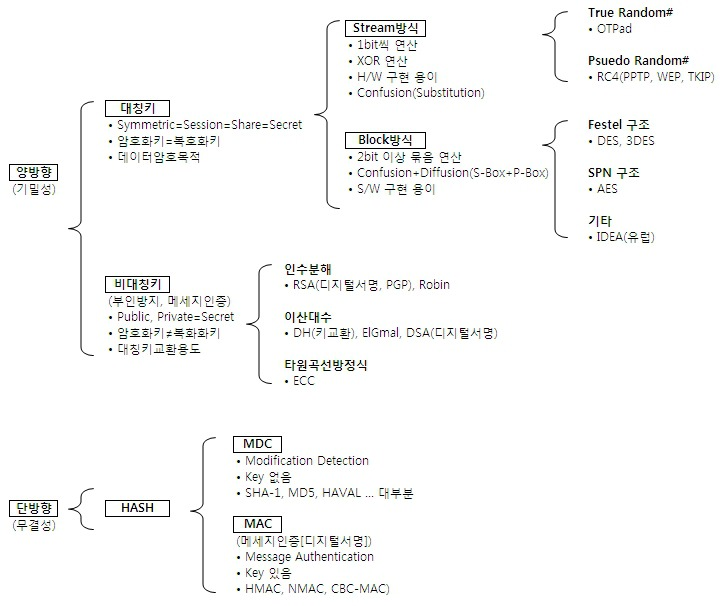
Stream 암호 (Stream Ciphers)
스트림 암호는 한번에 1비트 혹은 1바이트의 데이터 흐름(스트림)을 순차적으로 처리해가는 암호화
암호화 방식은 평문과 키 스트림을 XOR해서 생성
– Process messages a bit or byte at a time when en/decrypting
– Autokeyed Vigenère cipher, Vernam cipher
블록 암호 (Block Cipher)
평문을 일정한 크기의 블록으로 잘라낸 후 block 단위(고정된 비트 사이즈 단위)로 암/복호화 된다
– Process messages in blocks, each of which is then en/decrypted
– Like a substitution on very big characters (64-bits or more)
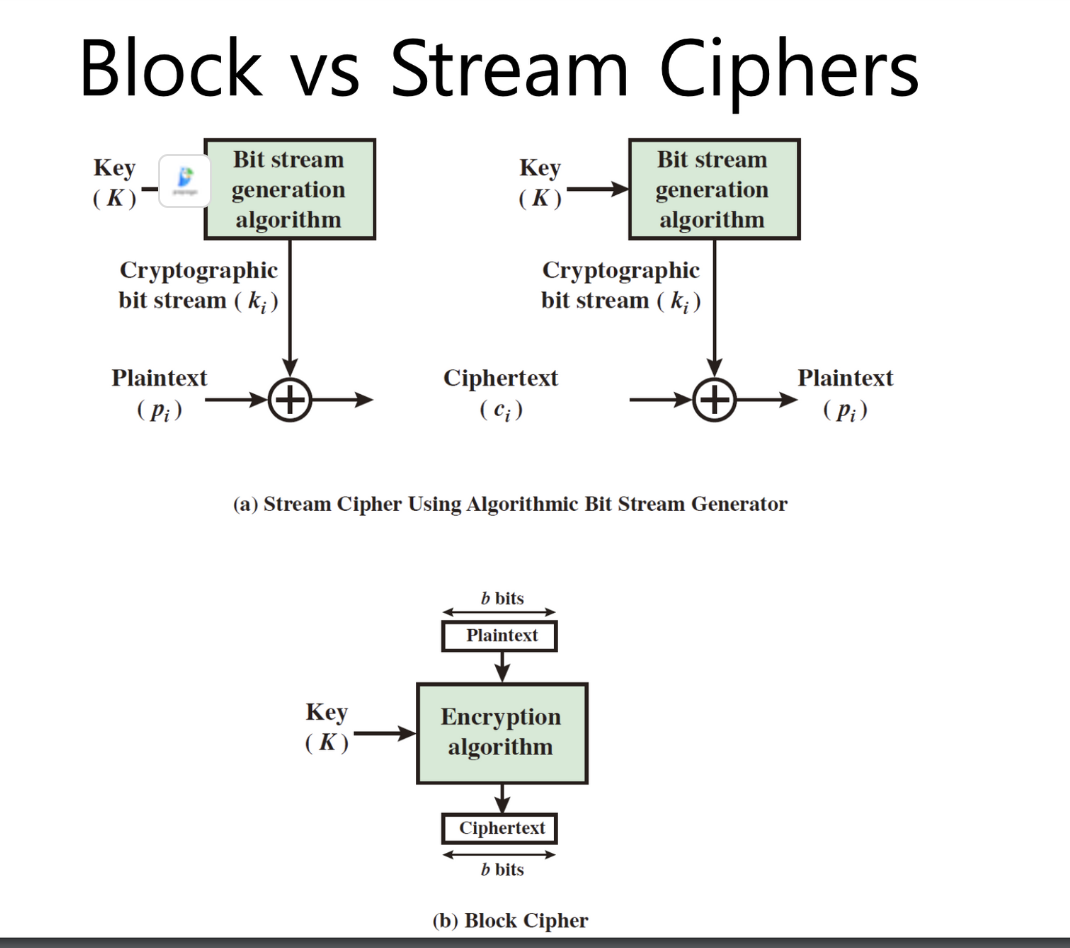
블록 암호 원리
• n비트 일반 텍스트 블록에서 n비트 암호문으로 작동
• 가역적(복호화 가능) 매핑의 경우 변환 번호는 2n!
reversible: a → b then b→ a
• Ideal block cipher
– Allows for the maximum number of possible encryption mappings from plaintext block
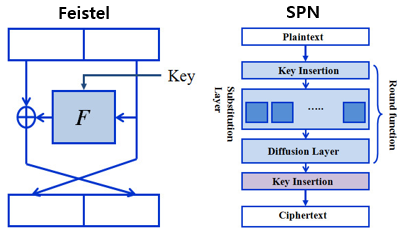
Feistel Cipher Structure
Approximate ideal block cipher
– Execution of two or more simple ciphers in sequence
– Substitution and permutation
• Approach
– With a key length of k bits, a block length of n bits, allowing 2k possible transformations, rather than the 2n! transformation
• Based on Shannon’s substitution- permutation (S-P) networks
Substitution-Permutation Ciphers
• Claude Shannon introduced idea of S-P networks in 1949
• Form basis of modern block ciphers
• S-P nets are based on the two primitive cryptographic operations: – Substitution (S-box)
– Permutation (P-box)
• Provide confusion & diffusion of message and key
Confusion and Diffusion
• Cipher needs to completely obscure statistical properties of original message
– A one-time pad does this
• More practically Shannon suggested combining S & P elements to obtain:
– Diffusion – makes statistical relationship between plaintext and ciphertext as complex as possible (achieved by repeated permutation)
– Confusion – makes statistical relationship between ciphertext and key as complex as possible (achieved by complex substitution)
정리하면, 파이스텔 구조는 치환(Substitution), 순열(Permutation)을 번갈아 수행하는 구조이다.데이터를 두부분으로 나누어 좌, 우 두 부분에 교대로 비선형 변환을 적용시키는 구조이기에 공격자가 키를 훔쳐도 function을 알지 못하기 때문에 보안성이 유지된다.
