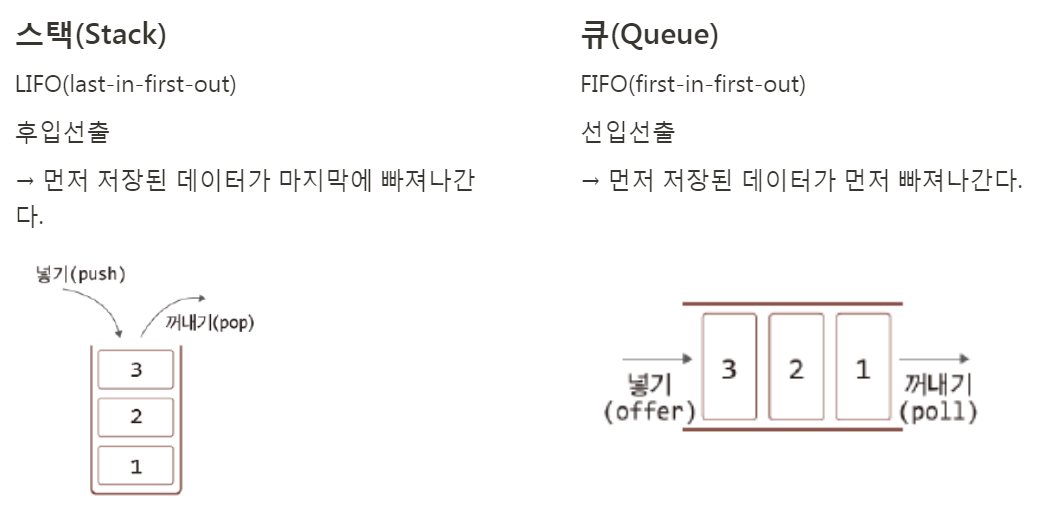
1. 큐와 스택에 대하여 설명하시오.(필수)
2. HashMap, TreeMap 의 차이는?
HashMap<K, V>
HashMap<K, V> 클래스는 Iterable 인터페이스를 구현하지 않아서 for-each ,Iterator로 순차적 접근을 할 수 없습니다.
그래서 Key는 Set으로 관리합니다.
Key값을 기준으로 for-each, Iterator 사용합니다.
public Set ks = map.keySet();
→ set 호출 메소드 / Key만 담고 있는 컬렉션 인스턴스 생성
TreeMap<K, V>
Tree 자료구조 특성상 반복자가 정렬된 순서대로 key들에 접근합니다.
(반복자의 접근 순서는 컬렉션 인스턴스에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다.)
3. 아래의 TreeMap의 Value를 확인 하기 위한 소스를 짜시오.(필수)
TreeMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(45, "Brown");
map.put(37, "James");
map.put(23, "Martin");
package Hw_2024_08_08;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(45, "Brown");
map.put(37, "James");
map.put(23, "Martin");
Set<Integer> ks = map.keySet();
// for-each문에 의한 반복
for (Integer n : ks) {
System.out.println(n.toString() + '\t');
System.out.println();
}
// Iterator 반복자에 의한 반복
for (Iterator<Integer> itr = ks.iterator(); itr.hasNext();)
System.out.print(map.get(itr.next()) + '\t');
System.out.println();
}
}4. Set 호출되는 원리와 순서를 설명하시오.
hash code 호출 (두 개 객체 주소-hash code가 같은지 비교)
hashCode 는 Object에 있습니다. 오버라이드한 함수를 통과해 리턴 되는 값으로 군집(집합, 캐비넷)을 만듭니다. 그리고 그 다음 equals를 호출합니다.
equals 호출 (문자열 비교 걸러냄)
hash code의 호출로 군집히 형성되면 그 군집 내의 요소들을 비교해 나갑니다.
Set 호출에는 2단계를 거쳐 진행됩니다.
1.클래스에 정의된 hashCode 메소드의 반환 값을 통해 분류.
2.선택된 부류 내에서 equals 메소드를 호출하여 비교.
