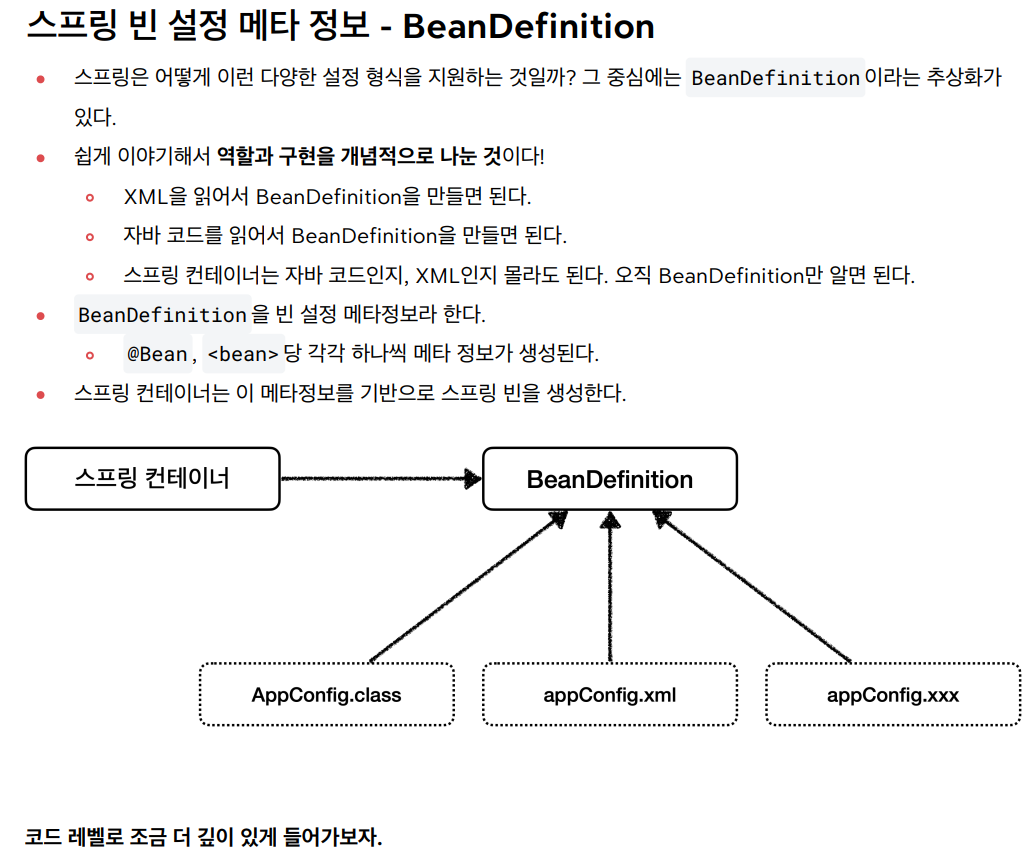
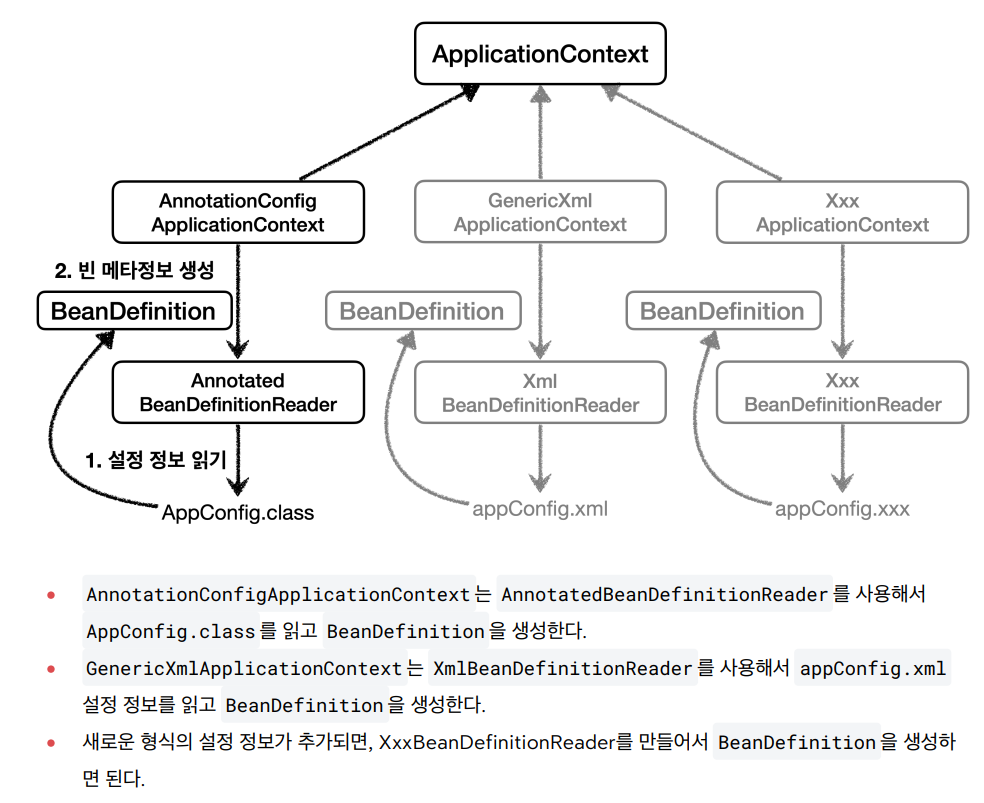
출처 : 인프런 > 스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편 강의를 듣고 작성한 글입니다.
강의 링크 : 