 # Outline
# Outline
- Motivation
- Overview
- Multicore programming
- Multi threading models
- Thread libraries
- Thread Programming API
1. Motivation
Many programs must perform several tasks that do not need to be serialized.
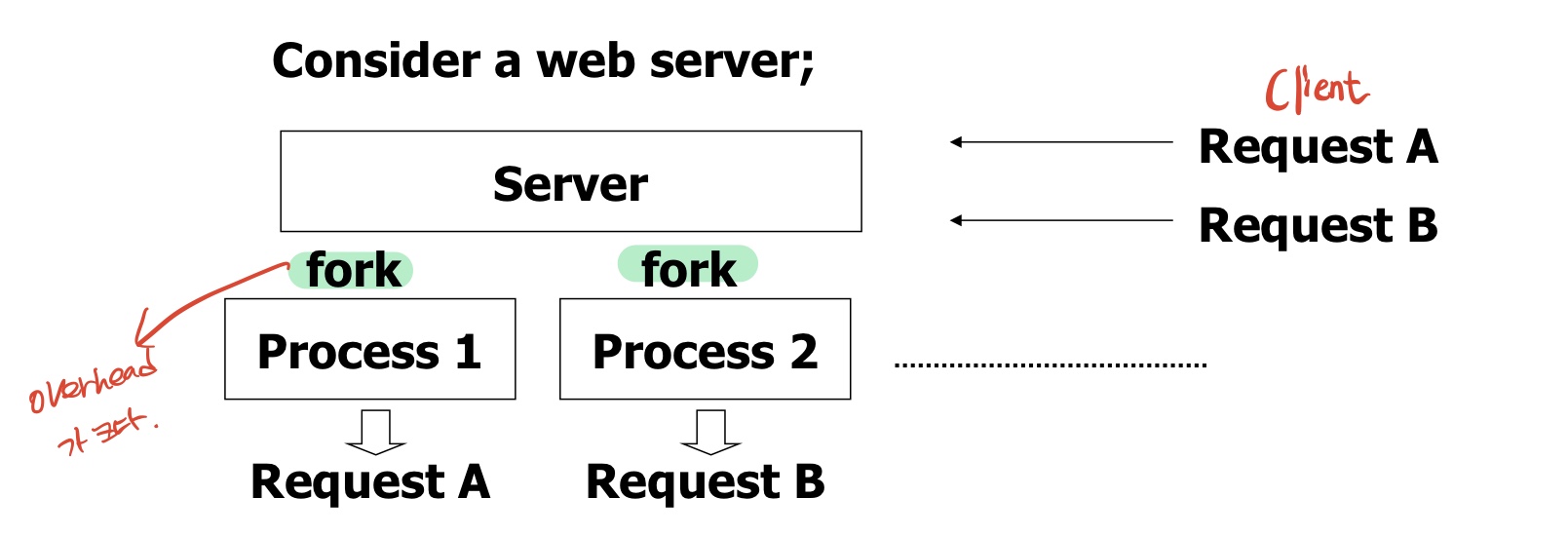
Process creation is resource-intensive and time-consuming.
-
Allocate a new pid, pcv and fill them in
-
Duplicate the address space
-
Make the child runnable.
-
IPC mechanism(EX: Shared-memory, Message pussing) is needed
Multithreading mechanism that reduces such overhead is required.
2. Overview
Benefits:
- Responsiveness(응답성):
멀티쓰레딩은 다른 파트가 blocked 되어도 프로그램을 실행할수있게 해준다.

