Natural Language Processing with Probabilistic Models - Week 2
Hidden Markov Models

- ; N = number of hidden states
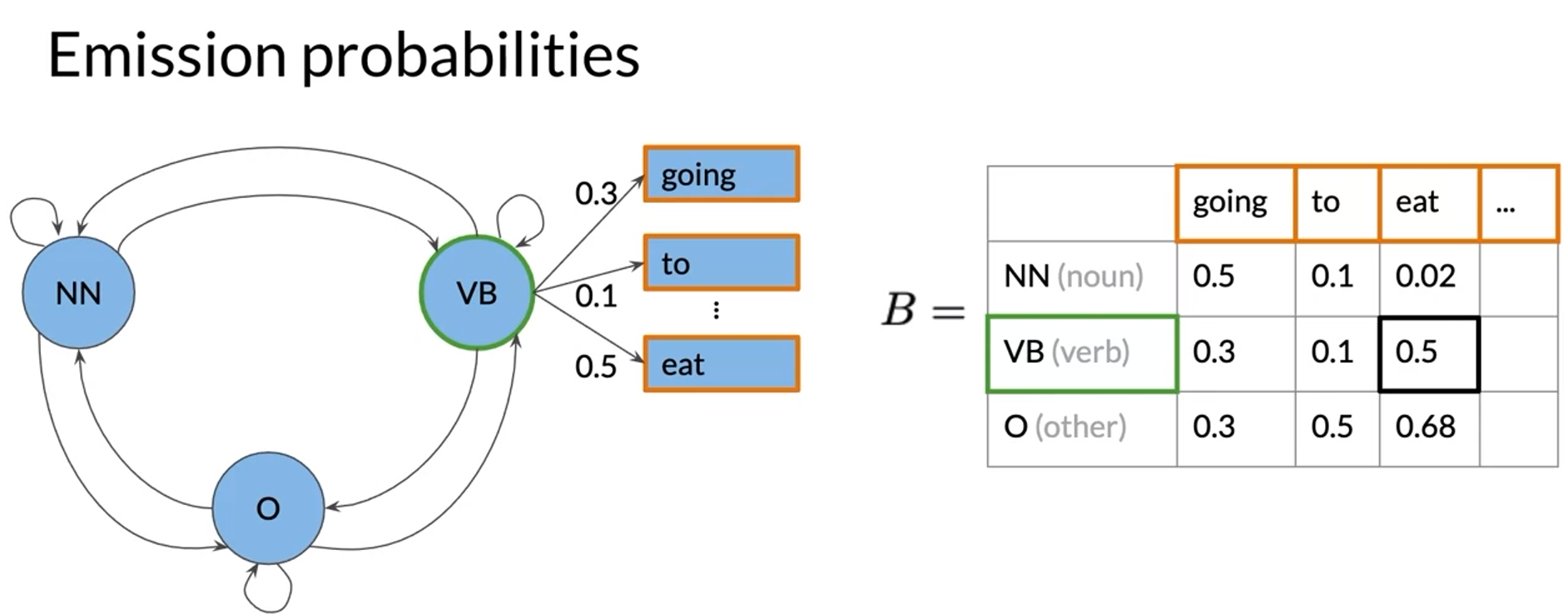
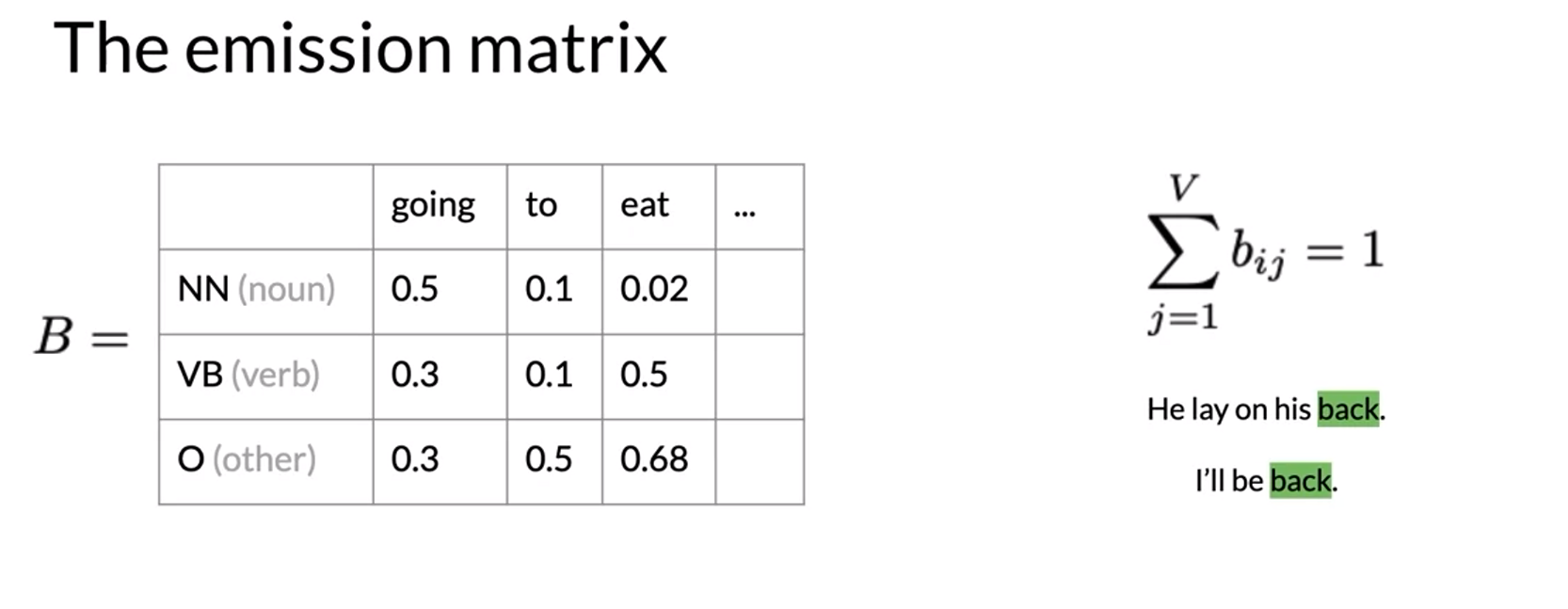
- context에 따라서 tag가 달라질 수 있어서 확률이 0이 아니다.
