관련 URL
What is Redux?
- Pattern and library for managing and updating application state
- Using events called
Action
- Centralized store for state that needs to be used across entire application
- With
rules ensuring that the state can only be updated in a predictable fashion
Why Should I Use Redux?
- Manage
global state (state that is needed across many parts of your application)
- Patterns and tools provided by Redux make it easier to understand
- When, where, why, and how the
state in your application is being updated
- How your application logic will behave when those changes occur
- Writing code that is predictable and testable
When Should I Use Redux
- Shared state management
- Large amounts of application state that are needed in many places in the app
- App state is updated frequently over time
- Logic to update that state may be complex
- App has a medium or large-sized codebase, and might be worked on by many people
Redux Terms and Concepts
State Management
function Counter() {
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0)
const increment = () => {
setCounter(prevCounter => prevCOunter)
}
return (
<div>
Value: {counter} <button onClick={increment}>Increment</button>
</div>
)
}
- State : Source of truth that drives our app
- View : Declarative description of the UI based on the current state
- Actions : The events that occur in the app based on user input, and trigger updates in the state
One-way Data Flow
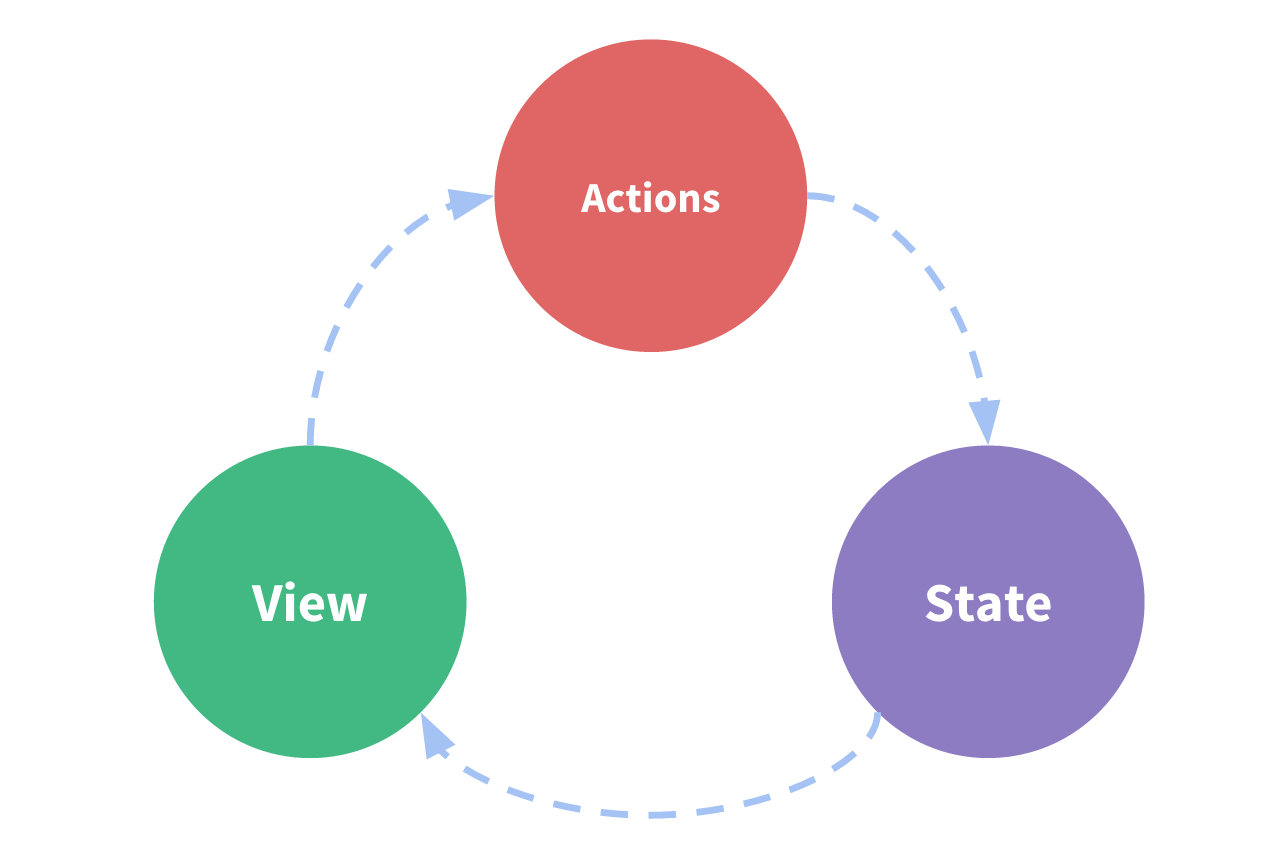
- State
describes the condition of the app at a specific point in time
- UI is rendered based on that
state
- When something happens (ex. User clicking a button), the state is
updated based on what occured
- UI re-renders based on the
new state
Problem
- Simplicity can break down when we have multiple components that need to share and use the same state
Solution
- To extract the
shared state from the components, and put it into a centralized location outside the component tree
- Our component tree becomes big view
- Any component can access the state or trigger actions, no matter where they are in the tree
Basic Idea Behind Redux
- A single centralized place to contain the global state in your application, and specific patterns to follow when updating that state to make the code predictable
Immutability
- JavaScript objects and arrays are all mutable by default
- If I create an object/array, I can change the contents of its field
Mutating the Object or Array
- Same object or array reference in memory, but the contents inside the object have changed
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2 }
obj.b = 3
const arr = ['a', 'b']
arr.push('c')
arr[1] = 'd'
- In order to update values immutably, your code must make
