객체 초기화
let name="noona"
let age =17
let cute = true
let person = {name, age, cute}
// let person = {name:name,age:age,cute:cute}와 같다
Destructuring
let person = {
name:"noona",
age:17,
cute:true
}
let {name, age, cute} = person
/ let name = person.name let age = person.age let cute = person.cute 와 같다 /
let array = [1,2,3]
let [a,b,c] = array
/ let a = array[0] let b = array[1] let c = array[2] 와 같다 /
Rest destructuring
let person = {
name:"noona",
age:17,
cute:true
}
let {name, ...rest} = person
console.log(rest) // {age:17, cute:true}
let array = [1,2,3]
let [a,...rest] = array console.log(rest)//[2,3]
Spread
let a = [1,2]
let b = [3,4]
let c = [5,6]
let result = [...a,...b,...c] // [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Template Literal
let name ="noona"
console.log(제 이름은 ${name}입니다)
화살표 함수
화살표 함수 표현식은 기존의 function 표현방식보다 간결하게 함수를 표현할 수 있다. 화살표 함수는 항상 익명이며, 자신의 this, arguments, super을 바인딩하지 않는다.자신만의 this를 생성하지 않고 자신을 포함하고 있는 context의 this를 이어 받는다.
let foo =()=>{
console.log("hello")
}
let zoo =()=>Date.now()
/ function zoo(){
return Date.now()
} 와 같음 /
let koo = (a,b) =>{
let result = ab
return result
}
//또는
let koo = (a,b) =>ab
//로도 표현 가능
화살표 함수를 쓰면 안돼는 경우
🍺object안에 함수 정의시
const person = {
points: 23,
score: function(){
this.points++; // 여기에선 화살표함수 쓰면 point가 증가 안함
}
}
🍺프로토타입 함수
class Car {
constructor(make, color) {
this.make = make;
this.color = color;
}
}
let hyundai = new Car("noona","white")
Car.prototype.summary = function () {
console.log(This car is a ${this.make} in the colour ${this.colour})
} // 여기서 화살표함수를 쓰면 안됀다 hyundai.summary()
this
let age = 20
var obj = {
age:12,
foo: function () {
console.log(this.age)
},
};
obj.foo()
forEach()
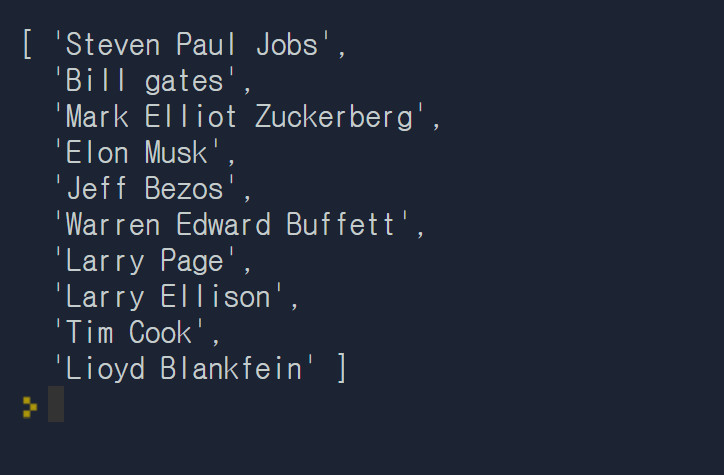
let names = ["Steven Paul Jobs","Bill gates","Mark Elliot Zuckerberg","Elon Musk","Jeff Bezos","Warren Edward Buffett","Larry Page","Larry Ellison","Tim Cook","Lioyd Blankfein"]
function printName(item){
console.log(item)
}
names.forEach(printName) // 또는 함수를 따로 만들지 않고 아예 한꺼번에
names.forEach(function (item){
console.log(item)
}) 이렇게 만들어도 된다.
또 새로운 ES6 문법을 보면 함수는 ()=>{} 형식으로 만들이 때문에
names.forEach((item)=>{console.log(item)}) 이렇게 ES6문법으로 만들수 있다.
map()
let data = names.map((item)=>{return item})
console.log(data) // map()도 forEach( )와 비슷하나 map( )은 반환 값으로 배열을 반환한다.
forEach( ) 반환 값이 없다 .
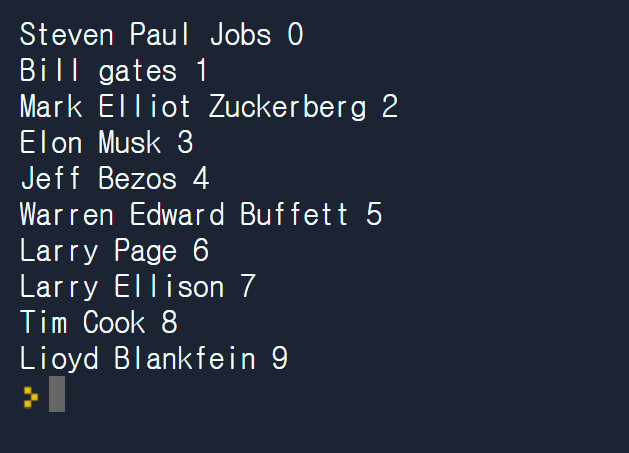
map( ) 반환 값이 있고 배열로 반환한다.
배열함수 리스트
filter: 조건에 충족하는(true) 아이템만 배열에 담아 반환한다.
some: 조건에 충족하는 아이템이 하나라도 있으면 true 반환, 아니면 flase.
every: 모든 배열에 아이템이 조건을 충족하면 true 반환, 아니면 false.
find : 조건에 충족하는 아이템 하나만 반환(여러개라면 첫번째것만 반환)
findIndex : 조건에 충족하는 아이템의 인덱스값 반환 (여러개라면 첫번째아이템의 인덱스번호만 반환)

