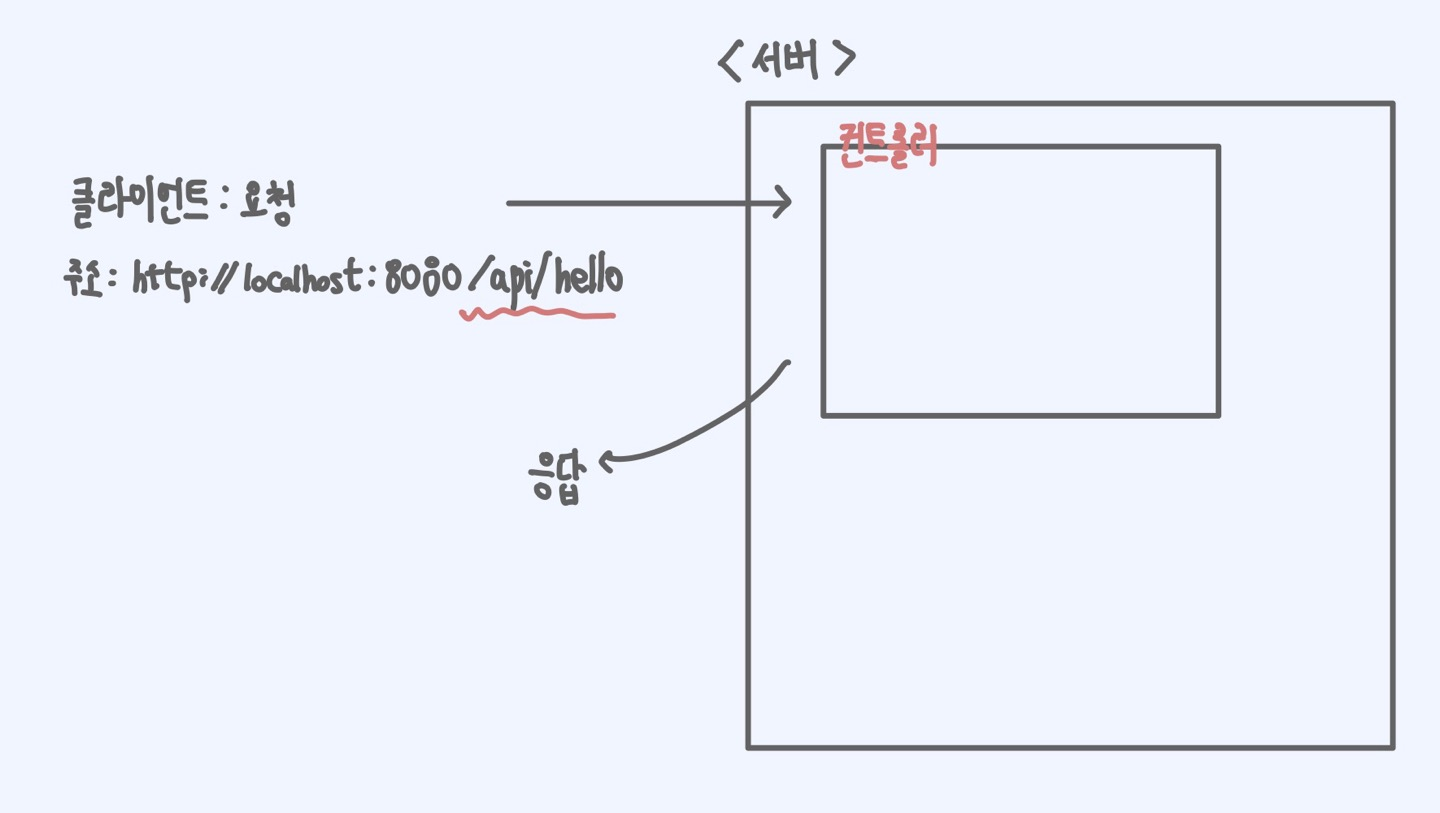
- 클라이언트는 서버에게 특정 주소를 주면서 요청을 한다
- 이때 컨트롤러는 요청을 처리하기 위하여, 특정한 주소를 받겠다고 지정을 할 수 있다
- 그리고 특정한 주소로 클라이언트로부터 요청이 오면, 컨트롤러는 지정된 주소의 요청을 처리한다
- 이때, API를 처리하는 컨트롤러임을 나타내는 어노테이션은
@RestController이다 - 그리고 특정 주소를 받겠다 라는 어노테이션은
RequestMapping이다
GET
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class RestApiController {
@GetMapping(path = "/hello")
public String hello(){
return "Hello Spring Boot";
}- 간단하게 다음 코드를 보자
@RestController로 컨트롤러를 설정하였고,@RequestMaping을 클래스 레벨로 설정해, 하위 메서드들이 모두 /api 라는 주소를 받는다는 것을 알 수 있다@GetMapping으로 RequestMapping을 Get메서드로 받는 다는 것을 알 수 있고- 최종 주소는 /api/hello임을 알 수 있다
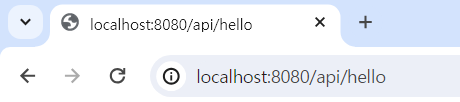

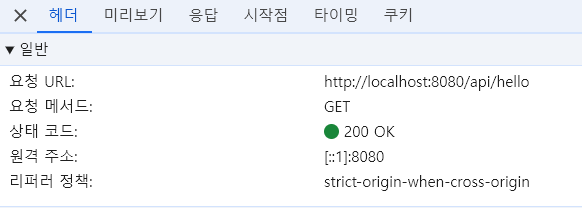
- 잘 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있다
여기서 우리는 응답은 결국 문자열이라는 것을 알 수 있다
- 그것을 예쁘게 꾸미는 것이다
- 결국 0,1들의 비트 단위의 데이터를 html, xml, json등으로 리소스를 표현하는 것이다
- ✅ 결국 통신이란 문자를 전달하는 것!
1.주소 내 정보를 전달하는 방법
- 우리가 url를 설계할 때 리소스를 잘 정의하고, 행위와 분리를 하는 것이 중요하였다
- 이렇게 🤔 Restful하게 설계를 하면, 우리는 주소 내에 정보를 전달하는 방법이 필요하다
- https://www.foo.bar/user-id/100
- 이 주소에 user-id가 회원마다 모두 다르다, 지금은 100인 형태인 것
- 우리는
@PathVariable어노테이션을 이용해서 주소 내에 정보를 전달할 수 있다
public String echo(
@PathVariable("message") String message
){
