서블릿은 톰캣 같은 웹 애플리케이션 서버를 직접 설치하고, 그 위에 서블릿 코드를 클래스 파일로 빌드해서 올린 다음, 톰캣 서버를 실행하면 된다. 하지만 이 과정은 매우 번거로워 스프링을 이용해서 수업을 진행한다.
스프링 부트는 톰캣 서버를 내장하고 있어, 별도의 톰캣 서버 설치, 세팅 없이 편리하게 서블릿 코드 예제를 실행할 수 있다.!
서블릿 등록하고 실행 해보기
실행 값 해석
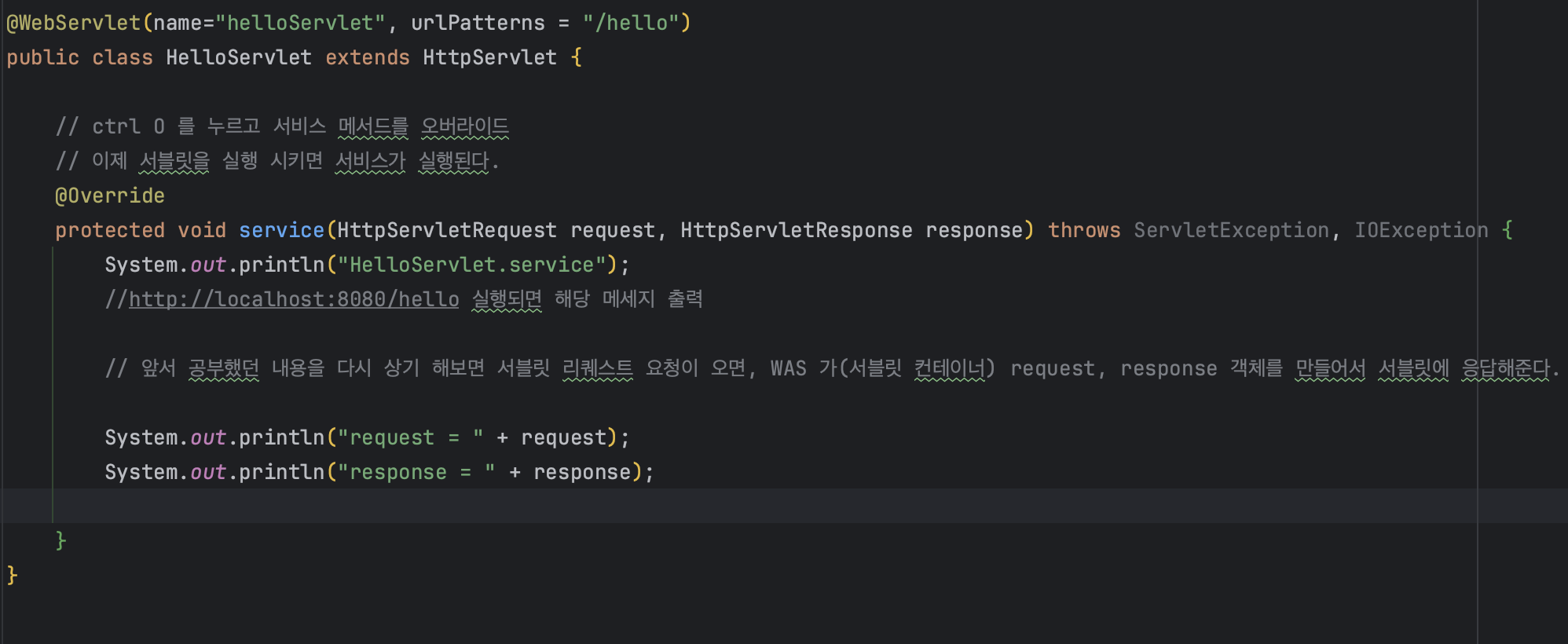
HttpServlet.service : 서블릿의 service 메서드가 실행 됐다는 내용.
request = org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@5e4e72 요청객체
org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade 클래스의 인스턴스로 Httprequest는 인터페이스로 아파치 톰캣이 구현한 구현체이다.@5e4e72는 요청 객체의 해시코드이다.
