💡 우선순위 큐 & 힙 관계
- 우선순위 큐는 "동작 방식"에 가까운 개념
- → 우선순위 높은 것 먼저 꺼내자
- 힙은 "이걸 구현하는 실제 자료구조"
우선순위 큐를 효율적으로 만들기 위해 → "힙"이라는 자료구조를 이용하는 것이다.
우선순위 큐(추상 자료형)
└── 힙으로 구현하는 경우가 많음 (O(log N))☑️ 힙이란?
- 완전 이진트리의 일종으로 우전순위 큐를 위하여 만들어진 자료구조이다.
- 부모와 자식 간의 우선순위 규칙 유지
(부모 ≤ 자식 → 최소 힙 / 부모 ≥ 자식 → 최대 힙) - 배열로도 표현 가능
☑️ 이진 탐색 트리 (BST) vs 힙 (Heap)
| 구분 | 이진 탐색 트리 (BST) | 힙 (Heap) |
|---|---|---|
| 정렬 기준 | 왼쪽 < 부모 < 오른쪽 (이진 탐색 성질) | 부모 ≤ 자식 (Min Heap) / 부모 ≥ 자식 (Max Heap) |
| 탐색 목적 | 빠른 탐색 (검색) | 빠른 "최댓값" or "최솟값" 추출 |
| 탐색 시간 | O(log N) - 원하는 값 찾기 | O(1) - 루트가 항상 최댓값 or 최솟값 |
