Arrays
How to define the arrays
- array litteral notation
const name = [value1, value2, ... ];- using the Array() constructor
const name = new Array(value1, value2, ... );
- 배열 리터럴 표기법을 사용하면 자바스크립트에서 간단하고 직관적으로 배열을 생성할 수 있습니다.
- 배열은 여러 줄에 걸쳐 작성할 수 있어 가독성을 높일 수 있습니다.
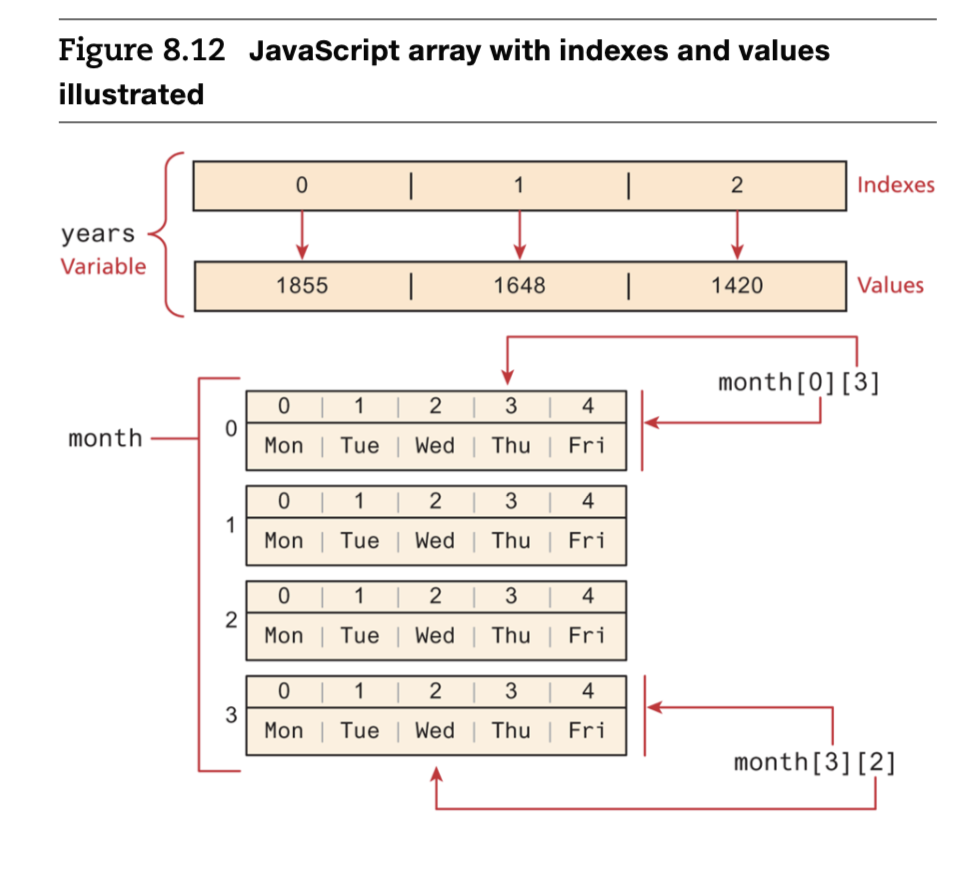
- 배열은 다차원 배열을 생성할 수 있으며, 배열 안에 배열을 포함할 수 있습니다.
- 자바스크립트 배열에는 다양한 데이터 타입이 함께 포함될 수 있습니다.
- 자바스크립트 배열은 0부터 시작하는 인덱스를 사용합니다.
- 배열의 마지막 요소는
array.length - 1을 통해 접근할 수 있습니다. - 대괄호 표기법을 사용하여 배열의 개별 요소에 접근하거나 수정할 수 있습니다.

