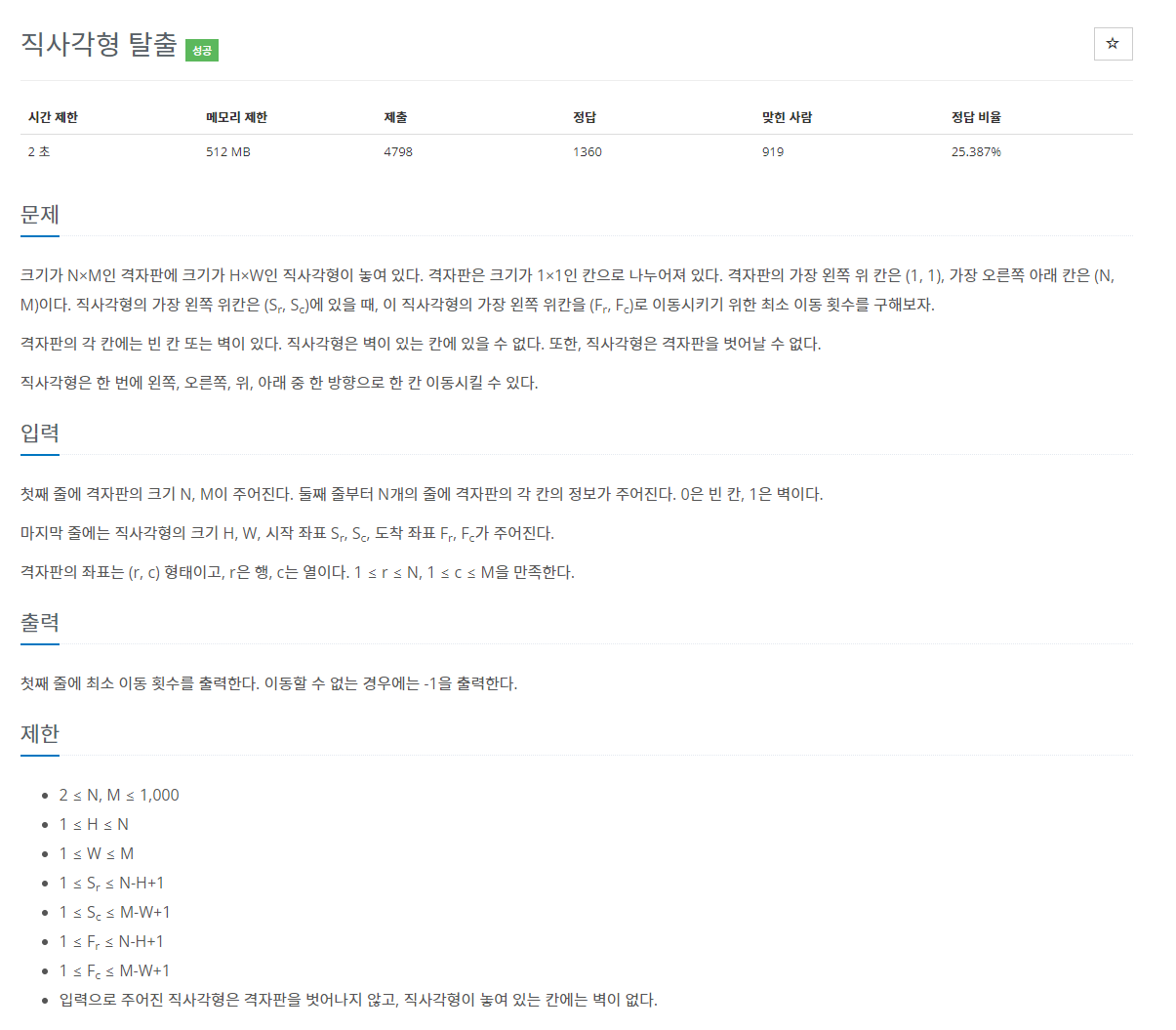
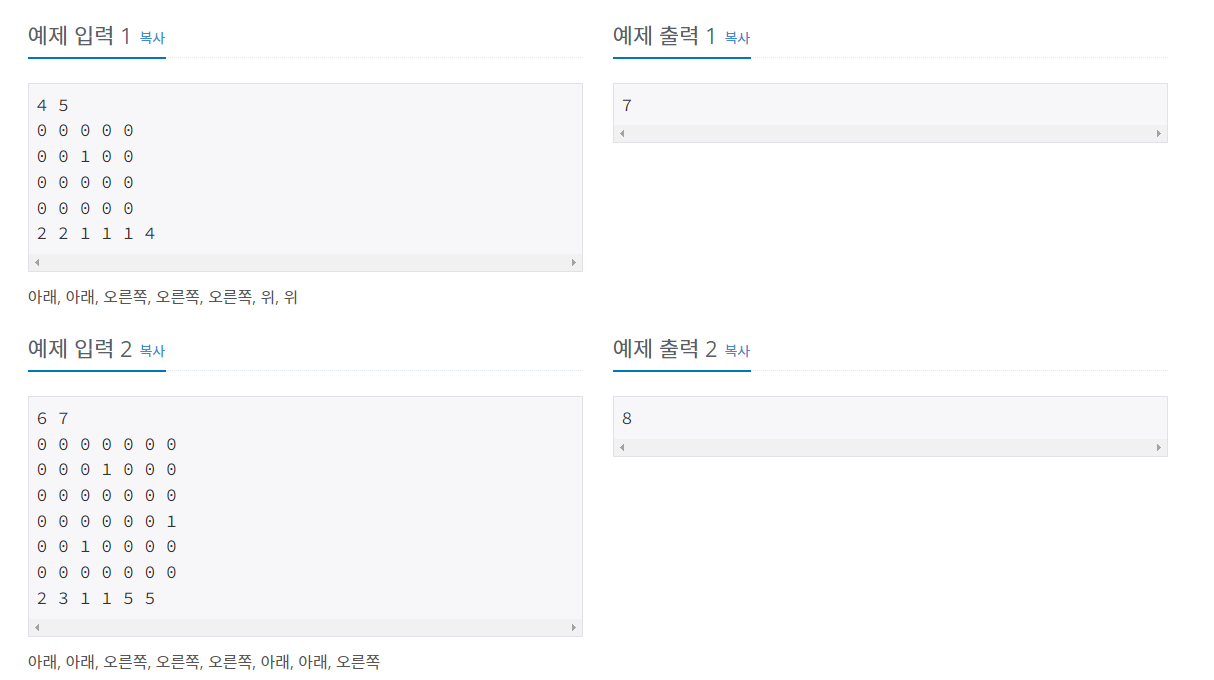
처음 문제를 읽고 정말 단순한 BFS 구현인줄 알고 바로 풀려고 했는데 생각보다 까다로운 구현이었다. 직사각형의 모양 H 와 W 로 주어졌고 난 처음에 직사각형 형태를 벡터로 담은 후에 상하좌우로 탐색을 해줘야 할까 고민했었다.
