"Django"(2)
어제하던 프로젝트에 이어서 진행해보도록 하겠다
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include # 여기까진 기본 url http://127.0.0.1:8000/이다 urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), # admin page 장고에서 기본적으로 지원됨 path('polls/', include('polls.urls')) # http://127.0.0.1:8000/뒤에 polls/라는 url # 즉 http://127.0.0.1:8000/polls/로 들어가게 되면 # include('polls.urls)를 통해 polls폴더의 url.py로 이동하여 url처리를 하라는 뜻 ]
- 각각의 기능이 가지는 url이 모두 다르다!
- root url에서 polls url이 추가가되면 polls.url로 이동하여 처리하게 된다.
- polls.urls.py
from django.urls import path, include # view에 대한 경로를 import 해준다. from polls import views app_name = "polls" urlpatterns = [ # 여기까지의 경로 http://127.0.0.1:8000/polls/ path('', views.index, name='index'), # path뒤에 공백이면 현재경로를 의미 # views.index : views에서 제공되는 index 함수를 이용한 로직처리를 요청 # name은 논리적인 이름을 의미한다. ]다음과 같이 polls.urls도 설정을 완료 했으면 views로가서 로직 처리를 진행해야 한다.
- views.py
from django.shortcuts import render, get_object_or_404 from polls.models import Question # models에서 Question을 가져온다. # Create your views here. # client의 request가 urlconf를 거쳐 view까지 들어와야 한다. def index(request): # logic 처리 # Database 처리 # HTML에 표현해야할 처리된 결과값들이 생길 수 있다! # 이 결과 값들을 dictionary에 담아요! question_list = Question.objects.all().order_by('pub_date') # question의 객첸데 다 가지고와 라는 의미 # 즉 Question객체인 모든 객체를 pub_date 기준으로 정렬해서 가져오라는 의미 context = { "q_list" : question_list } # Template을 이용해서 클라이언트에게 response를 돌려줘요! 이 response가 http 객체임 # render : 장고가 제공해주는 이 함수를 이용하자 # render() 함수는 template html을 이용해서 http response 객체를 생성해줌! return render(request, 'polls/index.html', context) #두번째인자로 template html이 들어감 # rquest와 polls안의 html을 이용하고 위에나온 context라는 결과객체를 이용할 것입니다이제 polls안에서 template라는 폴더를 만들고 여기아네 어플리케이션 이름으로 폴더를 하나 더 생성해준다, 그리고 그안에 rsponse를 보낼 index.html 문서를 만들어준다.
- index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <ul> {% for question in q_list %} <li><a href="/polls/{{ question.id }}/">{{ question.question_text }}</a></li> {% endfor %} <!-- 값을 찍을때는 {{ }}를 사용하고 {% %}는 로직을 실행할 때 쓴다 --> <!-- question 테이블에서 만든 객체를 보여주고 하이퍼 링크를 걸어 해당 목록을 선택시 관련된 선택 목록 페이지로 이동 시킨다.--> <!-- 즉 링크를 id번호에 따라 각각 부여해줘야한다. polls/1이면 1번항목 보여주세요 이런식--> </ul> </body> </html>
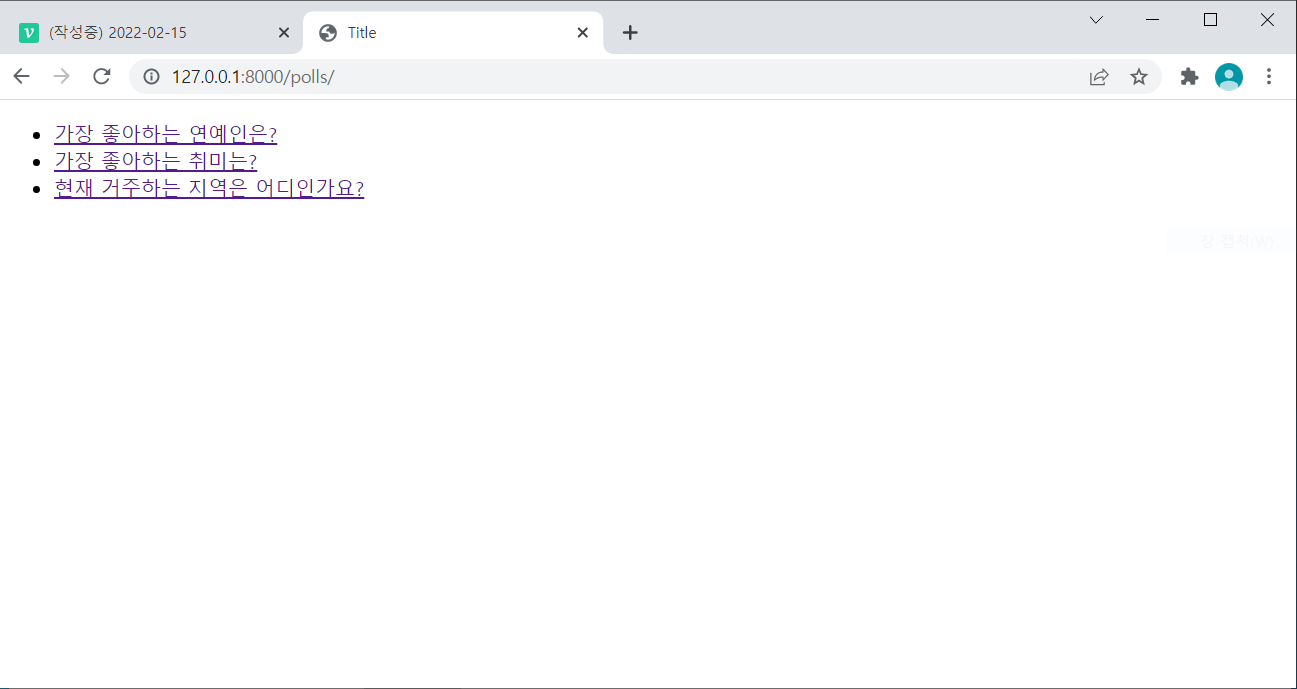
- runserver로 서버를 기동해 /polls/경로로 이동하면 다음과 같이 나온다.