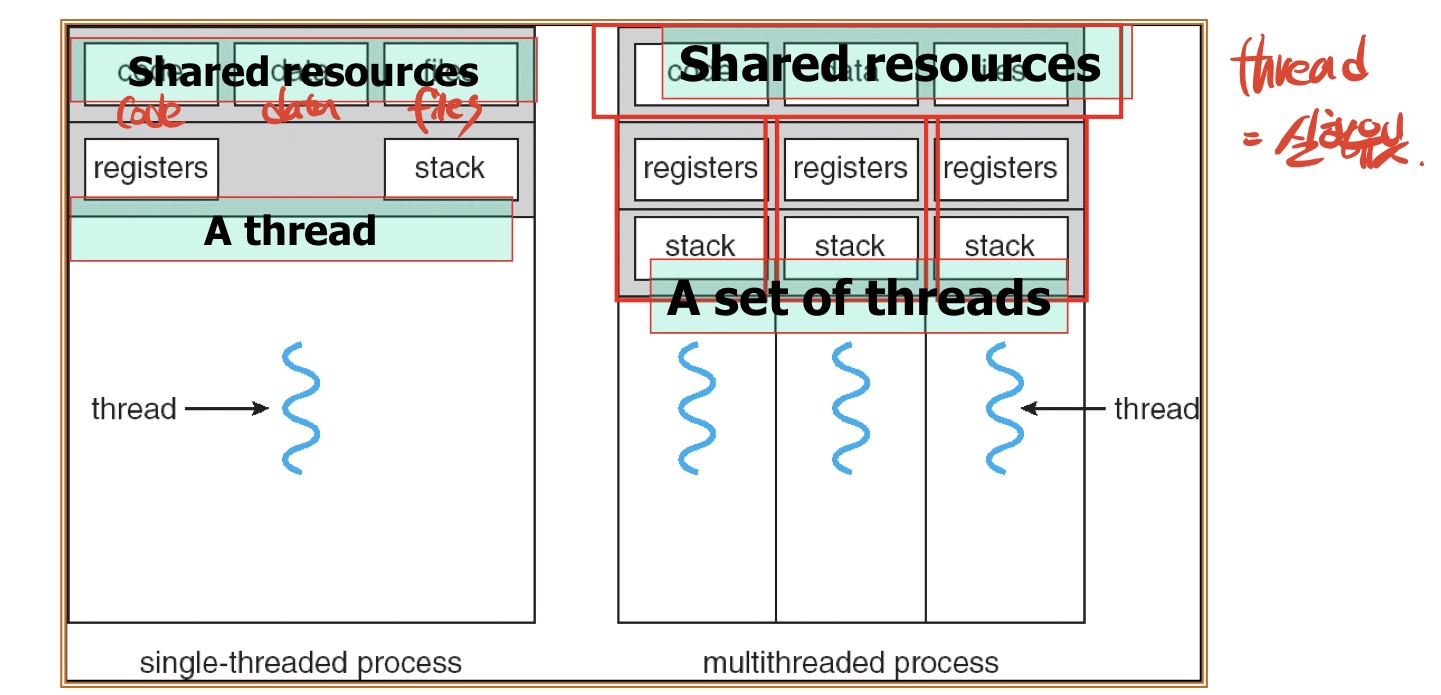
- Resource sharing:
쓰레드들은 프로세스의 코드,데이터,자원들을 공유한다.
- Economy:
process creation을 위해 메모리나 자원을 할당하는것은 꽤 비용이 든다.
- Utilization of MP(multi-processor) Architectures:
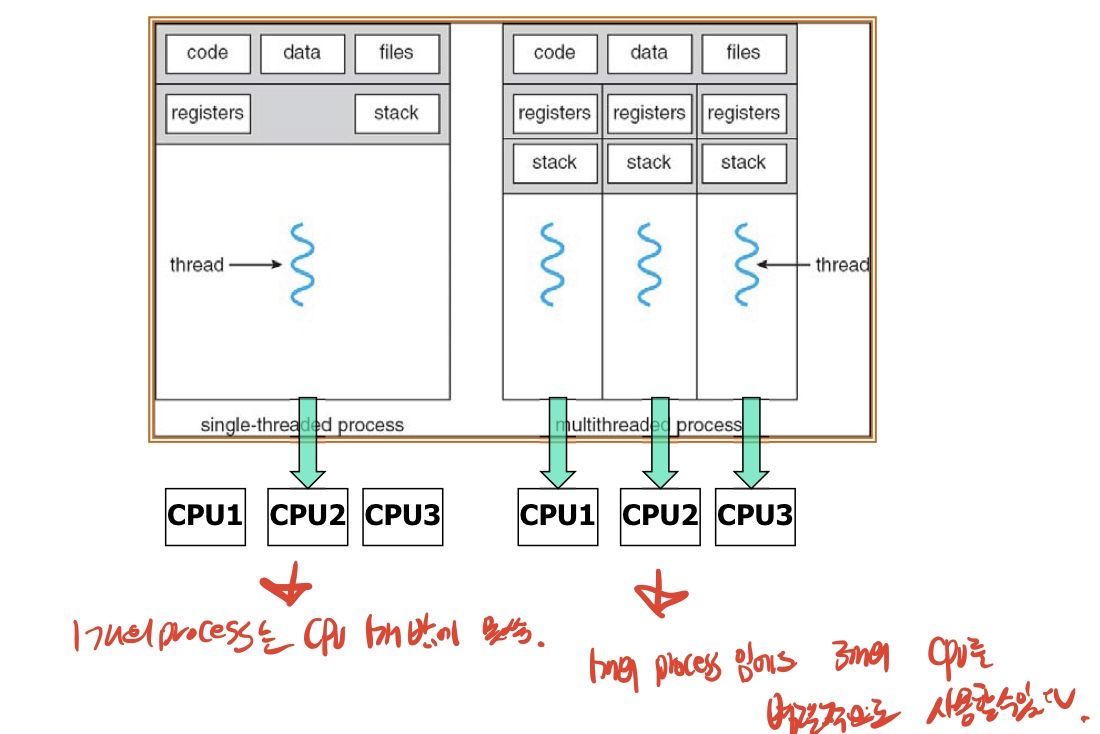
Fundamental concepts:
A process is a compound entity that can be divided into
1. set of threads
2. a collection of resources

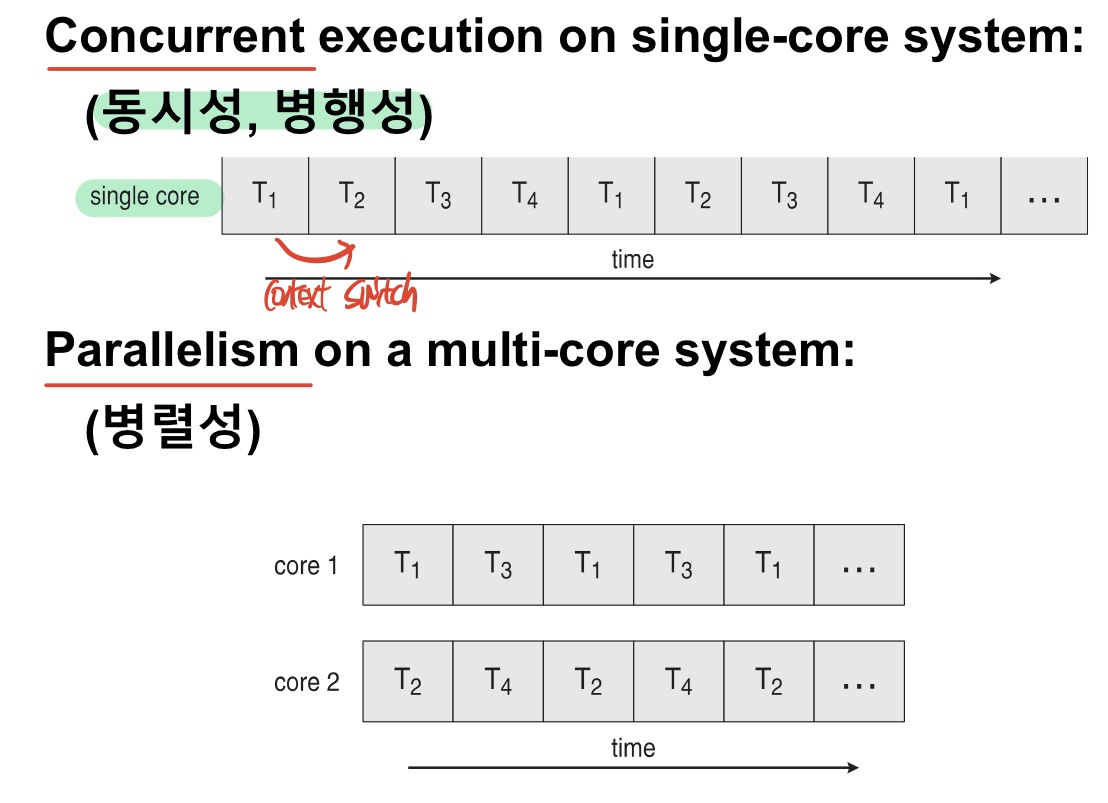
3. Multicore programming
- Types of parallelism:
1. Data parallelism- Task parallelism
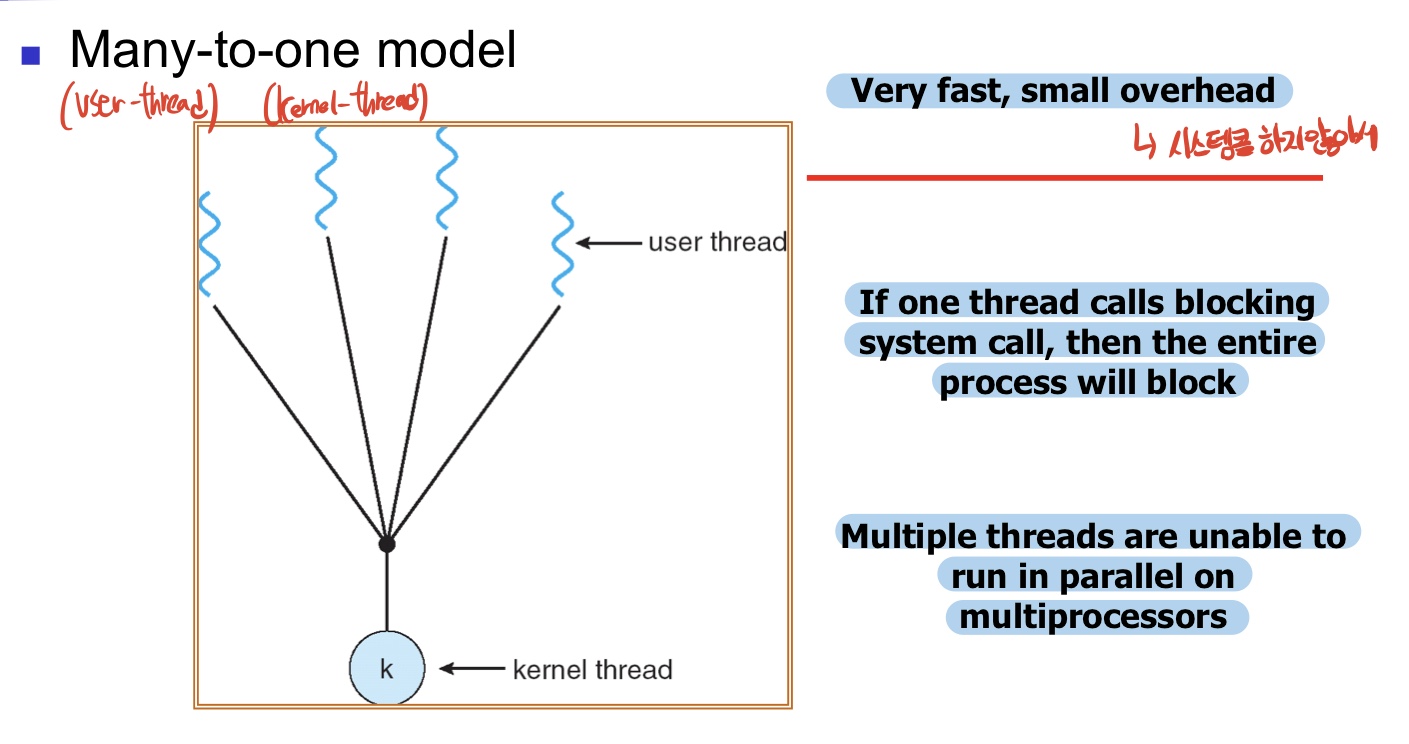
4. Multi threading models
- Two types of threads
- Kernel thread
created and destroyed internally by Kernel - User thread
supported above the Kernel and managed by the Thread library
does not involve Kernel

-
유저 쓰레드를 관리하는건 쓰레드 라이브러리이다.
-
OS가 관리하는 쓰레드는 Kernel 쓰레드이다.