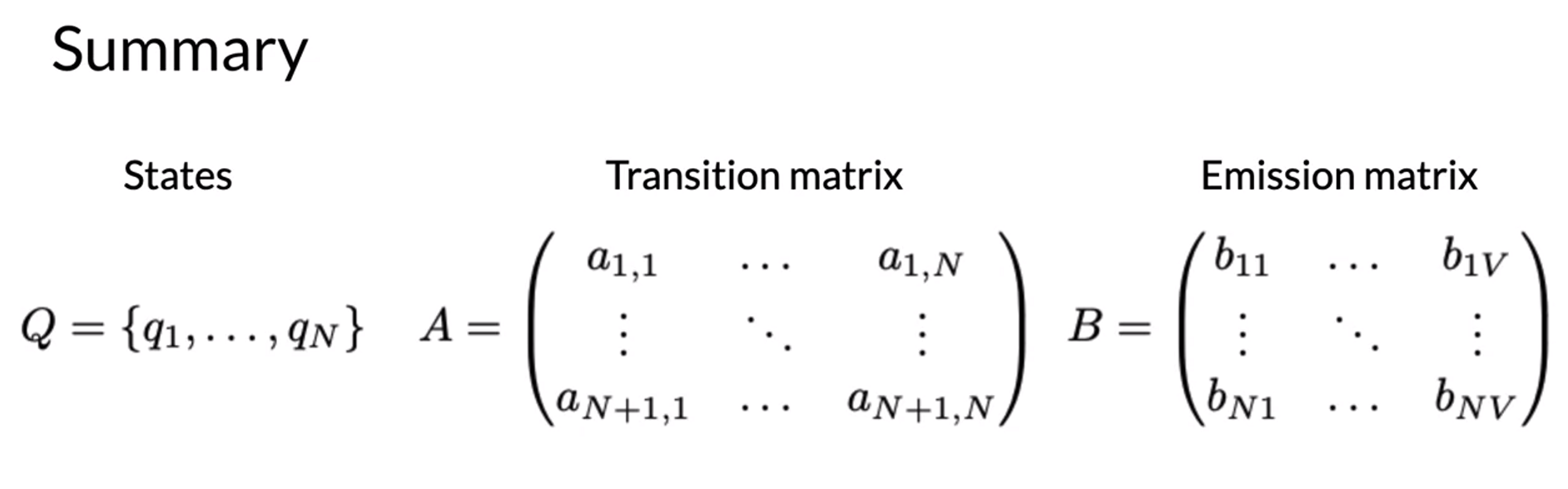
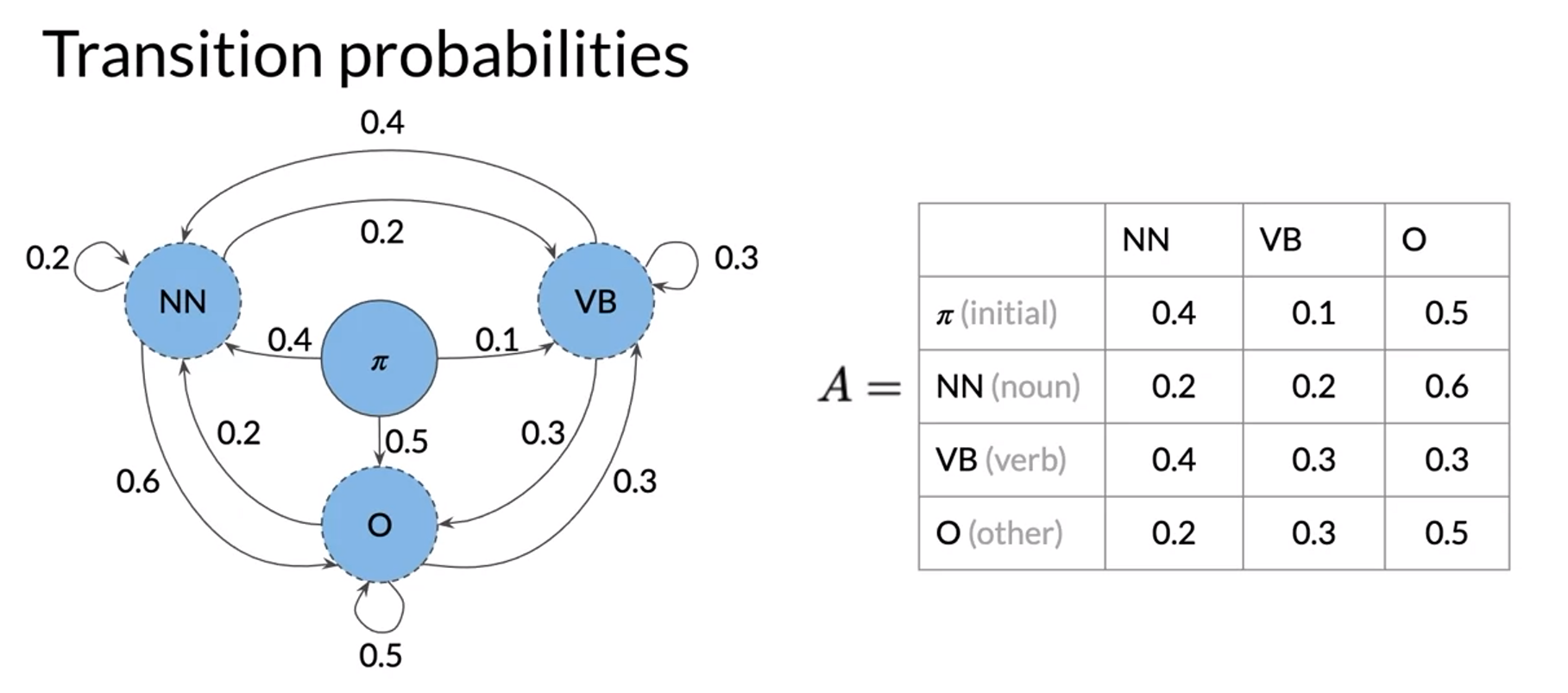
Calculating Probabilities
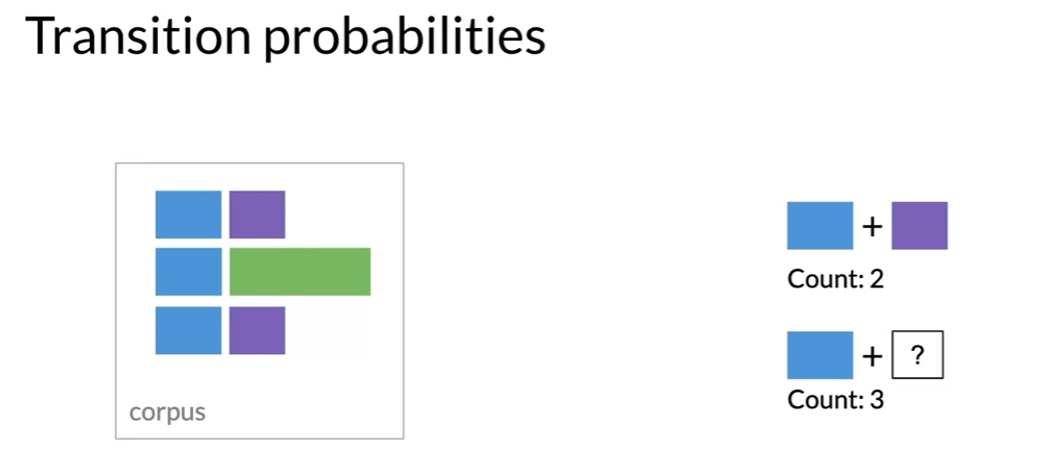

- Markov model, If you want to know transition probabilities you have