using the spread syntax

...sports, ...games를 사용해서 배열 정의 가능함.
JavaScript arrays method
1. push()
- 배열의 끝에 요소를 추가하고, 배열의 새로운 길이를 반환합니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana"];
fruits.push("cherry"); // ["apple", "banana", "cherry"`2. pop()
- 배열의 마지막 요소를 제거하고, 그 요소를 반환합니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
fruits.pop(); // ["apple", "banana"], 반환값: "cherry"3. unshift()
- 배열의 앞에 요소를 추가하고, 배열의 새로운 길이를 반환합니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana"];
fruits.unshift("mango"); // ["mango", "apple", "banana"]4. shift()
- 배열의 첫 번째 요소를 제거하고, 그 요소를 반환합니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
fruits.shift(); // ["banana", "cherry"], 반환값: "apple"5. splice()
- 배열의 특정 위치에서 요소를 추가, 제거, 또는 교체할 수 있습니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
fruits.splice(1, 1, "grape"); // ["apple", "grape", "cherry"]6. slice()
- 배열의 일부를 잘라서 새로운 배열을 반환합니다. 원본 배열은 수정되지 않습니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "mango"];
let sliced = fruits.slice(1, 3); // ["banana", "cherry"]7. concat()
- 두 개 이상의 배열을 합쳐서 새로운 배열을 반환합니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana"];
let moreFruits = ["cherry", "mango"];
let combined = fruits.concat(moreFruits); // ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "mango"]8. join()
- 배열의 모든 요소를 문자열로 결합하고, 구분자를 설정할 수 있습니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
let result = fruits.join(", "); // "apple, banana, cherry"9. reverse()
- 배열의 순서를 뒤집습니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
fruits.reverse(); // ["cherry", "banana", "apple"]10. sort()
- 배열을 정렬합니다. 기본적으로 문자열로 정렬되며, 숫자 정렬 시 콜백 함수를 사용할 수 있습니다.
let numbers = [10, 3, 2, 7];
numbers.sort(); // [10, 2, 3, 7] (문자열로 정렬됨)
//숫자 정렬 시
numbers.sort((a, b) => a - b); // [2, 3, 7, 10]11. forEach()
- 배열의 각 요소에 대해 지정된 함수를 실행합니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
fruits.forEach(fruit => console.log(fruit));
// apple
// banana
// cherry12. map()
- 배열의 각 요소에 대해 함수를 실행한 결과를 새로운 배열로 반환합니다.
let numbers = [1, 2, 3];
let doubled = numbers.map(num => num * 2); // [2, 4, 6]13. filter()
- 배열에서 특정 조건을 만족하는 요소들만 모아 새로운 배열을 반환합니다.
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let evenNumbers = numbers.filter(num => num % 2 === 0); // [2, 4]
14. find()
- 배열에서 조건을 만족하는 첫 번째 요소를 반환합니다. 없으면
undefined를 반환합니다.
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let firstEven = numbers.find(num => num % 2 === 0); // 2
15. reduce()
- 배열의 모든 요소를 하나의 값으로 축약합니다.
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
let sum = numbers.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0); // 1016. includes()
- 배열에 특정 요소가 포함되어 있는지 여부를 반환합니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
let hasBanana = fruits.includes("banana"); // true
17. indexOf()
- 배열에서 특정 요소의 인덱스를 반환합니다. 없으면
-1을 반환합니다.
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
let index = fruits.indexOf("banana"); // 1
18. findIndex()
- 배열에서 조건을 만족하는 첫 번째 요소의 인덱스를 반환합니다. 없으면
-1을 반환합니다.
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let evenIndex = numbers.findIndex(num => num % 2 === 0); // 1 (2의 인덱스)8.6.1 Iterating(반복) an array using for . . . of
- for...of 루프: 배열의 각 요소에 직접 접근하여 처리하며, 코드가 더 간결하고 직관적입니다. 인덱스를 신경 쓰지 않아도 되므로 단순 반복 작업에 적합합니다.
// iterating through an array
for (let yr of years) {
console.log(yr);
}- 전통적인 for 루프: 배열의 인덱스를 사용하여 반복하며, 인덱스가 필요한 경우에 유용합니다. 배열의 길이와 인덱스를 명시적으로 관리해야 하므로 더 복잡할 수 있습니다.
for (let i = 0; i < years.length; i++) {
let yr = years[i];
console.log(yr);
}8.6.2 Array Destructuring
Array Destructuring : 배열에서 여러 스칼라 값을 추출하는 과정을 단순화하는 방법을 제공
const league = ["Liverpool", "Man City", "Arsenal", "Chelsea"];
//before the ES6
let first = league[0];
let second = league[1];
let third = league[2];
//after the ES6
let [first, second, third] = league;
//요소 건너뛰기
let [first,,,fourth] = league; //첫 번째 요소와 네 번째 요소만 추출
// Spread 문법을 사용한 나머지 요소 추출
//스프레드 문법을 사용하면 배열의 나머지 요소를 새로운 배열로 쉽게 복사할 수 있습니다.
//first는 첫 번째 요소 "Liverpool"을 가지며, 나머지 "Man City", "Arsenal", "Chelsea"는 everyoneElse 배열에 복사됩니다.
let [first, ...everyoneElse] = league;
변수 값 교환
//before the ES6 --> 임시변수 필요
let tmp = first;
first = second;
second = tmp;
//after the ES6
[second, first] = [first, second];
Test your knowledge #3

//let billTotal = prompt("Please enter the total bill : ");
const billTotals = [50,150,20,500];
const tips = [];
for (const total of billTotals) {
let tipPercentage;
if (total > 75) {
tipPercentage = 0.1; // 10%
} else if (total >= 30 && total <= 75) {
tipPercentage = 0.2; // 20%
} else {
tipPercentage = 0.3; // 30%
}
// 5. 팁 계산 및 tips 배열에 추가
const tipAmount = total * tipPercentage;
tips.push(tipAmount);
}
// 6. 결과 출력
for (let i = 0; i < billTotals.length; i++) {
console.log(`For bill of $${billTotals[i]} the tip should be $${tips[i]}`);
}