- 이제 각각의 링크를 바꿔줘야한다. 3개가 각각 다른 링크를 실행해야 한다.
- 즉 polls/1,2,3숫자 (pk가 들어올때마다 링크가 바껴야함)
- polls/1이면 1번항목 보여주세요, polls/2면 2번항목에 대한 투표항목을 보여주세요 라는 request가 들어간다고 보면된다.
- views.py 파일에 로직처리를 위해 함수를 하나 선언해주자.
from django.shortcuts import render, get_object_or_404 from polls.models import Question # Create your views here. def detail(request,question_id): question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id) # 프라이머리키와 매칭되는 객체 하나만 가져오겠다는 의미이다. context = { "my_question": question } return render(request, "polls/detail.html", context)이제 투표 버튼을 만들 차례이다.
라디오 버튼을 만들면 체크박스처럼 다 선택이 된다. 그럼 라디오 버튼을 어떻게 처리해야하는가?
- 따로따로 선언하면 개별적으로 선택이 되지만 묶어서 선택하면 하나씩 선택 할 수있다!
<input type"radio">아이유><br> <input type"radio">아이유><br> <input type"radio"name="choice">아이유<br> <input type"radio"name="choice">김연아<br> <input type"radio"name="choice">홍길동<br> <input type"radio"name="choice">신사임당<br>
- 다음과 같이 하나씩 선언하는게 아니라 그룹으로 설정하면된다.
- 그룹은 name을 설정해 주면된다.
- 추가적으로 버튼 말고 이름을 눌렀을 때도 체크박스가 선택 되도록 만들어 보자!
<input type="radio" name="choice"> <label >아이유</label>
- input type과 label에 id를 설정하여 매칭시켜 준다.
<input type="radio" name="choice" id="my_1"> <label for="my_1">아이유</label> <input type="radio" name="choice" id="my_2"> <label for="my_2">김연아</label> <input type="radio" name="choice" id="my_3"> <label for="my_3">홍길동</label> <input type="radio" name="choice" id="my_4"> <label for="my_4">신사임당</label>
- 다음과 같이 선언해 주면 된다.
- 하지만 안에 내용은 데이터베이스에서 가져와야하는 내용이다 그렇기에 위 과정을 4번 반복해야한다.
- 작성은 다음과 같이 할 수있다.
{% for choice in my_question.choice_set.all %} <input type="radio"name="choice" id ="my_1"> <label for="my_1">{{ choice.choice_text }}</label> {% endfor % } <!-- my_question.choice_set.all --> <!-- my_question질문에대한 choice의 fk에 연결되어있는 항목들의 집합중에 싹다 이렇게 쓰면 항목들이 데이터베이스에서 직접 가져와서 조회가 된다 하지만 이렇게만 쓰면 id값(my_1)이 다 똑같이 겹처서 글자와 동그라미를 눌렀을 때 둘다 체크되는건 하나 뿐이다! --> <!--그렇담 어떻게 하는가? id를 loof를 돌면서 바꾸면된다.--> {% for choice in my_question.choice_set.all %} <input type="radio" name="choice" id="my{{ forloop.counter }}" value="{{ choice.id }}"> <label for="my_{{ forloop.counter }}">{{ choice.choice_text }}</label><br> {% endfor %} {% endfor %} <!-- forloop.counter: loop가 돌때마다 카운트값이 자동으로 1씩증가함 -->
- 이제 항목을 선택해서 투표를 하는 버튼을 만들 것이다.