to know all occurrences of tag pairs in training corpus
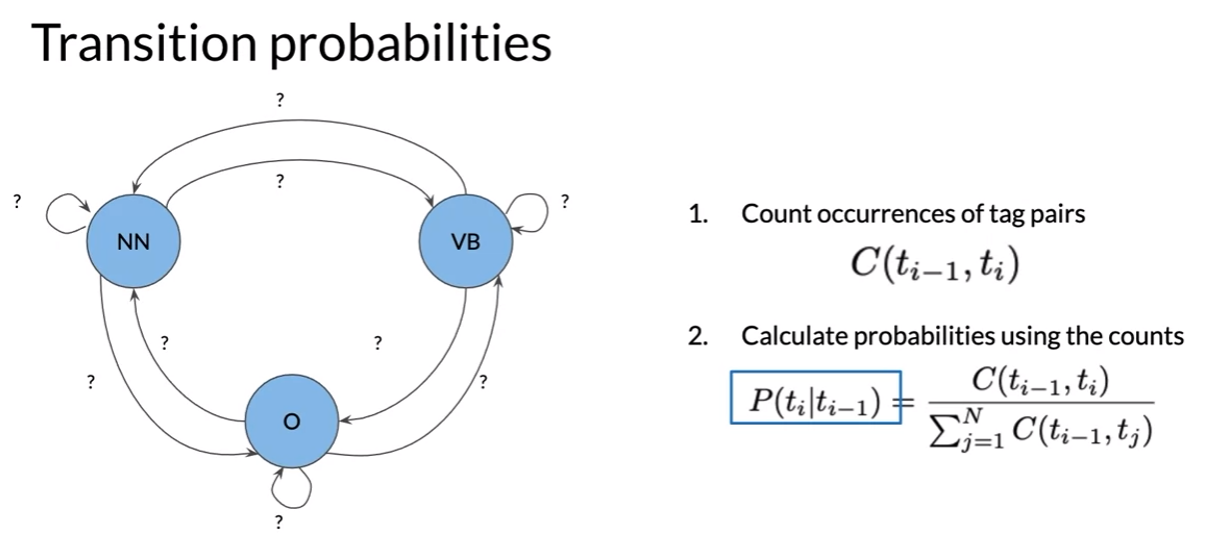


- start token

- transform all words to lowercase
Populating the Transition Matrix
고장남 수정 필요
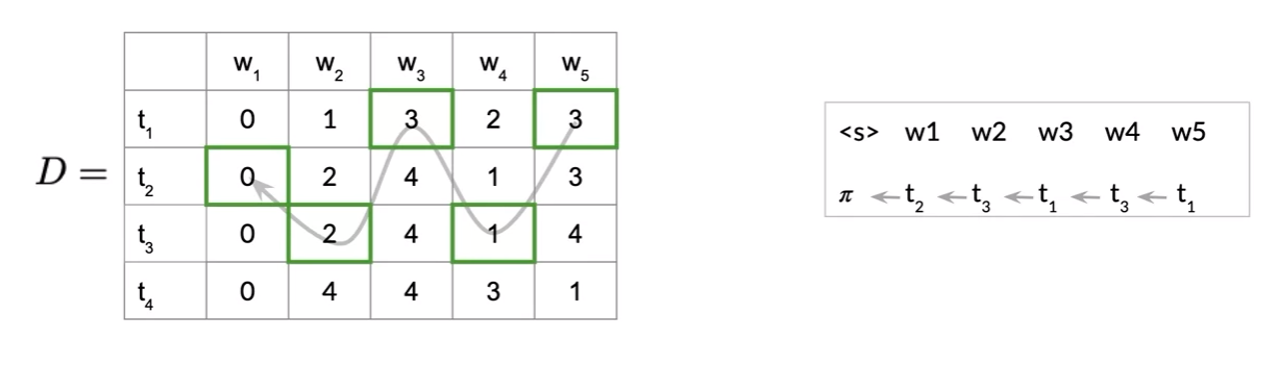
