원래 리트코드는 좀 가볍게? 푸는 목적으로 많이 사용했는데 이번 문제는 시뮬레이션이 섞인 구현을 좀 섞어야 하는 문제 였어서 기록을 남겨본다.
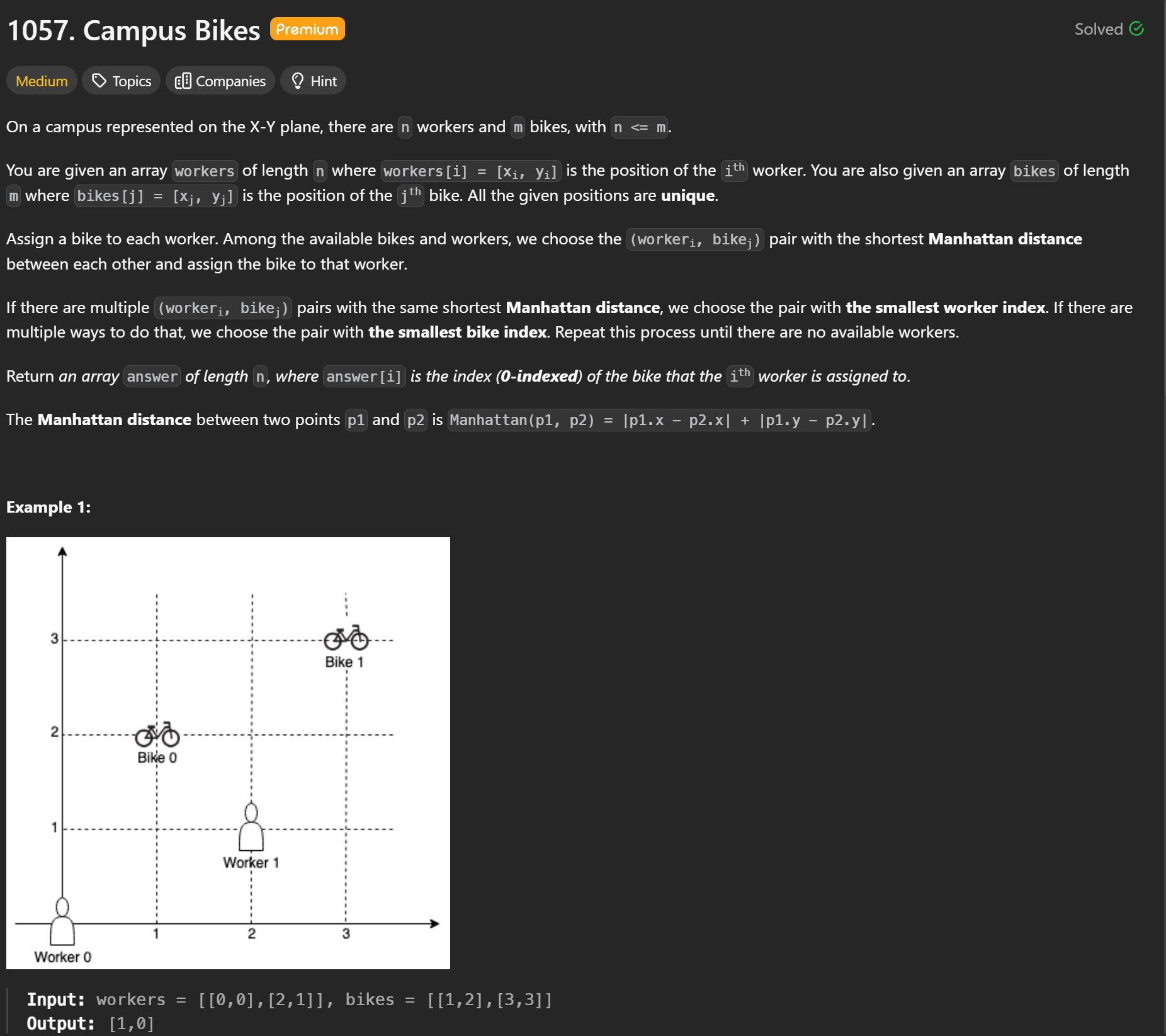
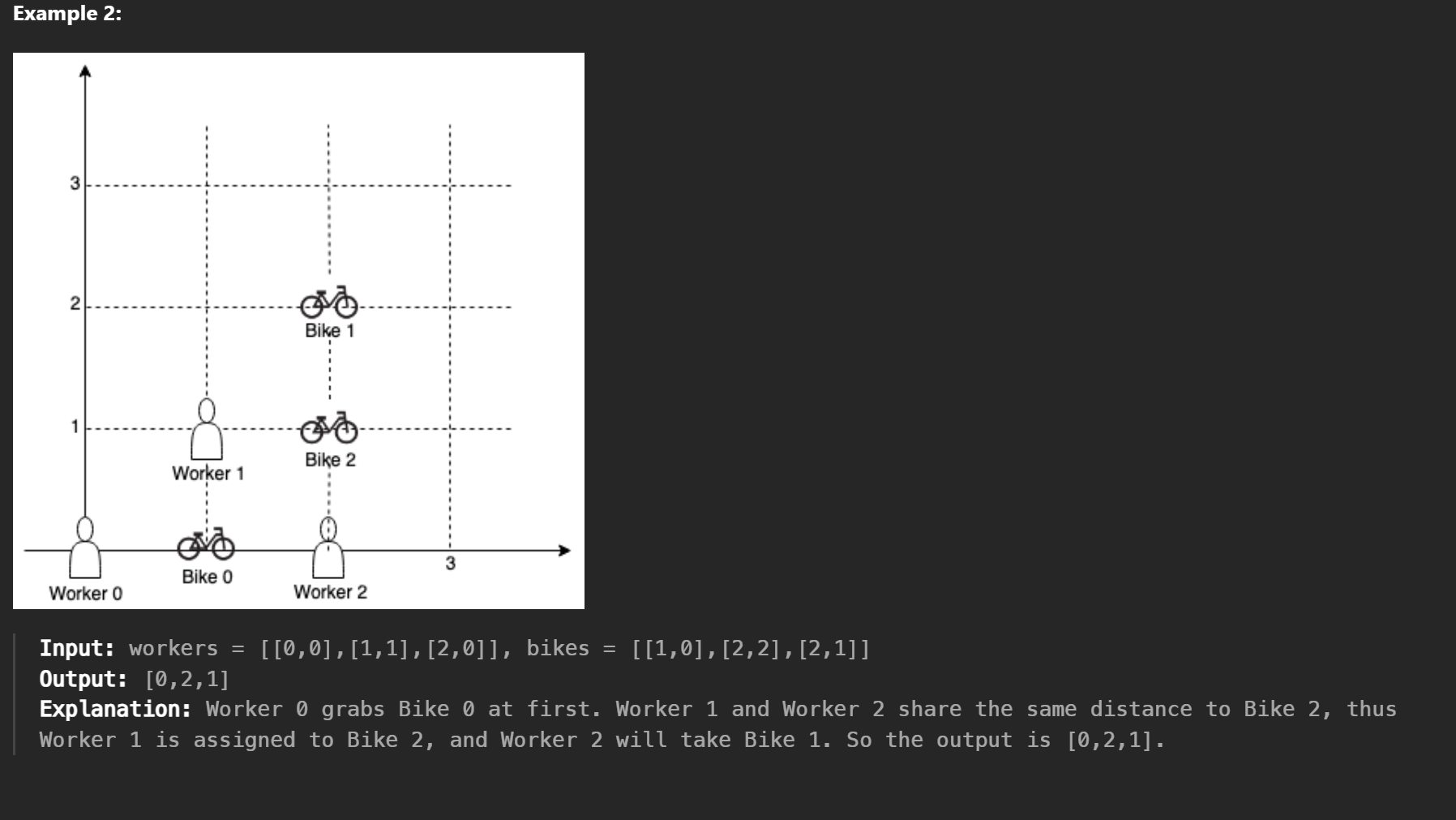
workers 와 bikes 의 좌표가 있다고 할 때 둘의 manhattan distance 를 구하고, 각자 worker 한테 제일 가까운 자전거를 배정해주면 되는 문제다.
처음에 이 문제를 어떻게 풀 수 있을지 고민하면서 노트에 이것저것 적다가 생각이 났다.
각자 worker 와 bike의 맨하탄 거리를 구한 다음에 가장 짧은 거리부터 계속 유지할 수 있는 우선순위큐를 사용하기로.
난 보통 큐를 사용할때 저렇게 struct 를 많이 사용하는데 비교 조건까지 적었다.
우선순위큐에 거리를 모두 담은 후에는 각 Node 가 pop 될때마다 인덱스 안에 있는 자전거가 아직 배정이 안되어 있다면 배정 해주는 방식으로 전부 구현할 수 있었다.
백준으로 따지면 골드 4 ~ 3문제 쯤 되지 않았을까 생각해본다.
class Solution {
struct Node{
int distance, windex, bindex;
};
struct NodeCompare{
bool operator()(Node& a, Node& b){
if(a.distance != b.distance){
return a.distance > b.distance;
} else if(a.windex != b.windex){
return a.windex > b.windex;
}
return a.bindex > b.bindex;
}
};
public:
vector<int> assignBikes(vector<vector<int>>& workers, vector<vector<int>>& bikes) {
vector<int> workerVec(workers.size(), -1);
vector<int> bikeVec(bikes.size(), -1);
vector<int> answer(workers.size(), -1);
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, NodeCompare> pq;
for(int i = 0; i < workers.size(); i++){
vector<int> currWorkers = workers[i];
for(int j = 0; j < bikes.size(); j++){
vector<int> currBikes = bikes[j];
int manDist = abs(currWorkers[0] - currBikes[0]) + abs(currWorkers[1] - currBikes[1]);
pq.push({manDist, i, j});
}
}
while(!pq.empty()){
int size = pq.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
Node node = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int distance = node.distance, workerIndex = node.windex, bikeIndex = node.bindex;
if(workerVec[workerIndex] == -1 && bikeVec[bikeIndex] == -1){
//workere did not get bikes yet, bike was not assigned yet
answer[workerIndex] = bikeIndex;
workerVec[workerIndex]++;
bikeVec[bikeIndex]++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
};