헤시코드는 인스턴스의 고유한 값이다. 인스턴스는 객체를 생성할 때 메모리에

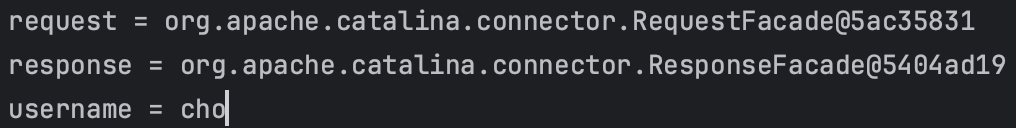
서블릿 컨테이너 동작 방식
일단 스프링 부트를 실행하게 되면, 스프링 부트 안의 내장된 톰캣 서버를 띄우게 되는데, 톰캣 서버는 서블릿 컨테이너 기능을 내장하고 있다. 이를 통해 helloServlet이 생성되게 되고 그 다음 HTTP 요청을 서버에 요청한다.
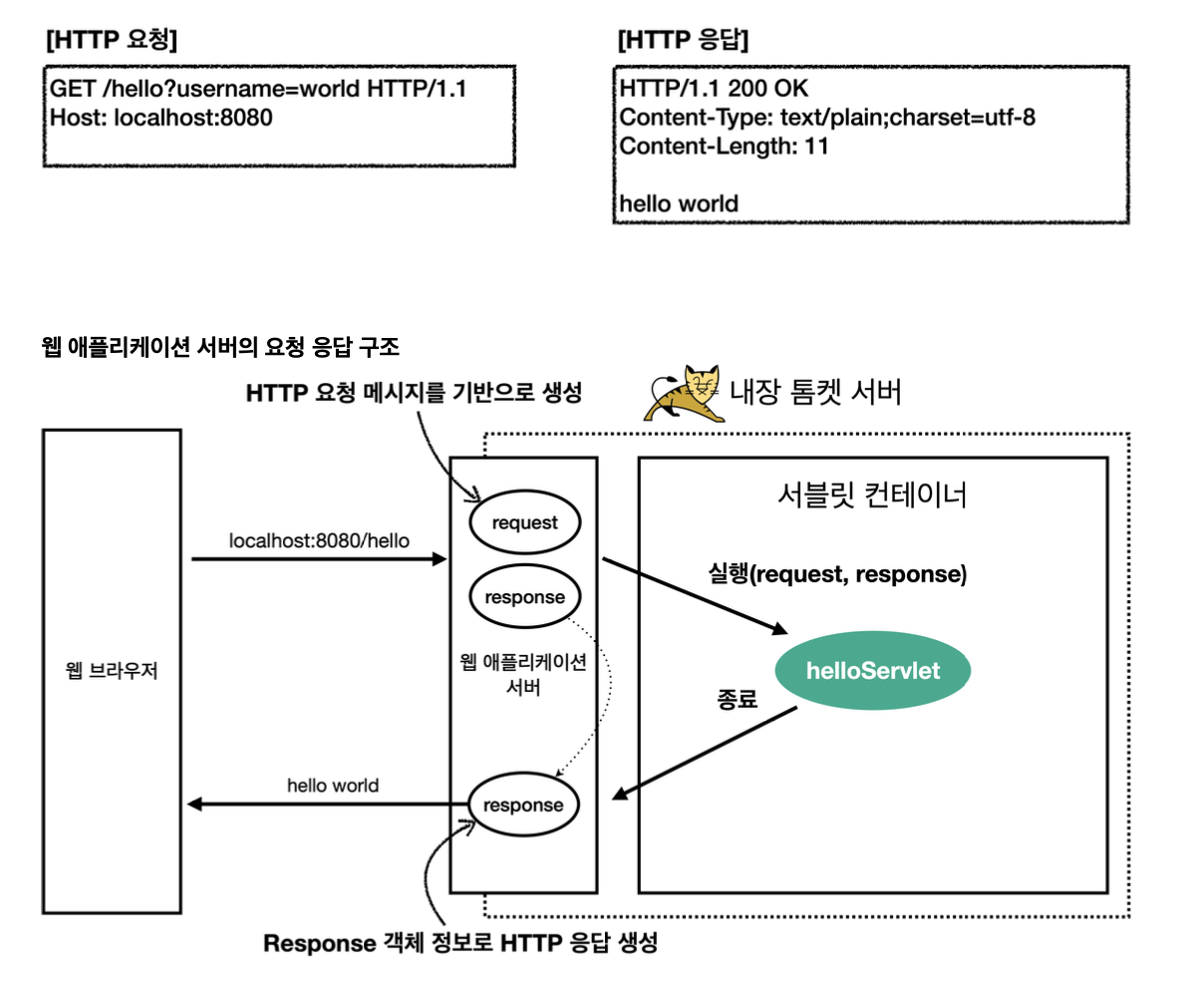
그 이후에 서버는 request, response 객체를 만들면서 싱글톤 객체인 helloServlet을 호출한다. 이 안에 있는 서비스 메서드를 호출 하면서 response를 넘겨준다. 이 데이터에다가 컨텐츠 타입, 바디에 담을 메세지 등을 담게 되면 종료되고 나가면서 WAS 서버가 response 메세지를 가지고 HTTP 응답을 만들어준다.
