Static
can be used without calling obj
public class RoundStuff
{
public static final double PI = 3.14
public static final double area(double radius)
{
return ( PI * ~~~)
}
}
public class RoundStuffDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println( RoundStuff.area(radius) + "square inches.");
}static method :
-cannot refer to an instance variable of the class
-cannot invoke a non-static method of the class
-a static method can invoke another static method
-a static method has no this (static method belongs to class area, so no instance created)
static variables:
-belongs to the class as a whole, and not just to one obj
-there's only one copy of a static variable per class (cf. each obj has its own copy of instance variables)
-all obj of the class can read and change a static variable
-a static method can access static variable
-static variables can be used in static, non static both
-non static variables cannot be used in static
private static int myStaticVariable;
-declared and initialized at the same time (recommended) / if not, explicitly initialized
private static int myStaticVariable = 0;
-a static variable should always be defined private
exception: constant ( pi=3.14, BIRTH_YEAR = 1954 ...)
math class
no import needed
all methods & data are static
pow a b a 의 b승
abs 절대값
min
max
round 반올림
ceil 올림
floor 버림
sqrt 제곱
Wrapper Classes
boxing
Byte bObj = 5;
Short sObj = 15;
unboxing
byte b = bObj.byteValue();
short s = sObj.shortValue();
short s = sObj; //automatic unboxing
Integer.MAX_VALUE, MIN
Double.MAX_VALUE, MIN
Boolean.TRUE
parseInt
parseDouble
toString
char toUpperCase
char toLowerCase
boolean isUpperCase, Lower
boolean isWhitespace
boolean isLetter
boolean isDigit
boolean isLetterOrDigit
References
main memory consists of a long list of num address called byte
memory location: entire chunk of memory that holds the data
reference: memory address where an obj is located
class type = reference type

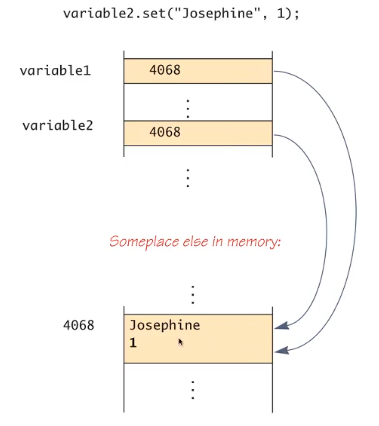
variable1과 variable2가 같은 주소를 가짐, 같은 변수를 갖게됨
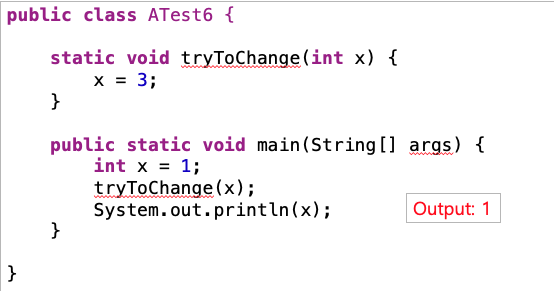
call by value - parameters in java
any change to the value of the parameter cannot change the value of its argument
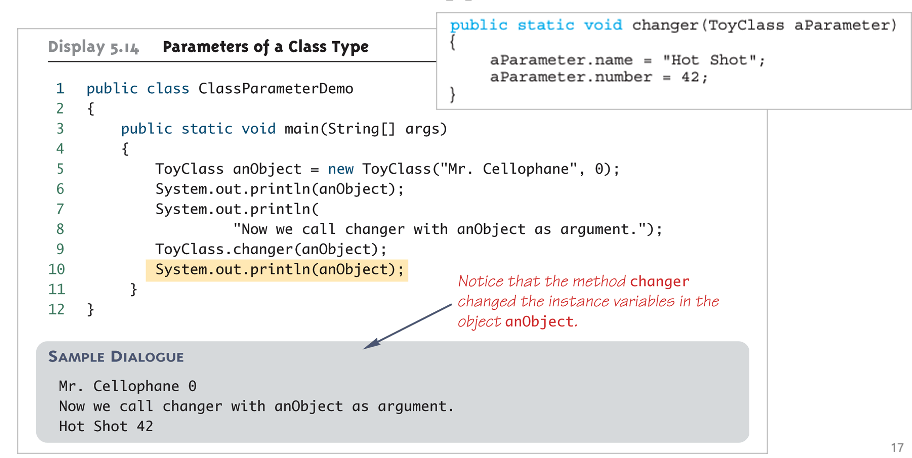
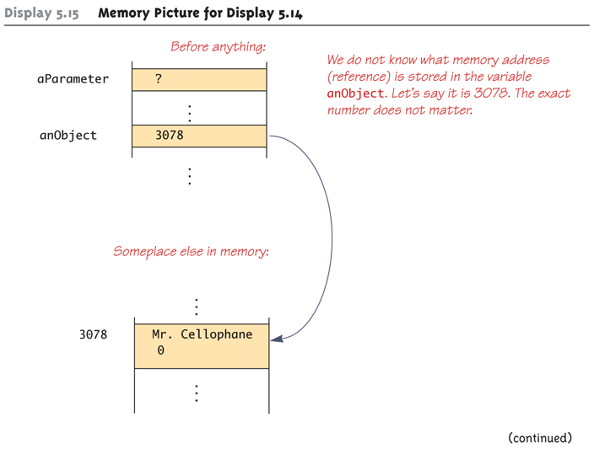
call by reference - class type parameters
any change to the value of parameter can change the value of its argument
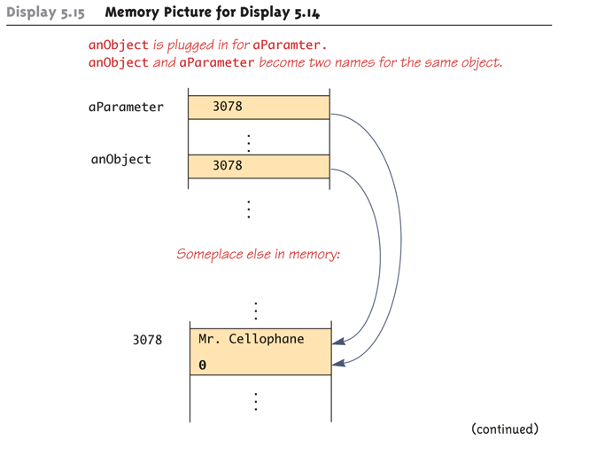
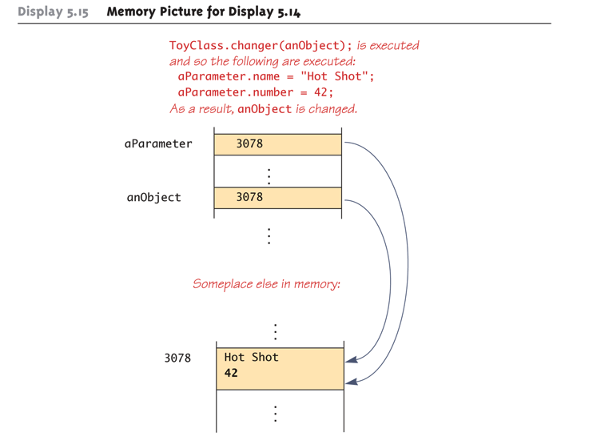
Pitfall: use of == with variables of a class type