log.info("echo message : "+message);
return message;
}- 이제 api/echo/ 라는 주소에 특정 PathVariable이 들어오면
- 그 값을 문자로 파싱해서 message라는 변수에 저장할 것이다
- 이때 @PathVariable의 파라미터 name에 파싱할 이름을 정의해준다
2.URL에서 쿼리 파라미터 받기
- 쿼리 파라미터는 특정 필터링을 걸 때 사용한다
- ?로 시작하고, 이어주는 형태는 &로 묶어서 사용한다
🤔 쿼리 파라미터에서 Wrapper vs primative 타입
- Integer의 Wraaper 타입은 null값이 들어올 수 있다
- 하지만 primative 타입인 Int는 null 값이 들어올 수 없다
- 👌 내 생각에는, 쿼리 파라미터에 null 값이 들어오면 안되기 때문에, 쿼리 파라미터에서는 Wrapper 타입 보단 primative 타입을
지향해야 한다!- 실제로 null값이 파라미터에 들어가면 404 Error가 발생한다!
@GetMapping(path="/book")
public void queryParam(
@RequestParam(name = "category") String category,
@RequestParam(name="issuedYear") String issuedYear,
@RequestParam(name = "issued-month") String issuedMonth,
@RequestParam(name = "issued_day") String issuedDay
){
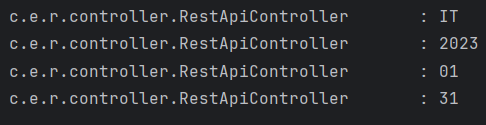
log.info(category);
log.info(issuedYear);
log.info(issuedMonth);
log.info(issuedDay);
}- URL 주소에는 대문자를 사용하지 않으므로 is-man 이렇게 하이픈을 사용해줘야 한다
@PathVariable에 매개변수로 이름을 알려줘서 파싱을 해준다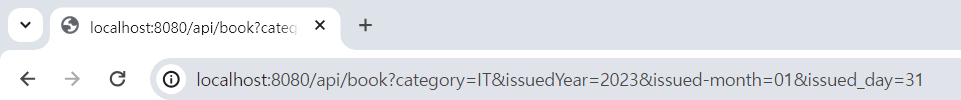
/api/book?category=IT&issuedYear=2023&issued-month=01&issued_day=31
- 다음 주소에 파라미터들을 받는다고 생각해보자
issuedYear: Camel caseissued-month: 하이푼이 들어간 경우issued_day: Snake case
- 가장 좋은 것은 파라미터와 변수이름을 매칭시키면 제일 좋은데...
