김영한 강사님의 스프링 MVC 2편 - 백엔드 웹 개발 활용 기술을 듣고 정리한 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 강의를 참고해주세요
이번강의에서는 thymelaf 에 대해서 알아보는 시간이다
- 공식 사이트: https://www.thymeleaf.org/
- 공식 메뉴얼 - 기본 기능
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html - 공식 메뉴얼 - 스프링 통합: https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/thymeleafspring.html
thymeleaf의 특징
- 서버 사이드 HTML 렌더링(SSR)
- 백엔드 서버에서 HTML을 동적으로 렌더링 하는 용도
- 네츄럴 템플릿
- HTML정적으로 열수 있고, 동적으로 열 수 있다
- 스프링 통합 지원
- thymeleaf에서 스프링과 자연스럽게 통합되고, 스프링의 다양한 기능을 편리하게 사용할 수 있다
thymleaf 기본 기능
- thymeleaf 사용 선언 :
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> - 간단한 표현:
◦ 변수 표현식: ${...}
◦ 선택 변수 표현식: {...}
◦ 메시지 표현식: #{...}
◦ 링크 URL 표현식: @{...}
◦ 조각 표현식: ~{...}
• 리터럴
◦ 텍스트: 'one text', 'Another one!',…
◦ 숫자: 0, 34, 3.0, 12.3,…
◦ 불린: true, false
◦ 널: null
◦ 리터럴 토큰: one, sometext, main,…
• 문자 연산:
◦ 문자 합치기: +
◦ 리터럴 대체: |The name is ${name}|
• 산술 연산:
◦ Binary operators: +, -, , /, %
◦ Minus sign (unary operator): -
• 불린 연산:
◦ Binary operators: and, or
◦ Boolean negation (unary operator): !, not
• 비교와 동등:
◦ 비교: >, <, >=, <= (gt, lt, ge, le)
◦ 동등 연산: ==, != (eq, ne)
• 조건 연산:
◦ If-then: (if) ? (then)
◦ If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
◦ Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
• 특별한 토큰:
◦ No-Operation: _
이제 하나하나 알아보자!
텍스트 - text, utext
th:text를 사용 :<span th:text="${data}">- HTML 콘텐츠 영역안에서 직접 데이터를 출력:
[[${data}]]
Escape- HTML 문서는 < , > 같은 특수 문자를 기반으로 정의된다. 따라서 뷰 템플릿으로 HTML 화면을 생성할 때는 출력하는데이터에 이러한 특수 문자가 있는 것을 주의해서 사용해야 한다.
- 웹 브라우저:
Hello <b>Spring!</b> - 소스보기:
Hello <b>Spring!</b>
Unescape- th:text th:utext
- [[...]][(...)]
변수 - SpringEL
- 변수 표현식 :
${...} - Object
- <span
th:text="${user.username}"></span> - <span
th:text="${user['username']}"></span> - <span
th:text="${user.getUsername()}"></span>
- <span
- List
- <span
th:text="${users[0].username}"></span> - <span
th:text="${users[0]['username']}"></ span> - <span
th:text="${users[0].getUsername()}"></ span>'
- <span
- Map
- <span
th:text="${userMap['userA'].username}"></span> - <span
th:text="${userMap['userA']['username']}"></span> - <span
th:text="${userMap['userA'].getUsername()}"></span>
- <span
지역 변수 선언
th:with를 사용하면 지역 변수를 선언해서 사용할 수 있다. 지역 변수는 선언한 테그 안에서만 사용할 수 있다.
<h1>지역 변수 - (th:with)</h1>
<div th:with="first=${users[0]}">
<p>처음 사람의 이름은 <span th:text="${first.username}"></span></p>
</div>기본 객체들
${#request}- 스프링 부트 3.0부터 제공하지 않는다.${#response}- 스프링 부트 3.0부터 제공하지 않는다.${#session}- 스프링 부트 3.0부터 제공하지 않는다.${#servletContext}- 스프링 부트 3.0부터 제공하지 않는다.${#locale}-> 이것만 지금 사용할 수 있다
Controller
@GetMapping("basic-objects")
public String basicObjects(Model model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("sessionData","Hello Session");
model.addAttribute("request", request);
model.addAttribute("response", response);
model.addAttribute("servletContext", request.getServletContext());
return "basic/basic-objects";
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>식 기본 객체 (Expression Basic Objects)</h1>
<ul>
<li>request = <span th:text="${request}"></span></li>
<li>response = <span th:text="${response}"></span></li>
<li>session = <span th:text="${session}"></span></li>
<li>servletContext = <span th:text="${servletContext}"></span></li>
<li>locale = <span th:text="${#locale}"></span></li>
</ul>
<h1>편의 객체</h1>
<ul>
<li>Request Parameter = <span th:text="${param.paramData}"></span></li>
<li>session = <span th:text="${session.sessionData}"></span></li>
<li>spring bean = <span th:text="${@helloBean.hello('Spring!')}"></span></
li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>유틸리티 객체와 날짜
- 타임리프 유틸리티 객체들
- #message : 메시지, 국제화 처리
- #uris : URI 이스케이프 지원
- #dates : java.util.Date 서식 지원
- #calendars : java.util.Calendar 서식 지원
- #temporals : 자바8 날짜 서식 지원
- #numbers : 숫자 서식 지원
- #strings : 문자 관련 편의 기능
- #objects : 객체 관련 기능 제공
- #bools : boolean 관련 기능 제공
- #arrays : 배열 관련 기능 제공
- #lists , #sets , #maps : 컬렉션 관련 기능 제공
- #ids : 아이디 처리 관련 기능 제공, 뒤에서 설명
URL 링크
-
@{...} 문법: thymeleaf에서 URL 생성 -
단순한 URL
- @{/hello} /hello
-
쿼리 파라미터
@{/hello(param1=${param1}, param2=${param2})}/hello?param1=data1¶m2=data2- () 에 있는 부분은 쿼리 파라미터로 처리된다.
