Definition of Computer Security
NIST computer security handbook “The protection afforded to an automated information system in order to attain the applicable objectives of preserving the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of information system resources (includes hardware, software, firmware, information/data, and telecommunications)”
—> but, 전통적인 의미에서 그 범위가 변경되고 있음
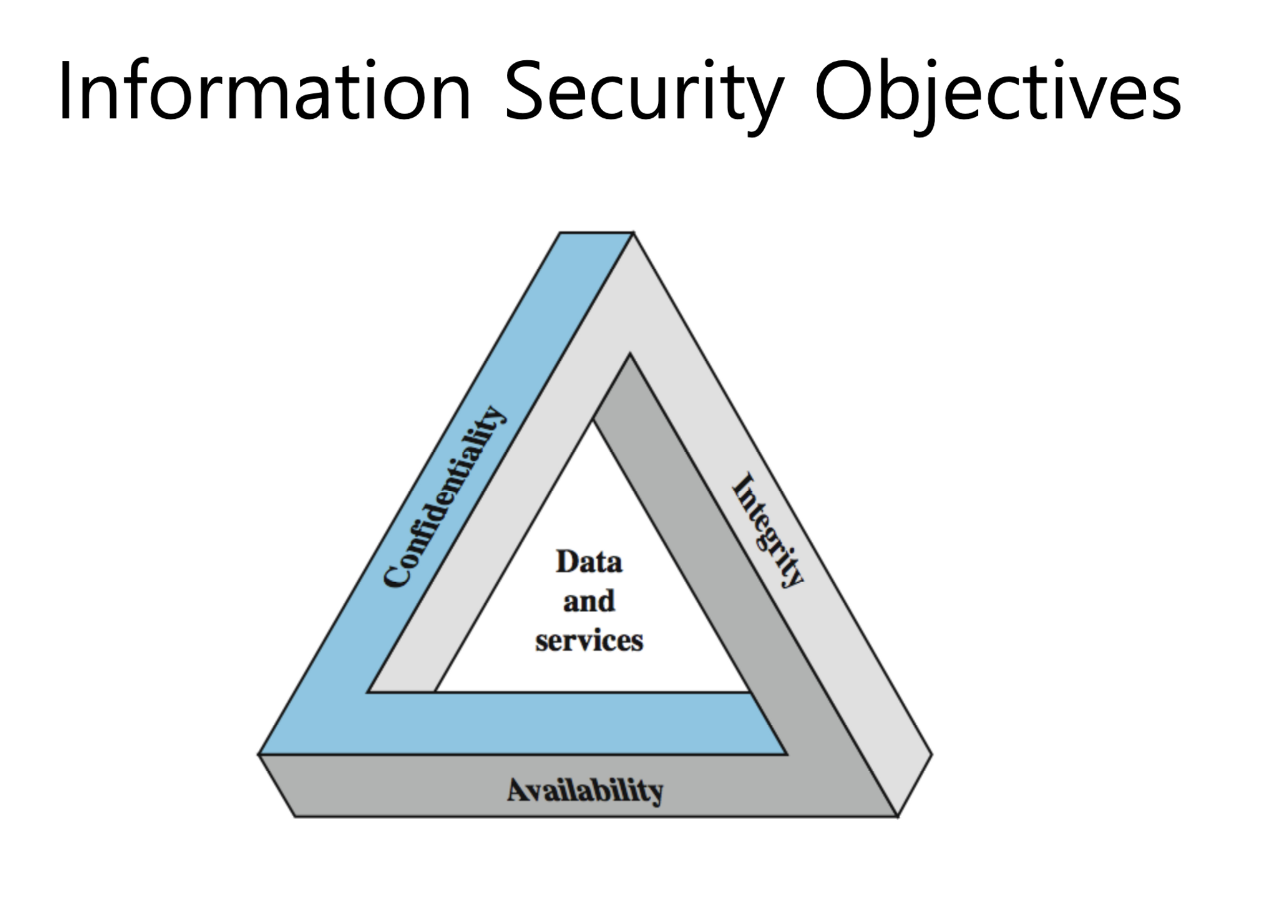
보안 기본 요소들 (완전 기초!)
