8.3 Variables and Data Types
- Variables in JavaScript are dynamically typed, meaning that you do not have to declare the type of a variable before you use it.
- If you do not specify an initial value its initial value will be undefined.
- JavaScript is a case-sensitive language.(대소문자를 구분하는 언어)
- Case-sensitive: 대소문자를 구분함. (예: JavaScript, Python, Java)
- Case-insensitive: 대소문자를 구분하지 않음. (예: HTML, SQL)
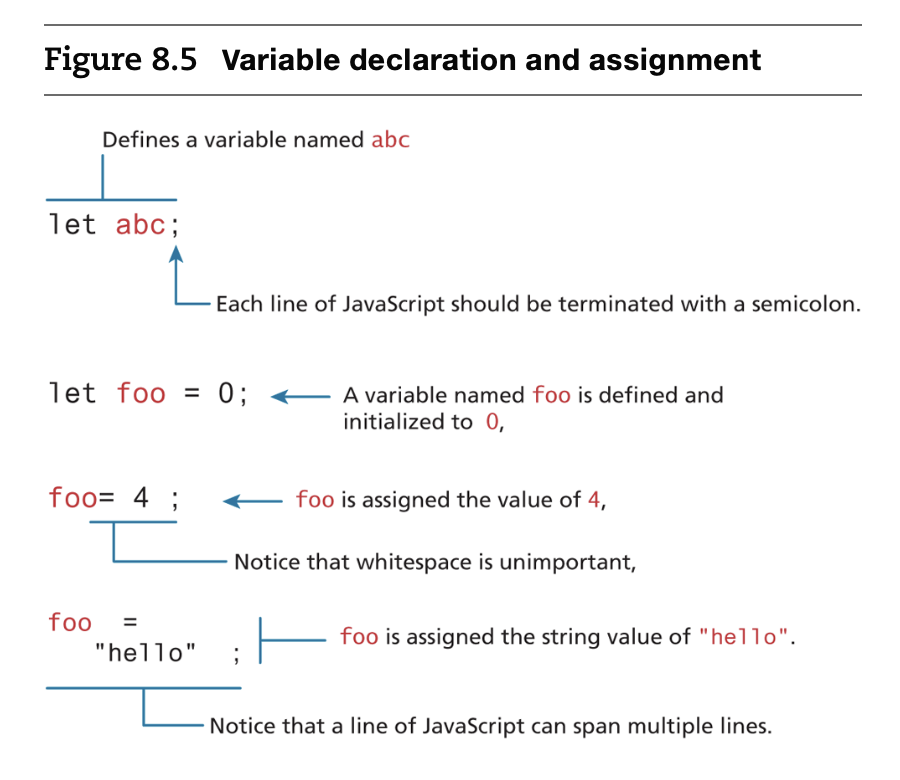
- var & let & const
- If you forget to add the semicolons, the JavaScript engine will still automatically insert them.