The Viterbi Algorithm
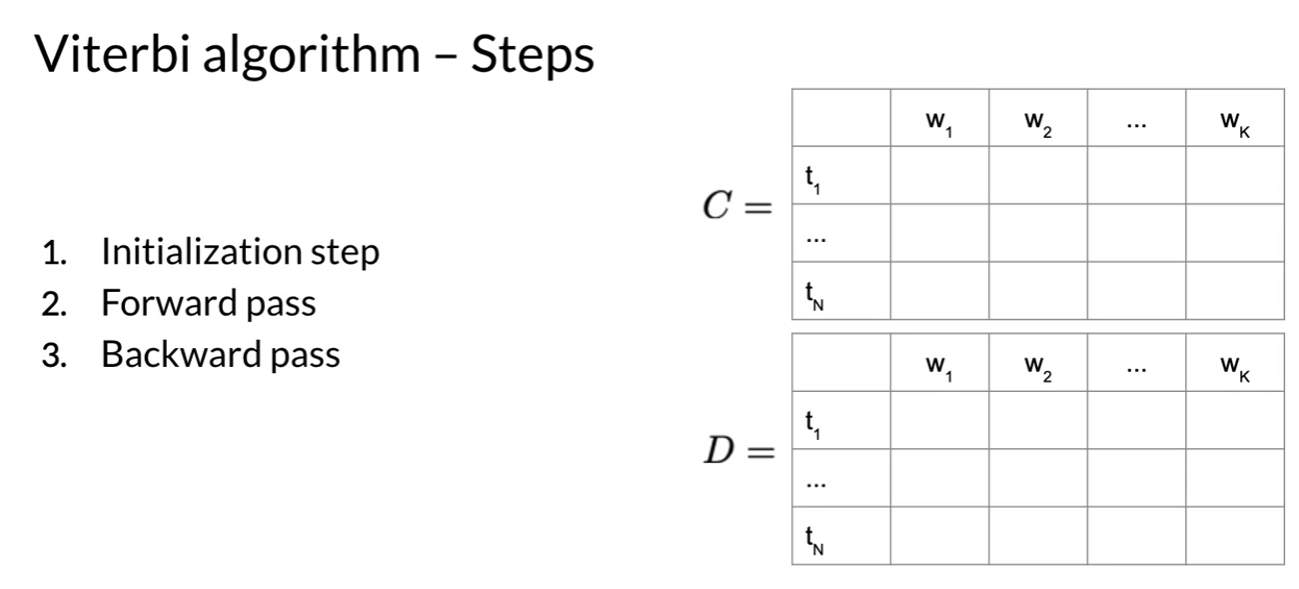
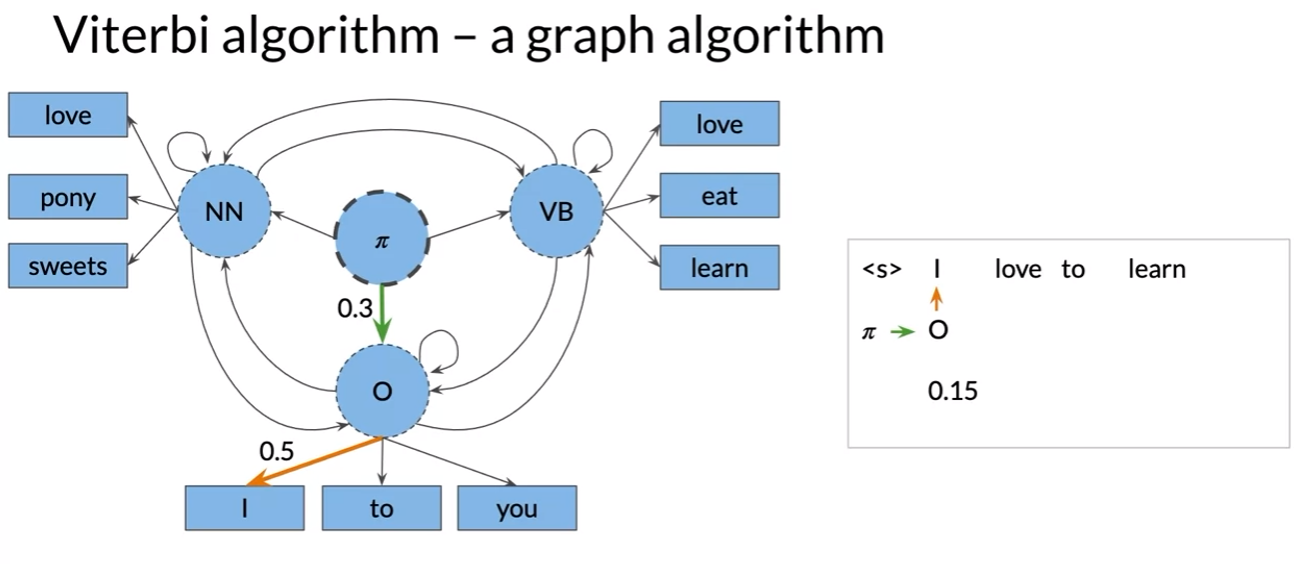
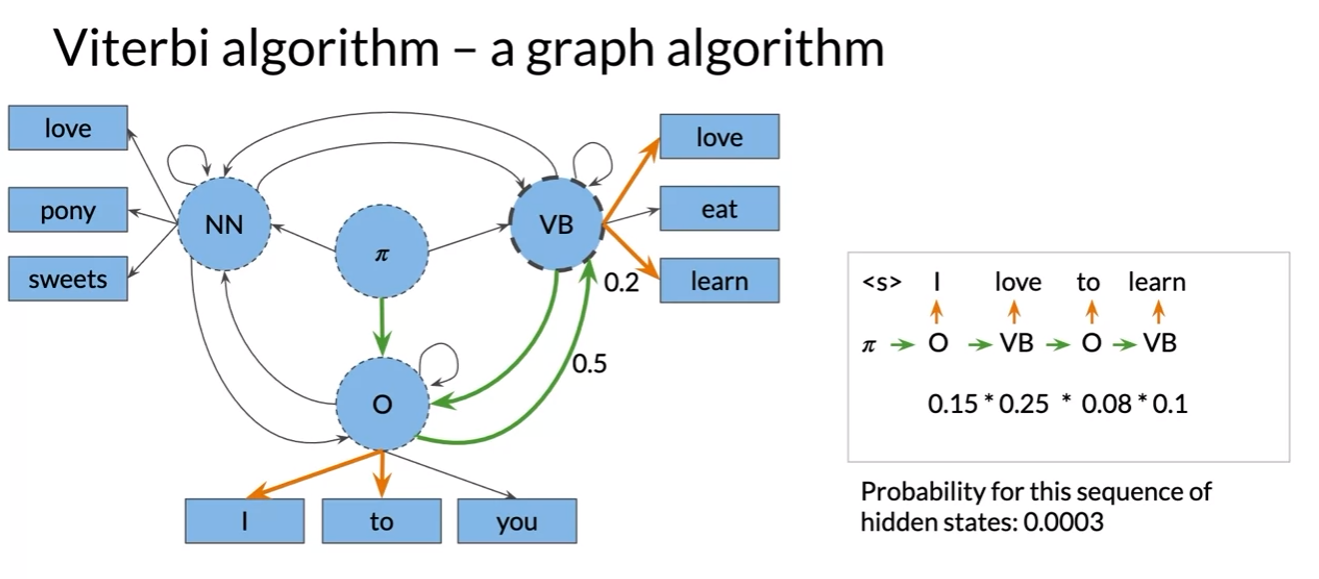
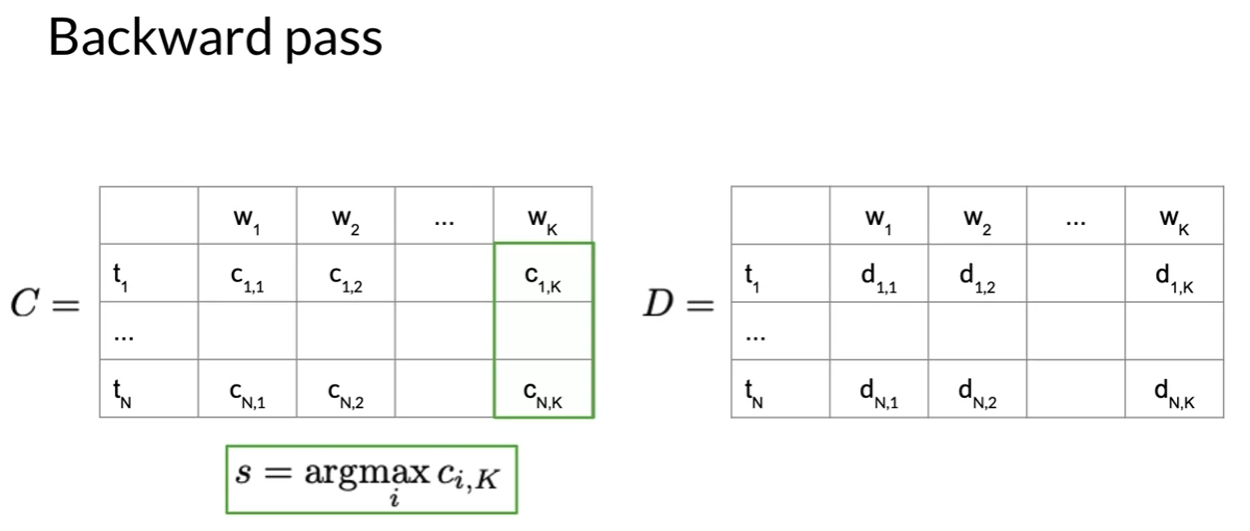
- auxiliary matrix C, D
