되고
vector <vector<int>> v 로 선언해야 하는지 모르겠지만..일단 정리하자면, 어떤 그래프 사이 경로를 표현할 때는 pair를 벡터 안에 넣어서 사용하는 것을 자제해야 할 것 같다.
왜냐하면 어떤 정점에서 다른 정점으로 가는 경우를 찾을 때도 for 문을 돌려야 한다!
-> 이렇게 되면 굉장히 비효율적인 작업이 발생할 수 있기 때문..
2. 정점 사이 경로(그래프) 벡터 표현
앞서 적은 것과 같이 각 정점 사이의 이동은 벡터로 간단히 표현할 수 있다.
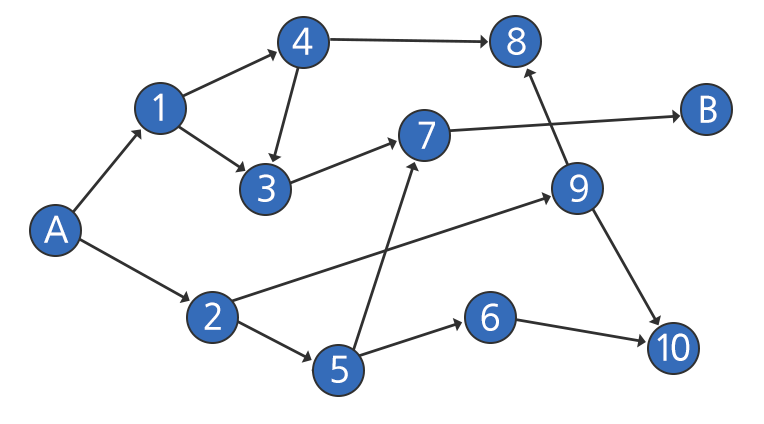
이와 같은 그림이 있고, 그래프에서 일방통행이라고 한다면 가장 먼저 벡터를 어떻게 선언해서 그래프를 표현할 지 생각해야 한다.
vector <vector<int>> v;
vector <bool> visited;다음과 같이 벡터를 선언하고, 그에 맞게 추가해주면 되는 것이다 !!
v.assign(100, vector<int>()); //인접 리스트 초기화
visited.assign(100,false); //방문 배열 초기화
벡터.assign(설정할 크기, 초기화할 값);
벡터.assign(벡터2.begin(), 벡터2.end()); // 벡터 2의 모든 요소로 초기화
벡터.assign(벡터2.begin() + 1, 벡터2.begin() +4);
vector <vector<int>> 벡터;
벡터.assign(3, vector<int>(3, 0)));// 3X3행렬, 모든 값은 0으로 초기화경로 정보 벡터를 추가할 때는 다음과 같이 추가한다.
void input() {
adj.assign(100, vector<int>()); // 인접 리스트 초기화
visited.assign(100, false); // 방문 배열 초기화
result = 0;
cin >> testcase_num >> road_size;
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < road_size; i++) {
cin >> a >> b;
adj[a].push_back(b); // 간선 저장
}
}3. 내 알고리즘에서 틀린 부분 찾기
아직도 잘 모르겠어서 일단 백업해 놓는다.
//BFS or DFS활용하는 길찾기
//길 순서쌍이 주어짐
/*
1. 갔던 길 체크, input 받기
int map[a][b] <- a에서 b로 이동
int visit[ ] =
2. queue에 계속해서 넣기
1)queue에 최초 시작점 삽입
2)해당 시작점과 연결된 정점 삽입
3)q.pop()으로 시작점 제거
4)q.front()의 정점과 연결된 정점 삽입
5)q.pop()으로 해당 정점 제거
6)반복
3. 위의 과정에서 if문으로 도착점에 도달할 경우 정지
1) q.front() == 99일 경우 1 출력
2) 다 찾아도 아닐 경우 0 출력
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
vector <pair<int, int>> v;
vector <bool> visited;
int testcase_num;
int road_size;
int result;
void input() {
v.clear();
visited.resize(100,false);
result = 0;
cin >> testcase_num >> road_size;
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < road_size; i++) {
cin >> a >> b;
v.push_back({ a, b });
}
}
void func() {
queue <int> q;
//시작점 삽입
q.push(0);
visited[0] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
//시작점과 연결된 정점 삽입
int current = q.front();
q.pop();
//탈출 조건, 성공 조건
if (current == 99) {
result = 1;
break;
}
//반복문, v의 크기만큼
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
if (v[i].first == current && !visited[v[i].second]) {
visited[v[i].second] = true;
q.push(v[i].second);
}
}
}
}
void output(int testcase_num) {
cout << "#" << testcase_num << " " << result << endl;
}
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
input();
func();
output(i);
}
return 0;
}4. 개선된 알고리즘
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> adj; // 인접 리스트
vector<bool> visited;
int testcase_num;
int road_size;
int result;
void input() {
adj.assign(100, vector<int>()); // 인접 리스트 초기화
visited.assign(100, false); // 방문 배열 초기화
result = 0;
cin >> testcase_num >> road_size;
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < road_size; i++) {
cin >> a >> b;
adj[a].push_back(b); // 간선 저장
}
}
void func() {
queue<int> q;
q.push(0); // 시작점 0 삽입
visited[0] = true; // 방문 처리
while (!q.empty()) {
int current = q.front();
q.pop();
if (current == 99) { // 도착점에 도달하면 성공
result = 1;
return;
}
for (int next : adj[current]) { // 현재 노드에서 이동 가능한 모든 노드 탐색
if (!visited[next]) {
visited[next] = true;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
result = 0; // 도달하지 못하면 실패
}
void output(int testcase_num) {
cout << "#" << testcase_num << " " << result << endl;
}
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { // 테스트 케이스 10개 처리
input();
func();
output(i); // 테스트 케이스 번호 출력
}
return 0;
}