| 트리 구조 | 보통 비균형 가능 (skewed) | 항상 완전 이진 트리 (좌→우로 꽉 채움) |
| 활용 | 검색, 정렬된 데이터 관리 | 우선순위 큐 (priority queue) |
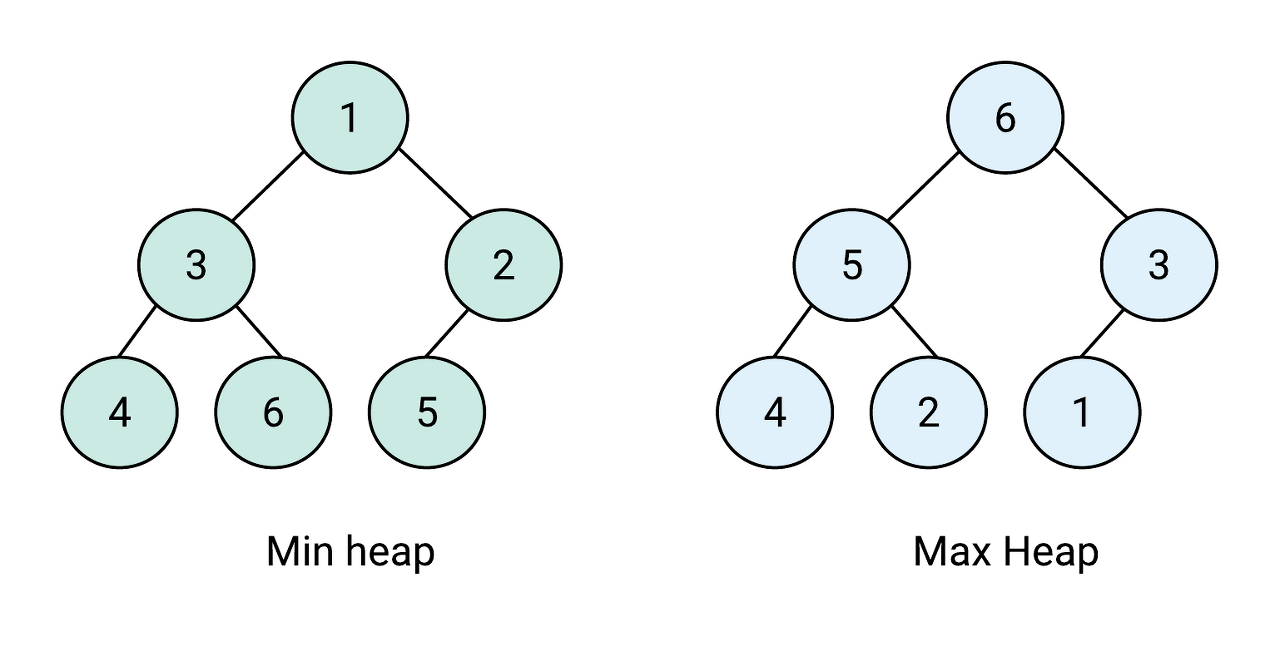
✅ 힙의 유형
1️⃣ 최소 힙 (Min-Heap)
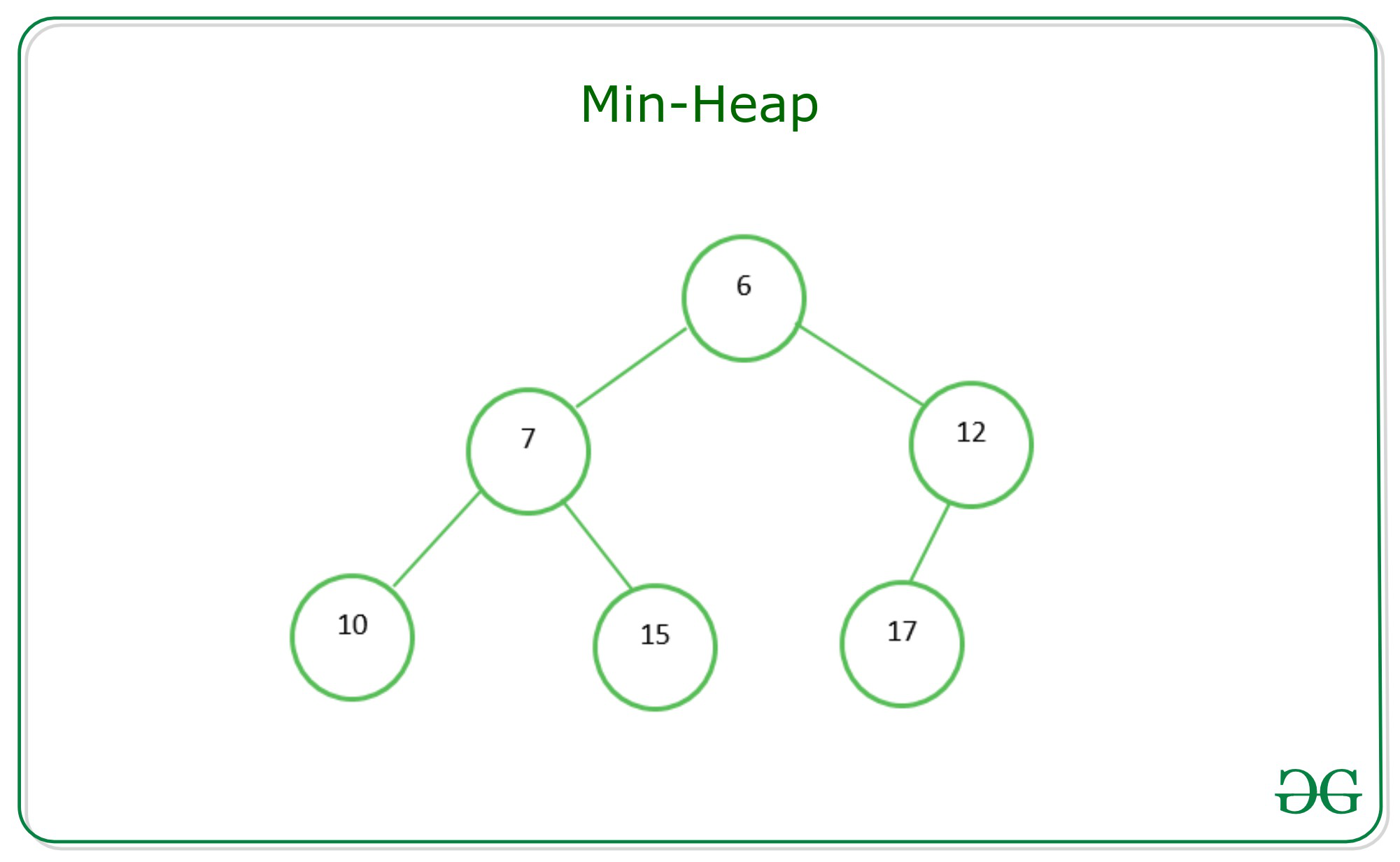
- 부모 ≤ 자식
2️⃣ 최대 힙 (Max-Heap)
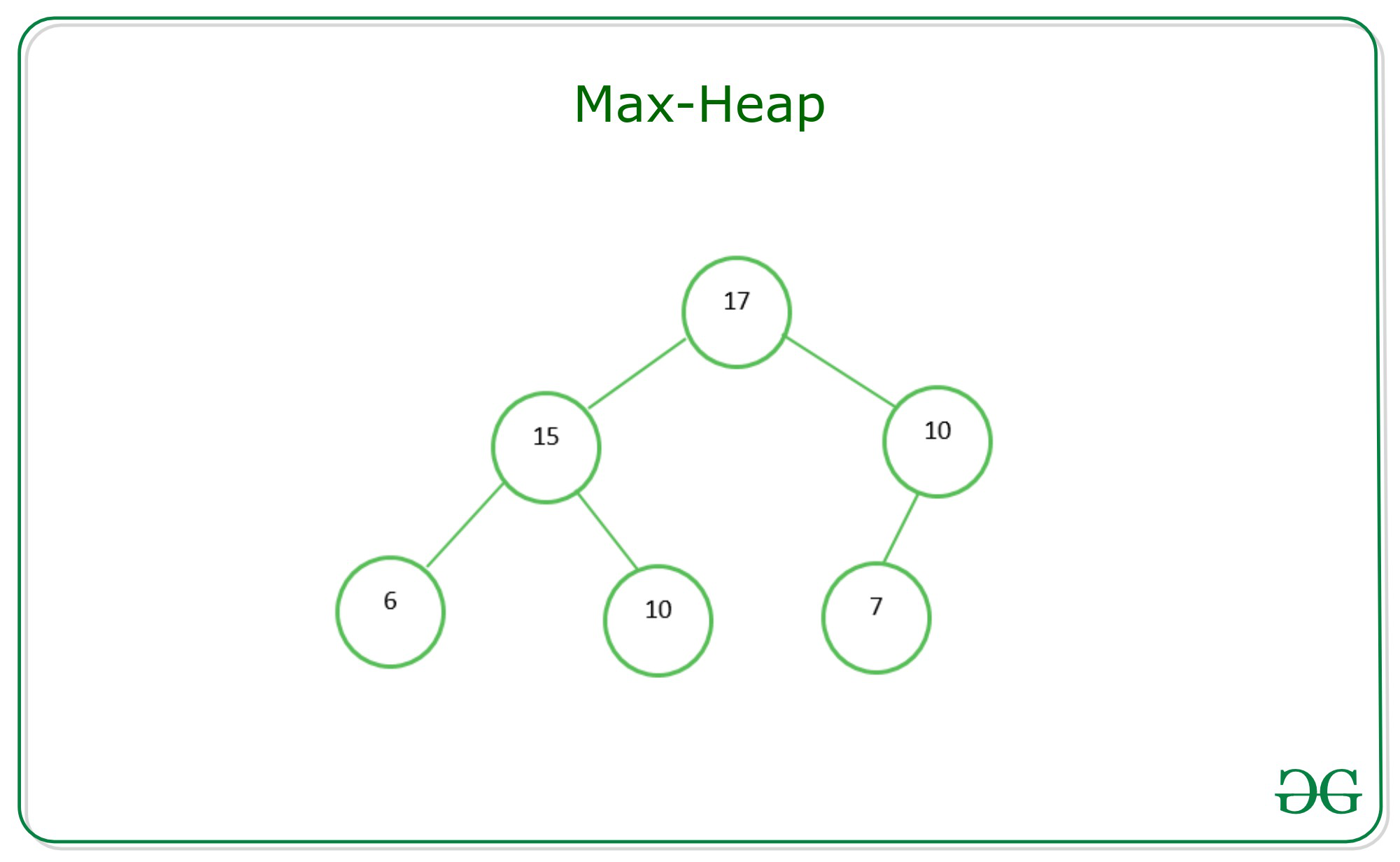
- 부모 ≥ 자식
heapq란?