스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편
섹션 4. 스프링 컨테이너와 스프링 빈
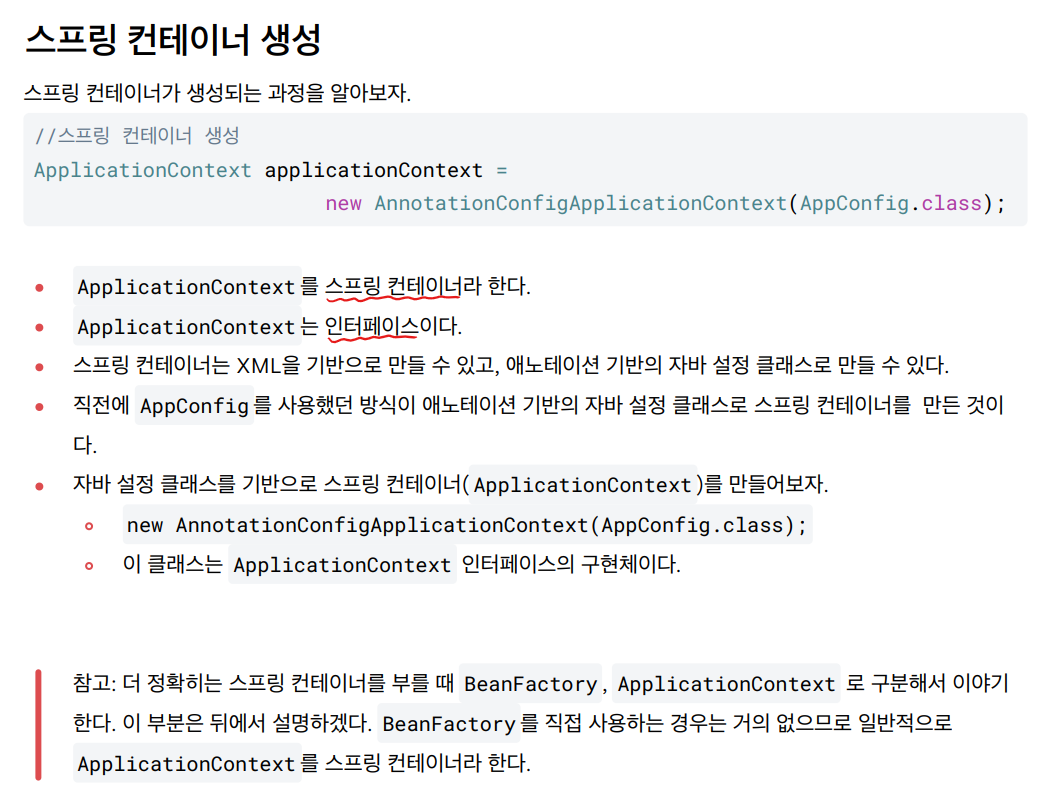
📘 스프링 컨테이너 생성
전 강의에서는 ApplicationContext가 스프링 컨테이너라 불리는 것을 알았고 이번 강의에서는 스프링 컨테이너가 생성되는 과정을 알아볼 것이다.
