문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1260

풀이
필요한 것: Graph와 방문여부에 대한 Visited
static ArrayList<Integer>[] graph;
static boolean[] visited;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int V = sc.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList[N + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
graph[a].add(b);
graph[b].add(a);
}
// 번호 작은 것부터 방문하기 위해 정렬
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Collections.sort(graph[i]);
}
// DFS
visited = new boolean[N + 1];
dfs(V);
sb.append("\n");
// BFS
visited = new boolean[N + 1];
bfs(V);
System.out.println(sb);
}
static void dfs(int idx) {
visited[idx] = true;
sb.append(idx).append(" ");
for (int next : graph[idx]) {
if (!visited[next]) {
dfs(next);
}
}
}
static void bfs(int idx) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(idx);
visited[idx] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int node = q.poll();
sb.append(node).append(" ");
for (int next : graph[node]) {
if (!visited[next]) {
visited[next] = true;
q.add(next);
}
}
}
}그래프 생성
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
graph[a].add(b);
graph[b].add(a);
}
// 번호 작은 것부터 방문하기 위해 정렬
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Collections.sort(graph[i]);
}깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)
for (int next : graph[idx]) 바로 다음 깊이로 넘어가는 것을 확인 가능
너비 우선 탐색(BFS)
바로 다음 깊이로 넘어가는 것이 아님
int node = q.poll();
sb.append(node).append(" ");
for (int next : graph[node]) {출발 지점에서 가까운 순서대로 노드를 방문하는 탐색 방법
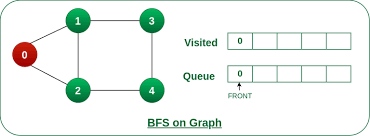
출발지에서 간선 개수가 적은 노드부터 방문
- 큐(Queue) 활용
- 노드를 큐에서 하나씩 꺼내 방문- 방문한 노드의 인접 노드를 큐에 넣음 (트리: 자식 노드 / 그래프: 연결된 노드)
큐의 선입선출(FIFO) 특성으로 인해, 한 수준이 끝난 후 큐에는 다음 수준의 노드가 차례대로 저장됨