파이썬 표준 라이브러리에서 제공하는
힙 기반의 우선순위 큐 모듈
- Min-Heap 형태로 동작 (항상 "가장 작은 값"이 루트)
- 내부적으로 리스트 기반의 완전 이진 트리 구조 사용
☑️ heapq 기본 사용법
import heapq
pq = []
heapq.heappush(pq, 5)
heapq.heappush(pq, 3)
heapq.heappush(pq, 7)
print(heapq.heappop(pq)) # 3 (가장 작은 값부터 나옴)✅ 주요함수
1) heapq.heappush(리스트, 값)
→ 힙에 값 삽입
2) heapq.heappop(리스트)
→ 힙에서 최솟값 추출
3) heapq.heapify(리스트)
→ 일반 리스트를 힙으로 변환
☑️ heapify는 어떻게 동작하는가?
arr = [7, 3, 5, 2, 8]
heapq.heapify(arr)
print(arr) # [2, 3, 5, 7, 8] (heap 형태로 재정렬)‘heapify’ 는 주어진 리스트를 한 번에 힙 구조로 재정렬하는 함수이다.
힙 구조로 재정렬된 리스트는 일반적인 오름차순 정렬이 아닌, 부모 ≤ 자식 관계를 만족하는 트리 형태로 배열된다. 이 과정을 통해 리스트가 힙으로 변환되며 이후 heappush, heappop 등의 힙 연산이 가능해진다.
☑️ 그렇다면 heapq를 어떻게 처음부터 구현해야 할까?
- 빈 리스트를 준비한다.
heapq.heappush()로 값을 하나씩 넣어가며 힙 구조를 만들어 나간다.- 이후
heapq.heappop()으로 항상 최솟값을 뽑아가며 사용한다.
예시 구현
import heapq
# Step 1: 빈 힙 준비
pq = []
# Step 2: 값 삽입 (삽입할 때마다 자동으로 heapify-up 수행)
heapq.heappush(pq, 9)
heapq.heappush(pq, 4)
heapq.heappush(pq, 6)
heapq.heappush(pq, 2)
heapq.heappush(pq, 7)
# Step 3: 최솟값부터 하나씩 pop
while pq:
print(heapq.heappop(pq))이 코드에서는 삽입할 때마다 O(log N)의 시간복잡도로 자동으로 힙 구조가 유지된다.
☑️ 직접 힙을 구현하면 어떻게 되는가?
파이썬의 heapq 모듈 대신 직접 힙을 구현할 수도 있다. 대표적인 방법은 다음과 같다.
직접 구현한 Min-Heap 예시
class MinHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = [0] # 0번 인덱스는 비워두어 인덱스 계산을 편하게 함
def push(self, val):
self.heap.append(val)
self._heapify_up(len(self.heap) - 1)
def pop(self):
if len(self.heap) <= 1:
return None
if len(self.heap) == 2:
return self.heap.pop()
root = self.heap[1]
self.heap[1] = self.heap.pop()
self._heapify_down(1)
return root
def _heapify_up(self, idx):
while idx > 1 and self.heap[idx] < self.heap[idx // 2]:
self.heap[idx], self.heap[idx // 2] = self.heap[idx // 2], self.heap[idx]
idx //= 2
def _heapify_down(self, idx):
while idx * 2 < len(self.heap):
min_child = self._get_min_child(idx)
if self.heap[idx] > self.heap[min_child]:
self.heap[idx], self.heap[min_child] = self.heap[min_child], self.heap[idx]
idx = min_child
else:
break
def _get_min_child(self, idx):
if idx * 2 + 1 >= len(self.heap):
return idx * 2
if self.heap[idx * 2] < self.heap[idx * 2 + 1]:
return idx * 2
else:
return idx * 2 + 1직접 힙을 구현하면 동작 원리를 깊이 이해할 수 있으며, 필요에 따라 Max-Heap 또는 커스텀 힙을 만들어낼 수 있다.