- n rows; number of parts of speech tags or hidden states in model
- k columns; number of words in the given sequence
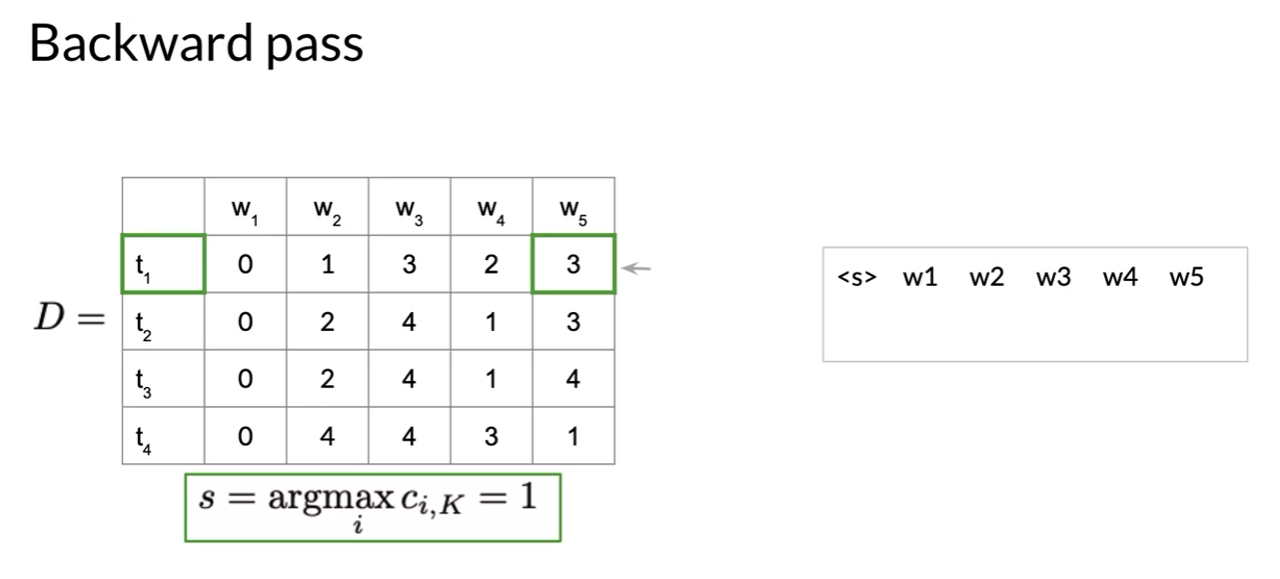
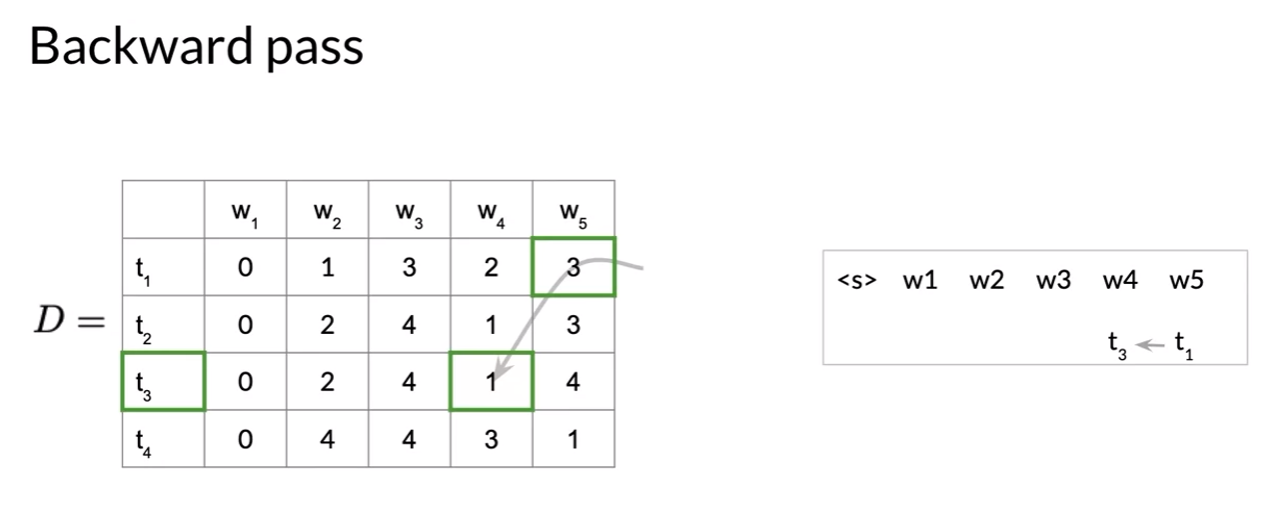
