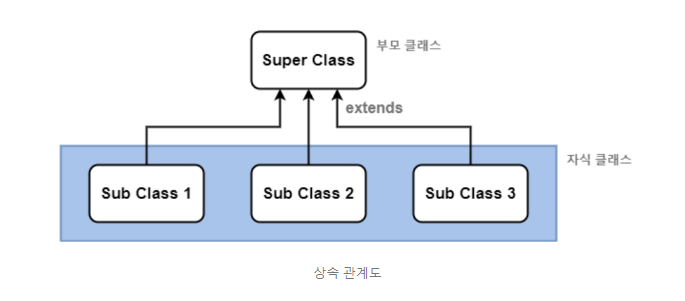
1. 상속을 UML로 표시하면?
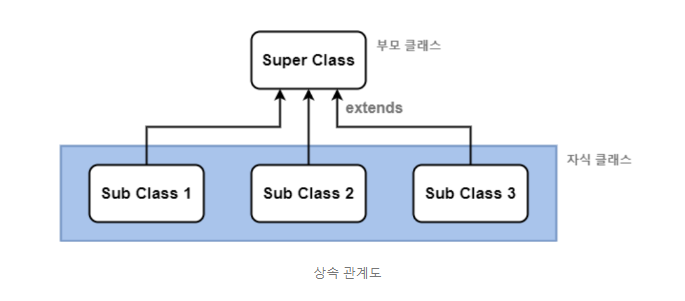
2. 부모 클래스와 자식 클래스의 다른 용어들은?
-
부모클래스는 상위클래스 또는 수퍼클래스 라고합니다.
-
자식클래스는 하위클래스 또는 서브클래스 라고합니다.
3. this 키워드와 super 키워드의 차이는 무엇인가요?
- this 클래스는 자신의 생성자 호출입니다.
- super 키워드는 부모 클래스의 생성자 호출입니다.
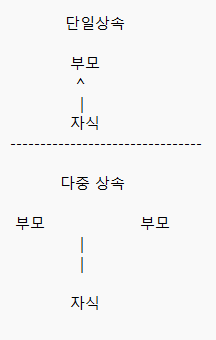
4. 단일 상속과 다중 상속 이란 무엇인가요? UML 로의 표기는?
단일 상속은 한 개의 클래스만 부모클래스로 받을 수 있습니다.
다중 상속은 부모클래스로 여러 개의 클래스를 상속받는 것입니다.
C++에서는 다중상속을 허용했지만 java에서는 다중상속은 불가능합니다.
5. 다음은 2차원 상의 한 점을 표현하는 Point 클래스이다. Point를 상속받아 색을 가진 점을 나타내는 ColorPoint 클래스를 작성하라. 다음 main() 메소드를 포함하고 실행 결과와 같이 출력되게 하라.
class Point {
private int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
public int getX() { return x; }
public int getY() { return y; }
protected void move(int x, int y) { this.x =x; this.y = y; }
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(5, 5, "YELLOW");
cp.setXY(10, 20);
cp.setColor("RED");
String str = cp.toString();
System.out.println(str+"입니다. ");
class Point {
private int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
protected void move(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point {
private String color;
public ColorPoint(int x, int y, String color) {
super(x, y);
this.color = color;
}
public void setXY(int x, int y) {
super.move(x, y);
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String toString() {
return this.color + "색 (" + super.getX() + "," + super.getY() + ")의 점";
}
}
public class PointMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(5, 5, "YELLOW");
cp.setXY(10, 20);
cp.setColor("RED");
String str = cp.toString();
System.out.println(str + "입니다.");
}
}6. 다음 main() 메소드와 실행 결과를 참고하여 TV를 상속받은 ColorTV 클래스를 작성하라. 다음 TV 클래스가 있다.
class TV{
private int size;
public TV(int size) { this.size = size; }
protected int getSize() { return size; }
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorTV myTV = new ColorTV(32, 1024);
myTV.printProperty();
}
/*
package day_2024_07_29;
class TV {
private int size;
public TV(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
protected int getSize() {
return size;
}
}
class ColorTV extends TV {
private int color;
public ColorTV(int size, int color) {
super(size);
this.color = color;
}
protected int getColor() {
return color;
}
public void printProperty() {
System.out.println(getSize() + "인치 " + color + "컬러");
}
}
public class TvMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorTV myTV = new ColorTV(32, 1024);
myTV.printProperty();
}
}7. 2차원 배열 4 * 3 을 선언하고, 각각의 방을 랜덤으로 값을 넣은뒤 모두 출력하시오.
package day_2024_07_29;
public class RandomMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arrRan = new int[4][3];
for (int i = 0; i < arrRan.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrRan[i].length; j++) {
arrRan[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 100 + 1);
System.out.print(arrRan[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
8. 정수를 몇 개 저장할지 키보드로부터 개수를 입력받아(100보다 작은 개수) 정수 배열을 생성하시오.