- 주소에는 대문자를 쓰지 않아서 camel case를 적용하는데 제약이 생긴다
- 또한 snake case는 자바의 컨벤션이 아니므로... @RequestParam에 파라미터 이름을 알려주어야 한다
3.쿼리 파라미터를 객체로 받기
- 먼저 쿼리 파라미터를 받을 객체를 만들어 주자
BookQueryParam
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class BookQueryParam {
private String category;
private String issuedYear;
private String issuedMonth;
private String issuedDay;
}RestApiController
@GetMapping(path="/book2")
public void queryParamDto(
BookQueryParam bookQueryParam
){
System.out.println(bookQueryParam);
}
- 이 때는 RequestParam을 붙이지 않고, 객체를 파라미터로 적어준다
@ModelAttribute를 붙이는데, 생략도 가능하다- 이때, ✅ 자동으로 BookQueryParam를 생성하고 요청 파라미터의 값들도 모두 들어가게 된다!
- 프로퍼티 규약을 기반으로 , argument resolver가 자동으로 넣어준다!
- 프로퍼티 규약을 기반으로 , argument resolver가 자동으로 넣어준다!
api/book2?category=IT&issuedYear=2023&issued-month=01&issued_day=31실행- 위의 주소는 issued-month와 issued_day가 객체의 변수명과 동일하지 않다
- 위에서 말했지만 프로퍼티 규약을 통해 getter와 setter로 값을 집어넣는데...
- 변수명이 달라서 객체에 파라미터가 잘 들어가지 않는다...
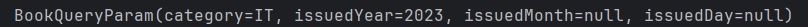
api/book2category=IT&issuedYear=2023&issuedMonth=01&issuedDay=31실행- 위의 주소는, BookQueryParam 의 필드값과 파라미터 명의 동일하다!

- BookQueryParam 객체에 값이 잘 들어간 것을 확인 할 수 있다
✅ 객체로 받는 방법 vs RequestParam으로 하나씩 받는 방법
- 객체로 받는 방법은, 변수의 내용이 많을 때 사용하면 유용하다
- 같이 협력하는 규칙을 주소에 Camel case가 아닌 하이푼 방식으로 하자라고 정한 것과 같이, 객체에 바로들어가지 않는다고 예상될 때는 @RequestParam을 쓸 수 있다
- 협력하는 개발자와 잘 정하고, 편의사항에 맞춰서 파싱을 해주자!
4. 발생 오류
🤔 PathVariable시 윈도우에서 한글 깨지는 문제...