copies of existing objects/arrays, and then modify the copies.
const obj = {
a: {
c: 3
},
b: 2
}
const obj2 = {
...obj,
a: {
...obj.a,
c: 42
}
}
const arr = ['a', 'b']
const arr2 = arr.concat('c')
const arr3 = arr.slice()
arr3.push('c')
- Redux expects that all state updates are done immutably.
Terminology
Actions
- Plain JavaScript object that has a
type field
- An event that describes something that happened in the application
- Type field should be a string that gives this action a descriptive name (ex.
todos/todoAdded, domain/eventName)
domain : Feature or category that this action belongs toeventName : Specific thing that happened
const addTodoAction = {
type: 'todos/todoAdded',
payload: 'Buy milk'
}
Action Creators
- A function that creates and returns an action object
- Use these so we don't have to write the action object by hand every time
const addTodo = text => {
return {
type: 'todos/todoAdded',
payload: text
}
}
Reducers
- A function that receives current
state and an action object
- Decides how to update the state if necessary
- Returns the new state:
(state, action) => newState
- An event listener which handles events based on the received action (event) type
- Specific Rules of Reducers
- They should only calculate the new state value based on the state and action arguments
- They are not allowed to modify the existing state. Instead, they must make immutable updates, by copying the existing state and making changes to the copied value
- They must not do any asynchronous logic, calculate random values, or cause othe "side effects"
const initialState = { value: 0 }
function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) {
if (action.type === 'counter/increment') {
return {
...state,
value: state.value + 1
}
}
return state
}
Store
- Current Redux application state lives in an object
- Redux 애플리케이션의 상태는 store 라는 객체에 있다
- Created by passing in a reducer
- Method called
getState that returns the current state value
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const store = configureStore({ reducer: counterReducer })
console.log(store.getState())
Dispatch
- Redux store has a method called
Dispatch
store.dispatch() : Update the state
store.dispatch({ type: 'counter/increment' })
console.log(store.getState())
const increment = () => {
return {
type: 'counter/increment'
}
}
store.dispatch(increment())
console.log(store.getState())
Selectors
- Functions that know how to extract specific pieces of information from a store state value
- Avoid repeating logic as different parts of the app
const selectCounter = state => state.value
const currentValue = selectCounterValue(store.getState())
console.log(currentValue)