Confidentiality (기밀성)
- Preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure
- prevent 관점에서 접근해야함! (접근 권한이 없는 외부 사용자가 접근 불가 하게)
Integrity (무결성)
- Guarding against improper information modification or destruction (부적절한 정보 수정이나 파괴에 대한 방어)
- 어려움… ㅎ, 차라리 무결성이 깨졌을 때 복구 할 수 있는 시스템을 구성
Availability (가용성)
- Ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of information
- 위에 두가지 원칙은 알고리즘으로 보호 가능한데, 가용성은 알고리즘으로 커버 불가, 대부분은 네트워크 공격 (Dos 공격) 방어하기 위해서는 일반적으로 네트웤 단위의 툴을 (FW IPS/IDS 같은 솔루션) 사용해야함 ㅎ
Authenticity (인증)
- Verifying users are who they say they are, and that each input arriving at the system came from a trusted source user, source 등에 대한 verification
Accountability (책임 - 그런데 어떠한 문제가 어떻게 발생했는지 trace 해주는 측면의 책임...)
- Actions of an entity to be traced uniquely to that entity
어떤 action을 trace 할 수 있는가? - example of method : sign (절대로 조작 불가능하다고 가정)
Three Fundamental Questions
- What assets do we need to protect? (우리가 프로텍션하고자하는 대상이 뭐야?)
- ex) network, software, environment
- How are those assets threatened? (그 대상이 어떻게 위협받을 수 있는지?)
- What can we do to counter those threats? (그런 위협에 닥치게 되면 우린 어떻게 해야해?)
Vulnerabilities, Threats and Attacks
Vulnerabilities (of computer or network asset)
- 아직 문제는 아니지만, 잠재적으로 문제가 될 수 있는 부분
- Corrupted (loss of integrity)
- Leaky (loss of confidentiality)
- Unavailable or very slow (loss of availability)
- ex) 종이로 만든 금고
Threats
- Capable of exploiting vulnerabilities
- Represent potential security harm to an asset
- ex) 불
Attacks
- threats carried out
- ex) 불지르는 행동
- 행위 기준, 행위자 기준으로 아래와 같이 나눌 수 있음

Computer Security Challenges
- not simple (간단하지 않음)
- must consider potential attacks (잠재적인 공격을 고려해야 함)
- procedures used counter-intuitive (직관적이지 않은 절차가 필요함)
- involve algorithms and secret info (알고리즘 및 비밀 정보가 포함됨)
- must decide where to deploy mechanisms (메커니즘을 배치할 위치를 결정해야 함)
- battle of wits between attacker / admin (공격자/ 관리자 간에 머리 싸움 해야함..)