- 일단 작성은 다음과 같이 하면된다.
<form> {% for choice in my_question.choice_set.all %} <input type="radio"name="choice" id ="my_{{ forloop.counter }}" value="{{ choice.id}}"> <label for="my_{{ forloop.counter }}"> {{choice.choice_text }}</label><br> {% endfor % } <br><br> <input type ="submit" value ="투표하기"> </form> <!-- <input type ="button" value ="투표하기"> 이렇게 하면 버튼이 생성되지만 버튼클릭시 해당 투표수가 카운트되는 액션을 취해야한다. 그러기에는 기존에 사용하는 button말고 submit을 사용해야한다. --> <!-- form은 하나의 양식으로 묶어준다는 의미다. 그러고나서 button대신 submit을 사용하면 form으로 선택된 데이터들을 서버쪽에 제출한다는 의미를 가진다.-->
- 추가적으로 알아보자
<form action = "http://www.naver.com" method="get"> {% for choice in my_question.choice_set.all %} <input type="radio"name="choice" id ="my_{{ forloop.counter }}" value="{{ choice.id}}"> <label for="my_{{ forloop.counter }}"> {{choice.choice_text }}</label><br> {% endfor % } <br><br> <input type ="submit" value ="투표하기"> </form> <!-- action은 내가 선택한 정보를 가지고 submit 버튼을 누르면 action을 취하겠다는 의미이다 즉 action 뒤에는 클라이언트가 서버쪽에 보내는 request url을 보낸다 즉 naver.com으로 이동된다--> <!--하지만 url만 보내줄게 아니라 내가 무엇을 선택했는지 부가적인 정보도 보내줘야한다. 즉 뒤에 method를 붙여 보내줄 수 있다.--> <!-- get 방식이니깐 query string으로 부가적인 정보가 같이가요! 즉 [?변수=값] name에 choice가 변수 이름이 됨 여기서 name의 역할을 radio 그룹으로 묶어주는 역할 request할때 부가적인 정보를 주기위한 parametar 이름 값은 input안에는 없지만 원래는 <input type="radio"name="choice" id ="my_{{ forloop.counter }}" value="tiger"> 이런식으로 value에 값이 들어가줘야한다. value가 변수 역할 즉 url이 다음과 같이 작성된다. http://www.naver.com?choice=tiger 근데 이렇게 작성하면 또 모든 radio 버튼에 tiger가 고정이된다 그러므로 위와 같은 형식으로 작성하고 선택을해서 버튼을 누르면 https://www.naver.com/?choice=1 이런식으로 나오게 된다. 이렇게되면 request url을 보내면서 내가 어떤것을 선택했는지 알 수 있게 된다.-->
- post 방식
<form action = "http://www.naver.com" method="post"> {% for choice in my_question.choice_set.all %} <input type="radio"name="choice" id ="my_{{ forloop.counter }}" value="{{ choice.id}}"> <label for="my_{{ forloop.counter }}"> {{choice.choice_text }}</label><br> {% endfor % } <br><br> <input type ="submit" value ="투표하기"> </form> <!-- post방식으로 보내면 query string이 안보임 request header에 들어가서 전달이 되기 때문에 get은 url 뒤에 부가적으로 전달할 데이터를 request url을 붙여보냄 즉 데이터가 보임 url의 길이가 제한적이기 때문에 get 방식은 내가 무한정 많이 데이터를 보낼 수없음 post방식은 url뒤에 데이터가 붙지않고 request header에 들어가 데이터를 무한정 보낼 수 있음 그렇기 때문에 이 방식만 post 방식을 이용한다! 꼭 꼭 꼭 알아두자 이제 naver로 호출하는 것이 아닌 우리가 사용할 url을 적어줘야한다.-->
- 여기까지 했으면 투표를 완료하고 투표수가 카운트 되는 url을 작성해야한다.
