백준 1260번 자바(JAVA)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1260
위 문제를 풀어보도록 하겠다.
문제
- 그래프를 DFS와 BFS로 탐색한 결과를 출력해야 함.
특이사항
- 정점이 여러개인 경우, 정점 번호가 작은 것을 먼저 방문해야 함.
테스트 케이스 분석
| -- | 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|---|
| 예제 입력 1 | 4 5 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 4 3 4 | 1 2 4 3 1 2 3 4 |
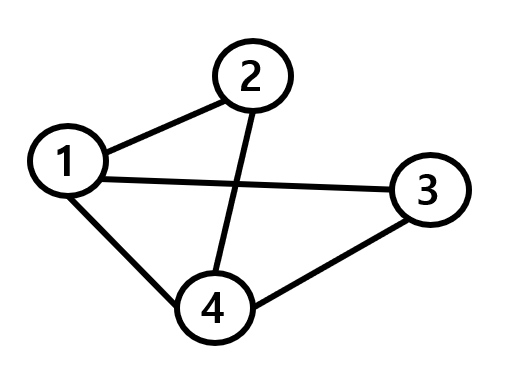
위는 1번 테스트 케이스의 그래프 이다.
- DFS로 탐색하는 경우
(1) 1에서 시작 (1 방문)
(2) 1과 연결된 가장 작은 노드는 2 이므로, 2 방문
(3) 2와 연결된 것 중 방문하지 않은 가장 작은 노드는 4이므로, 4 방문
(4) 4와 연결된 것 중 방문하지 않은 가장 작은 노드는 3이므로 3 방문
(5) 1-2-4-3 의 순서로 방문하게 됨
- BFS로 탐색하는 경우
(1) 1에서 시작 (1방문)
(2) 1과 연결된 가장 작은 노드인 2 방문
(3) 1과 연결된 다음 작은 노드 3 방문
(4) 1과 연결된 마지막 노드 4 방문
(6) 1-2-3-4 의 순서로 방문하게 됨
| -- | 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|---|
| 예제 입력 2 | 5 5 3 5 4 5 2 1 2 3 4 3 1 | 3 1 2 5 4 3 1 4 2 5 |
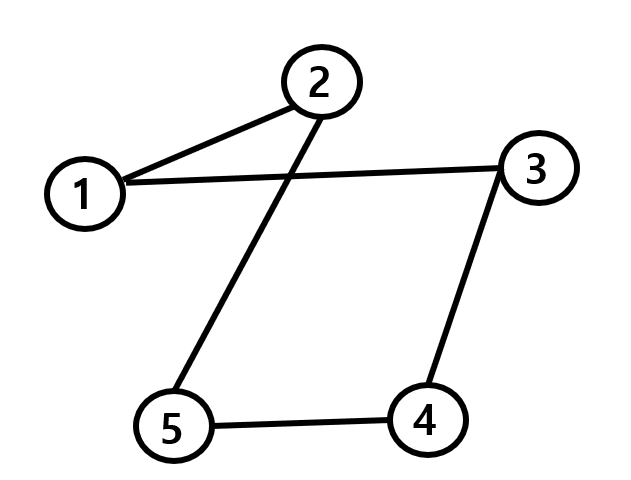
위는 2번 테스트 케이스의 그래프 이다.
- DFS로 탐색하는 경우
(1) 3에서 시작 (3 방문)
(2) 1과 연결된 가장 작은 노드는 1 이므로, 1 방문
(3) 1와 연결된 것 중 방문하지 않은 노드는 2이므로, 2 방문
(4) 2와 연결된 것 중 방문하지 않은 노드는 5이므로, 5 방문
(5) 5와 연결된 것 중 방문하지 않은 노드는 4이므로, 4 방문
(6) 3-1-2-5-4 의 순서로 방문하게 됨
- BFS로 탐색하는 경우
(1) 3에서 시작 (3방문)
(2) 3과 연결된 가장 작은 노드인 1 방문
(3) 3과 연결된 다음 작은 노드 4 방문
(4) 1과 연결된 노드 2 방문
(5) 4와 연결된 노드 5 방문
(6) 3-1-4-2-5 의 순서로 방문하게 됨
예제 출력 3은 생략.
구현 과정
- DFS (재귀로 구현함. Stack로 해도 된다)
(1) node를 방문하면, 방문을 기록하고 node의 값을 출력한다.
(2) 방문한 node에 연결된 다른 node배열을 받는다.
(3) node배열중에서 방문하지 않은 배열이 있다면, node를 방문하고 (1)부터 반복한다.
