👑 프로미스(Promise)
- 비동기 함수를 동기 처리하기 위해 고안한 객체
- 전통적인 콜백 패턴이 가진 단점을 보완함
- 비동기 작업이 완료된 이후에 다음 작업을 연결시켜 진행할 수 있음
- 작업 결과에 따라 성공 또는 실패를 리턴하며 결과 값을 전달 받을 수 있음
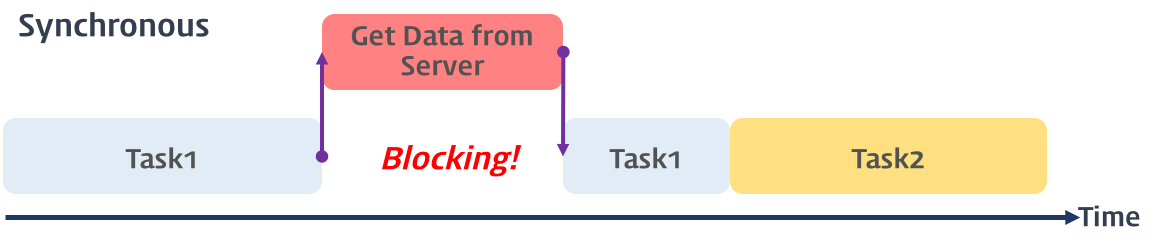
✏️ 동기식 처리 모델 (Synchronous processing model)
- 직렬적으로 태스트(task)를 수행
- 태스크는 순차적으로 실행되며 어떤 작업이 수행중이면 다음 태스크들은 블로킹됨
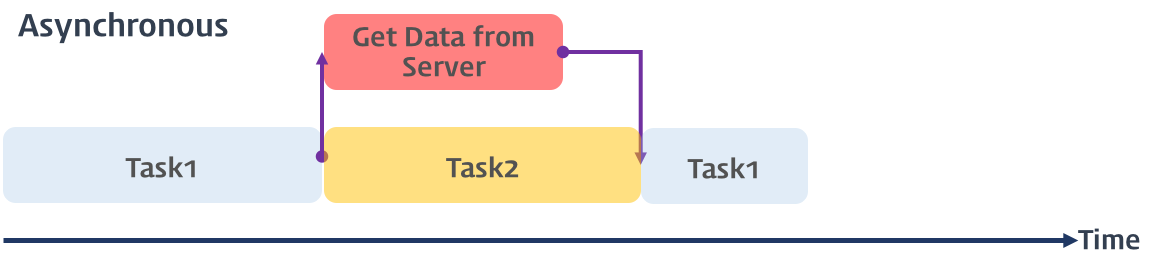
📐 비동기식 처리 모델 (Asynchronous processing model 또는 Non-Blocking processing model)
- 병렬적으로 태스크를 수행함
- 태스크가 종료되지 않은 상태라 하더라도 대기하지 않고 (Non-Blocking) 즉시 다음 태스크를 수행함
- 자바스크립트의 대부분 DOM 이벤트와 Timer 함수(setTimeout, setInterval), Ajax 요청은 비동기식 처리 모델로 동작함
✔️ 콜백 패턴
- 자바스크립트는 비동기 처리를 위한 하나의 패턴으로 콜백 함수를 사용함
- 전통적인 콜백 패턴은 콜백 헬로 인해 가독성이 나쁘고 비동기 처리 중 발생한 에러 처리가 곤란하며 여러 개의 비동기 처리를 한번에 처리에하는 데도 한계가 존재함
콜백 패턴의 단점
1. 콜백 헬 (Callback Hell)
- 처리 순서를 보장하기 위해 여러 개의 콜백 함수가 네스팅(nesting ,중첩)되어 복잡도가 높아지는 현상
- 가독성을 나쁘게 하며 실수를 유발하는 원인이 됨
step1(function(value1) {
step2(value1, function(value2) {
step3(value2, function(value3) {
step4(value3, function(value4) {
step5(value4, function(value5) {
// value5를 사용하는 처리
});
});
});
});
});2. 에러 처리의 한계
try {
setTimeout(() => { throw new Error('Error!'); }, 1000);
} catch (e) {
console.log('에러를 캐치하지 못한다..');
console.log(e);
}
-태스크 큐 (task queue): 콜백 함수들이 대기하는 큐(FIFO 방식) 형태의 배열이며, 호출 스택이 비워질 때마다 큐에서 콜백 함수를 꺼내와서 실행하는 역할을 함
-setTimeout 함수는 비동기 함수이므로 콜백 함수가 실행될 때까지 기다리지 않고 즉시 종료되어 호출 스택에서 제거됨
-이후 tick 이벤트가 발생하면, setTimeout 함수의 콜백 함수는 작업 큐로 이동한 후 호출 스택이 비어졌을 때 호출 스택으로 이동되어 실행됨
--> 이때 setTimeout() 함수는 이미 호출 스택에서 제거된 상태이므로, setTimeout 함수의 콜백 함수를 호출한 것은 setTimeout 함수가 아니다라는 것을 의미함..