5. hashcode() 를 호출 하여 나오는 값은?
객체 주소가 나옵니다.
6. 아래가 돌아 가도록 하시오.
HashSet hSet = new HashSet();
hSet.add(new Person("LEE", 10));
hSet.add(new Person("LEE", 10));
hSet.add(new Person("PARK", 35));
hSet.add(new Person("PARK", 35));
System.onut.println("저장된 데이터 수: " + hSet.size());
System.out.println(hSet);
저장된 데이터 수: 2
[LEE(10세), PARK(35세)]
package Hw_2024_08_08;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() { // 분류 알고리즘 작용
return age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
int age = ((Person) obj).age; // 상대방
String name = ((Person) obj).name;// 상대방
if (this.age == age && this.name.equals(name))
return true;
else
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name+"("+age+"세)";
}
}
public class HashSetMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Person> hSet = new HashSet<>();
hSet.add(new Person("LEE", 10));
hSet.add(new Person("LEE", 10));
hSet.add(new Person("PARK", 35));
hSet.add(new Person("PARK", 35));
System.out.println("저장된 데이터 수: " + hSet.size());
System.out.println(hSet);
}
}7.아래의 SQL 구문을 정리 하시오.
-- 사원 테이블의 사원들 중에서 커미션(COMM)을 받은 사원의 수를 구하는 쿼리문
select count(comm) from emp;
-- 사원들의 업무수
select count(*) from emp;
-- 소속 부서별 급여의 최대값을 구하는 쿼리문
select deptno, max(sal) from emp group by deptno;
-- 소속 부서별 급여 총액과 평균 급여를 구하는 쿼리문
-- GROUP BY절에 명시하지 않은 컬럼을 SELECT절에 사용하지 못한다.
select deptno,sum(sal)as 총액,avg(sal) as 평균 from emp group by deptno;
-- 소속 부서별 최대 급여와 최소 급여를 구하는 쿼리문
select deptno,max(sal)as 최대급여,min(sal) as 최소급여 from emp group by deptno;
-- 부서별 사원의 수와 커미션을 받는 사원의 수를 계산하는 쿼리문
select deptno, count(*),count(comm)from emp group by deptno;
-- 그룹 지어진 부서별 평균 급여가 2000 이상인 부서의 번호와 부서별 평균 급여를 출력하는 쿼리문
select deptno, avg(sal)from emp group by deptno having avg(sal)>=2000;
-- 부서의 최대값과 최소값을 구하되, 최대 급여가 2900 이상인 부서만 출력하는 쿼리문
select deptno,max(sal)as 최대급여,min(sal) as 최소급여 from emp group by deptno having max(sal)>2900;
9. Map을 활용하여 아래를 프로그래밍 하시오
참고) - containsKey
나라 이름과 인구를 입력하세요.(예: Korea 5000)
나라 이름, 인구 >> Korea 5000
나라 이름, 인구 >> USA 1000000
나라 이름, 인구 >> Swiss 2000
나라 이름, 인구 >> France 3000
나라 이름, 인구 >> 그만
인구 검색 >> France
France의 인구는 3000
인구 검색 >> 스위=
스위스 나라는 없습니다.
인구 검색 >> 그만
package day_2024_08_08;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Country {
private HashMap<String, Integer> map;
public Country() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public void getMap() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int people;
String country;
System.out.println("나라 이름과 인구를 입력하세요.");
while (true) {
System.out.print("나라이름, 인구>>");
try {
String stop=sc.next();
country = sc.next();
people = sc.nextInt();
map.put(country, people);
if (stop.equals("그만")) {
break;
}
} catch (Exception InputMismatchException) {
System.out.println("나라는 없습니다");
}
}
while(true) {
Scanner ac= new Scanner(System.in);
String stop=sc.next();
System.out.print("인구검색>>");
country = sc.next();
if(map.containsKey(country)) {
System.out.println(country+"나라는 없습니다");
}
if (stop.equals("그만")) {
break;
}
}
}
}
public class CountryMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Country country = new Country();
country.getMap();
}
}