📖 스프링 컨테이너의 생성 과정
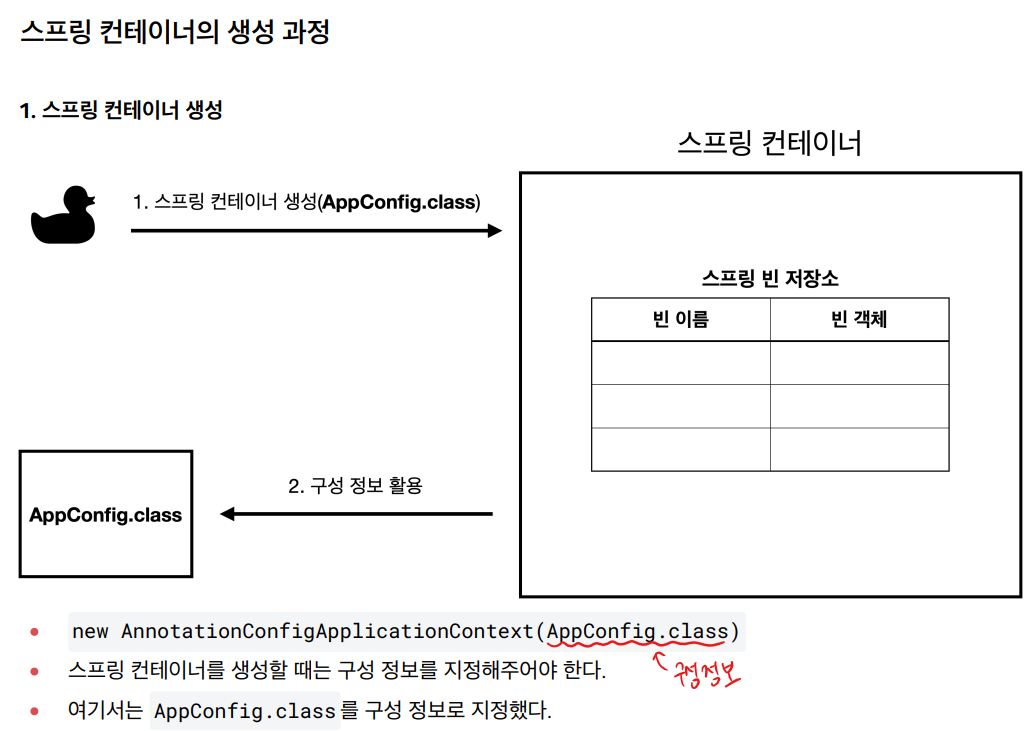
1번 과정: 스프링 컨테이너 안에 AppConfig의 정보를 넣는 순간 컨테이너가 생성이 된다. 컨테이너는 구성 정보를 AppConfig로 부터 받는다.