HttpServletRequest 개요
HttpServletRequest의 역할
HTTP요청을 대신 파싱(해석)하고 제공
HTTP 요청 메세지를 개발자가 직접 파싱해서 사용해도 되지만, 매우 불편할 것이다. 서블릿은 개발자가 HTTP 요청 메세지를 편리하게 사용할 수 있도록 개발자 대신에 HTTP 요청 메세지를 파싱한다. 그리고 그 결과를 HttpServletRequest 객체에 담아서 제공한다.
HttpServletRequest 를 사용하면 다음과 같은 HTTP 요청 메세지를 편리하게 조회할 수 있다.
HTTP 요청 메세지를 파싱한다는 게 무슨 말이지? (보충 내용)
HTTP 요청 메세지에서 필요한 정보를 추출하고 분석하는 과정 을 의미한다. 일반적으로 웹 서버는 클라이언트로부터 HTTP 용어을 받으면 해당 요청 메시지를 파싱하여 요청된 작업을 이해하고 처리한다.
크게 3가지 단계로 나눌 수 있다
1. 요청 라인 파싱
2. 헤더 파싱
3. 본문 파싱(생략 가능)
HTTP 요청 구조 예시
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.com
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0
Accept-Language: en-US
-
요청 라인(Request Line):
GET: HTTP 메서드로, 서버에게 리소스를 요청하는 것을 나타냅니다./index.html: 요청한 자원의 경로입니다. 이 요청은 서버의 루트 디렉토리에 있는 "index.html" 파일을 요청합니다.HTTP/1.1: 사용하는 HTTP 프로토콜의 버전입니다.
-
헤더(Headers):
Host: www.example.com: 요청한 리소스의 호스트 이름을 나타냅니다.User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0: 클라이언트의 사용자 에이전트 정보를 나타냅니다. 이 경우 Mozilla 브라우저를 사용하고 있는 것으로 보입니다.Accept-Language: en-US: 클라이언트가 지원하는 언어를 나타냅니다. 이 경우 영어(미국)을 지원한다는 것을 나타냅니다.
파싱
요청 라인 파싱
HTTP 메서드 (GET,POST,PATCH, PUT, DELETE.. )
요청한 자원의 경로( /index.html 등..)
HTTP 프로토콜 버전 등
헤더 파싱
HTTP 헤더는 클라이언트와 서버간의 통신을 제어한다.
호스트 이름, 사용자 에이전트 정보, 쿠키, 인증 정보 등
본문 파싱
POST 요청과 같이 본문(바디) 가 있는 경우 클라이언트가 보낸 데이터를 추출할 수 있다. 주로 JSON, XML 이 쓰인다.
파싱 예시
아래와 같은 코드를 서블릿이 전부 해준다고 생각하면 된다. 뒤에 나올 예시에서는 직접 써보기도 한다.
// 1. 요청 라인 파싱
String requestLine = requestReader.readLine(); // 요청 라인을 읽어옴
String[] requestLineParts = requestLine.split(" "); // 공백을 기준으로 요청 라인을 분할
String method = requestLineParts[0]; // HTTP 메서드 추출 (GET, POST 등)
String path = requestLineParts[1]; // 요청한 자원의 경로 추출 (/index.html 등)
String protocol = requestLineParts[2]; // HTTP 프로토콜 버전 추출 (HTTP/1.1 등)
// 2. 헤더 파싱
String headerLine;
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>(); // 헤더 정보를 저장할 맵 생성
while ((headerLine = requestReader.readLine()) != null && !headerLine.isEmpty()) {
// 빈 줄을 만날 때까지 헤더를 읽어옴
String[] headerParts = headerLine.split(": "); // 콜론과 공백을 기준으로 헤더를 분할
String headerName = headerParts[0]; // 헤더 이름 추출
String headerValue = headerParts[1]; // 헤더 값 추출
headers.put(headerName, headerValue); // 맵에 헤더 정보 추가
}
// 3. 본문 파싱 (생략 가능)
// 파싱된 정보를 기반으로 요청 처리
handleRequest(method, path, headers);
HTTP 요청 메세지
POST/ save HTTP/1.1
Host : localhost: 8000
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
username=kim&age=20START LINE
- HTTP 메소드
- URL
- 쿼리 스트링
- 스키마, 프로토콜(버전)
헤더 - 헤더 조회
바디
- form 파라미터 형식 조회
- message body 데이터 직접 조회
HttpServletRequest 부가 기능
임시 저장소 기능
해당 HTTP 요청이 시작부터 끝날 때 까지 유지되는 임시 저장소 기능
- 저장
-request.setAttribute(name,value) - 조회
-request.getAttribute(name)
세션 관리 기능
request.getSession(create:true)
중요
HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse를 사용할 때 가장 중요한 점은 이 객체들이 HTTP 요청 메세지, HTTP 응답 메세지를 편리하게 사용하도록 도와주는 객체라는 점이다. 따라서 이 기능에 대해서 깊이 있는 이해를 하려면 HTTp 스펙이 제공하는 요청, 응답 메세지 자체를 이해 해야한다.