- There are two styles of comment in JavaScript, the single-line comment, which starts with two slashes //, and the block comment, which begins with / and ends with /.
- JavaScript accepts a very wide range of symbols within identifier (that is, variable or function) names. An identifier must begin with a $, _, or any character within one of several different Unicode categories
8.3.1 JavaScript Output
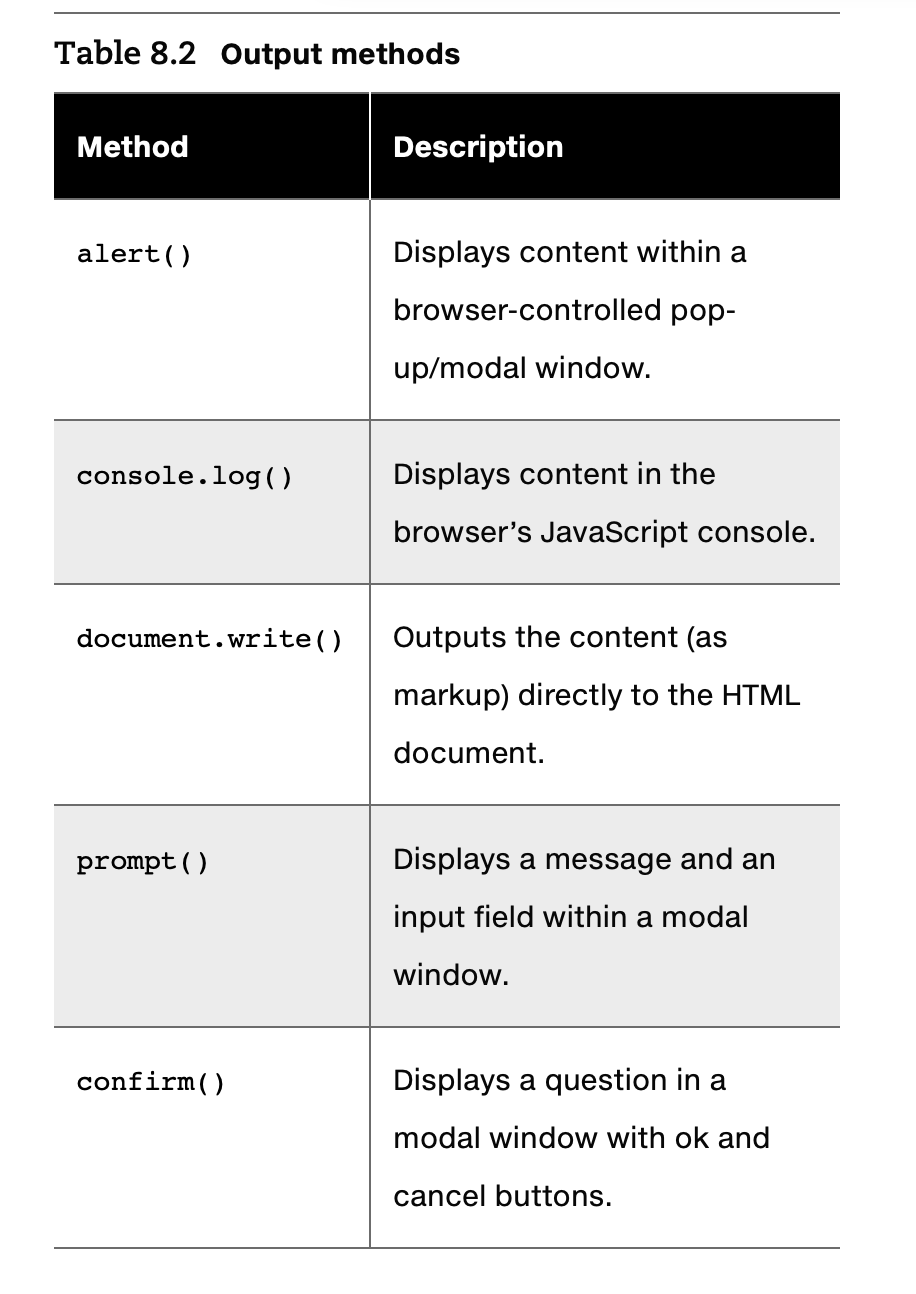
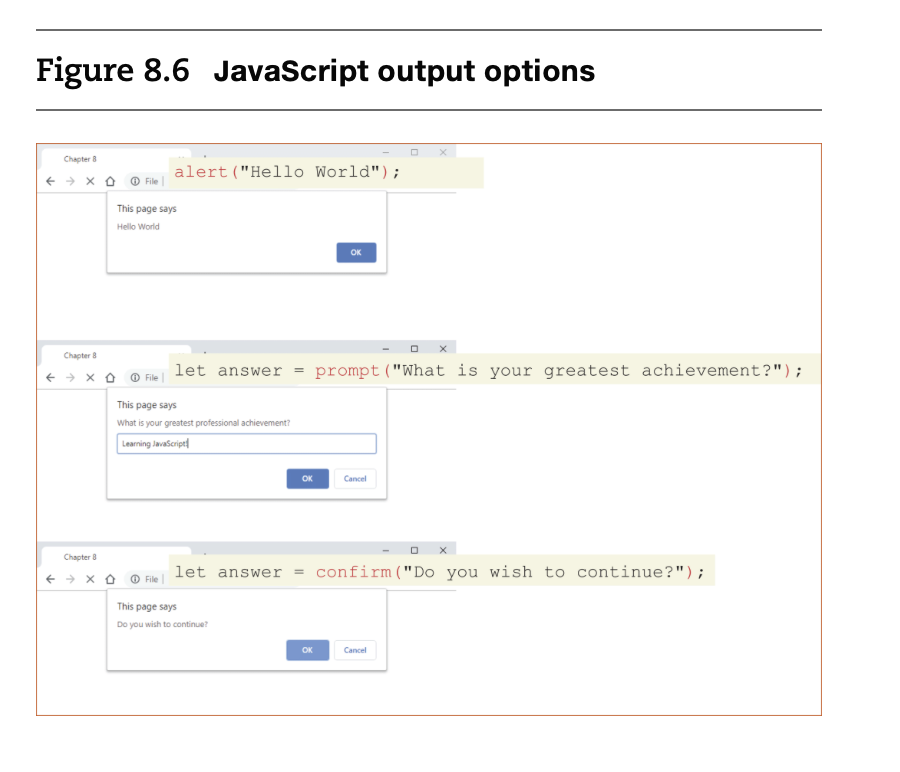
- Alerts are generally not used in production code but provide a quick way to temporarily display or gather simple information. However, using pop-ups can get tedious quickly.
