Callback
const delay = (wait, callback) => {
setTimeout(callback, wait);
}
function runCallback() {
resetTitle();
playVideo();
delay(1000, () => {
pauseVideo();
displayTitle();
delay(500, () => {
highlightTitle();
delay(2000, resetTitle);
});
});
}Promise
const sleep = (wait) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("hello");
}, wait);
});
};
function runPromise() {
resetTitle();
playVideo();
sleep(1000)
.then((param) => {
console.log(param);
pauseVideo();
displayTitle();
return "world";
})
.then((param) => {
console.log(param);
return sleep(5000);
})
.then(highlightTitle)
.then(sleep.bind(null, 2000))
.then(resetTitle)
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
});
}개념
Javascript에서 비동기를 간편하게 처리해 주는 내장 오브젝트
➡️ 콜백함수 대신 편리하게 사용
핵심 개념 ① 상태(state)
Q6. Promise의 세 가지 상태는 각각 무엇이며, 어떤 의미를 가지나요?
프로미스의 상태란 프리미스의 처리 과정을 의미한다.
new Promise()로 프로미스를 생성하고 종료 될때까지 3가지 상태를 갖는다.
Pending(대기): 비동기 처리 로직이 아직 완료되지 않은 상태
Fulfiled(이행): 비동기 처리가 완료되어 프로미스가 결과 값을 반환해준 상태
Rejected(실패): 비동기 처리가 실패하거나 오류가 발생한 상태
핵심 개념 ② Producer vs Consumer
- Producer(생산자): 새로운 프로미스가 생성되면, executor가 자동으로 실행된다.
- Consumers(소비자): then, catch, finally
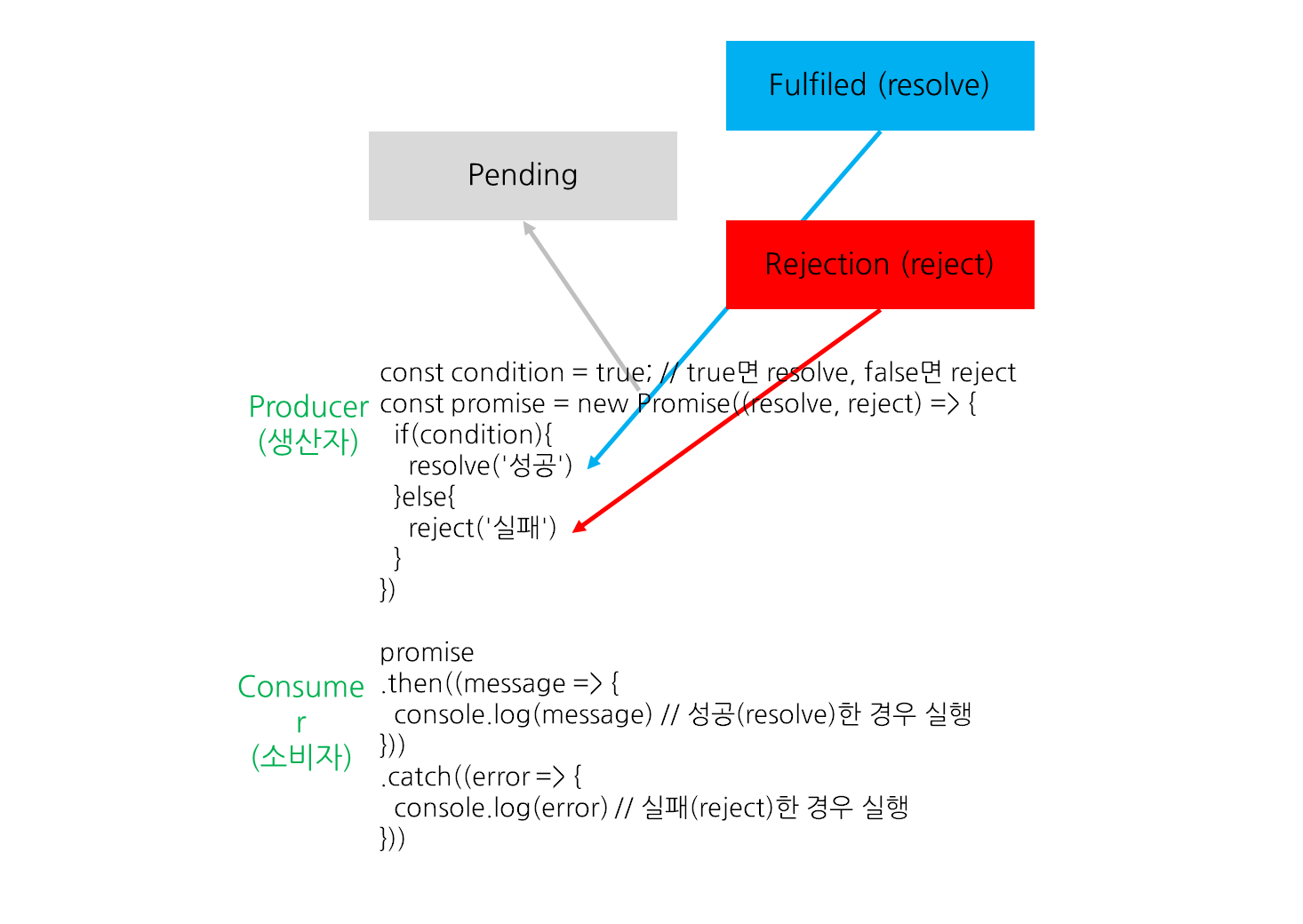
✅ "new Promise로 Promise를 생성한 다음, resolve한 값을 then 으로 넘겨준다"
const condition = true; // true면 resolve, false면 reject
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(condition){
resolve('성공')
}else{
reject('실패')
}
})
promise