- Viterbi path비터비 경로
Viterbi: Initialization
- from initialization the first column of C and D matrix is populated
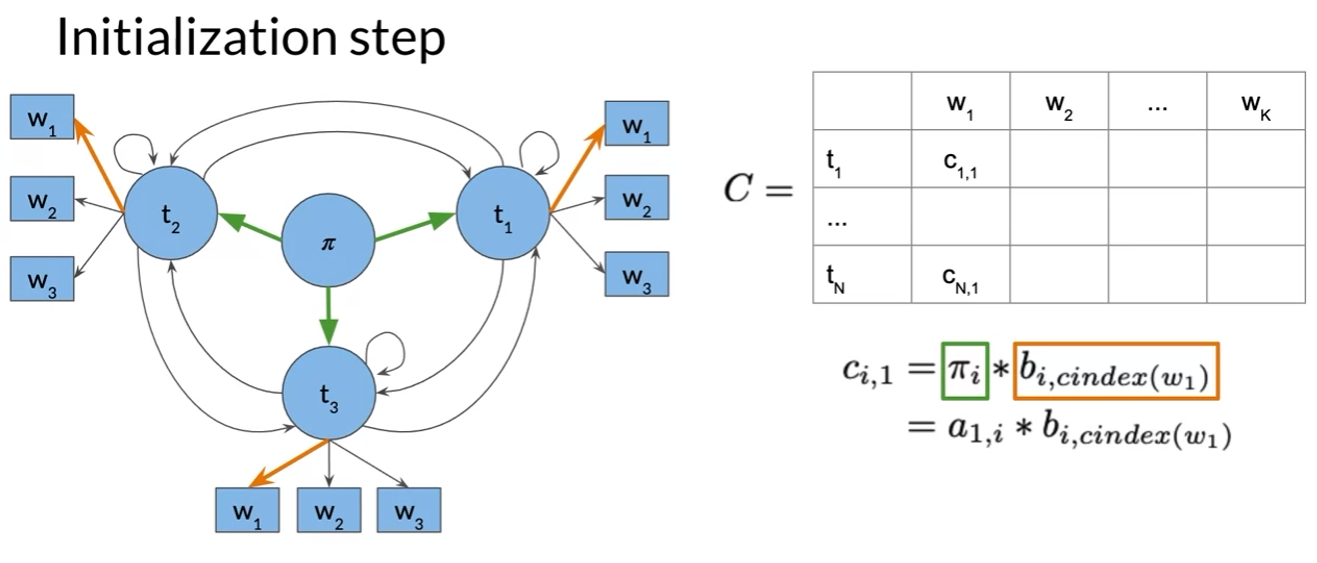
- first column entries, products of the transition probabilities of the