HttpServletRequest -기본 제공 기능
@WebServlet(name="requestHeaderServlet",urlPatterns = "/request-header")
public class RequestHeaderServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
printStartLine(request);
}
private static void printStartLine(HttpServletRequest request) {
System.out.println("--- REQUEST-LINE - start ---");
System.out.println("request.getMethod() = " + request.getMethod()); //GET
System.out.println("request.getProtocol() = " + request.getProtocol()); //HTTP/1.1
System.out.println("request.getScheme() = " + request.getScheme()); //http// http://localhost:8080/request-header
System.out.println("request.getRequestURL() = " + request.getRequestURL());// /request-header
System.out.println("request.getRequestURI() = " + request.getRequestURI());//username=hi
System.out.println("request.getQueryString() = " + request.getQueryString());
System.out.println("request.isSecure() = " + request.isSecure()); //https 사용유무
System.out.println("--- REQUEST-LINE - end ---");
System.out.println();
}
private void printHeaders(HttpServletRequest request) {
System.out.println("--- Headers - start ---");
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String headerName = headerNames.nextElement();
System.out.println(headerName + ": " + request.getHeader(headerName));
}
request.getHeaderNames().asIterator()
.forEachRemaining(headerName -> System.out.println("headerName"+headerName));
System.out.println("--- Headers - end ---");
System.out.println();
}
}그냥 지나가다가 든 의문점
왜 httepServlet이 제공하는 메서드는 왜 protected가 많을까?
일반적으로 HTTPServlet 클래스의 메서드들 중 대부분은
protected접근 제어자를 가지고 있다. 이는 서블릿의 생명주기에 관련된 메서드들이며, 이러한 메서드들은 서블릿 컨테이너에 의해 호출되기 때문에 직접적으로 외부에서 호출될 필요가 없기 때문이다.
서블릿은 서블릿 컨테이너에 의해 관리되며, 서블릿의 생명주기를 관리하기 위해 여러 메서드들이 호출됩니다. 예를 들어, 서블릿의 초기화(init)나 서비스(service), 소멸(destroy) 등의 과정은 서블릿 컨테이너에 의해 자동으로 처리됩니다. 이러한 메서드들은 일반적으로 외부에서 직접 호출되지 않으며, 서블릿 컨테이너에 의해 호출되므로protected접근 제어자를 가지고 있다.
따라서 서블릿 클래스의 메서드들은 주로 서블릿 컨테이너에 의해 관리되고 호출되므로, 대부분의 메서드들은
protected접근 제어자를 가지고 있다. 이러한 설계는 서블릿의 캡슐화를 유지하고, 외부에서의 직접적인 접근을 제한함으로써 안전성과 유지보수성을 높이는 데 도움이 된다.