- As an alternative, the examples in this chapter will often use the console.log() method (or one of its related cousins, such as console.warn() or console.dir())
- document.write() method
- often used to output markup or to combine markup with JavaScript variable.

- document.write()의 사용: 문서 스트림에 텍스트를 출력하지만, 출력 위치가 중요합니다.
- 문제점: 출력된 내용은 문서 트리에 추가되지 않기 때문에 JavaScript로 후속 조작이 불가능합니다
- often used to output markup or to combine markup with JavaScript variable.
8.3.2 Data Types
- reference types : array, object, function, class 등
- primitive types
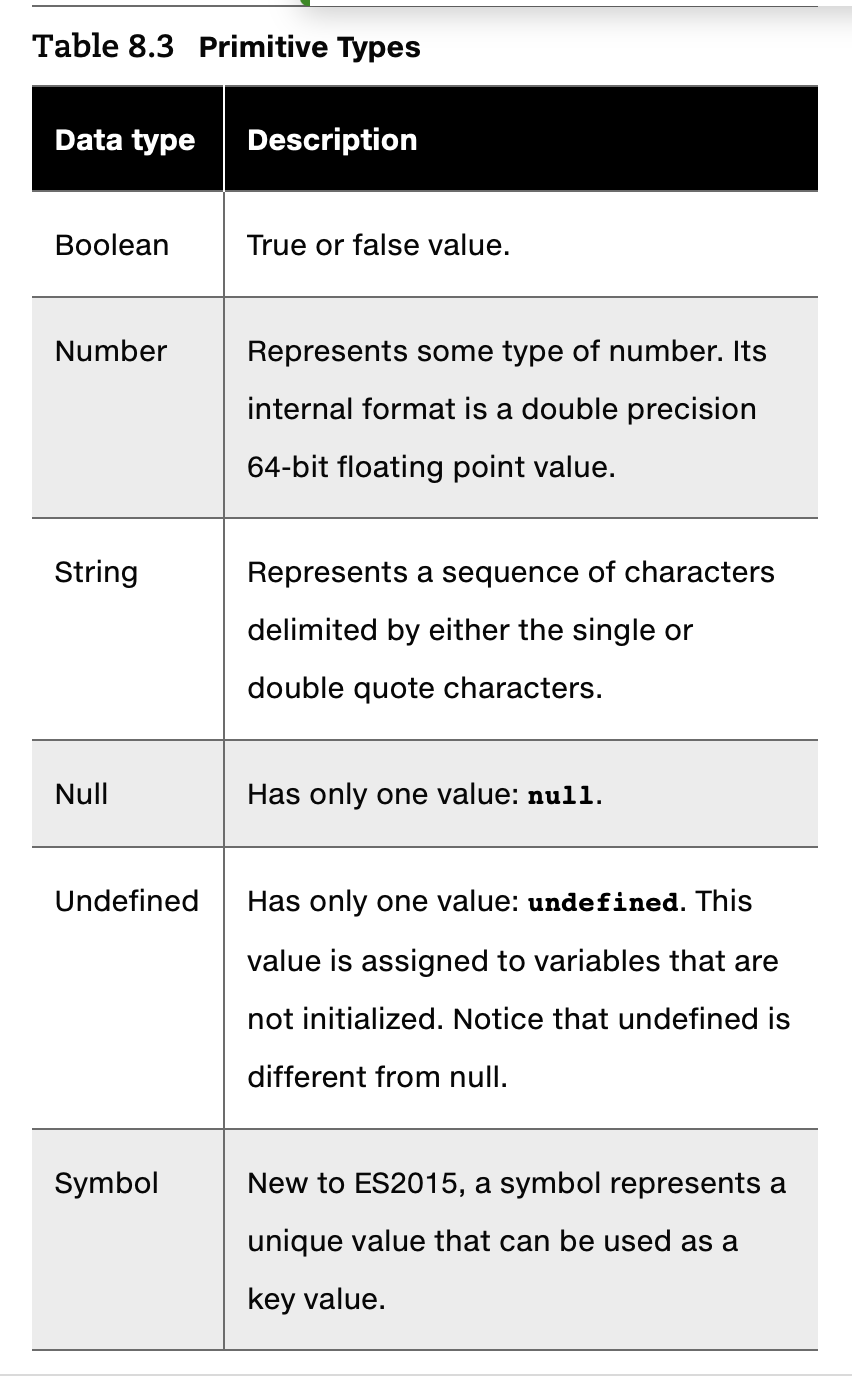
- Primitive variables contain the value of the primitive directly within memory.