- not perceived on benefit until fails (실패하기 전까지는 이점을 인식하지 못함 ㅠㅠ)
- requires regular monitoring (정기적인 모니터링 필요)
- too often an after-thought (사고 나야지 생각남)
- regarded as impediment to using system (시스템 사용에 대한 장애 요인으로 인식됨)
OSI Security Architecture
여기서 osi 는 그 많이 들어본 표준 만드는 거기임
거기서
- 보안 요구 사항을 정의하고 제공하는 체계적인 방법을 정의함
- 우리에게는 우리가 공부할 개념에 대한 유용하고 추상적인 개요를 제공함
정보 보안의 세 가지 측면
- 보안 공격
- 정보 보안을 저해하는 행위
- 보안 메커니즘 (다양한 방법으로 구현, ex): 액세스 제어: 인증 및 권한 부여)
- 보안 공격을 탐지 / 방지 / 복구하기 위한 프로세스
- 보안 서비스 (기밀성을 구현하기 위한 목표)
- 보안 공격에 대항하는 서비스
- 하나 이상의 보안 메커니즘을 사용함
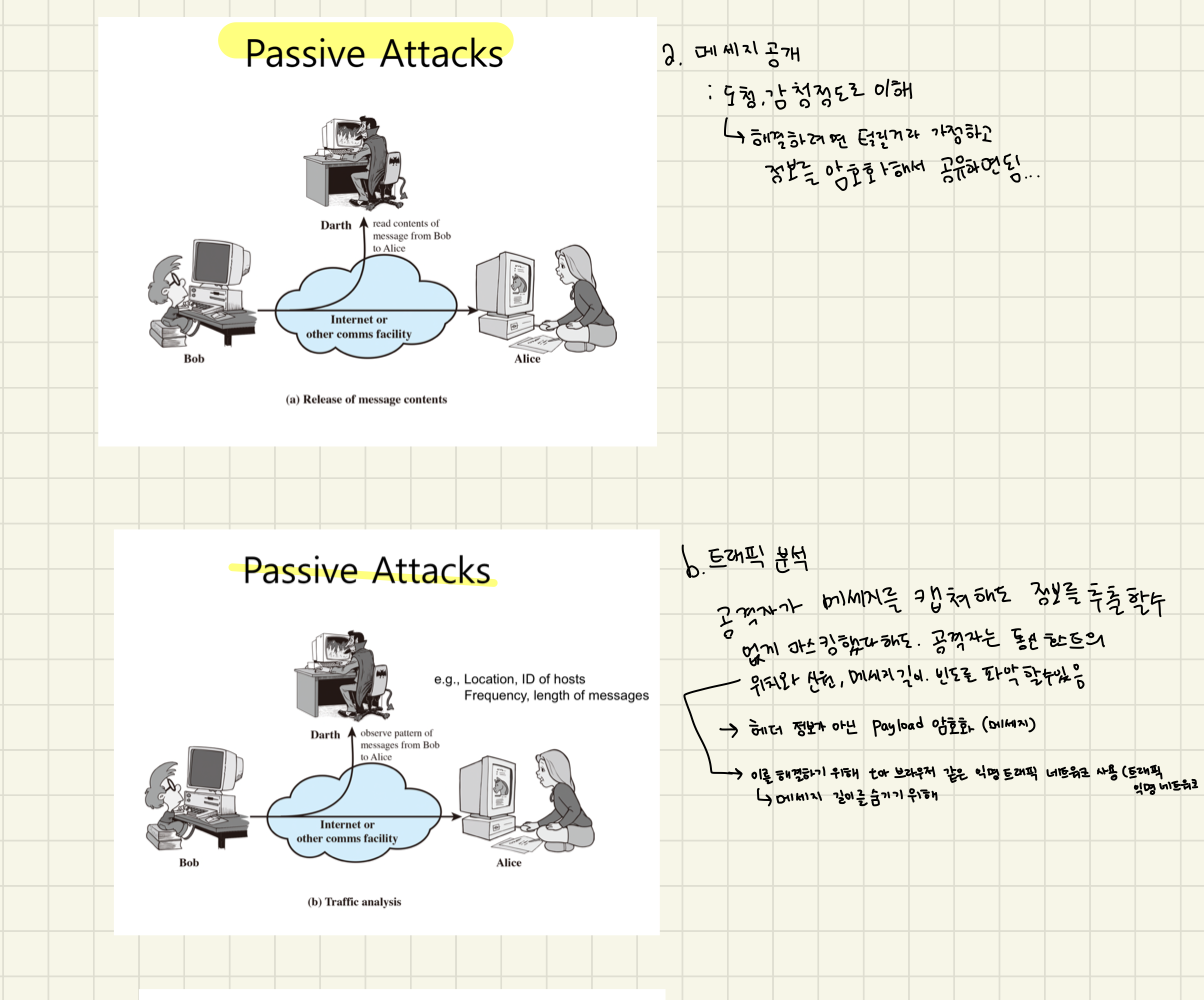
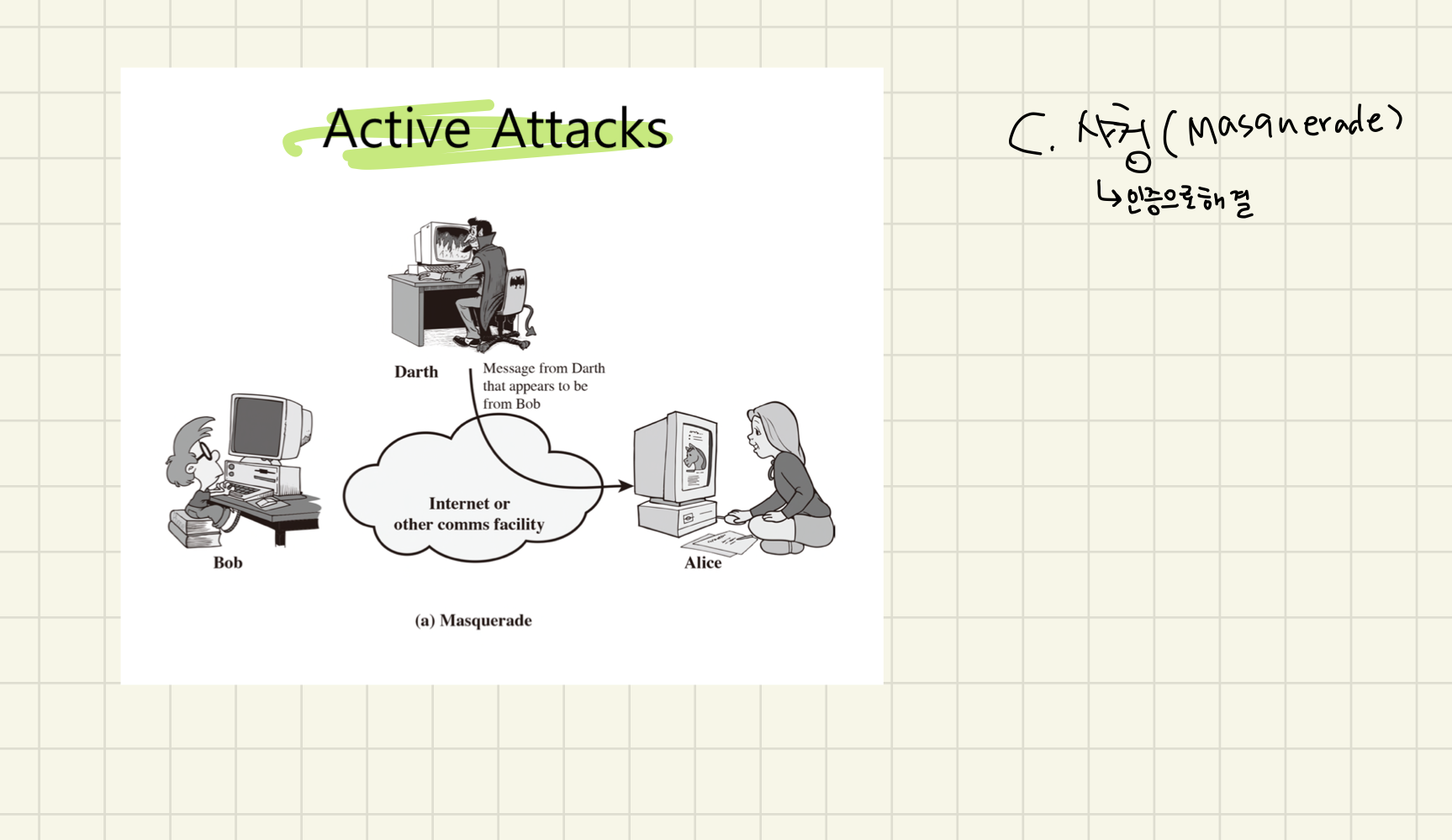
Security Attack (보안 공격)
그리고 위에 그림 처럼 security attack에는 passive attack과 active attack이 있음


Security Services (confidential을 구현하는 목표)
X.800:
– “a service provided by a protocol layer of communicating open systems, which ensures adequate security of the systems or of data transfers”
“통신하는 오픈 시스템의 프로토콜 계층에서 제공하는 서비스로 시스템 또는 데이터 전송의 충분한 보안을 보장함”
- 인증 : 통신 엔터티가 주장하는 것과 같은 것임을 보장
- 액세스 제어 :리소스의 무단 사용 방지
- 데이터 기밀성 : 권한 없는 공개로부터 데이터를 보호
- 데이터 무결성 : 권한 있는 엔터티에 의해 보낸 데이터임을 보장
- 부인 방지 : 통신 중 한 쪽 파트너가 부인할 수 없게 보호 (전자 서명)
- 가용성 : 리소스 접근 가능/사용 가능 (가용성)
Security Mechanism (보안 메커니즘)
• Feature designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack (보안 공격을 탐지, 방지 또는 복구하기 위해 설계된 기능)
• No single mechanism supports all services required (필요한 모든 서비스를 지원하는 단일 메커니즘은 없음)
• However one particular element underlies many of the security mechanisms in use: (그러나 현재 사용되는 많은 보안 메커니즘의 기초를 이루는 하나의 특정 요소가 있음:)
– Cryptographic techniques (암호기술)
Specific security mechanisms: (특정 보안 알고리즘)
– Encipherment, digital signatures, access
controls, data integrity, authentication
exchange, traffic padding, routing control,
notarization (암호화, 디지털 서명, 액세스 제어, 데이터 무결성, 인증,교환, 트래픽 패딩, 라우팅 제어,공증)
• Pervasive security mechanisms: (전반적인 보안 알고리즘)
– Trusted functionality, security labels, event detection, security audit trails, security recovery (신뢰할 수 있는 기능, 보안 레이블, 이벤트 감지, 보안 감사 추적, 보안 회복)
- RFC 2828: —> ietf (유선 인터넷 표준)
– “시스템이 특정 유형의 보호를 제공하기 위해 시스템에서 제공하는 처리 또는 통신 서비스”
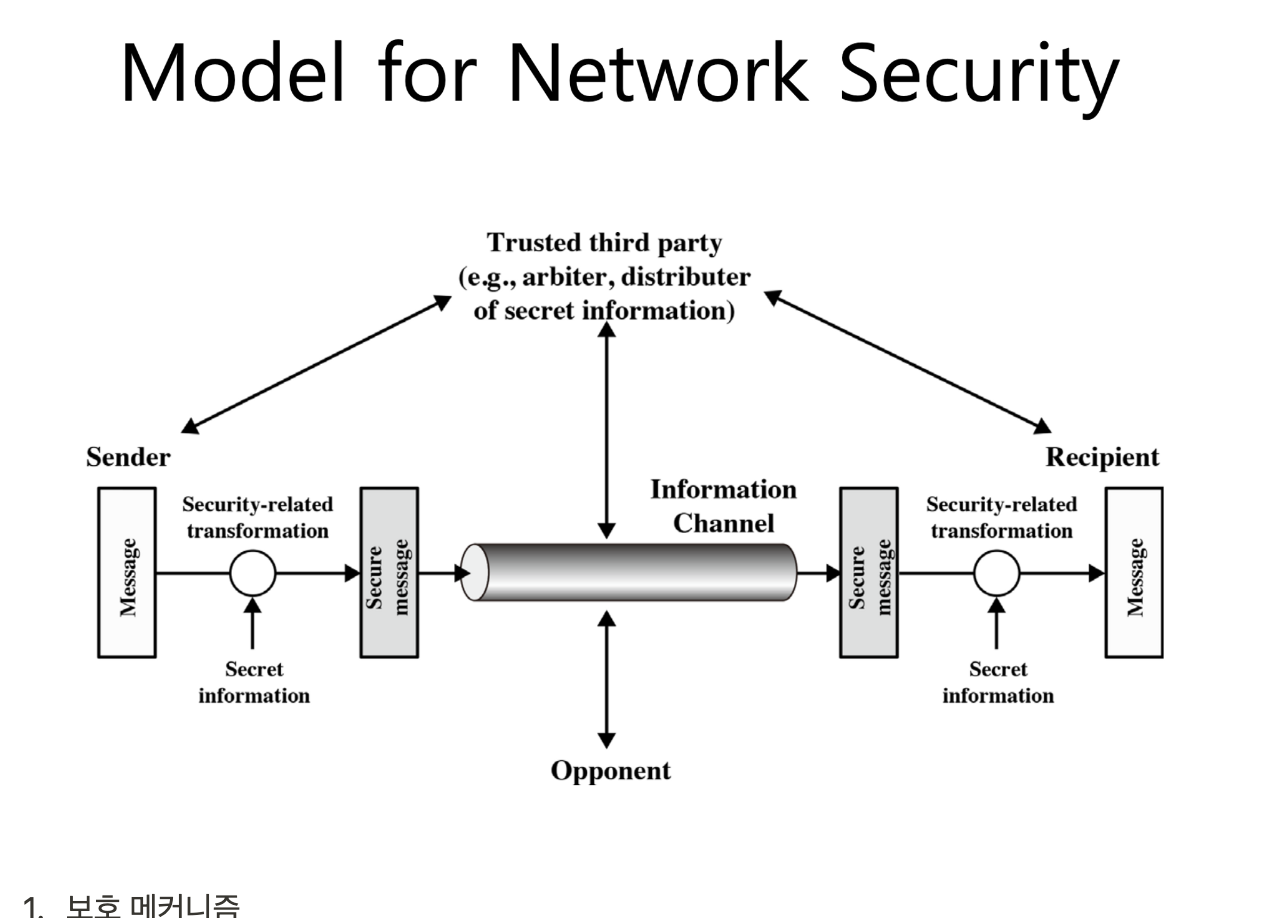
This model requires us to:
-
Design a suitable algorithm for the security transformation (보안 변환에 적합한 알고리즘 설계 -> 보호 매커니즘)
-
Generate the secret information (keys) used by the algorithm (알고리즘이 사용하는 비밀 정보(키) 생성 -> 특정 sender & receiver (input으로 secret information이 들어감) )
-
Develop methods to distribute and share the secret information (비밀정보의 유통 및 공유 방법 개발 -> 가정: 안전하게 키가 공유되어 있단 (trusted 3rd party 존재), 커뮤니케이션 채널은 오픈 채널)
-
Specify a protocol enabling the users to use the transformation and secret information for a security service (사용자가 보안 서비스를 위해 변환 및 비밀 정보를 사용할 수 있도록 하는 프로토콜 지정)

This model requires us to:
- Select appropriate gatekeeper functions to identify users (사용자 식별을 위한 적절한 게이트키퍼 기능 선택)
- Implement security controls to ensure only authorised users access designated information or resources(승인된 사용자만 지정된 정보 또는 리소스에 액세스할 수 있도록 보안 제어를 구현합니다.)
서버 - 클라이언트 모델
서버가 제공가능한 리소스가 다양 —> 서비스에 따라 공격자의 타겟이 달라짐
- 서버: 클라이언트 인증 안함 (넘 많아서)
- DOS attack, 권한 받지 않은 리소스에 접근하려는 공격 발생
클라이언트: 서버가 누군지 인증 진행