상속 관례에 따라 사용 범위를 최소화 하려는 의도 같다
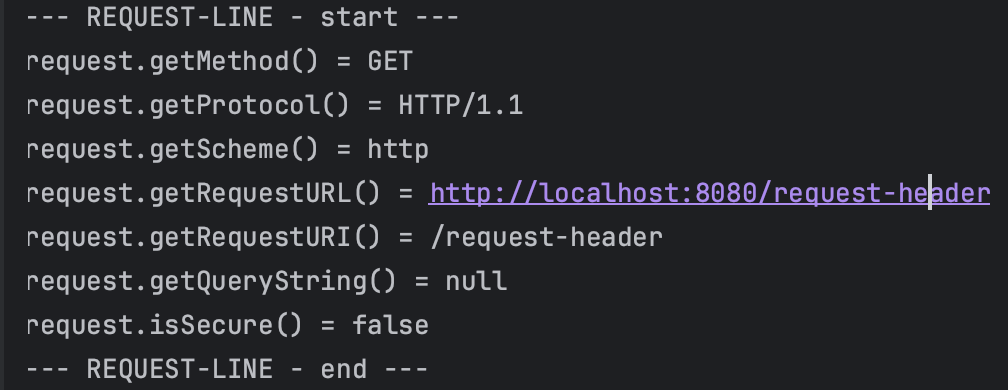
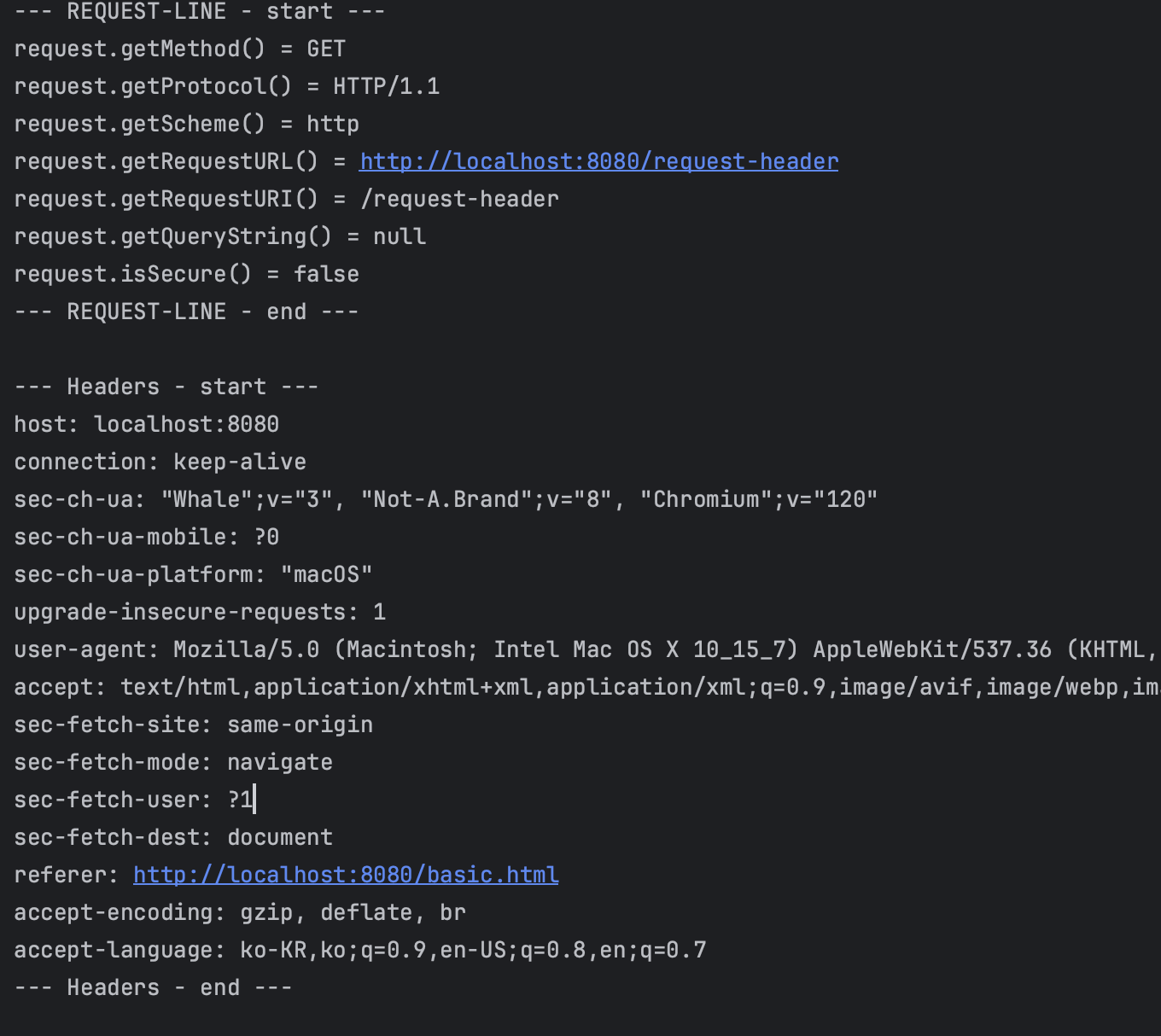
헤더, 요청, 기타 부 까지 메서드로 전부 꺼내볼 수 있다 정도만 인지하고 가자
HTTP 요청 데이터 -개요
HTTP 요청 메세지를 통해 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전달하는 방법 3가지
Get 쿼리 파라메터
GET /url?username=hello&age=20 HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com/url?username=hello&age=20
- 메세지 바디 없이, URL의 쿼리 파라메터에 데이터를 포함해서 전달한다
- 검색, 필터, 페이징 등에서 많이 사용한다
POST - HTML Form
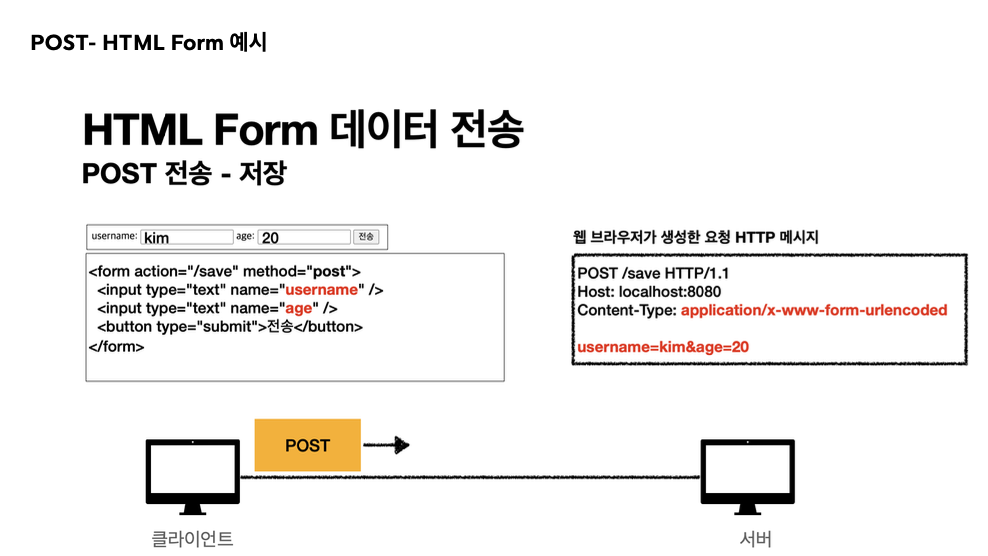
HTML 폼 양식을 통해 전달된 방식. Content-Type에서도 url에서 encoded된 형식이라고 쓰여있다.
POST /submit-form HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
username=hello&age=20content-type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메세지 바디에 쿼리파라메터 형식으로 전달한다.
-username=hello&age=20
- 쿼리 파라메터랑 비슷하게 생겨서 헷갈릴 수 있다.
- 차이점은 바디에 담는 다는 점 - 회워 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form 을 사용한다
HTTP message body