- BFS (Queue로 구현함)
(1) node를 방문하면, 방문을 기록하고 방문한 node를 Queue에 add하고 출력한다.
(2) node에 연결된 다른, 방문하지 않은 node들을 Queue에 add한다.
(3) Queue가 isEmpty가 참일때까지 반복한다.
코드
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int nodeCount = sc.nextInt();
int lineCount = sc.nextInt();
int startNode = sc.nextInt();
Node[] nodes = new Node[nodeCount+1];
for(int i=0; i<nodeCount+1; i++)
nodes[i] = new Node(i);
for(int i=0; i<lineCount; i++){
int s = sc.nextInt();
int e = sc.nextInt();
nodes[s].addSide(nodes[e]);
nodes[e].addSide(nodes[s]);
}
for(Node n : nodes)
n.neighbours.sort(new Com());
DFS(nodes[startNode]);
System.out.println();
reset(nodes);
BFS(nodes[startNode]);
}
static void reset(Node[] nodes){
for(Node v : nodes)
v.visited=false;
}
static void DFS(Node node){
node.visited=true;
System.out.printf("%d",node.info);
List<Node> list = node.getSide();
for(Node n : list){
if(!n.visited) {
System.out.print(" ");
DFS(n);
}
}
}
static Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
static void BFS(Node node){
node.visited = true;
queue.add(node);
System.out.print(node.info);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node v = queue.remove();
List<Node> neigh = v.neighbours;
for(Node w : neigh){
if(!w.visited){
System.out.print(" "+w.info);
w.visited = true;
queue.add(w);
}
}
}
}
}
class Com implements Comparator<Node>{
@Override
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1.info, o2.info);
}
}
class Node {
int info;
boolean visited;
List<Node> neighbours; //인접 목록
Node(int info){ //생성자
this.info = info;
this.visited = false;
this.neighbours = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addSide(Node n) { //인접 목록 채우기
this.neighbours.add(n);
}
public List<Node> getSide(){ //인접 목록 반환
return neighbours;
}
public void setSide(List<Node> n) { // 인접 목록 세팅
this.neighbours = n;
}
@Override
public String toString() { //출력 오버라이딩
return "" + info;
}
}만약, DFS를 재귀가 아닌 Stack으로 구현하고 싶다면, 아래의 코드를 참고하면 된다.
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int nC = sc.nextInt();
int lC = sc.nextInt();
int sNN = sc.nextInt();
// nC = nodeCount
// lC = lineCount
// sNN = startNodeNumber
Node[] nodes = new Node[nC];
for(int i=0; i<nC; i++){
nodes[i] = new Node(i);
}
for(int i=0; i<lC; i++){
int sN = sc.nextInt();
int eN = sc.nextInt();
// sN = startNode
// eN = endNode
nodes[sN].addNode(nodes[eN]);
nodes[eN].addNode(nodes[sN]);
}
DFS(nodes, sNN);
}
static void DFS(Node[] nodes, int sNN){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Node n = nodes[sNN];
n.setVisit(true);
System.out.print(n.getValue());
stack.push(n);
while(!stack.empty()){
Node tN = stack.peek();
boolean test = false;
// tN = topNode
for(Node sN : tN.getNodeList()){
// sN = sideNode (인접 노드)
if(!sN.getVisit()){
sN.setVisit(true);
System.out.print(" " + sN.getValue());
stack.push(sN);
test = true;
break;
}
}
if(!test)
stack.pop();
}
}
}
class Node {
private final int value;
private boolean visit;
private List<Node> nodeList;
public Node(int value) {
visit = false;
nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
this.value = value;
}
public void addNode(Node node) {
nodeList.add(node);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public boolean getVisit() {
return visit;
}
public void setVisit(boolean visit) {
this.visit = visit;
}
public List<Node> getNodeList() {
return nodeList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "" + value;
}
}구현상의 특징
-
node가 여러개인 경우, 숫자가 작은 node를 선택해야 하는데, 이것을 어떻게 할지 고민하다가 Comparator를 구현하고 sort메서드에 Comparator 인스턴스를 넘겨주었다.
따라서 node 목록이 크기순으로 정렬된다. -
이렇게 하면, node를 뽑을때 저장된 순서로 뽑히므로 작은 node부터 뽑을 수 있다.
-
인접 행렬을 사용하면 편하지만, 그래프의 크기가 커지면 인접 목록보다 성능이 급격하게 떨어지므로 목록을 사용해서 구현했다.

고생하셨습니당