
Git
1. Getting Started with Git for Windows
To begin using Git on Windows, you need to download and install it. Here’s how:
- Download Git for Windows: Visit Git for Windows website to get the latest version.
- Installation: After downloading, run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
Once Git is installed, you’ll have access to Git Bash, a terminal where you can execute Git commands.
2. Basic Git Commands
Git is a powerful tool that allows developers to manage changes to code repositories.
- git clone
This command allows you to copy an existing repository from a remote source (like GitHub) to your local machine. This is typically the first command you run when you want to start working on an existing project.
- git add
This command stages all changes made in the repository. The . signifies all files in the current directory and subdirectories.
- git status
Use this to check the status of your working directory. It tells you which files have been modified, staged, or are untracked.
- git commit -m "message"
This commits your staged changes with a message. It’s best practice to use a meaningful commit message describing what was changed.
- git push
Pushes your local commits to the remote repository, making them available to others.
- git pull
Fetches and merges changes from the remote repository to your local repository, keeping you up to date with the latest changes made by others.
Github
1. Configuring GitHub SSH Access
If you plan to push and pull code to/from GitHub, you’ll need to set up SSH keys for secure access. Here’s how:
Generate an SSH Key:
-
Open Git Bash.
-
Run the following command:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_email@example.com"
-
This will create a new SSH key pair. By default, it will be stored in C:/Users/user/.ssh/
Deploy the SSH Key on GitHub:
- Open the file id_ed25519.pub in a text editor, and copy its contents.
- Go to your GitHub account, and navigate to Settings > SSH and GPG keys.
- Click New SSH key, paste your copied key, and save.
Testing SSH Connection:
You can test the connection with:
ssh -T git@github.com
If successful, you'll see a message confirming that you've authenticated.
2. Git User Settings: Email and Name
Git associates your commits with a name and email. You can set these globally so they apply to all repositories:
git config --global user.email "your_email@example.com"
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
This ensures that every commit you make is properly attributed to you.
3. Issue Template settings
Github provides issue template in order to help users submit detailed bug reports or feature requests.
Go to the Repository and go to Settings > Features > Issues > Set up template.
you will fine the add template button to add issue templates.
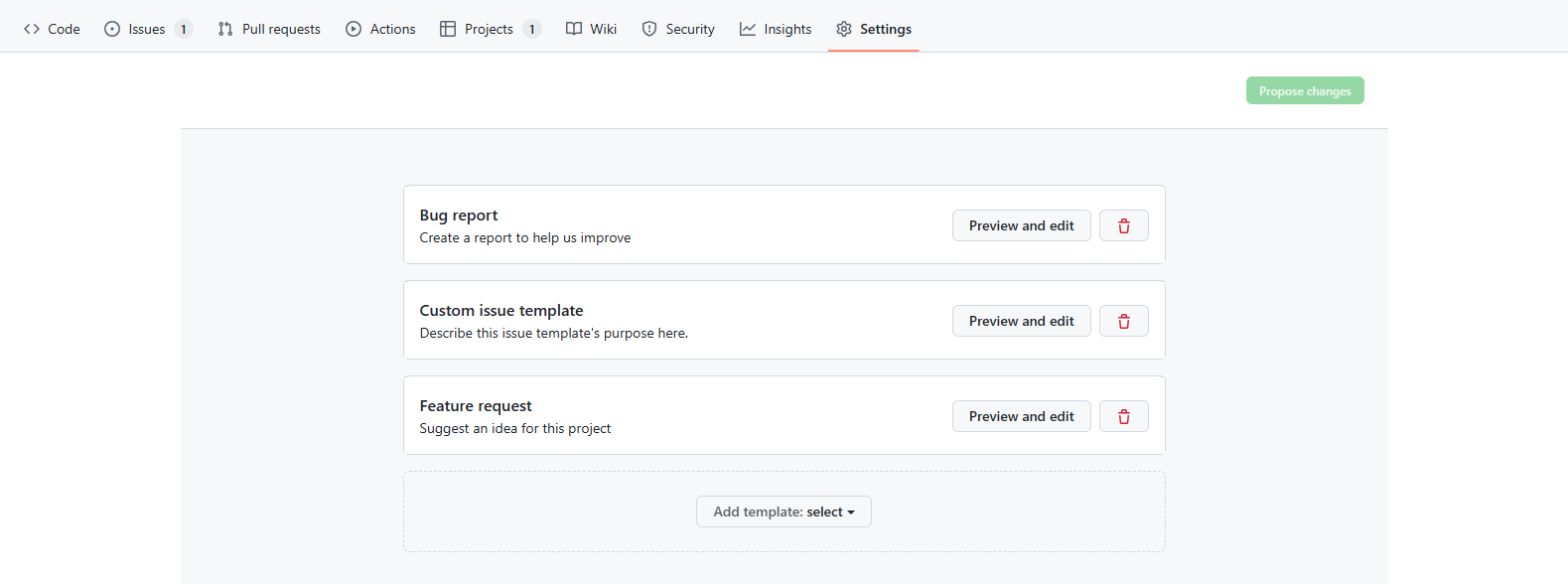
After you add templates, the issue template setting files are going to be created in .github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/.