POST /submit-form HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
{
username=hello&age=20
}바디에 직접 데이터를 담아서 요청한다
- HTTP API 에서 주로 사용, JSON,XML,TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
HTTP 요청 데이터 Get 쿼리 파라메터 사용 방법
아래의 데이터를 클라이언트에서 서버로 바디 없이 전송 해보자!
**전달 데이터
- username= hello
- age=20
메시지 바디 없이, URL의 쿼리파라미터를 사용해서 데이터를 전달하자.
검색, 필터, 페이징에 사용되는 방식
쿼리 파라미터는 URL에 다음과 같이 ?를 시작으로 보낼 수 있다. 추가 파라메터는 &로 구분한다
http://localhost:8080/request-param?username=hello&age=20
서버에서는 HttpServletRequest가 제공하는 다음 메서드를 통해 쿼리 파라미터를 편리하게 조회할 수 있다
String username= request.getParameter("username");
// 단일 파라미터 조회
Enumeration<String> parameterNames= request.getParameterNames();
// 파라미터 이름들 모두 조회
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();
//파라미터를 Map으로 조회
String [] usernames= request.getParameterValues("username");
//복수 파라미터 조회전체 파라미터와 단일 파라미터 예제
getParameter로 읽어 오고 사용할 때엔 asIterater로 꺼낸다.