initial states and their respective emission probabilities
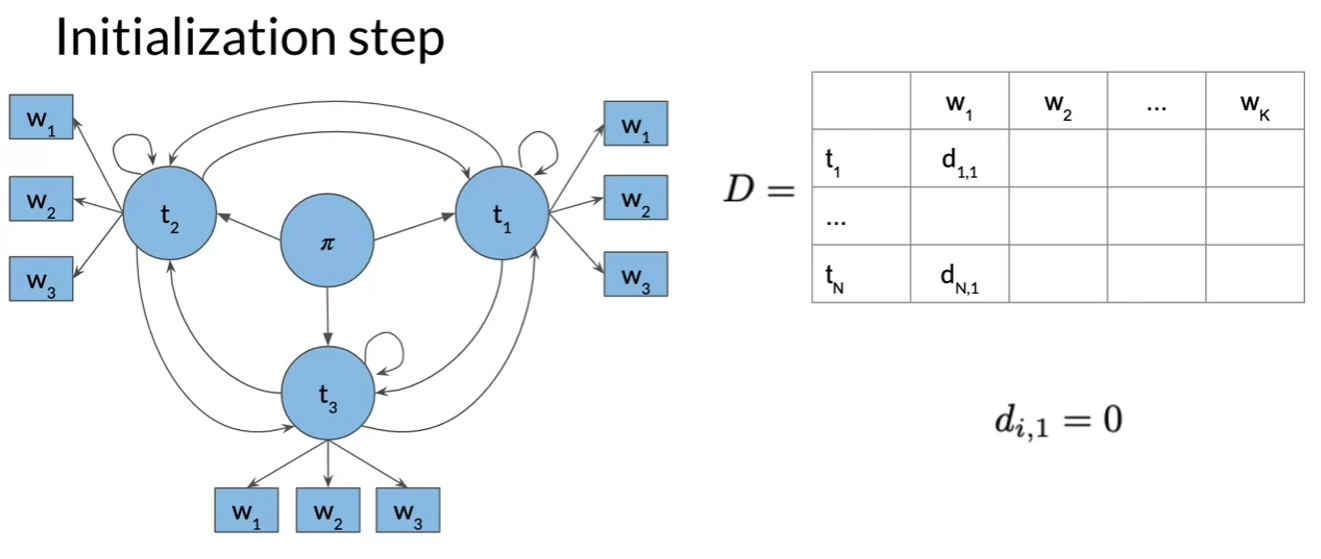
- set first column to 0, no preceding POS tag
Viterbi: Forward Pass
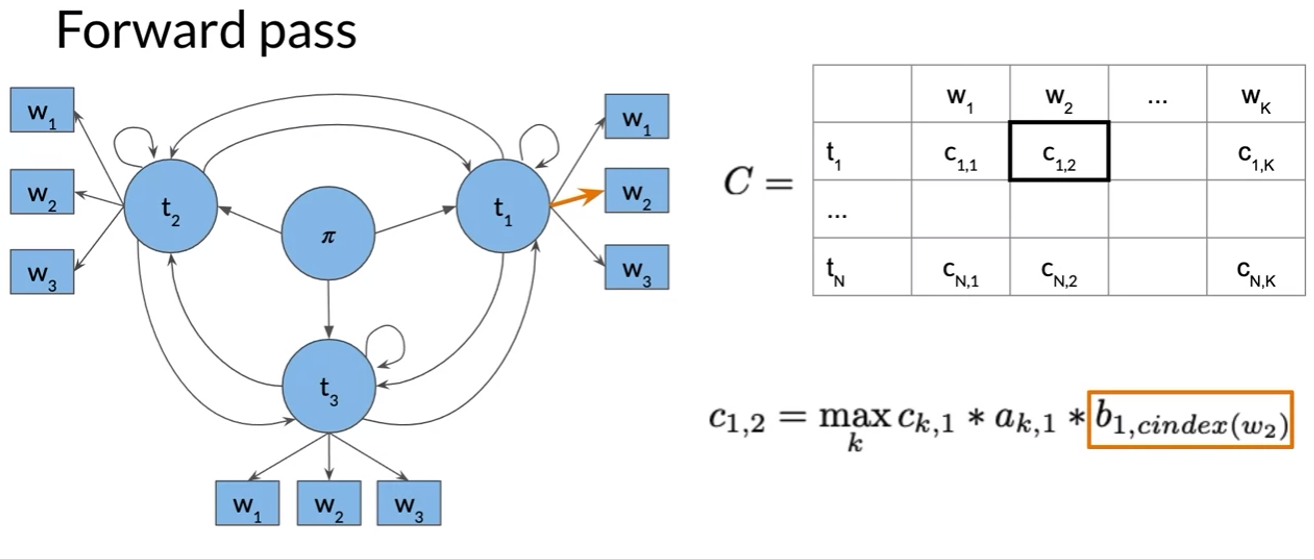
- calculate