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include from polls import views app_name = 'polls' # http://127.0.0.1:80000/polls/ 여기까지가 고정 urlpatterns = [ # http://127.0.0.1:80000/polls/ path('', views.index, name='index'), # http://127.0.0.1:80000/polls/2/ path('<int:question_id>/', views.detail, name='detail'), # name은 관계에 대한 내용을 의미 # http://127.0.0.1:80000/polls/1/vote/ path('<int:question_id>/vote/', views.vote, name='vote'), http://127.0.0.1:80000/polls/2/results/ path('<int:question_id>/results/', views.results, name='results'), ]
- views에서도 vote함수 및 results 함수를 설정해 줘야한다.
from django.shortcuts import render, get_object_or_404 from polls.models import Question from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect # 클라이언트에게 다시접속해 라는것을 만들어 낼 수 있음 from django.urls import reverse def vote(request, question_id): # 질문객체를 가지고 와요! question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id) # 해당 질문객체와 ForeignKey로 연결된 객체를 가져와요! choice = question.choice_set.get(pk=request.POST['choice']) choice.votes += 1 choice.save() # redirect를 사용해 보아요! # 클라이언트에게 응답을 주긴 주는데 그응답의 내용이 다른 URL에 바로 request를 보내라! # return HttpResponseRedirect(다른 URL, 전달할 값) 인자 두개들어감 return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('polls:results', args=(question.id,))) # reverse안에 url의 이름 즉 긴 url의 관계를 name으로 만든 name을 쓰는데 app_name과 url