.then((message => {
console.log(message) // 성공(resolve)한 경우 실행
}))
.catch((error => {
console.error(error) // 실패(reject)한 경우 실행
}))Q1. Promise 실행 함수가 가지고 있는 두 개의 파라미터 resolve 와 reject 는 각각 무엇을 의미하나요?
new Promise로 프로미스를 생성할 수 있으며, 안에 resolve와 reject를 매개변수로 갖는 콜백함수를 넣어준다.
이렇게 만든 promise 변수에 then과 catch 메서드를 붙일 수 있다.
promise 내부에서 resolve가 호출되면 then이 실행되고, reject가 호출되면 catch가 실행된다.
Q2. resolve, reject함수에는 전달인자를 넘길 수 있습니다. 이때 넘기는 전달인자는 어떻게 사용할 수 있나요?
resolve와 reject에 넣어준 인자는 각각 then과 catch의 매개변수에서 받을 수 있다.
즉, resolve('성공')가 호출되면 then의 message가 '성공'이 된다.
만약 reject('실패')가 호출되면 catch의 error가 '실패'가 된다.
Q4. Promise.prototype.then 메서드는 무엇을 리턴하나요?
Q5. Promise.prototype.catch 메서드는 무엇을 리턴하나요?
function runPromise() {
resetTitle();
playVideo();
sleep(1000)
.then((param) => {
console.log(param);
pauseVideo();
displayTitle();
return "world";
})
.then((param) => {
console.log(param);
return sleep(5000);
})
.then(highlightTitle)
.then(sleep.bind(null, 2000))
.then(resetTitle);
}then이나 catch에서 다시 다른 then이나 catch를 붙일 수 있다.
이전 then의 return 값을 다음 then의 매개변수로 넘긴다.
(프로미스를 return한 경우 프로미스가 수행된 후 다음 then이나 catch가 호출된다.)
- resolve 호출 ➡️ then 실행
const sleep = (wait) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("hello");
}, wait);
});
};hello
world- reject 호출 ➡️ catch 실행
const sleep = (wait) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error("에러"));
}, wait);
});
};Error: 에러Callback과 비교해 Promise는...