: emission probability from tag t1 towards w2
: transition probability from the POS tag to the current tag and
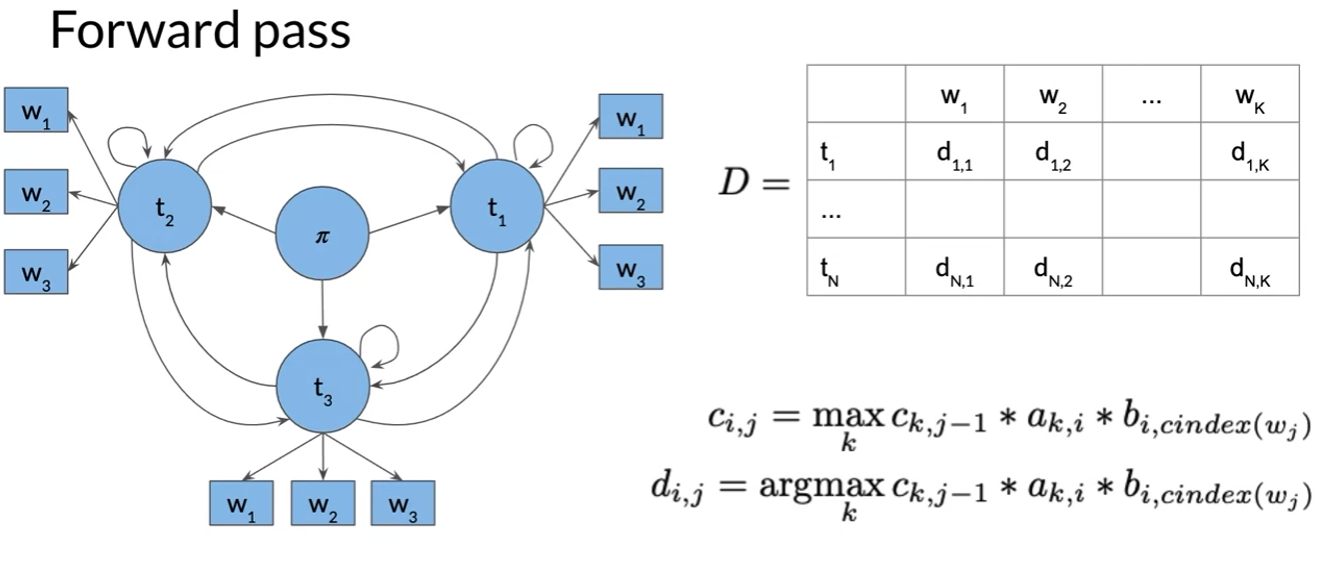
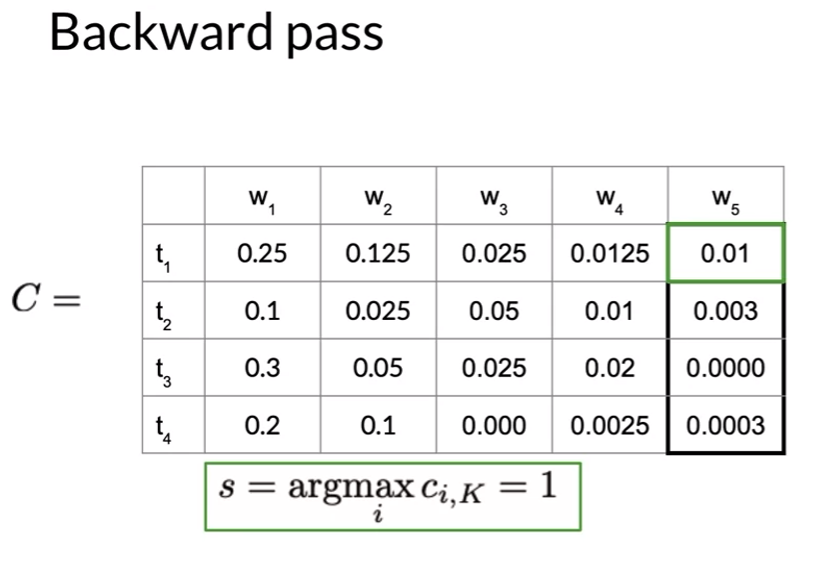
Viterbi: Backward Pass