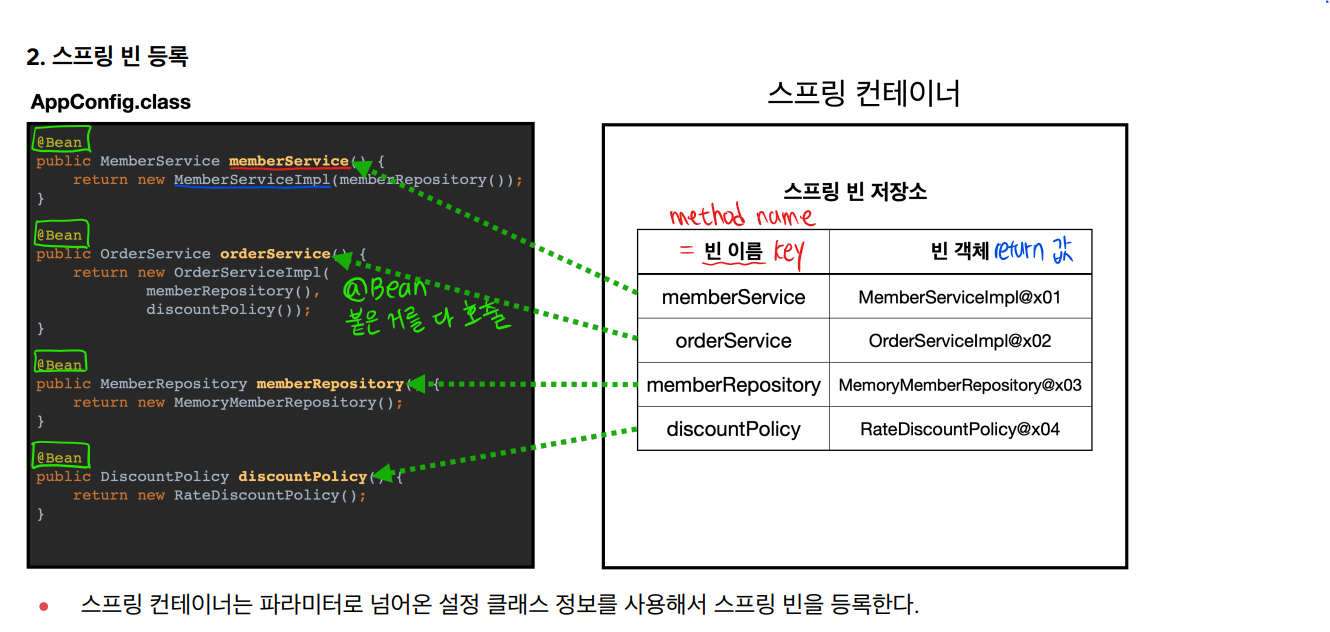
2번 과정: AppConfig.class안에 있는 정보를 통해서 @Bean이 적힌 클래스 정보가 스프링 빈 저장소에 등록된다. key인 빈 이름은 method name, 빈 객체는 return 하는 값이 저장된다.

📢 주의: 빈 이름은 항상 다른 이름을 부여해야 한다. 같은 이름을 부여하면, 다른 빈이 무시되거나, 기존 빈을 덮어버리거나 설정에 따라 오류가 발생한다.

3번 과정: 의존관계 주입(Dependency Injection)을 하기 전 준비상태
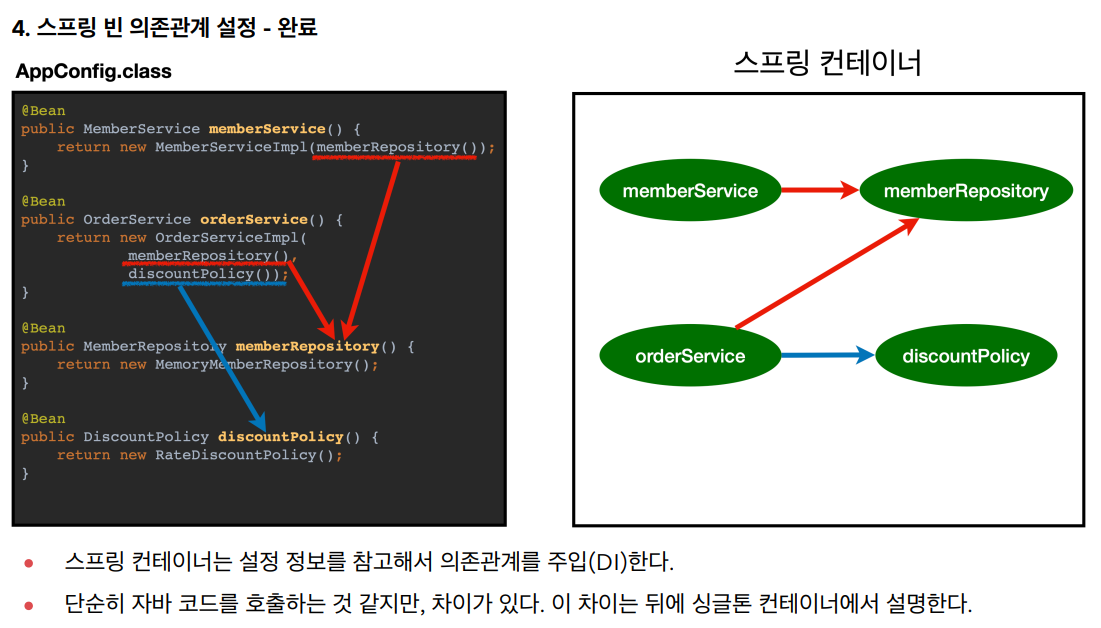
4번 과정: 스프링 컨테이너안에 있는 객체들은 서로의 클래스에 의존하는 관계를 유지하고 있고 컨테이너는 이러한 의존관계를 주입 시켜준다. 즉, 동적인 객체 인스턴스 의존관계를 스프링이 연결해준다.