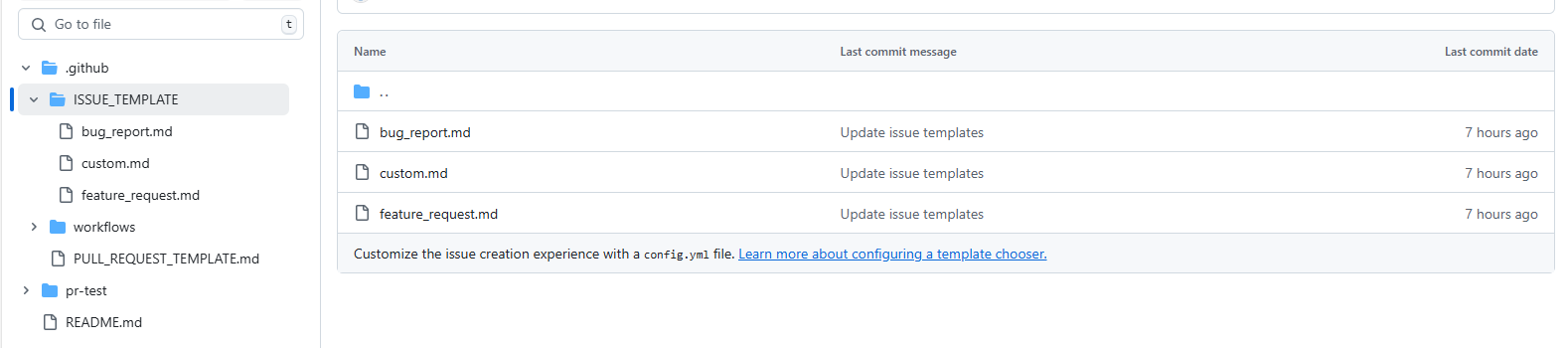
4. Pull Request Template settings
A pull request is a way to propose changes from one branch to another (typically from a feature branch to the main branch). You can set a template for PRs in your repository with the following steps:
- Create PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md file in .github/
- Add your template structure to help maintain consistent PR descriptions.
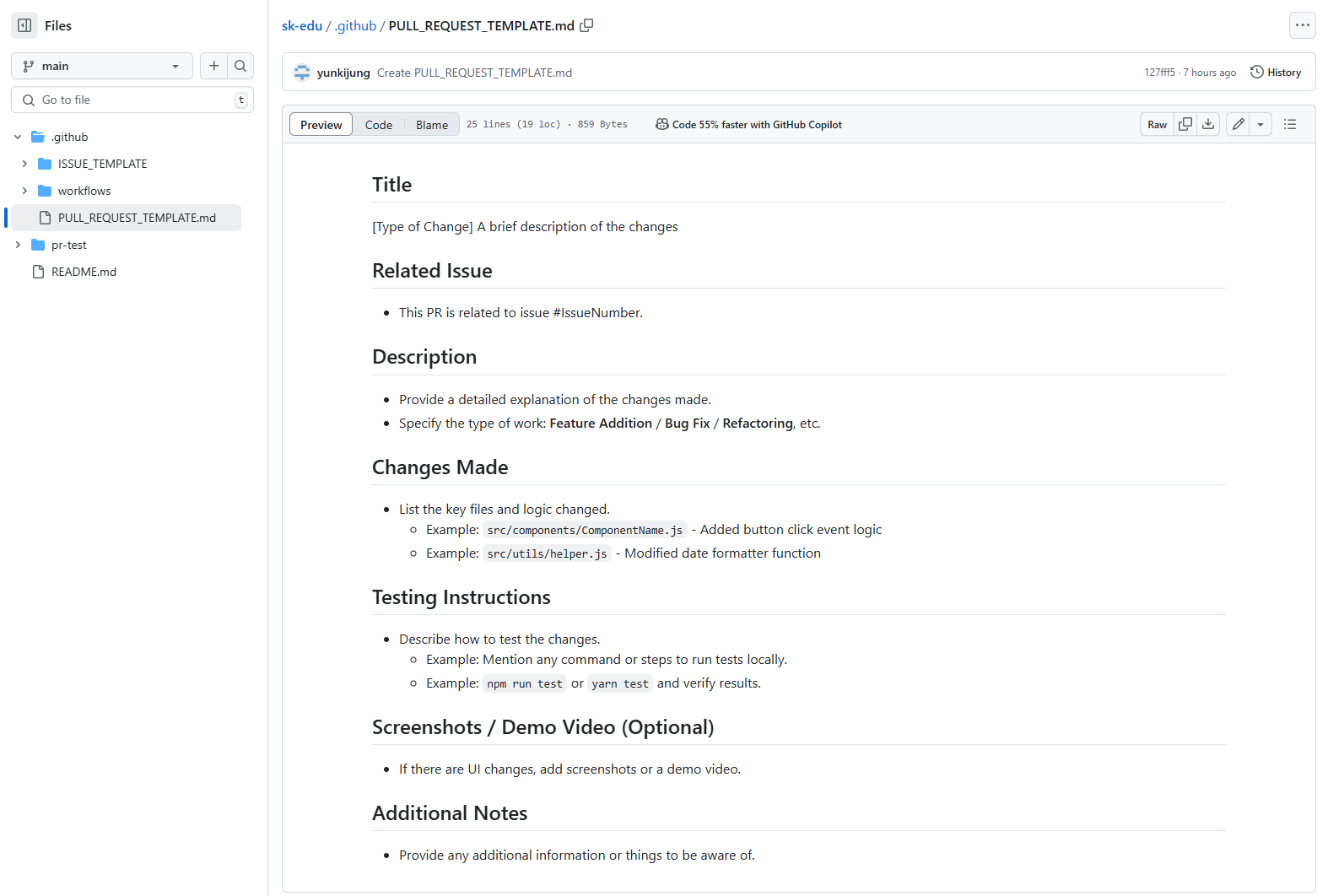
The template will show up when you create pull request.