- 보통 웹 서버는 utf-8(3byte)이라는 인코딩을 가진다
- 윈도우는 기본적으로 ms949(2byte)라는 인코딩을 사용한다
- 그런데 utf-8로 요청하면 인코딩이 일치하지 않기 때문에 글자가 깨지게 된다
- 인텔리제이의 File Setting encoding 검색 -> File Encoding
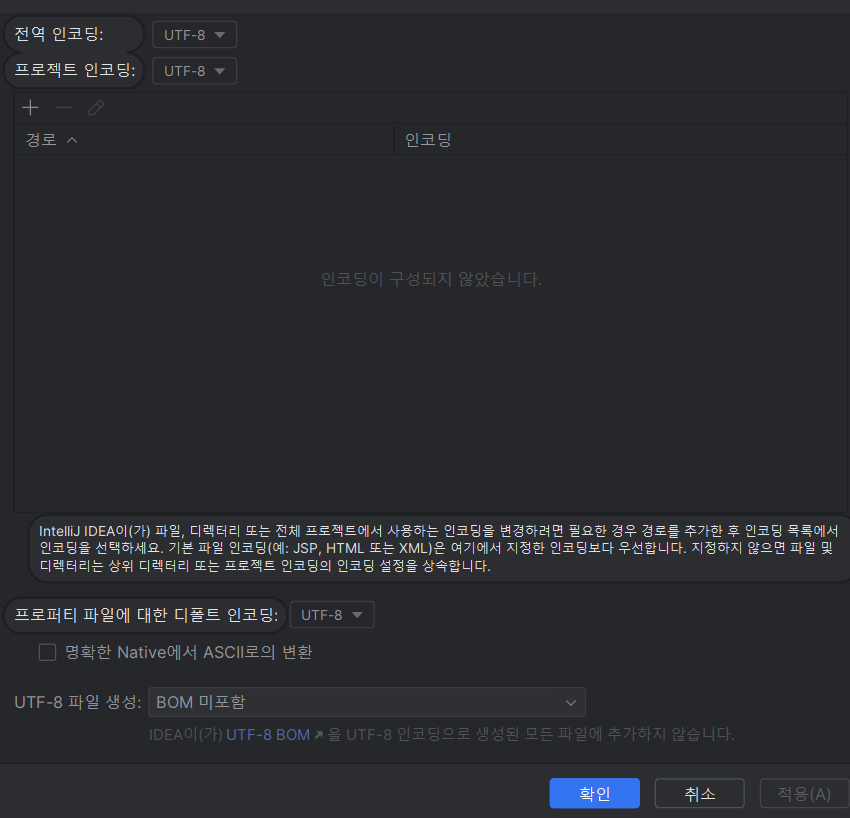
- 인코딩 설정을 utf-8로 변경하여 인코딩을 맞춘 후 사용하면 한글도 깨지지 않는다!
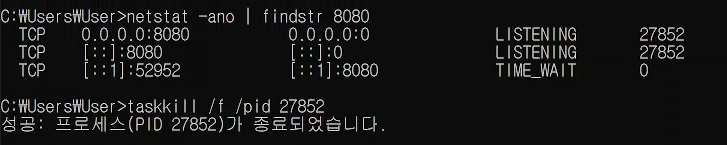
🤔 Web server failed to start. Port 8080 was already in use. 문제
- 8080 포트가 어디에서 사용되는지 확인하는 명령어(cmd)
netstat -ano | findstr 8080- 사용되는 포트를 종료시키는 명령어(cmd)
taskkill /f /pid 27852POST
- post 방식은 리소스를 추가하는 것을 의미한다 -> create
- 멱등성, 안정성 모두 없다
- path variable을 가질 수 있고
- 특정 데이터의 필터링을 사용하는 QueryParameter는 적절하지 않다
- http Body를 이용해 데이터를 전송한다
지금까지 get방식으로 데이터를 받을 때는, 특별한 객체 없이 @RequestParam을 통해 쿼리 파라미터를 받을 수 있었다
- 그런데, ✅ POST 방식은 default로 객체로 받아야 한다!