constant null
special constant that may be assigned to a variable of any class type
method cannot be invoked using a variable that is initialized to null
anonymous obj

usingMisusingReferences (중요)
public Person(Person original)
{
if (original == null)
{
System.out.println("Fatal error.");
System.exit(0);
}
name = original.name;
born = new Date(original.born);
if (original.died == null)
died = null;
else
died = new Date(original.died);
}Person class:
obj of the class Person has a date of birth(not null)
date of death is equal to or later than the date of birth
copy constructors
should create an obj that is a separate, independent
values are same as original
Privacy Leaks
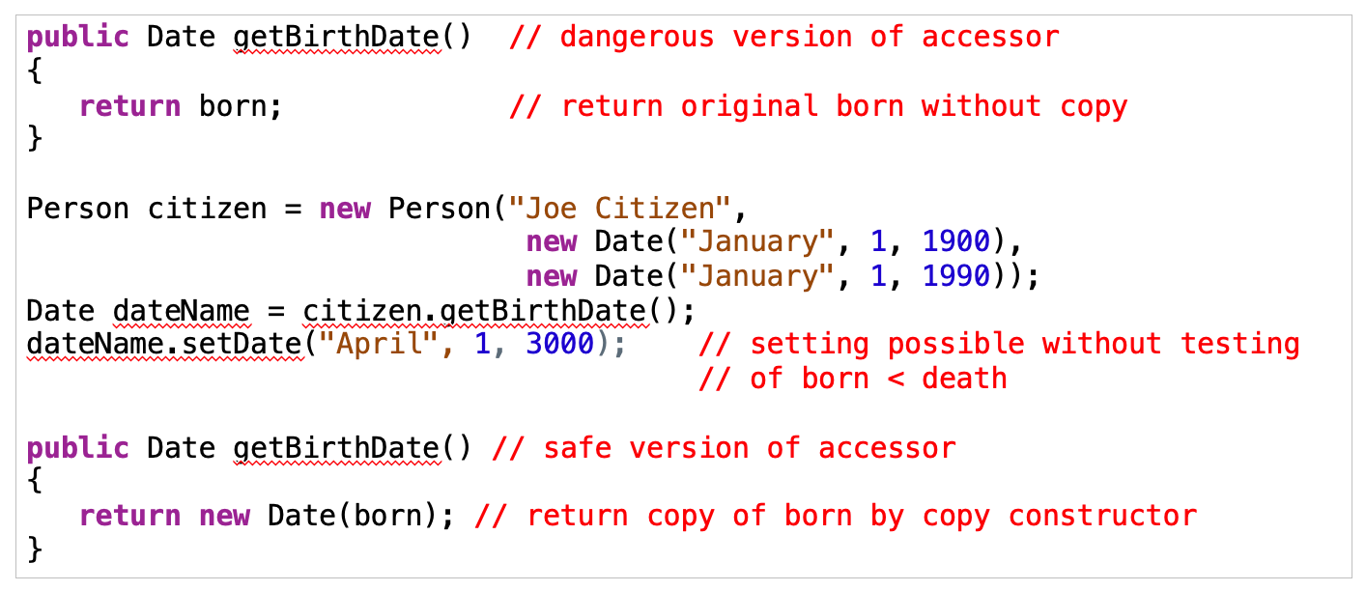
string은 copy constructors 안써도댐
Mutable & Immutable Classes
class String contains no mutator methods that can change any of the data in a String obj
String is immutable class
Deep copy vs Shallow copy
Deep copy: copy that has no references in common with the original (예외: immutable obj)
Shallow copy: not a deep copy, can cause dangerous privacy leak
Packages and Javadoc
- import A.B.C;
- import A.B.*;
2번이 1번을 포함하지 않음
java.lang
contains fundamental classes (Math, String, wrapper ...)
import automatically
javadoc
automatically produce documentation
/**
@param
@return
@throws
@deprecated
@see
@author
@version
*/ to run javadoc, give the following command in console
javadoc -d Documentation_Directory Package_Name
javadoc ClassName.java
javadoc *.java