System.out.println("전체 파라메터 조회");
request.getParameterNames()
.asIterator().forEachRemaining(paramName-> System.out.println(paramName + "=" +request.getParameter(paramName)));
System.out.println("전체 파라메터 조회 END END END");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("단일 파라메터 조회 START START ");
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
System.out.println("username = " + username);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println("단일 파라메터 조회 END END END ");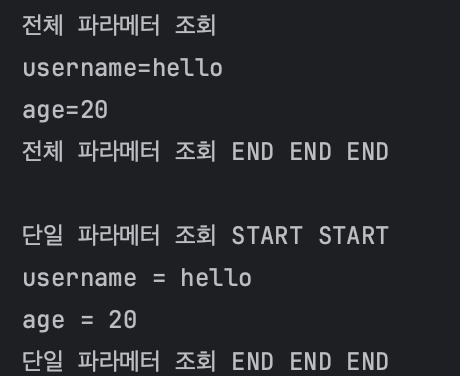
복수 파라미터로 단일 파라미터 조회
http://localhost:8080/request-param?username=hello&age=20&username=hello2
하나의 파라메터에 여러 값들을 보낼 수 있는데 이런 경우엔 단일 조회시 내부 우선순위가 우선으로 매김하는 것들이 나오게 되는데 복수 파라메터 조회로 하면 값을 다 불러 올 수 있다.
request.getParameter()는 하나의 파라미터 이름에 단 하나의 값만 있을때 사용해야 하며 중복일 때엔 request.getParameterValues()를 사용한다. 중복일 때에 getParameter()를 쓰면 위에서 언급했 듯 첫 번째 밸류만 반환한다.
System.out.println("이름이 같은 복수 파라미터 조회 START START");
String[] usernames = request.getParameterValues("username");
for (String s : usernames) {
System.out.println("s = " + s);
}
response.getWriter().write("ok");
System.out.println("이름이 같은 복수 파라미터 조회 END END ");
HTTP 요청데이터 - POST HTML Form
HTML Form은 회원가입 ,상품 주문 등에서 많이 사용하는 방식이다.
메시지 바디에 쿼리 파라메터 형식으로 전달
특징
- content-type :
application/x-www-form-urlencoded - 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 데이터를 전달한다.
username=hello&age=20
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/request-param" method="post">
username: <input type="text" name="username" />
age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<button type="submit">전송</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>위 코드로 POST 의 HTML Form 형식으로 전송 하면 웹 브라우저는 다음 형식으로 HTTP 메서드를 만든다.
요청 URL : http://localhost:8080/request-param
content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
message body: username=hello&age=20
참고:
.getParameter()
.getParameter()는 GET 쿼리 파라미터는 물론 HTML Form 형식이 Body 부분 안에 있는 메세지 또한 꺼낼 수 있다. 따라서 이전에 만들어 놓은 파라미터 조회 메서드( 단일 조회, 전체 조회, 중복 조회 등) 을 그대로 써도 문제 없이 작동한다. 서버의 입장에서는 둘의 형식이 동일 하기 때문에 구분지어 별도의 코드를 만들 수고가 필요 없다!
추가
application/x-www-form-urlencoded 란?
content-type은 HTTP 메시지 바디 데이터 형식을 지정한다
GET URL 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전달할 때는 HTTP 메세지 바디를 사용하지 않기 때문에 content-type이 없다
POST HTML Form으로 데이터 전달시 HTTP 메시지 바디에 해당 데이터를 포함해서 보내기 때문에 바디에 포함된 데이터가 어떤 형식인지 꼭 content-type을 지정 해야 한다. 이렇게 폼으로 데이터를 전송하는 형식을application/x-www-form-urlencoded라 한다.
Post HTML Form을 테스트 하려면 매번 Form 양식을 만들어야 하나요?
API 요청 테스트에 x-www-form-urlencoded 양식으로 요청하면 된다
###HTML Form 양식 테스트
POST http://localhost:8080/request-param
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
username=kim
age=256512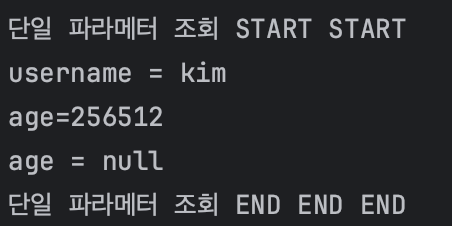
HTTP 요청 데이터 - API 메시지 바디 -단순 텍스트
HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
-
HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML,TEXT
-
데이터 형식은 주로 JSON
-
POST, PUT, PATCH
-
먼저 가장 단순한 텍스트 메세지를, HTTP메시지 바디에 담아서 전송하고 읽어본다.
-
HTTP 메시지 바디의 데이터를 InputStream을 사용해 직접 읽을 수 잇다.