📘 컨테이너에 등록된 모든 빈 조회
스프링 컨테이너에 실제 스프링 빈들이 잘 등록 되었는지 확인해보자.
테스트를 위한 beanfind 패키지를 만들고 그 안에 ApplicationContextInfoTest 클래스를 만들었다.
src\test\java\hello\core\beanfind\ApplicationContextInfoTest.java
package hello.core.beanfind;
import hello.core.AppConfig;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class ApplicationContextInfoTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
@Test
@DisplayName("모든 빈 출력하기")
void findAllBean(){
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
Object bean = ac.getBean(beanDefinitionName); // type을 지정 안했기 때문에 Object
System.out.println("name = " + beanDefinitionName + " object = " + bean);
}
}
@Test
@DisplayName("애플리케이션 빈 출력하기")
void findApplicationBean(){
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = ac.getBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionName);
//Role ROLE_APPLICATION: 직접 등록한 애플리케이션 빈
//Role ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE: 스프링이 내부에서 사용하는 빈
if (beanDefinition.getRole() == BeanDefinition.ROLE_APPLICATION) {
Object bean = ac.getBean(beanDefinitionName);
System.out.println("name = " + beanDefinitionName + " object = " + bean);
}
}
}
}
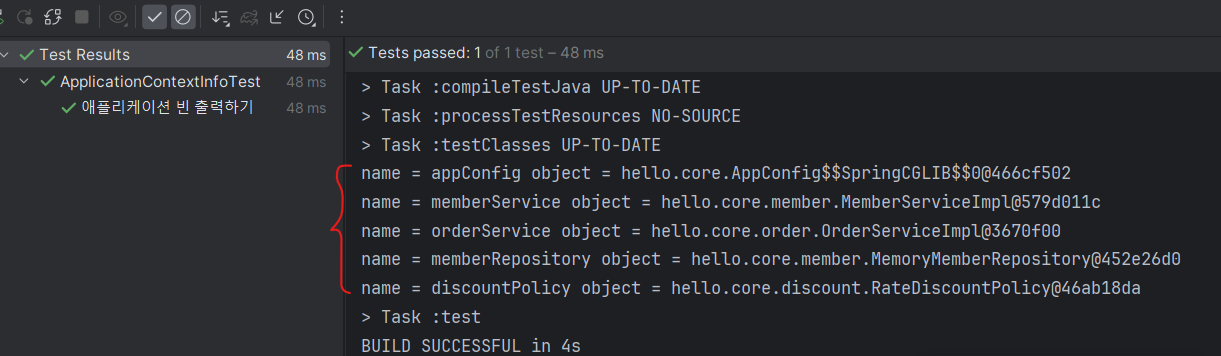
위와 같이 직접 등록한 애플리케이션 빈이 잘 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
📘 스프링 빈 조회 - 기본

src\test\java\hello\core\beanfind\ApplicationContextBasicFindTest.java
package hello.core.beanfind;
import hello.core.AppConfig;
import hello.core.member.MemberService;
import hello.core.member.MemberServiceImpl;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class ApplicationContextBasicFindTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
@Test
@DisplayName("빈 이름으로 조회")
void findBeanByName(){
MemberService memberService = ac.getBean("memberService", MemberService.class);
assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("이름 없이 타입으로만 조회")
void findBeanByType(){
MemberService memberService = ac.getBean(MemberService.class);
assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("구체 타입으로 조회") // 역할과 구현을 구분해야 한다. but 이 class는 구현에 의존하고 있음! -> bad
void findBeanByName2(){
MemberServiceImpl memberService = ac.getBean("memberService", MemberServiceImpl.class);
assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("빈 이름으로 조회X")
void findBeanByNameX(){
// MemberService memberService = ac.getBean("xxxxx", MemberService.class);
