
Passage Embedding
Passage Embedding은 텍스트의 일부분을 고차원 공간의 벡터로 표현하는 방법으로, 의미적으로 유사한 패시지가 유사한 벡터 표현을 갖도록 한다. 패시지 임베딩은 문장의 맥락적인 의미를 담아 정보 검색, 질문 응답, 의미 검색 등의 자연어 처리 작업에 쓰인다.
그 중에서도 Retrieval(검색)의 과정으로 질문과 지문을 임베딩하여 질문과 유사한 지문을 가져오기 위해 Passage Embedding을 사용한다.
Sparse Embedding
벡터화(임베딩)된 Passage를 이용하여 Passage 간 유사도 등을 알고리즘으로 계산할 수 있다. 이번 포스트에서는 Sparse Embedding을 통해 passage를 벡터로 표현하고 유사도를 구하는 방법을 설명한다.
Bag-of-Words (BoW)
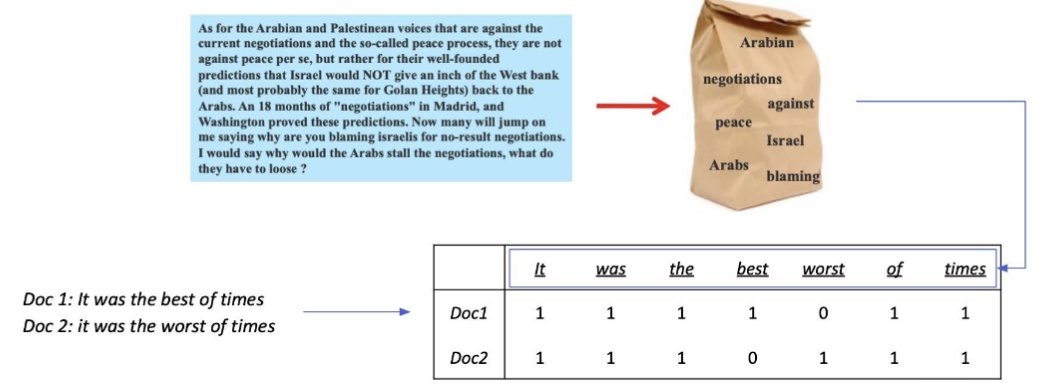
- BoW를 구성하는 방법 → n-gram
1. unigram(1-gram): It was the best of times → It, was, the, best, of, times
2. bigram(2-gram): It was the best of times → It was, was the, the best, best of, of times
TF-IDF (Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency)
Term Frequency(TF): 단어의 등장빈도
Inverse Document Frequency(IDF): 단어가 제공하는 정보의 양
ex) It was the best of times
→ It, was, the, of: 자주 등장하지만 제공하는 정보량이 적음
→ best, times: 좀 더 많은 정보를 제공
- Term Frequency (TF)
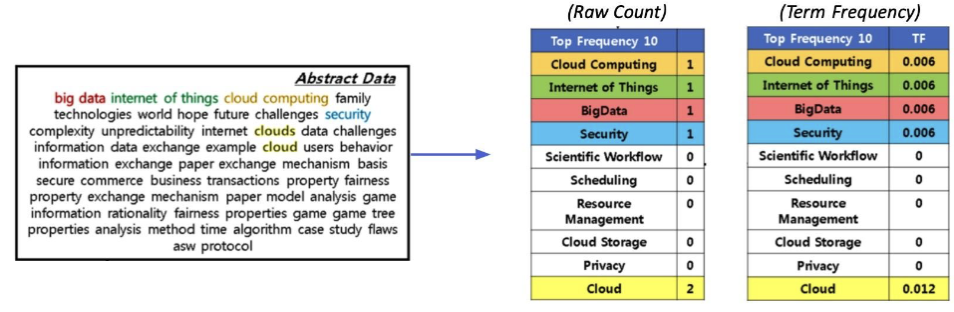
- Raw count
- Adjusted for doc length (TF): raw count / num words
-
Inverse Document Frequency (IDF)
Document Frequency (DF): Term t가 등장한 document의 개수
N: 총 document의 개수
-
Combine TF & IDF
TF-IDF(t, d): TF-IDF for term in document ,
TF-IDF 이해하기
i) ‘a’, ‘the’ 등 관사 ⇒ Low TF-IDF: TF는 높을 수 있지만, IDF가 0에 가까울 것 (거의 모든document에 등장 ⇒ N ≈ DF(t) ⇒ log(N / DF) ≈ 0)
ii) 자주 등장하지 않는 고유명사 (ex. 사람이름, 지명 등) ⇒ High TF-IDF: IDF가 커지면서 전체적인 TF-IDF값이 증가
TF-IDF를 이용해 유사도 구해보기
목표: 계산한 문서 TF-IDF를 가지고 질의 TF-IDF를 계산한 후 가장 관련있는 문서를 찾기
- 사용자가 입력한 질의를 토큰화
- 기존에 단어 사전에 없는 토큰들은 제외
- 질의를 하나의 문서로 생각하고, 이에 대한 TF-IDF계산
- 질의 TF-IDF값과 각 문서별 TF-IDF값을 곱하여 유사도 점수 계산
- 가장 높은 점수를 가지는 문서 선택
BM25
TF-IDF의 개념을 바탕으로, 문서의 길이까지 고려하여 점수를 매김
- TF 값에 한계를 지정해두어 일정한 범위를 유지하도록 함
- 평균적인 문서의 길이 보다 더 작은 문서에서 단어가 매칭된 경우 그 문서에 대해 가중치를 부여
- 실제 검색엔진, 추천 시스템 등에서 아직까지도 많이 사용되는 알고리즘
Sparse Embedding 특징
- Dimension of embedding vector = number of term
- 등장하는 단어가 많아질수록 증가
- N-gram의 n이 커질수록 증가 → 더 다양한 조합이 발생
- Term overlap을 정확하게 잡아내야 할 때 유용
- 반면, 의미(semantic)가 비슷하지만 다른단어인 경우 비교가 불가
TF-IDF Passage Retrieval
데이터 불러오기
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("squad_kor_v1")데이터 확인 및 토큰화
[Input]
corpus = list(set([example['context'] for example in dataset['train']]))
print("context_sample:", corpus[0])
tokenizer_func = lambda x: x.split(' ')
tokenized_sample = tokenizer_func(corpus[0])[:10]
print("tokenized_sample:", corpus[0])[output]
>> context_sample: 데스몬드 도스는 교회의 창문을 갈던 중 차에 깔린 남자를 발견하고 병원으로 데려가 그의 목숨을 구한다. ...