- reference types vs primitive types
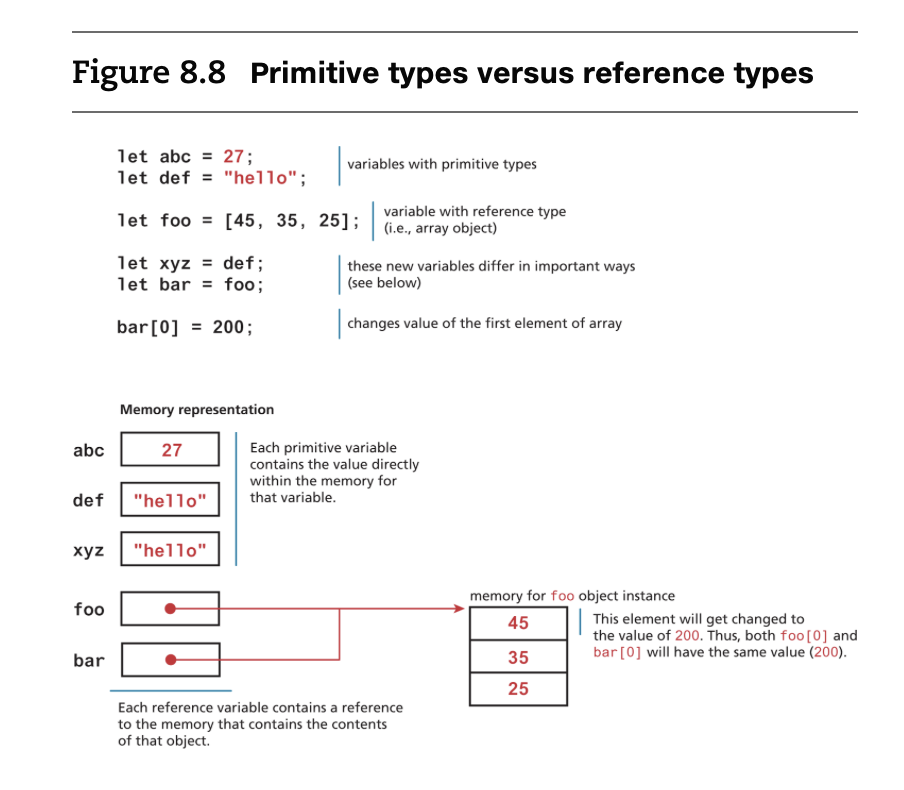
- as you can see, since the variables foo and bar are reference types, they point to the memory of an object instance.