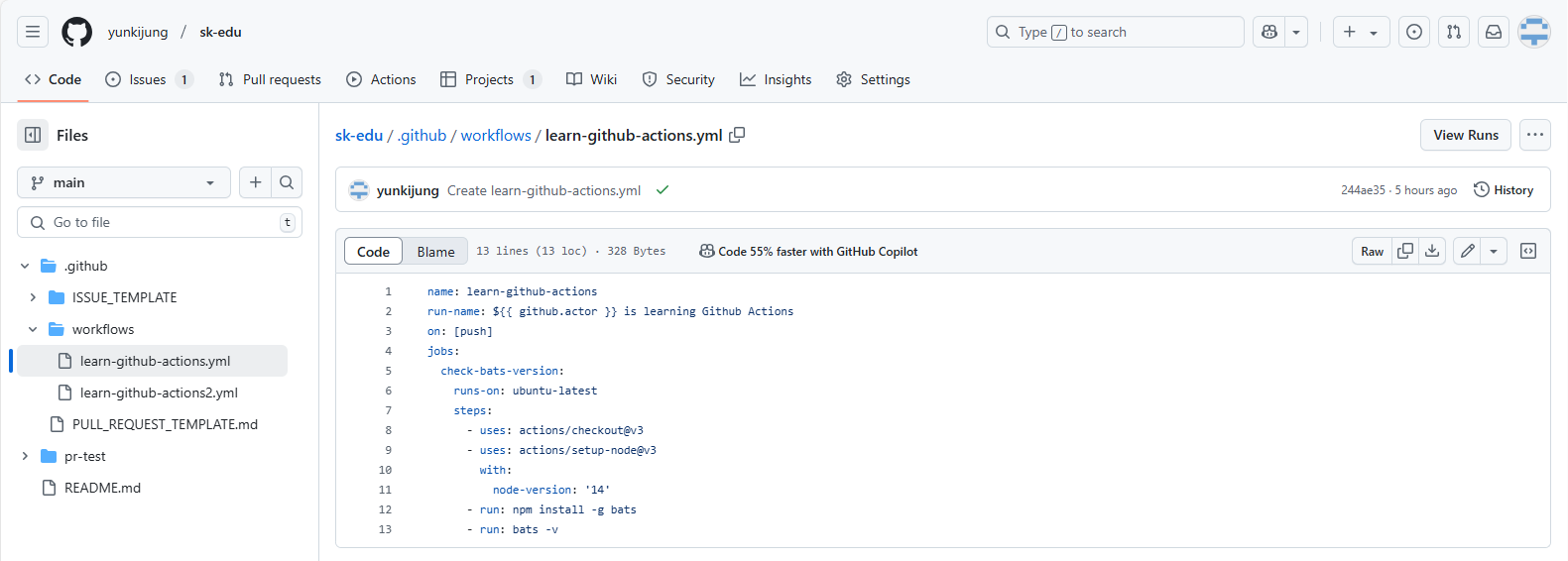
5. Automating Workflows with GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions automates your development workflow by running scripts when specific events occur. For example, you can set up actions to automatically test your code when you push changes.
- Create a .github/workflows/workflowname.yml file in your repository.
- Define the action workflow with specific steps, such as setting up dependencies or running tests.
GitHub Projects: Organizing Work and Tracking Progress
GitHub Projects provides a powerful way to organize and track your development process. It allows you to create boards (similar to Trello) where you can organize tasks, issues, and pull requests. Here's a breakdown of how to use GitHub Projects:
- Go to your GitHub repository.
- Click on the Projects tab.
- Click New Project to create a project board.
- Choose from Basic Kanban, Automated Kanban, or Bug Triage templates, or start with a blank project.