Many-to-one:
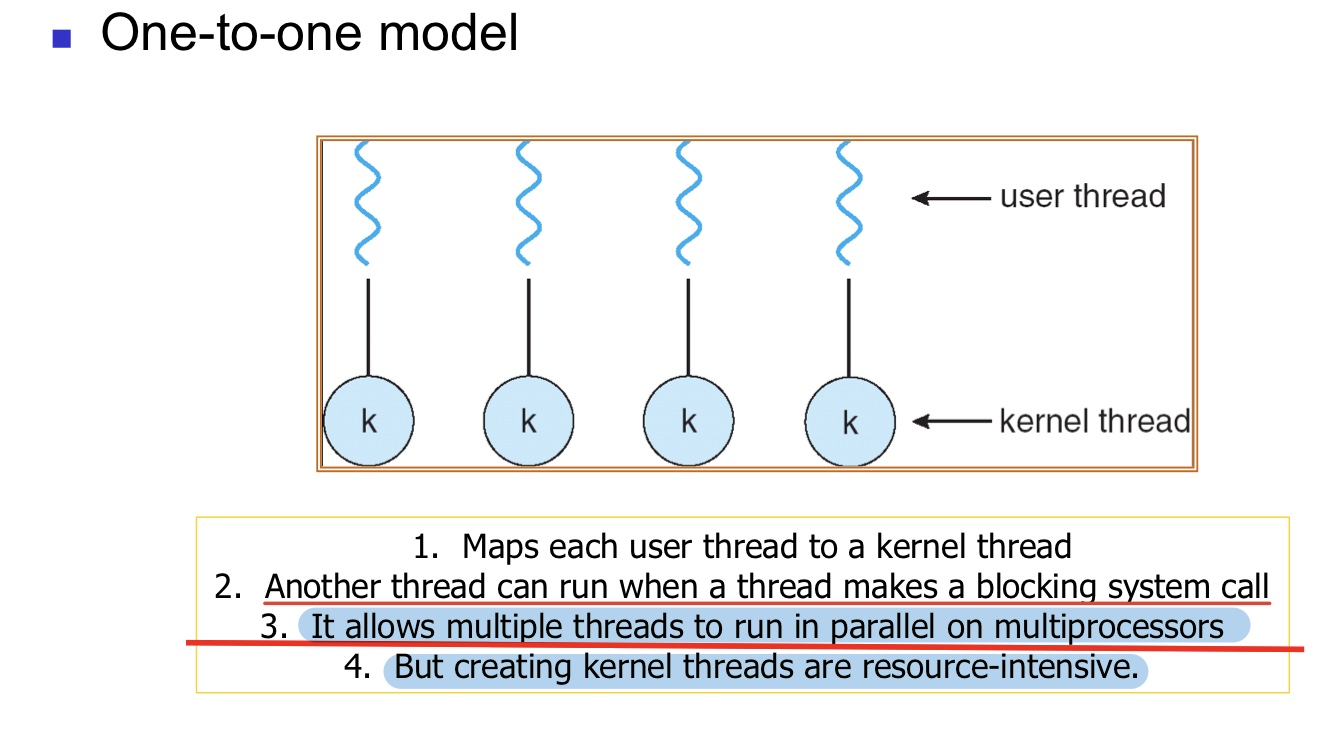
One-to-One:
Many-to-Many:
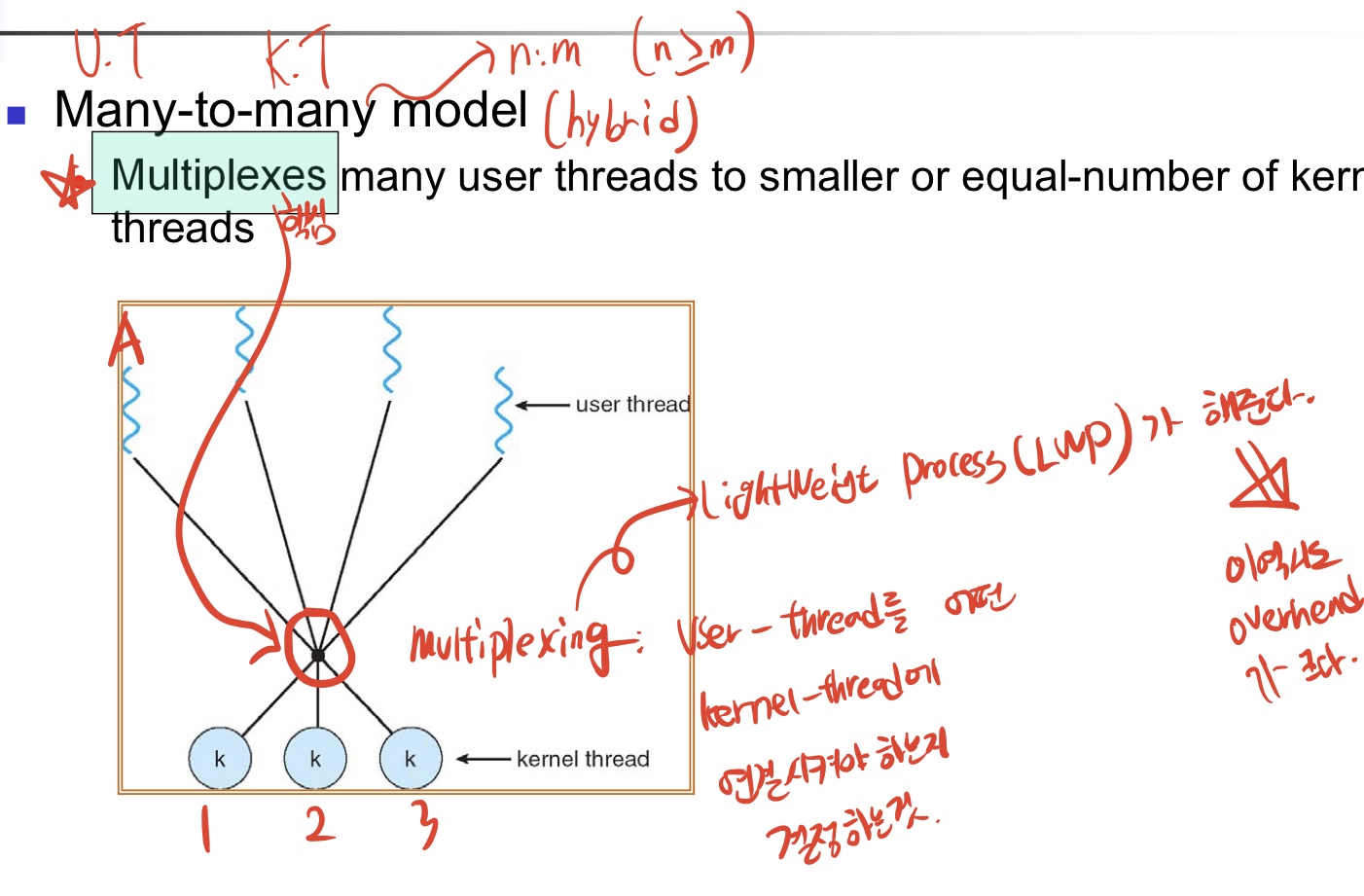
- Multiplex: LWP(light weight process)가 user-thread를 kernel-thread에 mapping 해주는것.
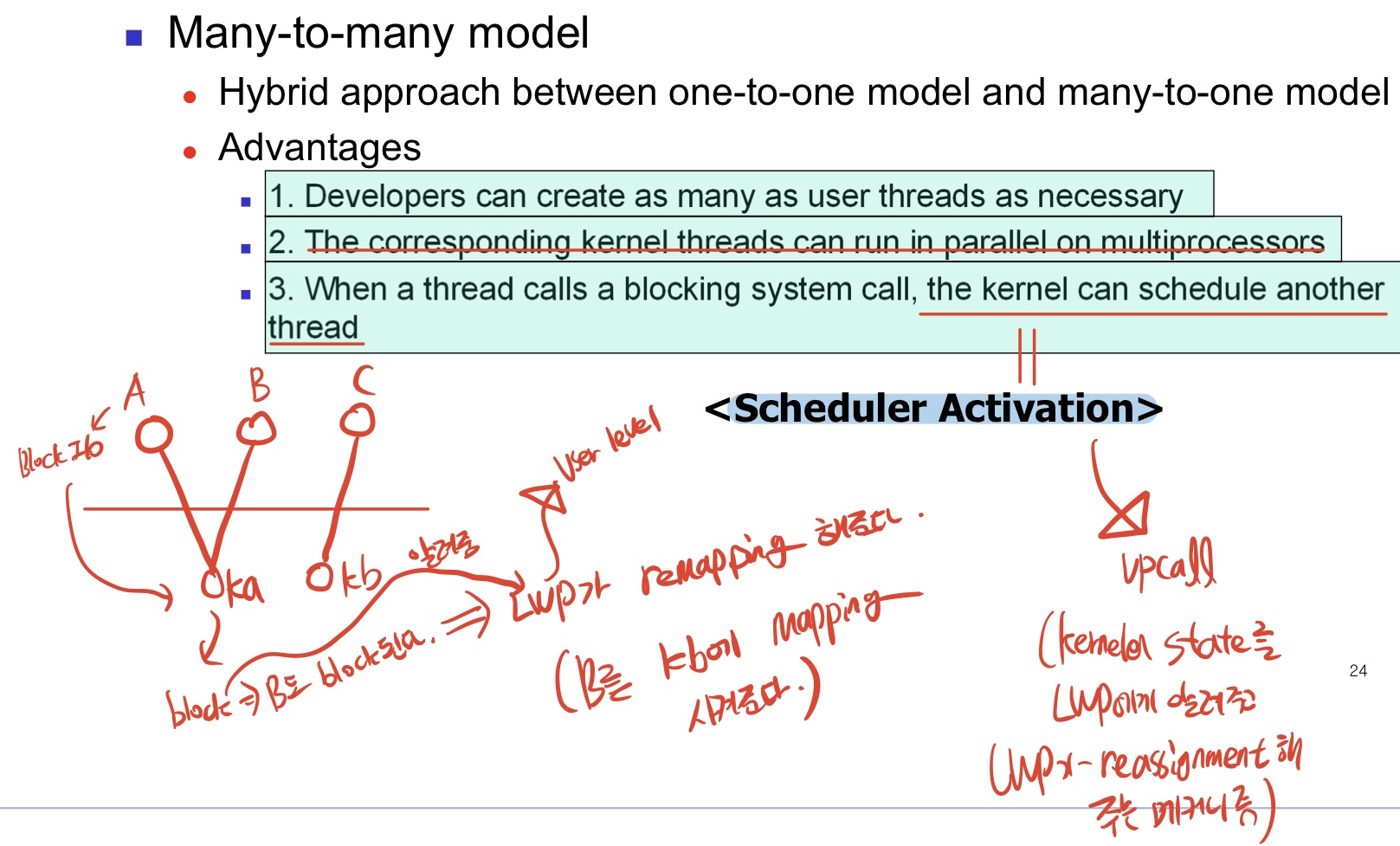
- Scheduler Activation : upcall(Kernel의 state를 LWP에게 알려주고 LWP가 reassignment 하게 하는 메커니즘)을 통해 user-thread와 kernel-thread를 remapping 하게해주는 메커니즘.
Linux use one-to-one model:

-