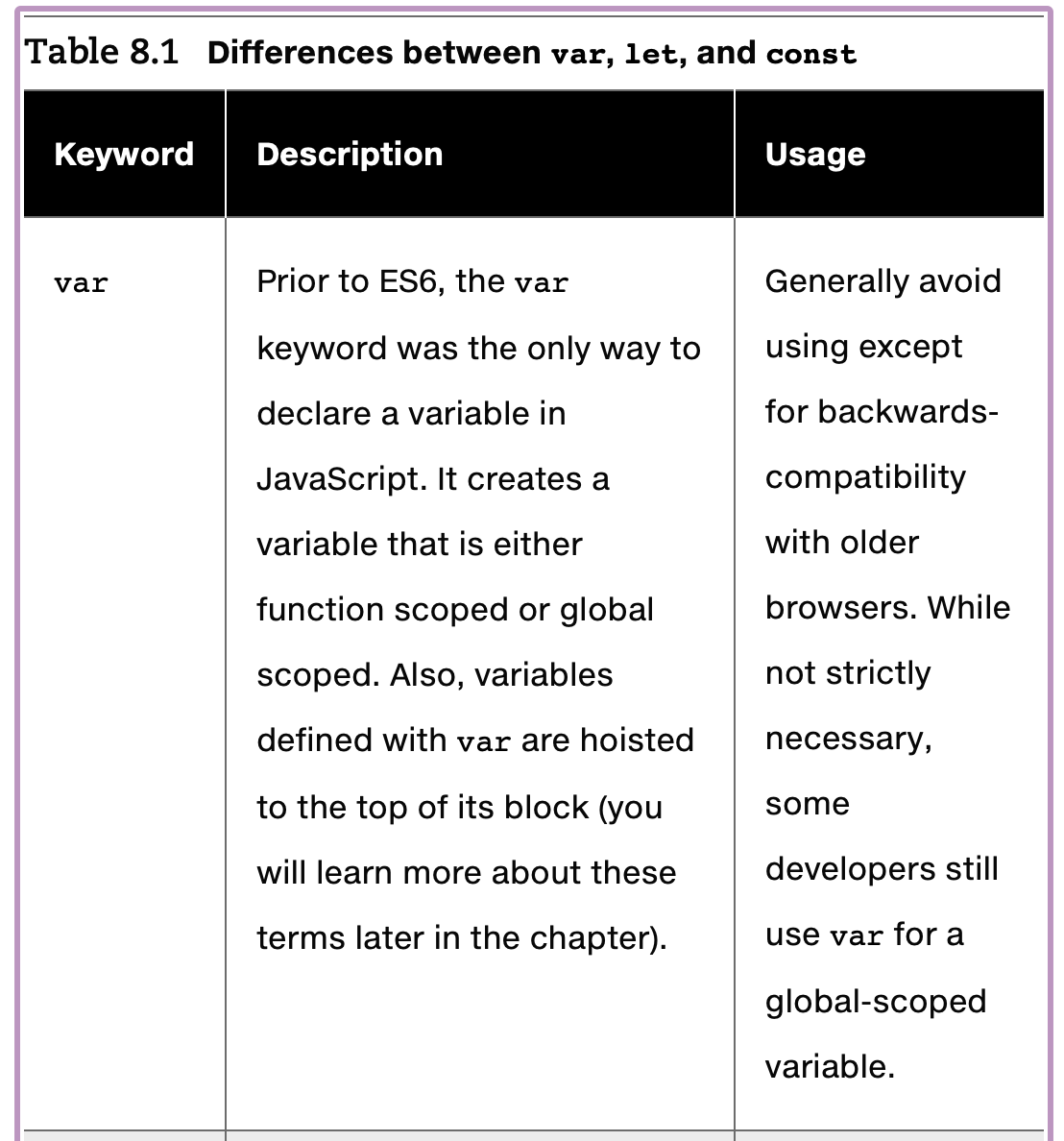
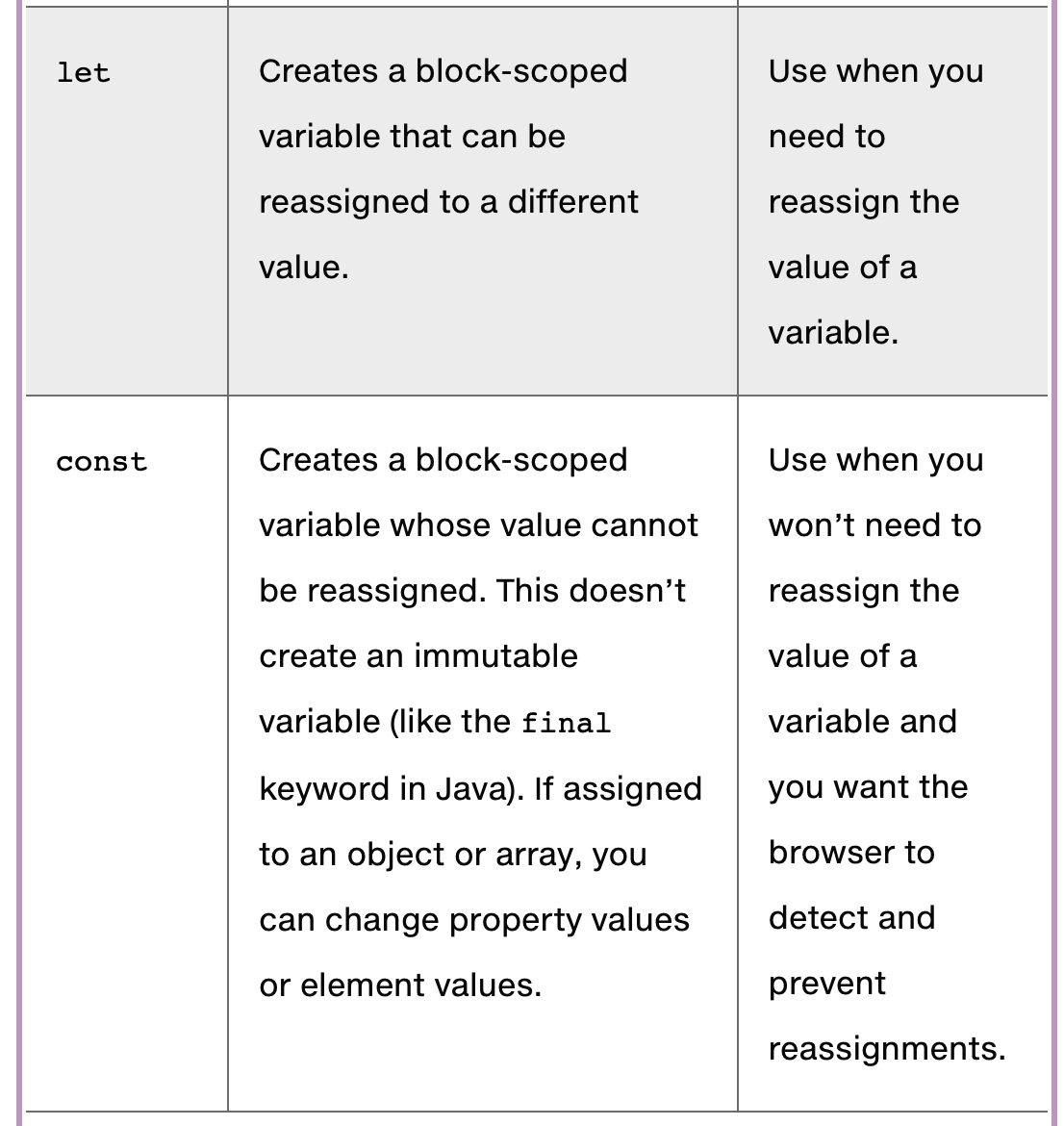
- let vs const
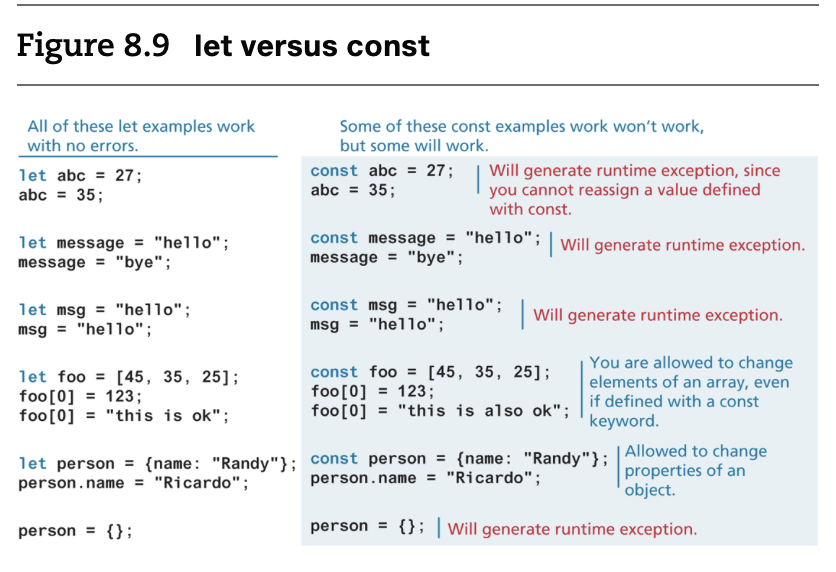
- you cannot reassign the value of a variable defined with a const. However, for a const variable that is assigned to a reference type (such as an object or array), its properties or elements can be changed.
- const를 사용할 때 발생할 수 있는 다양한 런타임 예외에도 불구하고 왜 const를 사용해야 하는가?