assertThrows(NoSuchBeanDefinitionException.class,
() -> ac.getBean("xxxxx", MemberService.class) );
}
}📘 스프링 빈 조회 - 동일한 타입이 둘 이상

src\test\java\hello\core\beanfind\ApplicationContextSameBeanFindTest.java
package hello.core.beanfind;
import hello.core.AppConfig;
import hello.core.discount.DiscountPolicy;
import hello.core.member.MemberRepository;
import hello.core.member.MemoryMemberRepository;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertThrows;
public class ApplicationContextSameBeanFindTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SameBeanConfig.class);
@Test
@DisplayName("타입으로 조회시 같은 타입이 둘 이상 있으면, 중복 오류가 발생한다.")
void findBeanTypeDuplicate() {
assertThrows(NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException.class,
() -> ac.getBean(MemberRepository.class));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("타입으로 조회시 같은 타입이 둘 이상 있으면, 빈 이름을 지정하면 된다.")
void findBeanByName() {
MemberRepository memberRepository = ac.getBean("memberRepository1", MemberRepository.class);
assertThat(memberRepository).isInstanceOf(MemberRepository.class);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("특정 타입을 모두 조회하기")
void findAllBeanType() {
Map<String, MemberRepository> beansOfType = ac.getBeansOfType(MemberRepository.class);
for (String key : beansOfType.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key = " + key + " value = " + beansOfType.get(key));
}
System.out.println("beansOfType = " + beansOfType);
assertThat(beansOfType.size()).isEqualTo(2);
}
@Configuration
static class SameBeanConfig {
@Bean
public MemberRepository memberRepository1() {
return new MemoryMemberRepository();
}
@Bean
public MemberRepository memberRepository2() {
return new MemoryMemberRepository();
}
}
}
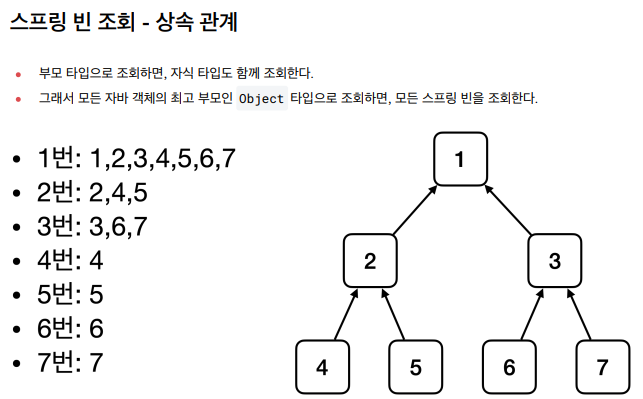
📘 스프링 빈 조회 - 상속 관계
📢 스프링 빈 조회에서 상속관계가 중요한 부분이다.
src\test\java\hello\core\beanfind\ApplicationContextExtendsFindTest.java
package hello.core.beanfind;
import hello.core.AppConfig;
import hello.core.discount.DiscountPolicy;
import hello.core.discount.FixDiscountPolicy;
import hello.core.discount.RateDiscountPolicy;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertThrows;
public class ApplicationContextExtendsFindTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfig.class);
@Test
@DisplayName("부모 타입으로 조회시, 자식이 둘 이상 있으면, 중복 오류가 발생한다.")