코드의 깊이가 더 이상 깊어지지 않는다.
(Callback Hell 🧟♀️)
then 메서드들은 순차적으로 실행된다.
콜백에서 매번 따로 처리해야 했던 에러도 마지막 catch에서 한 번에 처리할 수 있다.
Promise Method (부제: 프로미스 여러 개를 한 번에 실행하기)
Q3. new Promise()를 통해 생성한 Promise 인스턴스에는 어떤 메서드가 존재하나요? 각각은 어떤 용도인가요?
const promise1 = Promise.resolve('성공1');
const promise2 = Promise.resolve('성공2');
Promise.all([promise1, promise2])
.then((result) => {
console.log(result); // ['성공1', '성공2']
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
})Promise.resolve()
즉시 resolve 하는 프로미스를 만든다.
Promise.reject()
즉시 reject 하는 프로미스를 만든다.
✨ Promise.all()
프로미스가 여러 개 있을 때 모두 resolve될 때까지 기다렸다가 then 으로 넘어간다.
result 매개변수에 각각의 프로미스 결과값이 배열로 들어 있다.
Promise 중 하나라도 reject 되면 catch로 넘어간다.

✏️ 종합퀴즈
문제 10)
Promise.all에 대한 설명으로 옳지 않은 것을 고르세요.
정답)
A. Promise.all의 전달인자는 배열이다.
B. Promise.all은 동시에 두 개 이상의 Promise 요청을 한꺼번에 실행하는 함수이다.
✔️ C. Promise.all에 두 개 이상의 Promise 요청이 전달될 때, 직전 Promise 요청이 거부 되어도 다음 Promise 요청은 then 메서드를 따라간다.
D. Promise.all의 전달인자에 배열이 전달된다면, 요소 순서는 Promise.all의 Promise 순서와 상응한다.
풀이)
Promise.all 에 전달되는 Promise는 어느 하나라도 거부되는 순간 모든 요청이 거부됩니다. 따라서 직전 Promise가 거부된 직후에, 그 다음 요청이 then 메서드를 따라가는 것이 아니라, 모든 Promise 요청이 거부되면서 catch 메서드를 따라가게 됩니다.
async/await
Q7. await 키워드 다음에 등장하는 함수 실행은 어떤 타입을 리턴할 경우에만 의미가 있나요? => 프로미스
Q8. await 키워드를 사용할 경우, 어떤 값이 리턴되나요?
const sleep = (wait) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("hello");
}, wait);
});
};
async function runAsync() {
try{
resetTitle();
playVideo();
await sleep(1000);
pauseVideo();
displayTitle();
await sleep(500);
highlightTitle();
await sleep(2000);
resetTitle();
}catch(err){
console.log(err);
}
}함수 선언부를 일반 함수 대신 async function으로 교체한 후, 프로미스 앞에 await을 붙여준다.
함수는 해당 프로미스가 resolve될 때까지 기다린 뒤 다음 로직으로 넘어간다.
try/catch문의 catch를 사용해 에러를 처리한다.
- 일반 함수로 표현
async function runAsync() {
resetTitle();
playVideo();
await sleep(1000);
pauseVideo();
displayTitle();
await sleep(500);
highlightTitle();
await sleep(2000);
resetTitle();
}- 화살표 함수로 표현
const runAsync = async () => {
resetTitle();
playVideo();
await sleep(1000);
pauseVideo();
displayTitle();
await sleep(500);
highlightTitle();
await sleep(2000);
resetTitle();
}Promise과 비교해 async/await은...
비동기 함수를 마치 동기 함수처럼 코드를 작성한다. ➡️ 코드 가독성 ↑
그러나 실제로는 Promise를 이용하여 결과를 리턴한다.
중첩되는 콜백함수가 있다면 프로미스를 거쳐 async/await 문법으로 바꾸는 연습을 해보자!
코드가 훨씬 간결해질 것이다.