틀린 답
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
#define MAX 100010
using namespace std;
int N, M, sN, sM, Sr, Sc, Fr, Fc;
int matrix[1010][1010];
bool visited[1010][1010];
vector<pair<int,int>> dir = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
struct Square{
vector<pair<int,int>> square;
int dist;
};
void Input(){
cin >> N >> M;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= M; j++){
cin >> matrix[i][j];
}
}
cin >> sN >> sM >> Sr >> Sc >> Fr >> Fc;
}
void Solution(){
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
int sqSize = sN * sM;
queue<Square> q;
q.push({{},0});
for(int i = Sr; i <= sN; i++){
for(int j = Sc; j <= sM; j++){
q.front().square.push_back({i,j});
}
}
for(pair<int,int>& p : q.front().square) visited[p.first][p.second] = true;
vector<pair<int,int>> tmp;
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
Square first = q.front();
q.pop();
vector<pair<int,int>> square = first.square;
//int x = square[0].first, y = square[0].second, dist = first.dist;
int dist = first.dist;
if(!square.empty() && square[0].first == Fr && square[0].second == Fc){
cout << dist;
return;
}
for(pair<int,int>& p : dir){
for(pair<int,int>& sq : square){
int nX = sq.first + p.first;
int nY = sq.second + p.second;
if(nX < 1 || nY < 1 || nX > N || nY > M || matrix[nX][nY]==1){
tmp.clear();
break;
}
tmp.push_back({nX,nY});
}
if(tmp.size() == sqSize){
bool flag = false;
for(pair<int,int>& tp : tmp){
if(!visited[tp.first][tp.second]){
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
for(pair<int,int>& tp2 : tmp){
visited[tp2.first][tp2.second] = true;
}
q.push({tmp,dist+1});
}
}
tmp.clear();
}
}
}
cout << -1;
}
void Solve(){
Input();
Solution();
}
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
Solve();
return 0;
}그러나 이 접근이 틀렸단걸 알았다. 직사각형 형태를 유지하는 벡터를 유지하면서 visited 벡터를 계속 체크해주는거 자체가 시간적으로 많은 메모리와 런타임이 요구 되었고 문제 자체의 접근을 바꿨어야 했다.
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
#define MAX 100010
using namespace std;
int N, M, H, W, Sr, Sc, Fr, Fc;
int matrix[1001][1001];
bool visited[1001][1001];
vector<pair<int,int>> dir = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
struct Square{
int x, y, dist;
};
void Input(){
cin >> N >> M;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++){
cin >> matrix[i][j];
}
}
cin >> H >> W >> Sr >> Sc >> Fr >> Fc;
Sr--;Sc--;Fr--;Fc--;
}
bool canMove(int x, int y, int dir){
if(dir == 0){
int nY = y + W - 1;
if(nY >= M) return false;
for(int i = x; i < x + H; i++){
if(matrix[i][nY]) return false;
}
}
if(dir == 1){
for(int i = x; i < x + H; i++){
if(matrix[i][y]) return false;
}
}
if(dir == 2){
int nX = x + H - 1;
if(nX >= N) return false;
for(int i = y; i < y + W; i++){
if(matrix[nX][i]) return false;
}
}
if(dir == 3){
for(int i = y; i < y + W; i++){
if(matrix[x][i]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void Solution(){
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
queue<Square> q;
q.push({Sr,Sc,0});
visited[Sr][Sc] = true;
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
Square first = q.front();
q.pop();
int x = first.x, y = first.y, dist = first.dist;
if(x == Fr && y == Fc){
cout << dist;
return;
}
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++){
int nX = x + dir[j].first;
int nY = y + dir[j].second;
if(nX >= 0 && nY >= 0 && nX < N && nY < M){
if(!visited[nX][nY]){
if(canMove(nX,nY,j)){
visited[nX][nY] = true;
q.push({nX,nY,dist+1});
}
}
}
}
}
}
cout << -1;
}
void Solve(){
Input();
Solution();
}
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
Solve();
return 0;
}직사각형을 계속 유지하는게 아니고 그냥 좌표 하나를 옮겨서 방향에 따라서 계산을 해주는게 따로 메모리를 차지하는 tmp 벡터를 사용하지 않아도 됐고 훨씬 더 빨랐다. 솔직히 dir 변수를 활용한 문제풀이도 생각을 안했던건 아니였지만 꽤 고전 했던 문제고 아직도 BFS 관련으로도 풀 문제가 많다고 느낀거같다.
배운점:
1. BFS 와 시나리오의 활용
2. 문제 잘 읽고 깔끔하게 적기