블록 암호는 Round를 사용하고, 반복적으로 암호화 과정을 수행하여 암호화 강도 높임
→ '확산과 혼돈' 을 만족시키기 위하여 P-box(전치), S-box(치환), 이동요소(shift), 교환요소(swap) 등 구성요소를 결합하여 설계
- 라운드(Rounds) : 반복적으로 사용되는 합성 암호
- 확산(diffusion) : 암호문과 평문 사이의 관계를 숨기는 것
- 혼돈(confusion) : 암호문과 키 사이의 관계를 숨기는 것
블록 단위로 암호화가 수행되므로 암호화가 어디까지 진행되었는 지 내부 상태를 가질 필요가 없음
Feistel Cipher Structure
• Horst Feistel devised the feistel cipher
– Based on concept of invertible product cipher
• Partitions input block into two halves
– Process through multiple rounds which perform a substitution on left data half based on round function of right half & subkey
– Then have permutation swapping halves
• Implements Shannon’s S-P net concept
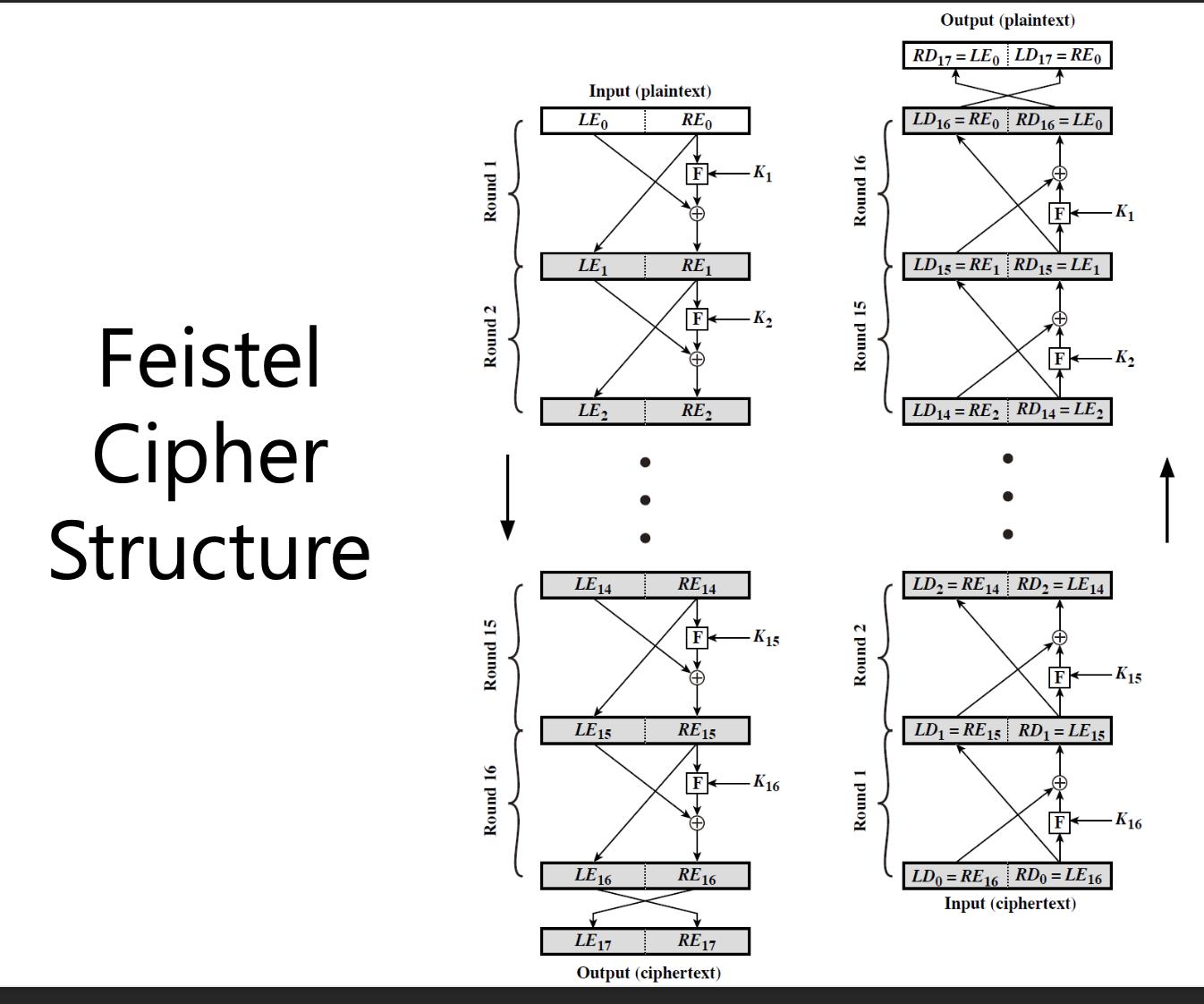
Left bit(LE) : 현재 비트의 XOR 의 결과
Right bit(RE) : 다음것의 left bit의 copy본
kEY(kn) : unknown 키
- F를 라운드 함수로 하고 K0, K1, ... , Kn을 각각 라운드 0, 1, ..., n의 하위 키로 한다.