void findBeanByParentTypeDuplicate(){
// DiscountPolicy bean = ac.getBean(DiscountPolicy.class);
assertThrows(NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException.class,
() -> ac.getBean(DiscountPolicy.class));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("부모 타입으로 조회시, 자식이 둘 이상 있으면, 빈 이름을 지정하면 된다.")
void findBeanByParentTypeBeanName(){
DiscountPolicy rateDiscountPolicy = ac.getBean("rateDiscountPolicy", DiscountPolicy.class);
assertThat(rateDiscountPolicy).isInstanceOf(RateDiscountPolicy.class);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("특정 하위 타입으로 조회")
void findBeanBySubType() {
RateDiscountPolicy bean = ac.getBean(RateDiscountPolicy.class);
assertThat(bean).isInstanceOf(RateDiscountPolicy.class);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("부모 타입으로 모두 조회")
void findAllBeanByParentType(){
Map<String, DiscountPolicy> beansOfType = ac.getBeansOfType(DiscountPolicy.class);
assertThat(beansOfType.size()).isEqualTo(2);
for (String key : beansOfType.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key = " + key + " value = " + beansOfType.get(key));
}
}
@Test
@DisplayName("부모 타입으로 모두 조회 - Object")
void findALlBeanByObjectType() {
Map<String, Object> beansOfType = ac.getBeansOfType(Object.class);
for (String key : beansOfType.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key = " + key + " value = " + beansOfType.get(key));
}
}
@Configuration
static class TestConfig {
@Bean
public DiscountPolicy rateDiscountPolicy() {
return new RateDiscountPolicy();
}
@Bean
public DiscountPolicy fixDiscountPolicy() {