이곳에 1에서 100까지 범위의 정수를 랜덤하게 삽입하라. 배열에는 같은 수가 없도록 하고 배열을 출력하라.
package day_2024_07_29
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RandomMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("원하는 배열의 갯수");
int[] arrRandom = new int[sc.nextInt()];
for (int i = 0; i < arrRandom.length; i++) {
arrRandom[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100 + 1);
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
while (arrRandom[i] == arrRandom[j]) {
arrRandom[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100 + 1);
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrRandom));
}
}9. 가위바위보를 완성하시오
컴퓨터와 독자 사이의 가위 바위 보 게임을 만들어보자. 예시는 다음 그림과 같다. 독자부터 먼저 시작한다. 독자가 가위 바위 보 중 하나를 입력하고 Enter키를 치면, 프로그램은 가위 바위 보 중에서 랜덤하게 하나를 선택하고 컴퓨터가 낸 것으로 한다. 독자가 입력한 값과 랜덤하게 선택한 값을 비교하여 누가 이겼는지 판단한다. 독자가 가위 바위 보 대신 "그만"을 입력하면 게임을 끝난다.
조건)
- main에 한꺼번에 짜지 말것
- class로 만들어서 해볼것
- String str[] = {"가위", "바위", "보"}; -> 스트링 배열을 이용해 볼것
출력
컴퓨터와 가위 바위 보 게임을 합니다.
가위 바위 보!>>보
사용자 = 보, 컴퓨터 = 보, 비겼습니다.
가위 바위 보!>>보
사용자 = 보, 컴퓨터 = 가위, 컴퓨터가 이겼습니다.
가위 바위 보!>>보
사용자 = 보, 컴퓨터 = 바위, 사용자가 이겼습니다.
가위 바위 보!>>가위
사용자 = 가위, 컴퓨터 = 보, 사용자가 이겼습니다.
가위 바위 보!>>그만
게임을 종료합니다.
import java.util.Scanner;
class RspPlayer {
public static final String[] arrRSP = { "가위", "바위", "보" };
private String name;
private String rsp;
// 컴퓨터
public RspPlayer(String name) {
this.name = name;
int num = (int) (Math.random() * 3);
rsp = arrRSP[num];
}
// 사용자
public RspPlayer(String name, String rsp) {
this.name = name;
this.rsp = rsp;
}
public void getResult(RspPlayer you) {
System.out.println(this.name + ":" + this.rsp + " " + you.name + ":" + you.rsp);
if (this.rsp.equals(you.rsp)) {
System.out.println("비겼습니다.");
return;
}
if (this.rsp.equals("가위")) {
if (you.rsp.equals("보")) {
System.out.println(this.name + "이겼습니다.");
} else if (you.rsp.equals("바위")) {
System.out.println(this.name + " 졌습니다.");
}
} else if (this.rsp.equals("바위")) {
switch (you.rsp) {
case "보":
System.out.println(this.name + "졌습니다.");
break;
case "가위":
System.out.println(this.name + "이겼습니다.");
break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다.");
break;
}
} else if (this.rsp.equals("보")) {
if (you.rsp.equals("바위")) {
System.out.println(this.name + "이겼습니다.");
} else if (you.rsp.equals("가위")) {
System.out.println(this.name + " 졌습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다.");
}
}
}
}
public class RSPGameMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("컴퓨터와 가위바위보 게임을 합니다");
while (true) {
RspPlayer computer = new RspPlayer("컴퓨터");
RspPlayer you; // =new RspPlayer("컴퓨터");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("가위바위보!>>");
String rsp = sc.next();
you = new RspPlayer("당신", rsp);
computer.getResult(you);
System.out.print("그만하시겠습니까? 그만 or no");
rsp = sc.next();
if (rsp.equals("그만")) {
break;
}
System.out.println("게임 종료입니다.");
}
}
}