- 평문 블록을 두 개의 동일한 조각으로 분할(L0, R0)
- 각 라운드의 경우 i = 0, 1, ..., n,
- ComputeLi+1 = Ri, Ri+1 = Li = Li = ⊕ F(Ri,Ki)
- 암호 텍스트는 (Rn+1, Ln+1)
- 특징
왼쪽에 R0L0이 메세지!! R0~Rn+1까지 그 라운드 별로 키가 다 다르다
ciphertext를 생성할 때, bits가 섞인 상태로 완성된다.
Decryption
• 각 라운드의 경우 i = n, n-1, ..., 0
• 암호 텍스트는 (Rn+1 | Ln+1)
• 원형 함수 F는 반전할 필요가 없다.(디크립션할 때 역함수를 취할 필요가 없다)
• 즉, 암호화와 암호 해독의 유일한 차이점은 서브키 순서!
decription : n~0
encryprion : 0~n
이 subkey : drive masterKey
Feistel Cipher Design Elements
• Block size & key size
– Larger block & key size mean greater security but reduced encryption/decryption speed
• Number of rounds
– Multiple rounds offer increasing security
• Subkey generation algorithm and Round function F
– Should be resistant to cryptanalysis
• Fast software en/decryption
• Ease of analysis
https://pongsoyun.tistory.com/113
DES 암호 알고리즘 특징
-
DES(데이터 암호화 표준)은 세계에서 가장 널리 사용되는 블록 암호