@RequestBody라는 어노테이션을 사용하는데 PUT, POST 방식에서 Http Body로 들어오는 데이터를 해당 객체에다가 매핑을 해주는 역할을 한다- 먼저 데이터를 받을 객체를 만든다
- 이 때, 순수한 엔티티를 위한 데이터 전송만을 위한 DTO객체를 만들어주는 것이 좋다
BookRequest
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class BookRequest {
private String name;
private String number;
private String category;
}@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "/api")
public class PostApiController {
@PostMapping("/post")
// http://localhost:8080/api/post
public BookRequest post(
@RequestBody BookRequest bookRequest
){
log.info(bookRequest.toString());
return bookRequest;
}
}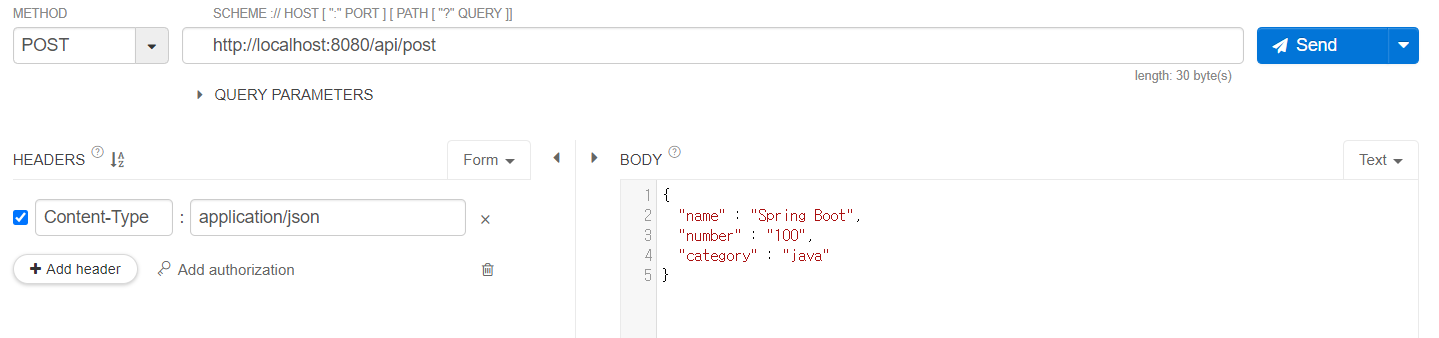
- post방식으로 json타입을 보내면
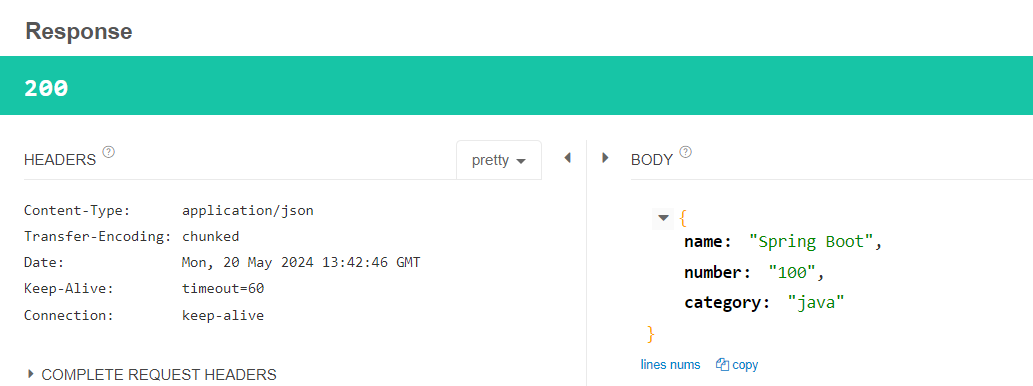
- 응답으로 Content-Type이
application/json으로 json 타입의 데이터가 Body에 실려오는 것을 알 수 있다
🤔 만약 return 타입을 String으로 보낸다면...?
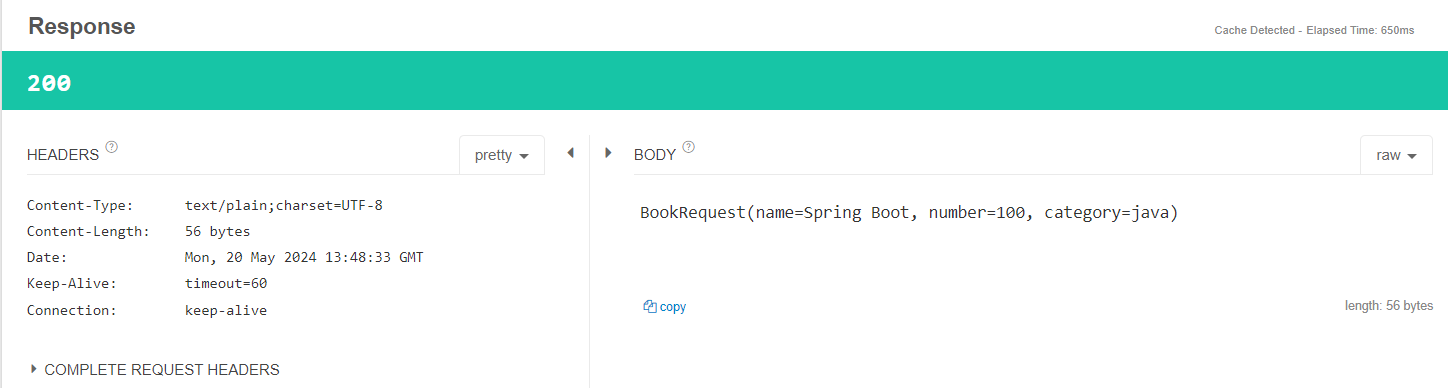
- 응답으로 Content-Type이
text/plain;charset=UTF-8로 오는 것을 확인할 수 있다!
