[참고문헌]
- https://peps.python.org/pep-0008/
- https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html
- https://www.w3schools.com/python/
파이썬이 실행되는 과정
파이썬 명령문
-> 파이썬 컴파일러
-> 바이트코드(.pyc)
-> 파이썬 인터프리터(가상머신)
-> 저급 기계어
-> CPU
Built-in Data Types
text type
- str
numeric types
- int: integers = 정수
4- float: floating point numbers(double in C) = 실수
3.4- complex: a real part + an imaginary part(each a floating point numbers) = 복소수
10.4jsequence types
- list: mutable(liable to change)
[[1], 2, [3, 4], 5.6]-
파이썬 공식 문서에서 hash 관련 내용
immutable sequence type에서는 지원하고 mutable sequence type은 지원하지 않는 기능은 hash()뿐
-
tuple: immutable, hashable
- iteration과 accessing에 있어 list에 비해 빠르다
- 해싱이 가능하므로 dictionary의 key로 사용 가능
- 해싱이란?: 많은 양의 데이터를 하나의 integer와 같이 작은 양의 데이터로 변환해주는 알고리즘, O(1)의 시간 복잡도 안에 자료를 찾을 수 있는 것이 장점
- 해시 알고리즘으로부터 얻은 hash key가 변할 수 있다면 해시테이블과 같은 자료구조(data structure) 내에서 객체가 저장된 위치 또한 변함
- 실제로 element가 hashable한지와 무관하게 hash 가능
x = 5, # 쉼표로 tuple 타입을 선언(괄호는 가독성을 위한 것)
(1, 2, 3)
([1, 2], [3, 4]) # hash 기능 사용 가능하지만 element가 list이므로 hashable x- range: immutable sequence of numbers (commonly used for looping in for loops)
class range(stop)
class range(start, stop[, step])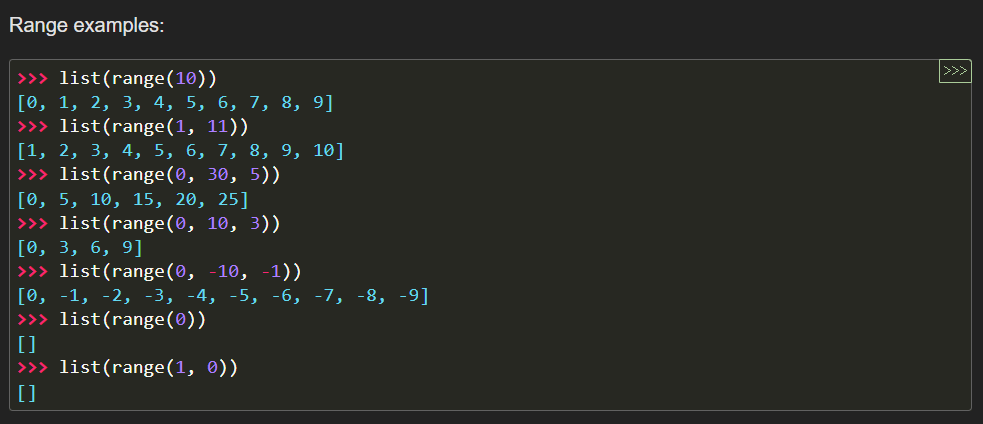
mapping type
- dict: for storing key-value pairs, unordered, mutable
set types
- set: unordered collection of unique items, mutable
- frozenset: immutable set
boolean type
- bool: True or False
binary types
- bytes: sequences of bytes (integers from 0 to 255)
- bytearray: mutable bytes
- memoryview: a view into an array's buffer
none type
- NoneType: absence of a value of a null value
Syntax
condition
- if, elif, else
- 삼항조건식: A if B else C
loop
- while
- continue: 해당 조건이 발생하면 다음 루프 실행
- break: 반복 종료
- for
- list comprehension: [a.value for a in aList]
- enumerate: returns a tuple containing a count and the values
errors and exceptions
try:
do_something()
except Exception as err:
print('unexpected error: ' + err)PEP 8
- indentation: 4 spaces (not tabs)
- comments
- 모순되는 주석은 없는 주석보다 더 나쁘다. 코드가 바뀌면 항상 주석도 고쳐야 한다.
- block comments:
- 주석 아래의 코드를 설명하기 위해 사용되는 경우가 많다
- #과 스페이스 한 칸으로 시작# comment code1 code2 code3``` - inline comments: 코드에서 스페이스 2칸 띄우고 시작
code # comment
- docstrings: 공공에 제공하는 모듈/메서드/클래스가 아니면 반드시 필요하지는 않으나, document string이 없다면 주석은 써야 한다.
"""docstring
explain something
"""-
variable: 변수는 값(value)을 저장하기 위한 그릇(container)이다.
-
변수 할당 시 타입을 선언하지 않아도 된다.
x = "Hello" y = 6 print(type(x)) # <class 'int'> print(type(y)) # <class 'str'> -
타입을 명시하거나 형변환을 하고 싶으면 캐스팅casting을 사용한다.
x = str(3) # x will be '3' y = int(3) # y will be 3 z = float(3) # z will be 3.0 -
한 줄에 여러 변수를 할당할 수도 있다. (권장x)
x, y, z = '10', 9, 7.0
-
