문제

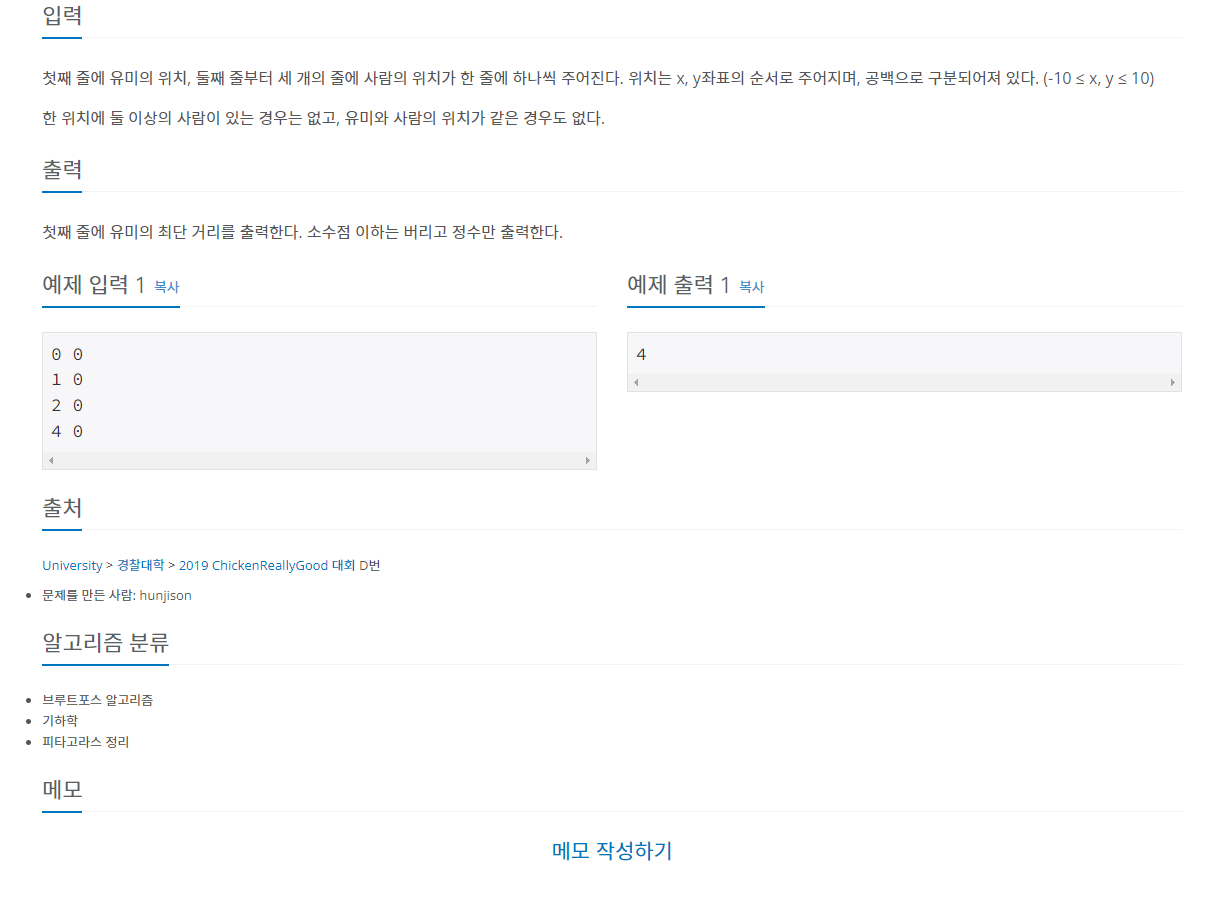
내가 생각했을때 문제에서 원하는부분
첫째 줄에 유미의 위치, 둘째 줄부터 세 개의 줄에 사람의 위치가 한 줄에 하나씩 주어진다.
위치는 x, y좌표의 순서로 주어지며, 공백으로 구분되어져 있다. (-10 ≤ x, y ≤ 10)
한 위치에 둘 이상의 사람이 있는 경우는 없고, 유미와 사람의 위치가 같은 경우도 없다.
첫째 줄에 유미의 최단 거리를 출력한다. 소수점 이하는 버리고 정수만 출력한다.내가 이 문제를 보고 생각해본 부분
Point를 점(x,y)의 객체를 만들어주고
dist 배열을 통해서 점들간 거리를 미리 계산하여 저장, dfs에서 반복 계산 방지하기위해서
visit 배열은 dfs 탐색 중에 중복 방문 체크
dfs 함수 모든 조합 탐색이 필요한 경우에 적합한 깊이우선탐색
ans 변수의 초기값을 큰 값으로 잡은 이유
이 값보다 작은 어떤 값이라도 ans에 저장되도록 하기 위해서이다.코드로 구현
package baekjoon.baekjoon_19;
import java.util.Scanner;
// 백준 17286번 문제
public class Main657 {
static class Point {
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static Point[] points = new Point[4];
static double[][] dist = new double[4][4];
static boolean[] visit = new boolean[4];
static int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
points[i] = new Point(x, y);
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
for(int j=i+1; j<4; j++) {
dist[i][j] = dist[j][i] = getDistance(points[i], points[j]);
}
}
dfs(0, 0, 0);
System.out.println(ans);
sc.close();
}
public static double getDistance(Point a, Point b) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(a.x - b.x, 2) + Math.pow(a.y - b.y, 2));
}
public static void dfs(int idx, double sum, int cnt) {
if(cnt == 4) {
ans = Math.min(ans, (int)sum);
return;
}
if(visit[idx]) return;
visit[idx] = true;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
dfs(i, sum + dist[idx][i], cnt+1);
}
visit[idx] = false;
}
}
마무리
이런 문제의 유형을 많이 접해보지 못해서 푸는 내내 어려움이 있었다. 아직 부족함을 많이 느끼는것같다.