리눅스는 thread를 생성할 때마다 쓰레드를 관리하는 PCB(process control block)가 생성된다.
-
PCB가 존재한다는 것은 별도로 scheduling 되는 객체가 된다는 것이다. -> 별도로 CPU를 할당받을수있는 객체가 된다.
-
쓰레드를 관리하는 PCB의 역할을 위에서 보여줬던 Kernel-thread의 역할로 생각하면 된다.
-
리눅스에서 Kernel-Thread는 커널에서 해야할일들을 담당하고, user-thread와 mapping 관계는 없다.
5. Thread libraries
Thread library
프로그래머들에게 쓰레드를 생성하고 관리하는 api를 제공해준다.제공방법:
-
User-space에서 라이브러리 전체를 제공하는 방법
-
OS에 의해 제공되는 커널레벨 라이브러리를 User-space에서 구현하는 방법
One to One 모델은 user-thread 마다 kernel-thread를 만들어야하기 때문에 2번 방식이다.
Thread programming example (pthread library)

Threading issues
- Semantics of fork() and exec()

- Thread cancellation

- Signal handling:
-
Signal은 프로세스에게 특정 이벤트가 발생했다고 알려주는 notification 이다.
-
Signal이 발생하면 프로세스는 signal handler를 실행한다.

- Thread pools:
- 제한없이 쓰레드를 생성하면 시스템의 resource를 독점한다.
-
제한된 숫자의 쓰레드를 허락받거나
-
쓰레드 풀안에 미리 정해진 수의 쓰레드를 만들어 놓고 만든 쓰레드를 계속 이용한다.

