Database week 2
RAID 이란? (Redundant Array of Independent Disk)
2개 이상의 디스크를 병렬로 처리하여 성능 및 안전성을 향상시키는 방식
데이터 손실 방지를 위한 대비책
레이드 종류
레이드 0 레이드 1 레이드 2 레이드 3
parity bits x x error corr. dedicateddisk
mirroring x 0
striping block level x bit byte
레이드 0 데이터 분산 처리
레이드 1 데이터 복제
레이드 2 에러 체크와 수정을 할 수 있도록 해밍 코드 사용
페리티 정보 디스크 별도 저장 레이드 3 바이트 단위 데이터 저장
레이드 4 블록 단위 데이터 저장
Select Execution
Q1. How does the DBMS find the pieces of Data on Disk?
Logical Physical Schema Database
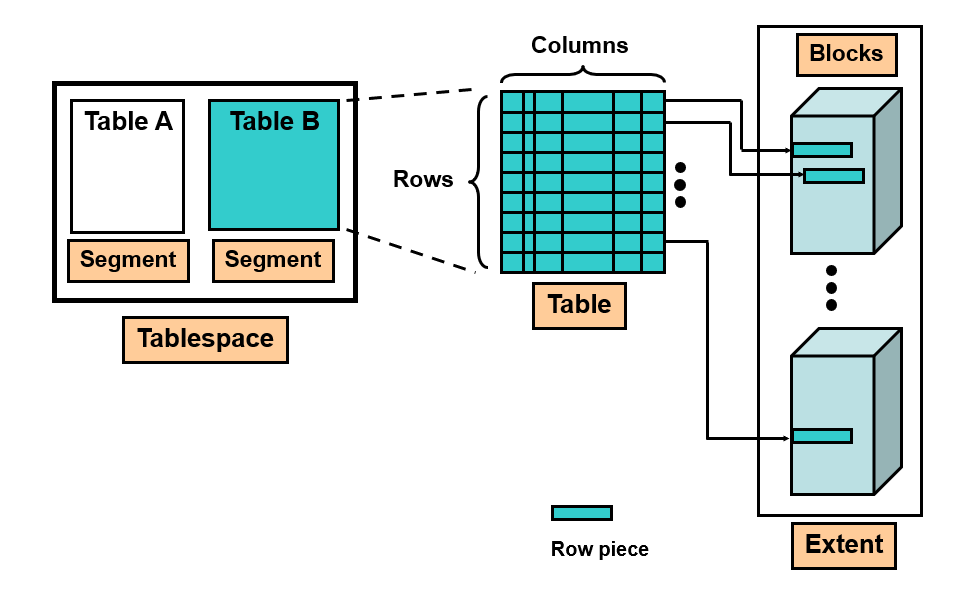
Tablespace DataFile
Segment
Extent
Oracle data block OS block
Fixed length records formats vs Variable length record fomats
Fixed-length records fomats: fileds stored consecutively
Varialbe-length record formats: array of offsets, null values when start offset = end offset
File Structure
Data Items -> Records -> Blocks -> Files -> Memory
Records: Collection of related data items (fields)
Records into blocks
<4 options>
-
Separating records
fixed size recs are not need to separate
special marker
give record lengths ( or offsets / within each record, in block header -
Spanned vs Unspanned
Spanned need indication of partial record/continuation
if record size > block sizeUnspanned records within one block
-
Sequencing
ordering records in file ( and block ) by some key value
read records efficiently<3 options>
#1 next record physically contiguous
#2 linked
#3 overflow area -
Indirection
완전 물리적(fully physical):
physical<->indirect
물리적 파일 구조는 데이터를 직접적으로 가리킴
파일을 구성하는 데이터 블록들이 물리적 주소나 위치에 바로 매핑
완전 간접(fully indirect):
모든 데이터가 간접적으로 참조
하나의 인덱스 블록이 다른 인덱스 블록을 가리키고, 그 인덱스 블록이 실제 데이터를 가리키는 방식
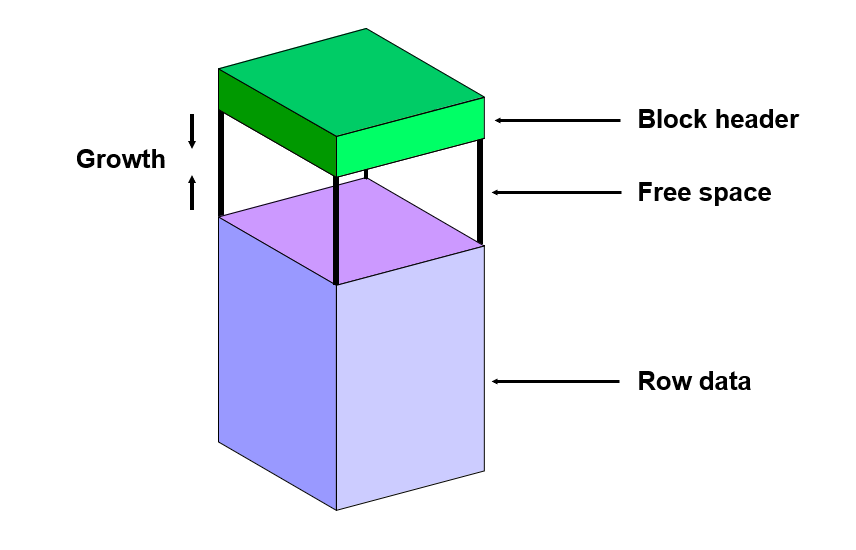
매우 큰 파일을 처리할 때 사용되며, 계층적인 구조를 통해 데이터를 관리Block header - data at beginning that describes block
Advantages of Column Storemore compact storage
efficient reads on data mining operations
Advantages of Row Storewrites (multiple fields of one record) more efficient
efficient reads for record access (OLTP)