- 자바스크립트에서 객체와 배열은 원시 데이터 타입보다 더 자주 사용되므로, const의 제한이 그렇게 크지 않다는 점을 강조하고 있습니다.
8.3.3 Built-In Objects
-
자바스크립트 객체는 이름과 값으로 구성된 순서가 없는 속성들의 리스트.
-
함수도 객체이기 때문에 속성 값으로 함수가 될 수 있으며, 이를 메서드라고 부른다.
-
객체의 속성이나 메서드에 접근할 때는 점 표기법(dot notation)을 사용한다.
-
자주 사용되는 내장 객체에는 Object, Function, Boolean, Error, Number, Math, Date, String, RegExp 등
-
Array : 배열을 다루기 위한 객체로, 배열의 메서드와 속성을 제공합니다.
** 예시 method : push(), pop(), forEach(), map() -
Date : 날짜와 시간을 처리하는 객체입니다. 현재 날짜와 시간을 가져오거나, 특정 날짜를 계산하는 데 사용됩니다.
** 예시 method : getDate(), getFullYear(), toLocaleDateString() -
RegExp (정규 표현식): 문자열 내에서 특정 패턴을 찾거나 대체하는 데 사용됩니다.
@ 예시 method : test(), exec()
@ RegExp 플래그:
RegExp에서 자주 사용되는 플래그는 다음과 같습니다:
g: 전역 검색. 일치하는 모든 항목을 찾습니다.
i: 대소문자를 구분하지 않고 검색합니다.
m: 여러 줄 검색. 여러 줄에서 시작 또는 끝을 확인합니다.
u: 유니코드 모드로 검색합니다.// 이메일 형식을 확인하는 정규 표현식 let emailPattern = /^[a-zA-Z0-9._-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,6}$/; let email = "example@example.com"; console.log(emailPattern.test(email)); // true email = "invalid-email"; console.log(emailPattern.test(email)); // false -
Error: 오류 객체는 프로그램에서 발생하는 오류를 처리하는 데 사용됩니다.
** 예시 method : new Error(), throwtry { throw new Error("Something went wrong!"); } catch (e) { console.log(e.message); // 출력: "Something went wrong!" }
-
-
브라우저 환경에서 사용되는 내장객체
- document : 현재 웹 페이지를 나타내는 객체로, DOM(Document Object Model)을 통해 HTML 요소를 조작할 수 있습니다.
** 예시 method : getElementById(), querySelector() - console : 디버깅을 위해 콘솔에 출력을 할 수 있는 객체입니다.
** 예시 method : console.log(), console.error() - window : 브라우저의 전역 객체로, 브라우저 창에 관련된 다양한 속성 및 메서드를 제공합니다.
** 예시 method : alert(), setTimeout(), location
- document : 현재 웹 페이지를 나타내는 객체로, DOM(Document Object Model)을 통해 HTML 요소를 조작할 수 있습니다.
test your knowledge #1
Requirement
1. Provide a prompt to the user to enter a bill total.
2. Convert this user input to a number (don’t worry about error handling for non-numbers).
3. Calculate the tip amount assuming 10% (simply multiply the user input by 0.1). Use a const to define the 10% tip percentage.
4. Display the bill total and tip amount on the same console output line, for example,
let billTotal = prompt("Please enter the total bill : ");
//string --> float
billTotal = parseFloat(billTotal);
const tip = 0.1;
let tipTotal = billTotal * tip;
console.log(`For bill of ${billTotal} the tip should be ${tipTotal}`);8.3.4 Concatenation(문자열 연결)
- using the concatenate operator(+)
const country = "France";
const city = "Paris";
const population = 67;
const count = 2;
let msg = city + " is the capital of " + country;
// msg는 "Paris is the capital of France"로 설정됨.
msg += " Population of " + country + " is " + population;
// msg에 " Population of France is 67"이 추가되어 최종적으로 msg는
// "Paris is the capital of France Population of France is 67"이 됨.
let msg2 = population + count;
// msg2는 숫자 67 + 숫자 2 이므로 69가 됨.
// 콘솔에 출력
console.log(msg); // "Paris is the capital of France Population of France is 67"
console.log(msg2); // 69
- Newer versions of JavaScript have added an alternative technique for concatenation, namely, template literals, which can be seen demonstrated in Listing 8.2
const country = "France";
const city = "Paris";
let msg = `${city} is the capital of ${country}`;