-
Feistel 암호 구조에 기초
-
1970년대에 개발됨
-
Lucifer cipher에 기반해서 만들어진 암호화 알고리즘
-
U.S. 정부의 표준
-
잘만들어진 암호화 알고리즘
-
대칭키 암호화
-
기존에 암호화된 문서를 복호화 하는 용도로만 사용하고 신규 암호화 문서를 생성하는데는 절대로 사용하지 말 것을 권장
DES는 파이스텔 암호화
-
64 bit(글자 8개정도)의 block으로 쪼갬
-
key의 길이는 56 bit -> 54bit + 2bit는 parity bit(오류검증)
-
round는 16번
-
매번 라운드마다 48 bit의 subkey 사용
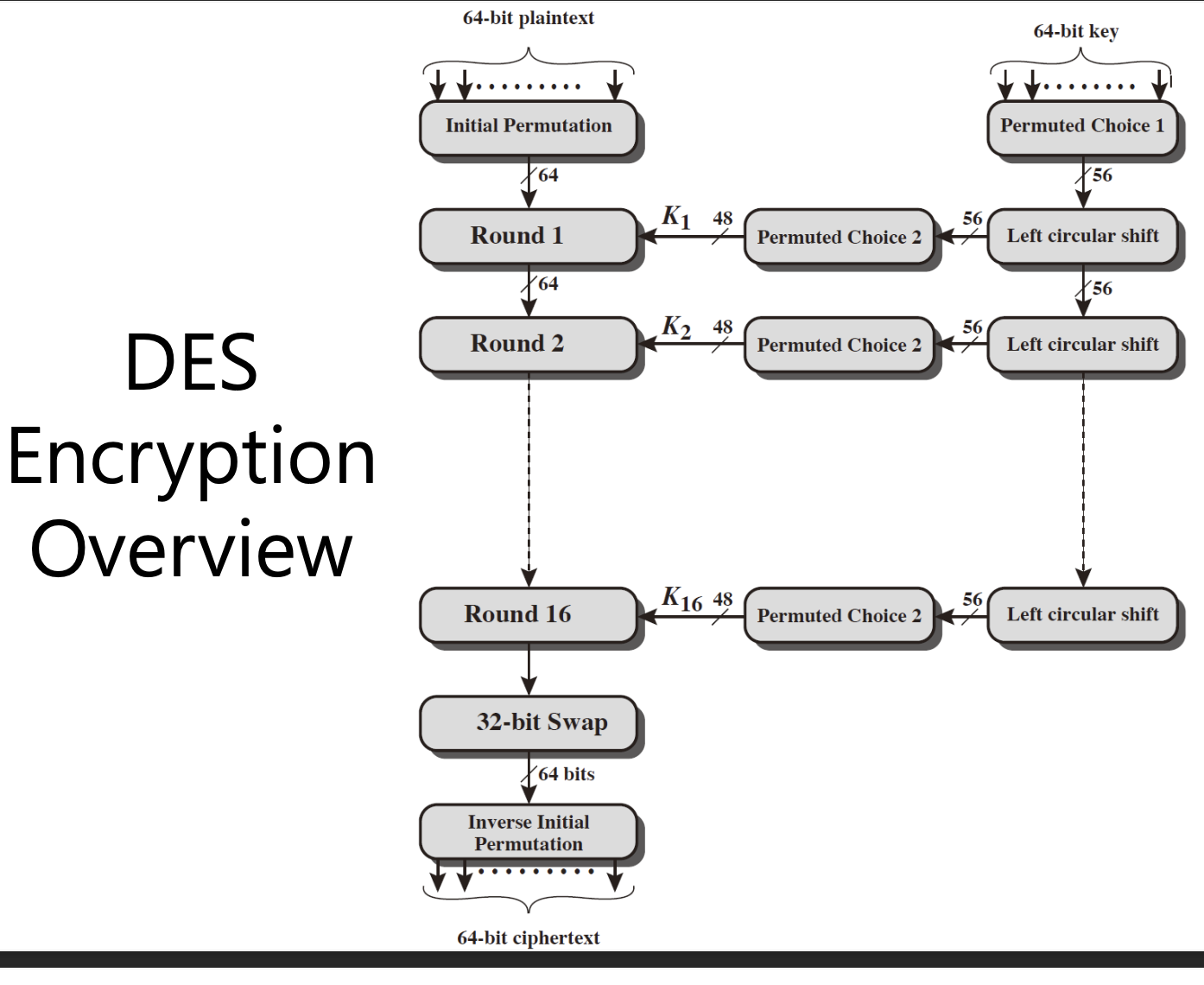
이때 라운드 키는 키 스케줄에 의해 라운드 키를 발생시킨다.
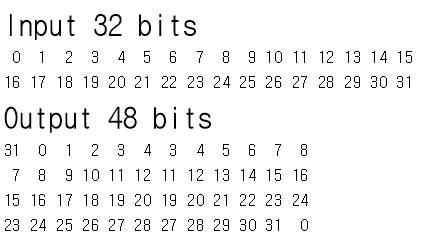
0) 최초로 섞음.

1) expand 확장 : 32비트를 48비트로 확장
DES Expansion Permutation - 섞는다.(순열)
2) DES subkey 를 만들기
(1) 56 비트를 순서를 섞어서 반으로 나눔
Left half key bits (LK)
49 42 35 28 21 14 7
0 50 43 36 29 22 15
8 1 51 44 37 30 23
16 9 2 52 45 38 31
Right half key bits (RK)
55 48 41 34 27 20 13
6 54 47 40 33 26 19
12 5 53 46 39 32 25
18 11 4 24 17 10 3
(2) shift하여 순서를 이동한뒤, 압축 (compress)
8,17,21,24를 LK에서 빼고, 6,9,14,25를 RK에서 뺀다.