name을 붙여 적어야한다! # <> 안의 값을 넣어주기위해 args를 사용하여 넣어준다. def results(request, question_id): # 질문객체를 가지고 와요! question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id) context ={ "my_question": question } return render(request,'polls/result.html', context)
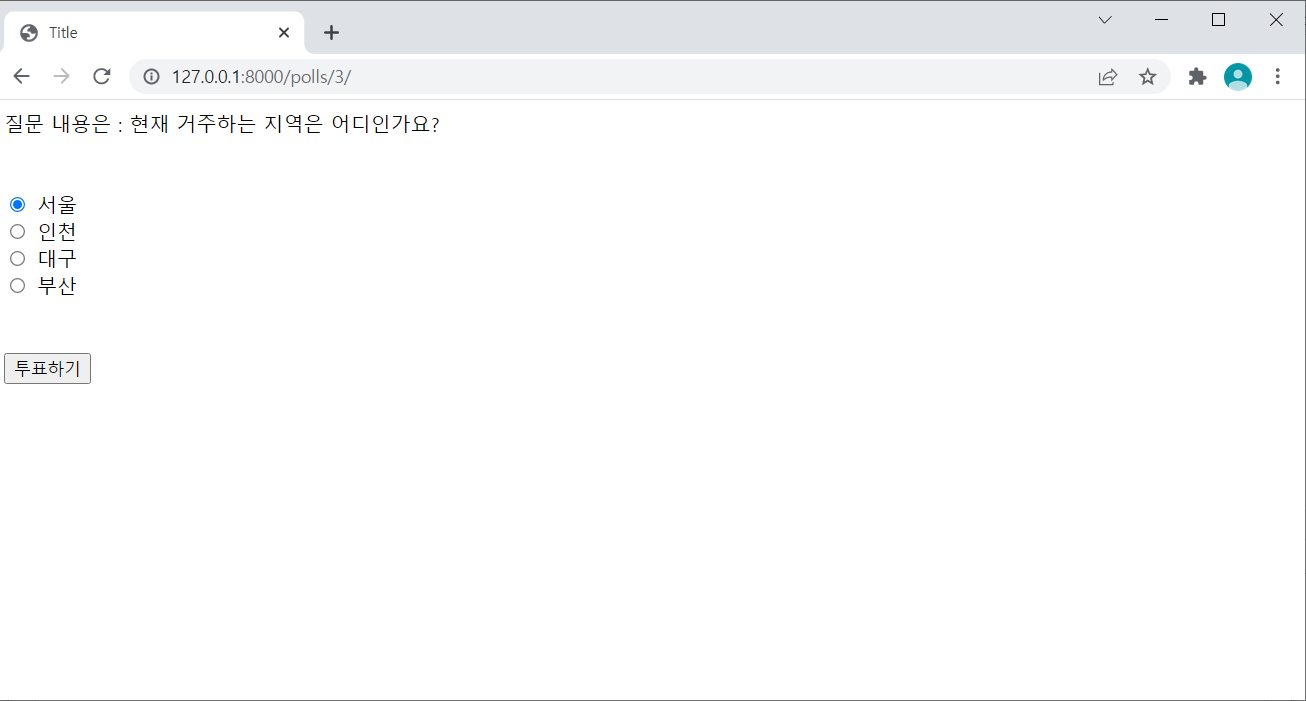
- 전체 detail.html코드는 다음과 같다.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> 질문 내용은 : {{ my_question.question_text }} <br><br><br> <form action="/polls/{{ my_question.id }}/vote/" method="post"> {% csrf_token %} {% for choice in my_question.choiceset.all %} <input type="radio" name="choice" id="my{{ forloop.counter }}" value="{{ choice.id }}"> <label for="my_{{ forloop.counter }}">{{ choice.choice_text }}</label><br> {% endfor %} <br><br> <input type="submit" value="투표하기"> </form> </body> </html>
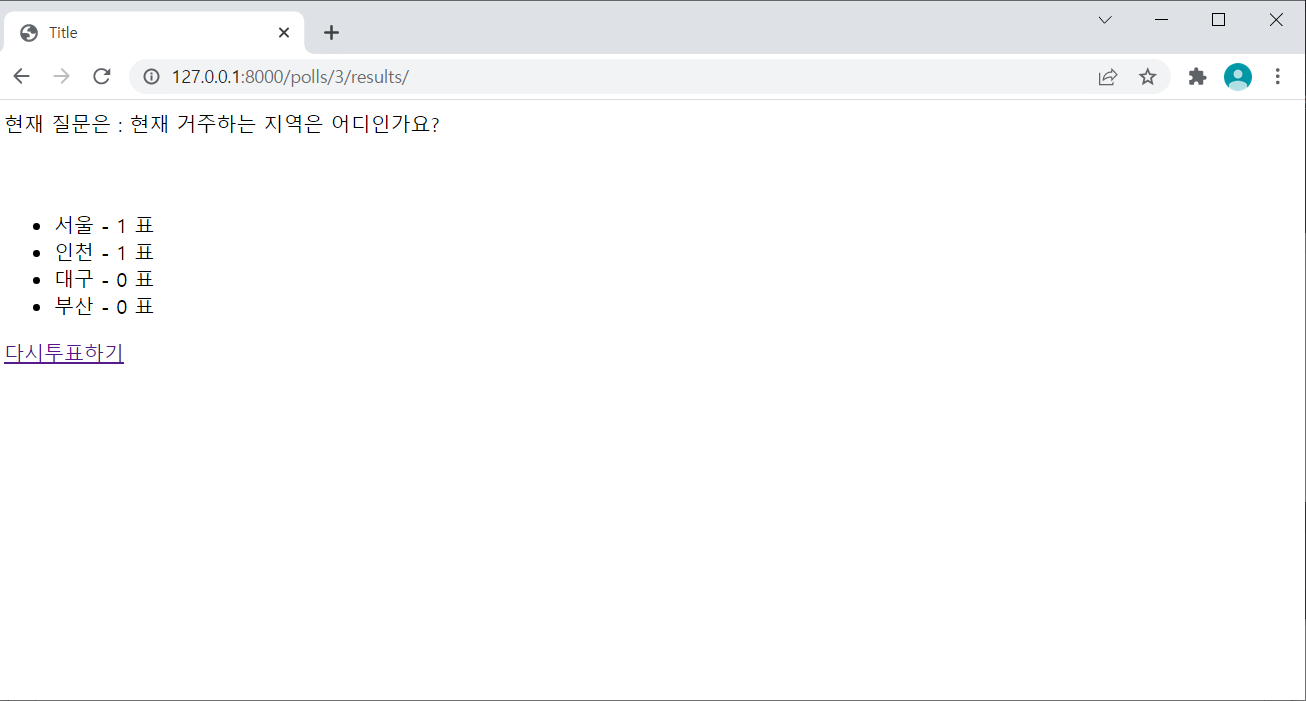
- result.html도 작성하면 끝이다.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> 현재 질문은 : {{ my_question.question_text }} <br><br><br> <ul> {% for choice in my_question.choice_set.all %} <li>{{ choice.choice_text }} - {{ choice.votes }} 표</li> {% endfor %} </ul> <!-- <a href="/polls/">다시투표하기</a> 이렇게 써도된다.--> <a href="{% url 'polls:index' %}">다시투표하기</a> {# 이렇게 써도 된다! #} <!-- 값을 찍을때는 {{ }}를 사용하고 {% %}는 로직을 실행할 때 쓴다--> <!-- 아래처럼 작성하면 관리의 용이성때문에 사용한다--> </body> </html>
- 이제 서버를 기동하면 다음과 같은 결과를 얻을 수 있다.