-
경로 변수
@{/hello/{param1}/{param2}(param1=${param1}, param2=${param2})} /hello/data1/data2- URL 경로상에 변수가 있으면 () 부분은 경로 변수로 처리된다.
-
경로 변수 + 쿼리 파라미터
{/hello/{param1}(param1=${param1}, param2=${param2})} /hello/data1?param2=data2- 경로 변수와 쿼리 파라미터를 함께 사용할 수 있다.
리터럴
- 리터럴: 소스 코드상에 고정된 값을 말하는 용어이다
- 타임리프에서 문자 리터럴은 항상 ' (작은 따옴표)로 감싸야 한다.
<span th:text="'hello'"> - 공백 없이 하나의 의미있는 토큰(띄어쓰기 x) : 작은 따음표 생략 가능
<span th:text="'hello world!'"></span>- 리터럴 대체(Literal substitutions)
<span th:text="|hello ${data}|">
||안에 리터럴을 적어주면 된다!!! -> 여기 안에서는 같은 토큰으로 다 생각함- 마지막의 리터럴 대체 문법을 사용하면 마치 템플릿을 사용하는 것 처럼 편리하다
연산
- 비교연산: HTML 엔티티를 사용해야 하는 부분을 주의하자,
> (gt), < (lt), >= (ge), <= (le), ! (not), == (eq), != (neq, ne) - 조건식: 자바의 조건식과 유사하다.
- Elvis 연산자: 조건식의 편의 버전
- No-Operation: _ 인 경우 마치 타임리프가 실행되지 않는 것 처럼 동작한다. 이것을 잘 사용하면 HTML의 내용 그대로 활용할 수 있다. 마지막 예를 보면 데이터가 없습니다. 부분이 그대로 출력된다.
속성 값 설정
-
타임리프는 주로 HTML 태그에 th:* 속성을 지정하는 방식으로 동작한다. th:* 로 속성을 적용하면 기존 속성을 대체한다.
-
기존 속성이 없으면 새로 만든다.
-
속성 설정
th: 속성을 지정하면 타임리프는 기존 속성을 th: 로 지정한 속성으로 대체한다. 기존 속성이 없다면 새로 만든다.
<input type="text" name="mock" th:name="userA" />
타임리프 렌더링 후<input type="text" name="userA" /> -
속성 추가
th:attrappend: 속성 값의 뒤에 값을 추가한다.
th:attrprepend: 속성 값의 앞에 값을 추가한다.
th:classappend: class 속성에 자연스럽게 추가한다 -
checked 처리
-
HTML에서는
<input type="checkbox" name="active" checked="false" />이 경우에도checked 속성이 있기 때문에 checked 처리가 되어버린다. -
HTML에서 checked 속성은 checked 속성의 값과 상관없이 checked 라는 속성만 있어도 체크가 된다.
-
이런 부분이 true , false 값을 주로 사용하는 개발자 입장에서는 불편하다.