- 예외(exception)는 호출자(caller) 방향으로 전파되는데, setTimeout 함수의 콜백 함수를 호출한 것은 setTimeout 함수가 아니기 때문에 setTimeout 함수의 콜백 함수 내에서 발생시킨 에러는 catch 블록에서 캐치되지 않아 프로세스는 종료됨🌼 프로미스의 생성
- Promise 생성자 함수를 통해 인스턴스화함
- Promise 생성자 함수는 비동기 작업을 수행할 콜백 함수를 인자로 전달받는데 이 콜백 함수는
resolve와reject함수를 인자로 전달받음
// Promise 객체의 생성
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 비동기 작업을 수행한다.
if (/* 비동기 작업 수행 성공 */) {
resolve('result');
}
else { /* 비동기 작업 수행 실패 */
reject('failure reason');
}
});🚓 프로미스의 상태
1. pending (대기)
- 비동기 처리가 아직 수행되지 않은 상태- resolve 또는 reject 함수가 아직 호출되지 않은 상태
2. fulfilled(이행)
- 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태 (성공)- resolve 함수가 호출된 상태
3. rejected(거부)
- 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태 (실패)- reject 함수가 호출된 상태
4. settled(처리)
- 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태 (성공 또는 실패)- resolve 또는 reject 함수가 호출된 상태
🎮 프로미스의 후속 처리 메소드
- Promise로 구현된 비동기 함수는 Promise 객체를 반환하여야 함
- Promise로 구현된 비동기 함수를 호출하는 측(promise consumer)에서는 Promise 객체의 후속 처리 메소드(then, catch)를 통해 비동기 처리 결과 또는 에러 메시지를 전달받아 처리함
then: 두 개의 콜백 함수를 인자로 전달받는데, 첫 번째 콜백 함수는 성공(fulfilled, resolve 함수가 호출된 상태) 시 호출되고 두 번째 함수는 실패(rejected, reject 함수가 호출된 상태) 시 호출됨catch: 예외(비동기 처리에서 발생한 에러와 then 메소드에서 발생한 에러)가 발생하면 호출됨
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<pre class="result"></pre>
<script>
// document.querySelector(): 선택자에 부합하는 요소 중에서 첫 번째 요소만을 반환함
// $변수명: document.getElementById() 대신 아이디 값처럼 단일한 변수를 표시함.
// 변수명으로 사용도가 낮은 $를 변수명 앞에 붙여서 다른 변수와 충돌이 일어나지 않도록 하는 것
const $result = document.querySelector('.result');
// querySelector().textContent: 텍스트 가져고 새로운 값을 할당하여 내용 변경함
const render = content => { $result.textContent = JSON.stringify(content ,null ,2);
const promiseAjax = (method ,url ,payload) => {
return new Promise((resolve ,reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open(method ,url);
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-type' ,'application/json');
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(payload));
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
// XMLHttpRequest.DONE: The operation is complete
if(xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return;
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status <400) {
resolve(xhr.response); // Success !
} else {
reject(new Error(xhr.status)); // Failed ..
}
};
});
}
};
/*
비동기 함수 promiseAjax는 Promise 객체를 반환함
Promise 객체의 후속 메소드를 사용하여 비동기 처리 결과에 대한 후속 처리를 수행함
*/
promiseAjax('GET' ,'http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1')
.then(JSON.parse)
.then(
render // 첫 번째 콜백 함수는 성공(fulfilled, resolve 함수가 호출된 상태) 시 호출됨
,console.error // 두 번째 함수는 실패(rejected, reject 함수가 호출된 상태) 시 호출됨
)
</script>
</body>
</html>💊 프로미스의 에러 처리
- 비동기 처리 결과에 대한 후속 처리는 Promise 객체가 제공하는 후속 처리 메서드
then,catch,finally를 사용하여 수행함 then메서드의 두 번째 콜백 함수는 첫 번째 콜백 함수에서 발생한 에러를 캐치하지 못하고 코드가 복잡해져서 가독성이 좋지 않음catch메서드를 모든 then 메서드를 호출한 이후에 호출하면 비동기 처리에서 발생한 에러(reject 함수가 호출된 상태)뿐만 아니라 then 메서드 내부에서 발생한 에러까지 모두 캐치할 수 있음- 에러 처리는
then메서드에서 하지 않고,catch메서드를 사용하는 것을 권장함
promiseAjax(wrongUrl) //부적절한 URL이 지정되었기 때문에 에러가 발생함
// .then(res => console.log(res), err => console.error(err));
.then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.error(err)); ⛓️ 프로미스 체이닝 (chainning)
- 각각의 함수가 Promise 객체를 리턴하는 비동기 작업이라고 가정한다면