Let LK = (LK circular shift left by ri) : 28
Let RK = (RK circular shift left by ri)
Left half of subkey Ki is of LK bits : 24
13 16 10 23 0 4 2 27 14 5 20 9
22 18 11 3 25 7 15 6 26 19 12 1
Right half of subkey Ki is RK bits
12 23 2 8 18 26 1 11 22 16 4 19
15 20 10 27 5 24 17 13 21 7 0 3
- 매 라운드마다 subkey생성
3) expand한 다음에 key와 XOR하여 sboxes를 통해 6비트를 4비트로 매핑 (sboxes는 8개)
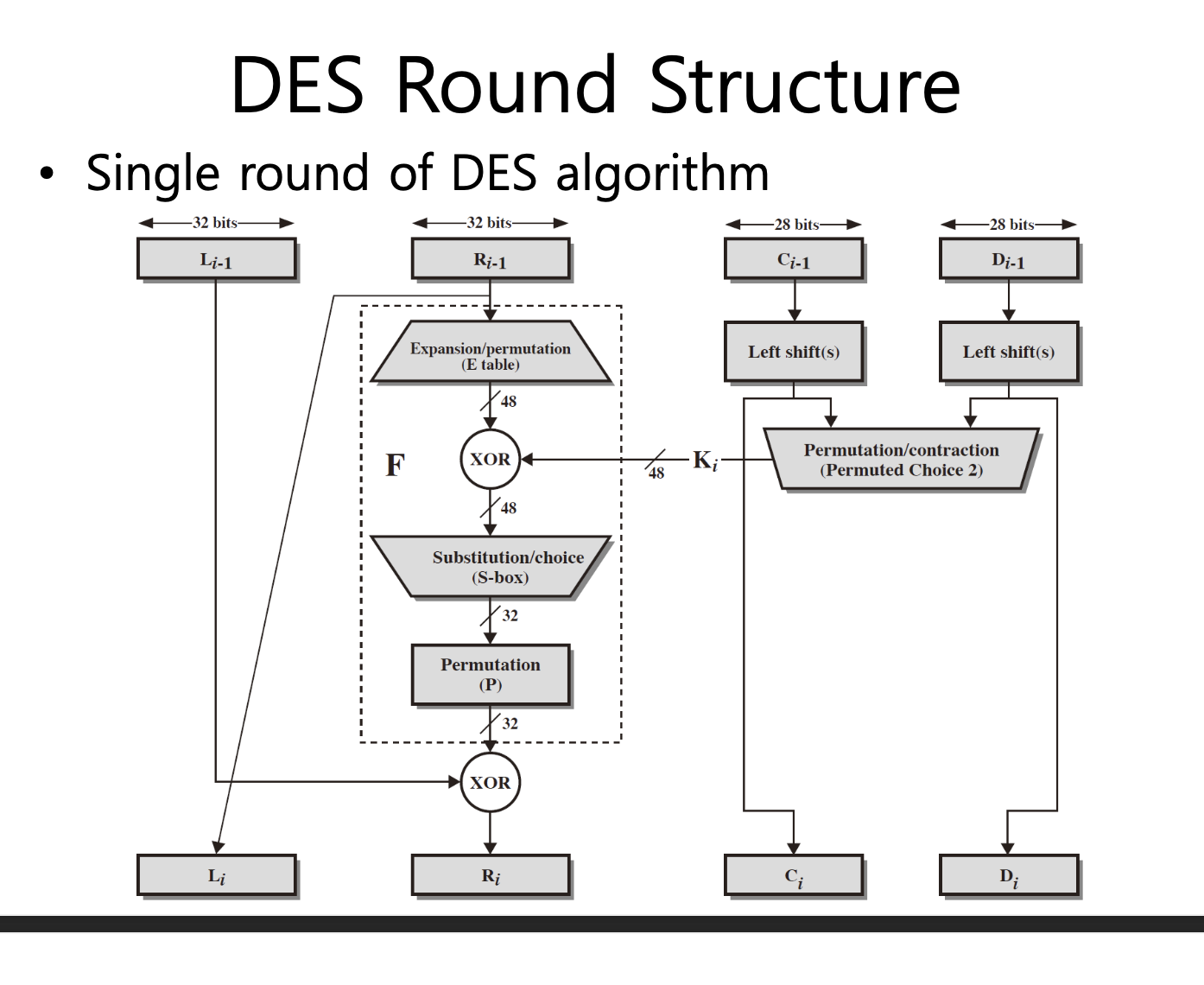
One Round of DES
DES Round Structure
• Uses two 32-bit L & R halves
• As for any Feistel cipher can describe as: Li = Ri–1
• F takes 32-bit R half and 48-bit subkey:
- Expands R to 48-bits using E table
- Adds to subkey using XOR
- Passes through 8 S-boxes to get 32-bit result
- Finally permutes using 32-bit perm P table
sbox에서 매핑방법
예를들어 100001이 오면 맨앞과 맨뒤 한자리를 짤라 11, 그리고나머지 0000 두개가 생긴다.
2자리수를 왼쪽 기준, 나머지 4자리수를 오른쪽기준으로하여 표에 맞춰 보면 1111을 출력하게 된다.
이런방식으로 sbox 8 개가 매핑을 통해 48비트를 32비트로 변경 시킴.
4) DES P-box를 통해 32비트를 섞는다.
5) swap하고 최종적으로 섞어 ciphertext를 만든다.
