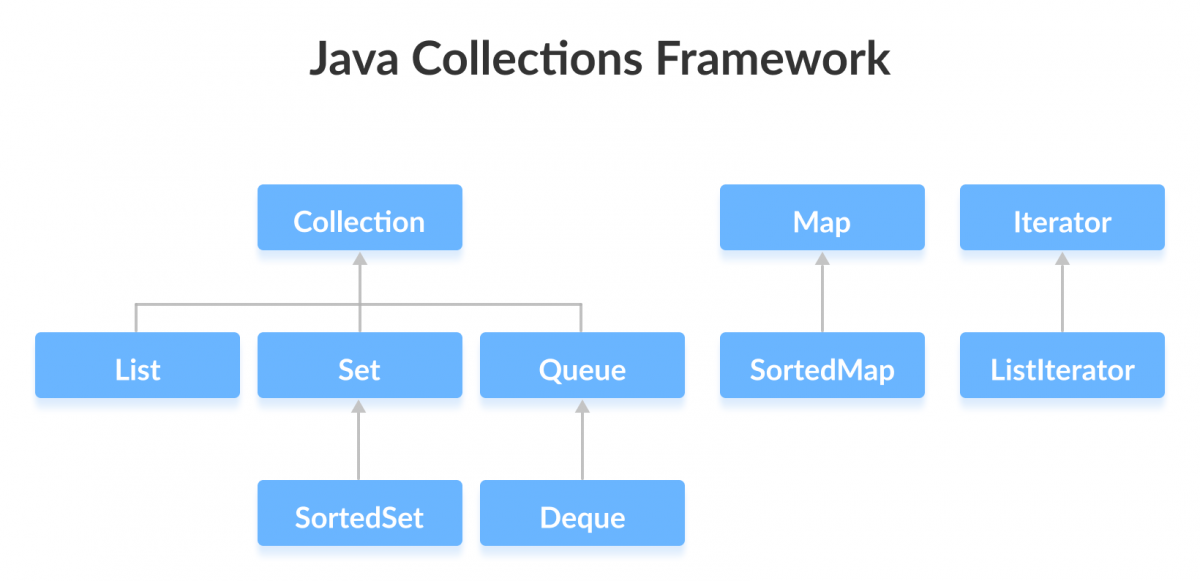
Map<K,V>
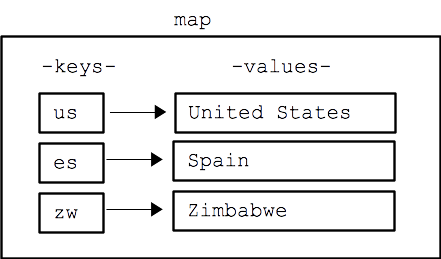
- import java.util.Map;
- Key, Value가 한세트
- key는 중복불가, 덮어쓰기 가능
- 보편적으로 Key에는 String,Integer / Value에는 객체가 사용됨
HashMap
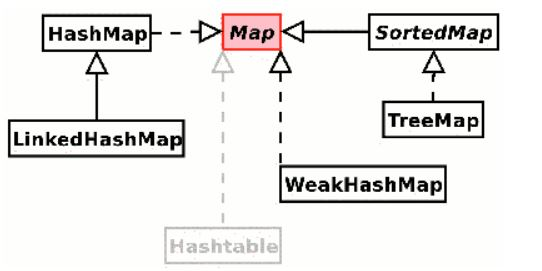
- import java.util.HashMap;
- Map interface를 구현(implements) 한 클래스
주요메서드
static class Product{
private int no;
private String name;
private int price;
public Product(int no, String name, int price) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public int getNo() {return no;}
public void setNo(int no) {this.no = no;}
public String getName() {return name;}
public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}
public int getPrice() {return price;}
public void setPrice(int price) {this.price = price;}
}Map<Integer, Product> abc = new HashMap<>();- 맵이름.put(key, value): key, value값 저장
no name price
abc.put(101, new Product(101, "포카칩", 1500));
abc.put(102, new Product(102, "육개장", 800));
abc.put(103, new Product(103, "삼각김밥", 1200));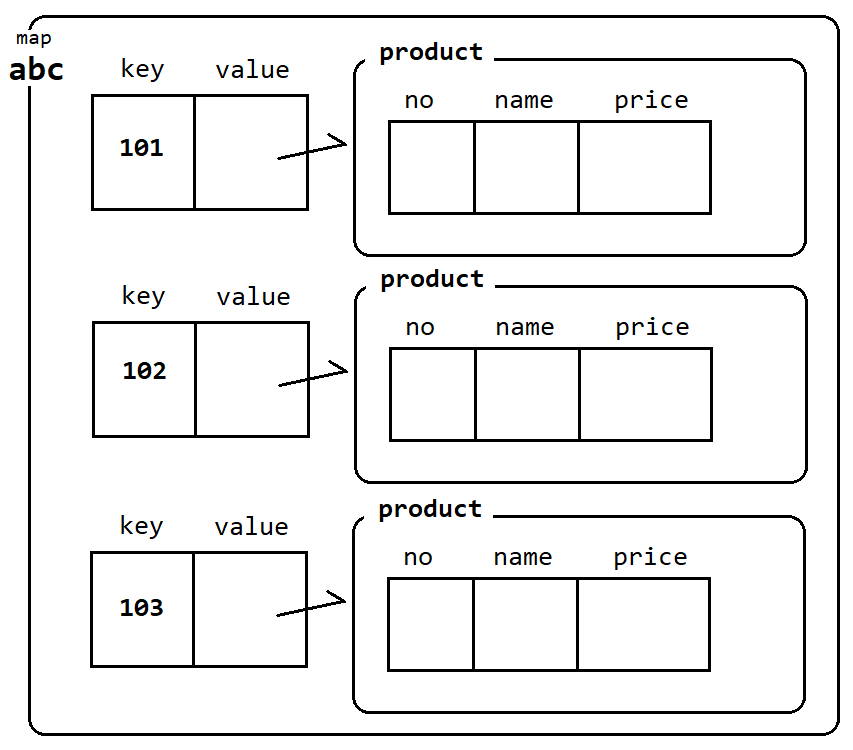
- 맵이름.get(key): key값에 해당하는 value 조회
Product product1 = abc.get(102);
System.out.println(product1.getNo());
System.out.println(product1.getName());
System.out.println(product1.getPrice());
// 출력값
102
육개장
800- 맵이름.size(): key&value 갯수 반환
System.out.println(abc.size());
// 출력값 3- 맵이름.remove(key): key&value쌍 삭제
abc.remove(101);
// key 101과 value new Product(101, "포카칩", 1500))전부 삭제
102 육개장부터 시작됨- 맵이름.isEmpty(): 저장된 데이터가 하나도 없으면 true 반환
- 맵이름.clear(): 저장된 모든 정보 삭제
Map의 활용
- valueObject저장: 식별가능한 고유 값으로 ValueObject를 Map에 저장해서 관리함
- ValueObject대체: 데이터가 가변적인 경우 Map이 훨씬 유용함
- 값 조회 시 key를 틀리게 적어도 오류체크 불가능
- Map에서 값을 꺼낼 때 마다 강제 형변환 필요
- if ~ else if문 대체 가능
- 값을 종류별로 치환하기 용이함
Arrays
- import java.util.Arrays;
- 배열과 관련된 다양한 메서드가 포함되어있음
주요메서드
- Arrays.asList(값1, 값2, 값3): 배열을 List화함
List<String> a = Arrays.asList("a","b","c");
System.out.println(a);
// 출력값 [a, b, c]- Collection.sort(List): List 내 요소를 오름차순으로 정렬
Collection.reverse(List) : List 내 요소를 내림차순으로 정렬
ArrayList<String> a = new ArrayList<>();
a.add("a");
a.add("3");
a.add("A");
a.add("1");
a.add("가");
// a = [a, 3, A, 1, 가]
Collection.sort(a);
// 오름차순(숫자, 대문자, 소문자, 한글순)으로 정렬됨
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
System.out.print(a.get(i));
}
// 출력값 1, 3, A, a, 가
Collection.reverse(a);
// 내림차순(한글, 소문자, 대문자, 숫자 순)으로 정렬됨
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