tokenized_sample: ['데스몬드', '도스는', '교회의', '창문을', '갈던', '중', '차에', '깔린', '남자를', '발견하고']TF-IDF Embedding
[Input]
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer_func, ngram_range=(1,2))
vectorizer.fit(corpus)
sparse_matrix = vectorizer.transform(corpus)
print(sparse_matrix.shape)[output]
>> (9606, 1272768)ngram_range=(1,2)은 벡터화할 때 unigram과 bigram을 모두 포함하는 경우를 말한다.
ngram_range=(1, 1) → unigram만 사용 (단어 하나씩만)
ngram_range=(1, 2) → unigram + bigram (단어 하나와 두 단어 묶음 모두)
ngram_range=(2, 2) → bigram만 사용 (두 단어 묶음만)
ngram_range=(1, 3) → unigram, bigram, trigram까지 포함
이는 텍스트의 연속된 단어 간의 관계를 더 잘 반영할 수 있도록 도와주는 설정이다.
[Input]
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(sp_matrix[0].T.todense(), index=vectorizer.get_feature_names_out(), columns=["TF-IDF"])
df = df.sort_values('TF-IDF', ascending=False)
print(df.head(10))[output]
>> TF-IDF
도스는 0.297943
헌혈을 0.148971
도스가 0.148971
허리띠를 0.148971
남자를 0.126206
쉬트에게 0.077815
뛰어요'라고 0.077815
꽂은 뒤로 0.077815
내쫓는다. 0.077815
앉는다. 아버지 0.077815희소 행렬: 메모리 효율성이 높음. 0이 아닌 원소들만 저장.
밀집 행렬: 모든 원소를 저장하여 메모리 사용량이 큼. 모든 값을 명시적으로 저장.
todense(): 희소행렬 to 밀집행렬
get_feature_names_out(): n-gram된 텍스트 데이터를 벡터로 변환할 때 사용된 특성 이름 목록을 반환
Passage retrieval with TF-IDF embedding
import random
import numpy as np
random.seed(42)
sample_idx = random.choice(range(len(dataset['train'])))
query = dataset['train'][sample_idx]['question']
ground_truth = dataset['train'][sample_idx]['context'][Input]
query_vec = vectorizer.transform([query])['context']
result = query_vec * sparse_matrix.T # Dot Product로 유사도를 계산한다.
print(query_vec.shape)
print(result.shape)[output]
>> (1, 1272768)
(1, 9606)Top-3개의 passage를 retrieve 하고, 실제 ground_truth와 비교
[Input]
sorted_result = np.argsort(-result.data) # result.data의 값을 내림차순으로 정렬했을 때, 값이 원래 어느 위치에 있었는지를 알려주는 인덱스 배열
doc_scores = result.data[sorted_result]
doc_ids = result.indices[sorted_result]
k = 3
print(sorted_result[:k])
print(doc_scores[:k])
print(doc_ids[:k])[output]
>> array([312, 137, 298])
array([0.16595357, 0.04368785, 0.03937975])
array([2775, 7138, 798], dtype=int32)[Input]
print("[Search query]\n", query, "\n")
print("[Ground truth passage]")
print(ground_truth, "\n")
for i in range(k):
print("Top-%d passage with score %.4f" % (i + 1, doc_scores[i]))
doc_id = doc_ids[i]
print(corpus[doc_id], "\n")[output]
>> [Search query]
구식 군인들의 월급인 쌀에 모래와 돌멩이가 들어가있던 사건을 말미암아 일어난 사태의 이름은?
[Ground truth passage]
1882년 6월 민영익의 귀국 권고로 일시 귀국했다가 다시 되돌아갔다. ...
Top-1 passage with score 0.1660
1882년 6월 민영익의 귀국 권고로 일시 귀국했다가 다시 되돌아갔다. ...
Top-2 passage with score 0.0437
6월 13일, 런던에서 일어난 사태의 소식이 전해지자 하트퍼드셔 세인트올번스 읍도 들끓기 시작했다. ...
Top-3 passage with score 0.0394
그리고 이러한 만민공동회 활동과 관련하여, 독립협회에서 만민공동회에 사주하여 결의한 헌의 6조에 배치되는 활동이 자주 나타났고, ...