-
타임리프의
th:checked는 값이false인 경우 checked 속성 자체를 제거한다.<input type="checkbox" name="active" th:checked="false" />- 타임리프 렌더링 후:
<input type="checkbox" name="active" />
반복
th:each를 사용한다.- 추가로 반복에서 사용할 수 있는 여러 상태 값을 지원한다
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>기본 테이블</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>username</th>
<th>age</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user : ${users}">
<td th:text="${user.username}">username</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">0</td>
</tr>
</table>
<h1>반복 상태 유지</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>count</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>age</th>
<th>etc</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user, userStat : ${users}">
<td th:text="${userStat.count}">username</td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">username</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">0</td>
<td>
index = <span th:text="${userStat.index}"></span>
count = <span th:text="${userStat.count}"></span>
size = <span th:text="${userStat.size}"></span>
even? = <span th:text="${userStat.even}"></span>
odd? = <span th:text="${userStat.odd}"></span>
first? = <span th:text="${userStat.first}"></span>
last? = <span th:text="${userStat.last}"></span>
current = <span th:text="${userStat.current}"></span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html><tr th:each="user : ${users}">- 반복시 오른쪽 컬렉션
( ${users} )의 값을 하나씩 꺼내서 왼쪽 변수( user )에 담아서 태그를 반복 실행합니다. th:each는 List 뿐만 아니라 배열, java.util.Iterable,java.util.Enumeration 을 구현한 모든 객체를 반복에 사용할 수 있습니다.- Map 도 사용할 수 있는데 이 경우 변수에 담기는 값은 Map.Entry 입니다.
반복 상태 유지
<tr th:each="user, userStat : ${users}">- 반복의 두번째 파라미터를 설정해서 반복의 상태를 확인 할 수 있습니다.
- 두번째 파라미터는 생략 가능한데, 생략하면 지정한
변수명( user ) + Stat가 됩니다. - 여기서는 user + Stat =
userStat이므로 생략 가능합니다
반복 상태 유지 기능
index: 0부터 시작하는 값count: 1부터 시작하는 값size: 전체 사이즈even , odd: 홀수, 짝수 여부( boolean )first , last:처음, 마지막 여부( boolean )current: 현재 객체
조건부 평가
if, unless- 타임리프는 해당 조건이 맞지 않으면 태그 자체를 렌더링하지 않는다.
0 만약 다음 조건이 false 인 경우<span>...<span>부분 자체가 렌더링 되지 않고 사라진다. <span th:text="'미성년자'" th:if="${user.age lt 20}"></span>switch*은 만족하는 조건이 없을 때 사용하는 디폴트이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>if, unless</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>count</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>age</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user, userStat : ${users}">
<td th:text="${userStat.count}">1</td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">username</td>
<td>
<span th:text="${user.age}">0</span>
<span th:text="'미성년자'" th:if="${user.age lt 20}"></span>
<span th:text="'미성년자'" th:unless="${user.age ge 20}"></span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<h1>switch</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>count</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>age</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user, userStat : ${users}">
<td th:text="${userStat.count}">1</td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">username</td>
<td th:switch="${user.age}">
<span th:case="10">10살</span>
<span th:case="20">20살</span>
<span th:case="*">기타</span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>주석
- 표준 HTML 주석
- 자바스크립트의 표준 HTML 주석은 타임리프가 렌더링 하지 않고, 그대로 남겨둔다.
<!-- <span th:text="${data}">html data</span> -->
- 타임리프 파서 주석
- 타임리프 파서 주석은 타임리프의 진짜 주석이다. 렌더링에서 주석 부분을 제거한다.
<!--/* [[${data}]] */-->
- 타임리프 프로토타입 주석
- 타임리프 프로토타입은 약간 특이한데, HTML 주석에 약간의 구문을 더했다.
- HTML 파일을 웹 브라우저에서 그대로 열어보면 HTML 주석이기 때문에 이 부분이 웹 브라우저가 렌더링하지 않는다.
- 타임리프 렌더링을 거치면 이 부분이 정상 렌더링 된다.
- 쉽게 이야기해서 HTML 파일을 그대로 열어보면 주석처리가 되지만, 타임리프를 렌더링 한 경우에만 보이는 기능이다.
<!--/*/ <span th:text="${data}">html data</span> /*/-->
블록
<th:block>은 HTML 태그가 아닌 타임리프의 유일한 자체 태그다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<th:block th:each="user : ${users}">
<div>
사용자 이름1 <span th:text="${user.username}"></span>
사용자 나이1 <span th:text="${user.age}"></span>
</div>
<div>
요약 <span th:text="${user.username} + ' / ' + ${user.age}"></span>
</div>
</th:block>
</body>
</html>- thymleaf가 속성으로 동작하지, 태그로 동작하지 않는다
- 그런데 해결하기 어려운 것들을 해결하기 위해서 thymleaf가 제공하는 <th:block>의 태그가 있다
<div>2개를 딱딱 맞춰서 반복하고 싶다<div>1개는 그냥<div th:each="user:${users}">써서 하면 되는데,, 이렇게 속성 단위로!each만으로 해결하기 어려울 때,th:block을 같이 쓴다
자바스크립트 인라인
- 타임리프는 자바스크립트에서 타임리프를 편리하게 사용할 수 있는 자바스크립트 인라인 기능을 제공한다.