System.out.print(a.get(i));
}
// 출력값 가, a, A, 3, 1Comparable과 Comaparator
- 객체의 값을 비교할 수 있게 해주는 인터페이스
Comparable
클래스명 implements Comaparable<T>
- 기본정렬기준(오름차순)을 구현하는데 사용하는 인터페이스
public interface Comparable{
int compareTo(Object o);
}- Comparable 사용 시, compareTo 메서드를 Override해주어야 함
- 자기 자신과 compareTo의 매개변수 객체 비교
★구현클래스에서 implements Comparable`<T>`선언 후, 기준 지정★
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
String name;
int age;
Student(int age, String name){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
// 1. 나이순으로 비교
public int compareTo(Class c){
return this.age - c.age;
}
// 2. 이름순으로 비교
// public int compareTo(Class c){
// return this.name.compareTo(c.name);
// }
/*
* 이 객체와 다른 객체를 비교했을 때
* 양수 이 객체가 큼
* 음수 이 객체가 작음
* 0 같음
*/
}★실행 클래스에서 Collection.sort(배열명)을 실행하여 구현클래스에서 지정한 기준대로 정렬★
public class StudentApp{
public static void main(String[]args){
List<Student> list = Arrays.asList(new Student("홍길동", 20),
new Student("김유신", 24),
new Student("을지문덕", 21));
Collection.sort(list);
for(Student arr: list){
System.out.println(arr.getName()+": "+arr.getAge()+"세");
// 나이순으로 정렬되어 출력됨
}
}
}Comparator
클래스명 implements Comparator
- import java.util.Comparator;
- 두 객체의 Compare매개변수를 비교
public interface Comparator{
int compare(Object o1, Object o2);
boolean equals(Object obj);
}- Comparator 사용 시, compare 메서드를 Override해주어야 함
★구현 클래스
class Student{
String name;
int age;
Student(int age, String name){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
}★실행클래스에서 implements Comparator<T>선언★
☆ Comparable은 구현클래스에서 implements Comparable<T>
☆
public class StudentApp implements Comparable<Student>{
public static void main(String[]args){
List<Student> list = Arrays.asList(new Student("홍길동", 20),
new Student("김유신", 24),
new Student("을지문덕", 21));
/*
* 두 객체의 값을 비교했을 때
* 양수 이 객체가 큼
* 음수 이 객체가 작음
* 0 같음
*/
// 이름으로 오름차순 정렬
Comparator<Student> nameComparator = new Comparator<>() {
public int compare(Student name1, Student name2) {
return name1.getName().compareTo(name2.getName());
}
};
Collections.sort(list, nameComparator);
for(Student arr : list) {
System.out.println(arr.getName()+": "+arr.getAge()+"세");
}
// 나이로 오름차순 정렬
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Student>(){
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
});
for(Student arr : list) {
System.out.println(arr.getName()+": "+arr.getAge()+"세");
}
}
}