6. Thread Programming API
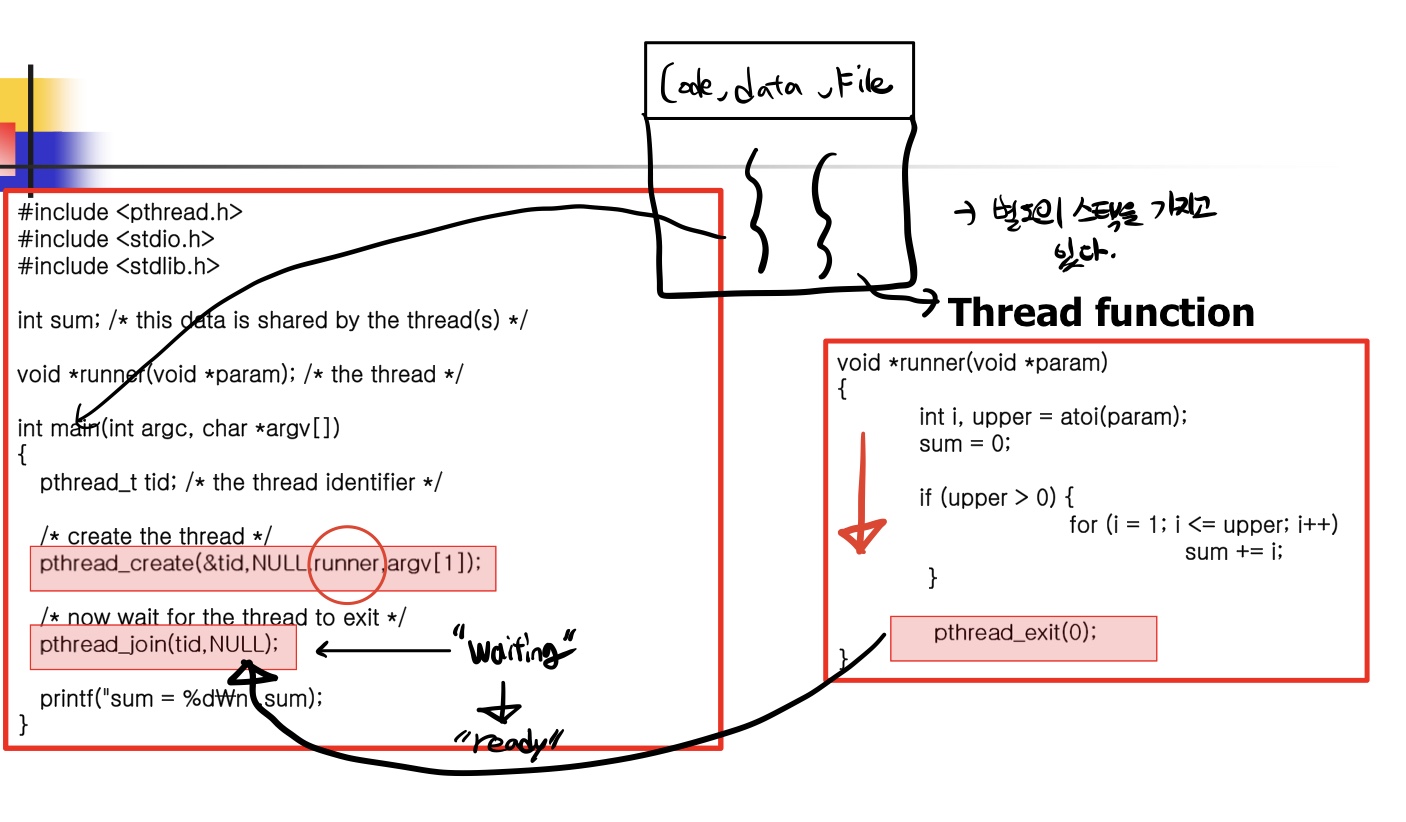
1. pthread_create:
int pthread_create(pthread_t * tid, pthread_attr_t * attr, (void *) f, void *arg);- create a new thread and run the thread routine f with an input argument of arg
- when pthread_create returns, argument tid contains cotains the ID of the newly created thread.
- pthread_attr_t is setting of thread attributes. null setting lis default setting.
2. pthread_join:
int pthread_join(pthread_t tid, void *thread_return);- pthread_join function blocks until thread tid terminates
- It is similar to wait function but can only wait for a specific thread to terminate
3. pthread_exit
int pthread_exit(void *thread_return);- terminating the thread with a return value of thread_return that will be transferred to pthread_join