- 자바스크립트 인라인 기능은 다음과 같이 적용하면 된다
<script th:inline="javascript">- 문자의 경우 쌍따움표를 넣어주고 이런 처리를 타임리프가 다해준다
- 이렇게 타입마다 처리를 해준다
- 네츄럴템플릿을 처리해준다
- 객체를 json으로 바꿔서 렌더링 해준다
자바스크립트 인라인 each
자바스크립트 인라인은 each를 지원하는데, 다음과 같이 사용한다.
<!-- 자바스크립트 인라인 each -->
<script th:inline="javascript">
[# th:each="user, stat : ${users}"]
var user[[${stat.count}]] = [[${user}]];
[/]
</script>템플릿 조각
- 웹 페이지에는 공통 영역이 많다
- 상단,하단, 왼쪽에 내비게이션등등
- html을 영역별로 재활용해야할 때가 많다
- 마치 우리가 복잡한 코드를 짤 때 메서드를 분리해놓고 메서드를 재활용 하듯이!
- thymleaf도 이런식으로 thymleaf 파일을 조각조각 내서, 불러다가 쓸 수 있게 한다
이번 예시에서는 html의 하단 부분을 footer로 지정하고, 이를 다른 html에 적용하는 예제를 보겠다!
<footer th:fragment="copy">
푸터 자리 입니다.
</footer>fragment: 템플릿 조각의 이름 -> "copy"로 두었다
<body>
<h1>부분 포함</h1>
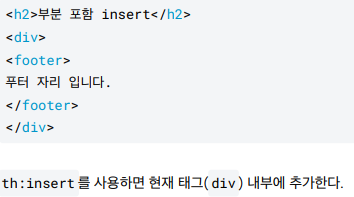
<h2>부분 포함 insert</h2>
<div th:insert="~{template/fragment/footer :: copy}"></div>
<h2>부분 포함 replace</h2>
<div th:replace="~{template/fragment/footer :: copy}"></div>
<h2>부분 포함 단순 표현식</h2>
<div th:replace="template/fragment/footer :: copy"></div>
<h1>파라미터 사용</h1>
<div th:replace="~{template/fragment/footer :: copyParam ('데이터1', '데이터2')}"></
div>
</body>-
template/fragment/footer :: copy : template/fragment/footer.html템플릿에 있는th:fragment="copy"라는 부분을 템플릿 조각으로 가져와서 사용한다는 의미이다. -
insert
- 부분포함
<div th:insert="~{template/fragment/footer :: copy}"></div>
-
replace
- 부분 포함
<div th:replace="~{template/fragment/footer :: copy}"></div>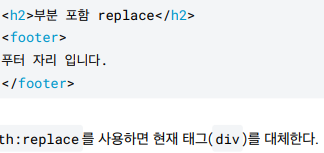
-
파라미터 사용
<div th:replace="~{template/fragment/footer :: copyParam ('데이터1', '데이터2')}"></div>
템플릿 레이아웃
- 이전의 템플릿 조각은 일부 코드 조각을 가져와서 넣었다면
- 이번에는 개념을 더 확장해 코드 조각을 레이아웃에 넘겨서 사용하는 방법이다
- 레이아웃 틀을 둔다
- 공통인 부분은 공통으로 사용하고, 각 페이지마다 필요한 정보를 더 추가해서 사용하는 방법이다!!!
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html th:fragment="layout (title, content)" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title th:replace="${title}">레이아웃 타이틀</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>레이아웃 H1</h1>
<div th:replace="${content}">
<p>레이아웃 컨텐츠</p>
</div>
<footer>
레이아웃 푸터
</footer>
</body>
</html>- 다음과 같이 레이아웃 html 코드가 있다
- 이 레이아웃은 title, content를 받아서 적용한다
- 나머지 부분은 공통적인 부분이 된다
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html th:replace="~{template/layoutExtend/layoutFile :: layout(~{::title},
~{::section})}"
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>메인 페이지 타이틀</title>
</head>
<body>
<section>
<p>메인 페이지 컨텐츠</p>
<div>메인 페이지 포함 내용</div>
</section>
</body>
</html>- html 코드에 th:replace를 통해 변경을 각 페이지에 수정을 할려고 한다
- title태그와, section 태그에서 데이터를 받아서
- 다시 레이아웃 코드에 돌아가 title,content 매개변수에 집어넣어서 완성한다
- 공통부분 유지, 파라미터로 수정부분 받아서 수정한다

- layoutFile.html 을 보면 기본 레이아웃을 가지고 있는데,
<html>에th:fragment속성이 정의되어 있다. 이 레이아웃 파일을 기본으로 하고 여기에 필요한 내용을 전달해서 부분부분 변경하는 것으로 이해하면 된다. layoutExtendMain.html는 현재 페이지인데,<html>자체를th:replace를 사용해서 변경하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.- 결국 layoutFile.html 에 필요한 내용을 전달하면서
<html>자체를 layoutFile.html 로 변경한다.