@WebServlet(name = "requestBodyStringServlet", urlPatterns = "/request-body-
string")
public class RequestBodyStringServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream,
StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("messageBody = " + messageBody);
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
}###HTML Form 양식 테스트
POST http://localhost:8080/request-body-string
Content-Type: text/plain
message body: hello결과 message body= hello
HTTP 요청 데이터- API 메시지 바디- JSON
HTTP API에서 주로 사용하는 JSON 형식으로 데이터를 전달 해보자
JSON 형식 전송
POST http://localhost:8080/request-body-json
- content-type:application/json
- messagebody :
{"usename":"hello","age":20}
결과
messageBody = {"username":"hello","age":20}
JSON 형식 파싱 추가
JSON 파싱 객체 생성
@Getter @Setter public class HelloData {
private String username;
private int age;
}요청 출력 부분
@WebServlet(name = "requestBodyJsonServlet", urlPatterns = "/request-body-json")
public class RequestBodyJsonServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse
) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream,
StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("messageBody = " + messageBody);
HelloData helloData = objectMapper.readValue(messageBody,
HelloData.class);
System.out.println("helloData.username = " + helloData.getUsername());
System.out.println("helloData.age = " + helloData.getAge());
response.getWriter().write("ok");
} }- 서블릿 클래스 정의
- ObjectMapper 초기화 : JSON 객체로 변환하기 위함
- service() 오버라이드
- HTTP 요청 본문 읽기: getInputStream()
- 스트림 문자열로 변환 : StreamUtils.copyToString() 서블릿 기본 제공 메서드
- JSON 데이터 파싱 : ObjectMapper.readValue()
- 자바 객체로 변환된 데이터 처리 : JSON -> JAVA 객체로 캐스팅 됨 여기서는 각 필드의 값 출력
- 응답 전송 (ok)
HttpServletResponse 기본 사용법
HttpServletResponse역할
HTTP 응답 메세지 생성
개발자가 일일히 만들지 않는 대신 메서드의 값만 넣어주며 생성해준다
- HTTP 응답코드 지정
- 헤더 생성
- 바디 생성
편의 기능 제공
- Content-Type, 쿠키, Redirect(300)
@WebServlet(name = "responseHeaderServlet", urlPatterns = "/response-header")
public class ResponseHeaderServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//[status-line]
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); //200
//[response-headers]
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, no-store, must-
revalidate");
response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
response.setHeader("my-header","hello");
//[Header 편의 메서드] content(response);
cookie(response);
redirect(response);
//[message body]
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("ok");
}
}Content 편의 메서드
private void content(HttpServletResponse response) {
//Content-Type: text/plain;charset=utf-8
//Content-Length: 2
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=utf-8"); response.setContentType("text/plain"); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //response.setContentLength(2); //(생략시 자동 생성)
}
쿠키 편의 메서드
private void cookie(HttpServletResponse response) {
//Set-Cookie: myCookie=good; Max-Age=600;
response.setHeader("Set-Cookie", "myCookie=good; Max-Age=600");
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("myCookie", "good");
cookie.setMaxAge(600); //600초
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
redirect 편의 메서드
private void redirect(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//Status Code 302
//Location: /basic/hello-form.html
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FOUND); //302
response.setHeader("Location", "/basic/hello-form.html");
response.sendRedirect("/basic/hello-form.html");
}
HTTP 응답 데이터 - 단순 텍스트, HTML
HTTP 응답 메시지는 주로 다음 내용을 담아서 전달한다
- 단순 텍스트 응답
- 앞에서 살펴봄(`writer.println("ok");) - HTML 응답
- HTTP API - MessageBody JSON 응답
@WebServlet(name = "responseHtmlServlet", urlPatterns = "/response-html")
public class ResponseHtmlServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("<html>");
writer.println("<body>");
writer.println(" <div>안녕?</div>");
writer.println("</body>");
writer.println("</html>");
//Content-Type: application/json
response.setHeader("content-type", "application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
HelloData data = new HelloData();
data.setUsername("kim");
data.setAge(20);
//{"username":"kim","age":20}
String result = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(data);
response.getWriter().write(result);
} }

정리
HttpServletRequest
- 각 요청 파싱(요청부,헤더,본문)
- 임시 저장소
- 세션 관리 기능
HTTP 요청 데이터 - GET 쿼리 스트링 파라메터
- POST HTML Form
- POST message body
HttpServletResponse - 헤더생성
- 바디생성
- 편의 기능
- Content-Type, 쿠키, Redirect(300)
HTTP 응답 데이터 - 단순 텍스트
- HTML
- HTTP API - JSON
그 외 - 요청 데이터 파라메터로 꺼내기
- 응답 데이터 꺼내기