암호화는 Permutation(순열), Substitution(대체) 방식으로 이루어지게 된다.
Securtiy of DES
-
S-boxes가 안정성에 영향을 준다.
-
back door가 없는 것으로 밝혀짐, key를 직접 하나하나 넣어보는 수 밖에없음
- F함수
- 각 라운드마다 오른쪽(R)의 32비트가 E(expansion)을 거쳐 48비트가 된다.
- 이렇게 얻은 48비트와 키 스케줄을 거친 키 48비트가 XOR을 거치고 F함수로 들어간다.
- XOR로 얻은 48비트는 8부분으로 나뉘어 각각 6비트씩 S-BOX에 들어간다.
- S-BOX에 들어갔다 나온 값들은 4비트로 나오게 되고 결국 모두 합치면 8*4인 32비트가 나온다.
- 결국 32비트는 P(permutation)을 거쳐 F함수의 결과인 32비트를 도출해낸다.
(SBOX 참고 :: http://terms.naver.com/entry.nhn?docId=3431991&cid=58437&categoryId=58437)
- 키 스케줄
처음 64비트 key는 PC1을 거쳐 56비트의 키가 된다. 이때 사용되지 않은 8비트는 패리티 비트로 사용된다.
56비트는 left, right로 28비트씩 반반 가는데 이때 각 라운드마다 키 회전 스케쥴에따라 왼쪽으로 1비트 혹은 2비트 회전하게 된다.
(1,2,9,16번째는 한번 쉬프트, 나머지는 두번 쉬프트한다.)
첫번째 키는 1번 쉬프트를 하고 두 부분을 합쳐 PC 2를 통과시켜 48비트가 된다.
두번째 키는 1번 쉬프트를 하고 두 부분을 합쳐 PC 2를 통과시켜 48비트가 된다.
세번째 키는 2번 쉬프트를 하고 두 부분을 합쳐 PC 2를 통과시켜 48비트가 된다.
...
열여섯번째 키는 1번 쉬프트를 하고 두 부분을 합쳐 PC 2를 통과시켜 48비트가 된다.
- DES 복호화(DES 취약점)
반대 방향으로. 16번째 키, 15번째 키, ... 를 이용해 16라운드를 다시 거친 뒤 IP의 역연산을 거치면 처음 평문을 얻을 수 있다.