then메서드를 연속적으로 사용하여 순차적인 작업을 할 수 있음 - 비동기 함수의 처리 결과를 가지고 다른 비동기 함수를 호출해야 하는 경우, 함수의 호출이 중첩(nesting)이 되어 복잡도가 높아지는 콜백 헬이 발생함
- 프로미스는 후속 처리 메소드를 여러 개의 프로미스를 연결하는 체이닝 기법을 활용함으로써 콜백 헬을 해결할 수 있음
/*
then 메서드에서 값을 return 키워드를 사용하면 결과 값이 기본 자료형이 아닌
Promise 객체로 반환되기 때문에 이와같은 체인 형식이 가능하게 됨
*/
add(1,1)
.then(function(res){ // res: 2
return res + 1; // 2 + 1 = 3
})
.then(function(res){ // res: 3
return res * 4; // 3 * 4 = 12
})
.then(function(res){ // res: 12
console.log(res); // 12 출력
});// then 메서드 내에서 직접 Promise를 return 할 수 있음
goToSchool()
.then(function(){
return arriveAtSchool();
})
.then(function(){
return studyHard();
})
.then(function(){
return eatLunch();
}); const url = 'http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts';
promiseAjax('GET' ,`${url}/1`)
// 포스트 id가 1인 포스트를 작성한 사용자의 아이디로 작성된 모든 포스트를 검색하고 프로미스를 반환함
.then(res => promiseAjax('GET' ,`${url}?userId=${JSON.parse(res).userId}`))
.then(JSON.parse)
.then(render)
.catch(console.error);🚀 프로미스의 정적 메소드
- Promise는 주로 생성자 함수로 사용되지만 함수도 객체이므로 메소드를 갖을 수 있음
1. Promise.resolve/Promise.reject
-존재하는 값을 Promise로 래핑하기 위해 사용함
const resolvedPromise = Promise.resolve([1,2,3]);
// const resolvedPromise = new Promise (resolve => resolve([1,2,3]))
resolvedPromise.then(console.log); // [1,2,3]
2. Promise.all
-전달받은 모든 프로미스를 병렬로 처리함 (처리 순서 보장)
-모든 프로미스의 처리가 종료될 때까지 기다린 후 아래와 모든 처리 결과를 resolve 또는 reject함
-모든 프로미스의 처리가 성공하면 각각의 프로미스가 resolve한 처리 결과를 배열에 담아 resolve하는 새로운 프로미스를 반환함
-프로미스의 처리가 하나라도 실패하면 가장 먼저 실패한 프로미스가 reject한 에러를 reject하는 새로운 프로미스를 즉시 반환함
/*
Promise.all()
- 프로미스가 담겨 있는 배열 등의 이터러블을 인자로 전달 받음
- 전달받은 모든 프로미스를 병렬로 처리하고 그 처리 결과를 resolve하는 새로운 프로미스를 반환함
*/
//
Promise.all([
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 3000)), // 1
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 2000)), // 2
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 1000)) // 3
]).then(console.log) // [1,2,3]
.catch(console.log); // Error: Error 3!
/* 예제) github id로 github 사용자 이름을 취득하기 */
const githubIds = ['jeresig', 'ahejlsberg', 'ungmo2'];
Promise.all(githubIds.map(id => fetch(`https://api.github.com/users/${id}`)))
// [Response, Response, Response] => Promise
.then(responses => Promise.all(responses.map(res => res.json())))
// [user, user, user] => Promise
.then(users => users.map(user => user.name))
// [ 'John Resig', 'Anders Hejlsberg', 'Ungmo Lee' ]
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.log);3. Promise.race
-
Promise.all메소드와 동일하게 프로미스가 담겨 있는 배열 등의 이터러블을 인자로 전달 받는다. -
모든 프로미스를 병렬 처리하는 것이 아니라 가장 먼저 처리된 프로미스가
resolve한 처리 결과를resolve하는 새로운 프로미스를 반환한다 -
Promise.race 메소드에 전달된 프로미스 처리가 하나라도 실패하면 가장 먼저 실패한 프로미스가
reject한 에러를reject하는 새로운 프로미스를 즉시 반환한다.
Promise.race([
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 3000)), // 1
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 2000)), // 2
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 1000)) // 3
]).then(console.log)
.catch(console.log); // Error: Error 3!출처
https://poiemaweb.com/es6-promise
https://sangminem.tistory.com/284
https://velog.io/@parkseonup/JS-%EB%B3%80%EC%88%98%EB%AA%85%EC%97%90-%EC%82%AC%EC%9A%A9%EB%90%9C-%EB%8B%AC%EB%9F%AC-%EA%B8%B0%ED%98%B8%EC%9D%98-%EC%9D%98%EB%AF%B8
https://www.daleseo.com/js-document-query-selector/
https://ko.javascript.info/promise-basics