return new FixDiscountPolicy();
}
}
}
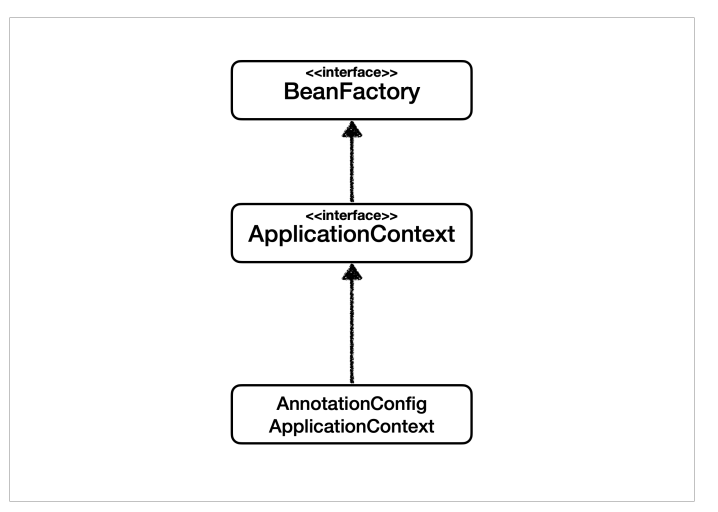
📘 BeanFactory와 ApplicationContext

- ApplicatonContext가 제공하는 부가기능
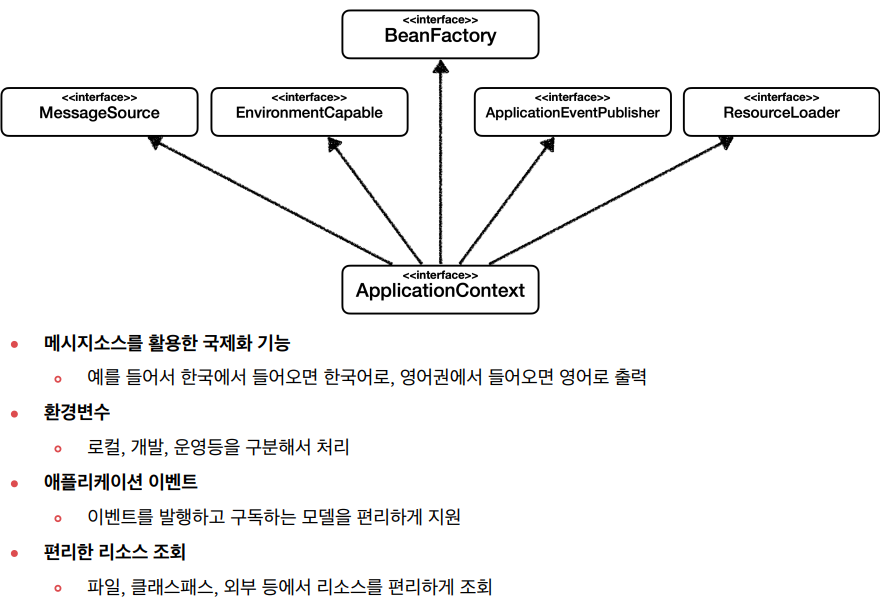
-> interface 분리 원칙

📘 다양한 설정 형식 지원 - 자바 코드, XML

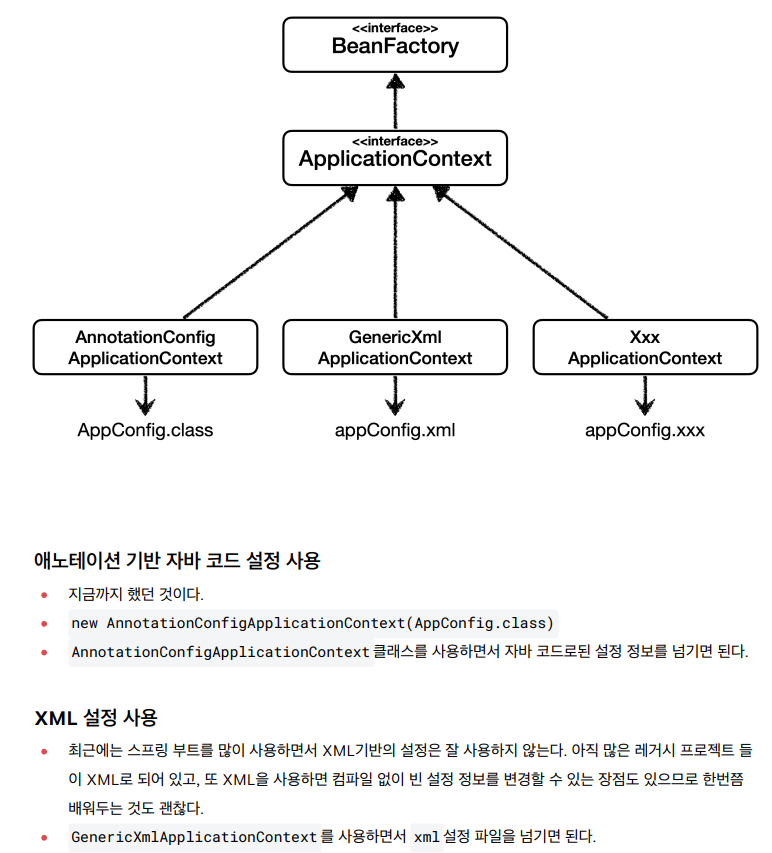
- XmlAppConfig 사용 자바 코드
src\test\java\hello\core\xml\xmlAppContext.java
package hello.core.xml;
import hello.core.member.MemberService;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.support.GenericXmlContextLoader;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
public class xmlAppContext {
@Test
void xmlAppCOntext() {
ApplicationContext ac = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("appConfig.xml");
MemberService memberService = ac.getBean("memberService", MemberService.class);
assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberService.class);
}
}
- xml 기반의 스프링 빈 설정 정보
src\main\resources\appConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="memberService" class="hello.core.member.MemberServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="memberRepository" ref="memberRepository" />
</bean>
<bean id="memberRepository"
class="hello.core.member.MemoryMemberRepository" />
<bean id="orderService" class="hello.core.order.OrderServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="memberRepository" ref="memberRepository" />
<constructor-arg name="discountPolicy" ref="discountPolicy" />
</bean>
<bean id="discountPolicy" class="hello.core.discount.RateDiscountPolicy" />
</beans>
📘 스프링 빈 설정 메타 정보 - BeanDefinition