Json의 형식
{
"key" : "value",
"array" : [
10,
20,
30
],
"string_array" : [
"홍길동","이순신","유관순"
],
"object_array" : [
{
"name" : "홍길동"
},
{
"name" : "이순신"
},
{
"name" : "유관순"
}
]
}- json안에는 여러 데이터 들이 들어갈 수 있다
- 제네릭과, 공통스펙을 지정해서 범용성 있게 만들어줘야 한다
- https://velog.io/@yys/2.%EB%B0%B0%EB%8B%AC%ED%94%8C%EB%9E%AB%ED%8F%BC-API-%EA%B3%B5%ED%86%B5-%EC%8A%A4%ED%8E%99-%EC%A0%95%EC%9D%98
- 예전에 만들었던, 공통 스펙을 참고하자!
Snake case, Camel case
- 항상 java를 통해 만들다 보니 java 컨밴션인 Camel case를 가지고 지정해서 아무 문제가 없었다..

- 이렇게 snake case로 -> http body 메시지가 온다면...?
- 우리 java의 DTO나 Entity는 Camel case 컨밴션을 따르기 때문에, 값이 들어가지 않을 것이다!
- 그렇기에 snake case로 변경 하는 방법을 알아야 한다
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategies.SnakeCaseStrategy.class) - 다음 어노테이션은, 헤당 클래스의 변수들을 snake_case로 매핑하겠다!는 의미이다!
- 더 나아가, 전역적으로 snake case, camel case를 설정하는 방법을 알아놔야겠다!
🤔 Entity,Dto에서 Wrapper vs primative 타입
- 앞단에서 쿼리 파라미터에서는 null을 받으면 404 에러가 나므로, primative타입을 사용하자고 했다
- Entity,Dto에서는 Wrapper 클래스를 써주자!
- primative 타입은 null이면 0을 넣기 때문에, 🤔값이 들어가지 않았는데 들어간 것 처럼 볼 수 있다
- null을 허용하는 Wrapper클래스로 Entity나 Dto에 사용하자!
Put
- post와 차이점 : 기본이 리소스 갱신, 없다면 생성한다 -> create, update
- 멱등하다! (요청할때마다 갱신, 없다면 생성해서 -> 항상 같은 응답)
- 안정성은 없다
- post와 마찬가지로, path variable을 가질 수 있고, 데이터를 필터링하는 query parameter는 사용하지 않는다
- http body에 data를 넣어서 보내준다
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "/api")
public class PutApiController {
@PutMapping("/put")
public void put(
@RequestBody
UserRequest userRequest
){
log.info("Request : {}", userRequest);
}
}UserRequest
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategies.SnakeCaseStrategy.class) // 헤당 클래스의 변수들을 snake_case로 매핑하겠다!
public class UserRequest {
private String userName;
private String userAge;
private String email;
private boolean isKorean;
}🤔boolean? Boolean?
- 원시형과 참조형 뭐를 쓸까? -> 이번엔 기본값을 false로 지정하기 위해서 원시형을 썼다
- 그런데...
- primitive type에서 is 시리즈는 boolean을 듯하기 때문에 setIsKorean이 아닌 SetKorean으로 만들어진다
- 다음을 요청해도, 우리는 false를 받게 된다
- 해결방법 1. korean으로 요청한다
- 하지만 이는, json에 우리가 전송하는 파라미터의 의미를 제대로 전달하지 못한다
- 해결방법 2. wrapper 클래스인 Boolean으로 바꾼다
- wrapper 클래스로 바꾸자 잘 들어간 것을 볼 수 있다!
Delete
- 리소스를 삭제한다
- 멱등하다(리소스가 있으면 삭제, 없으면 없는 상태 유지)
- 당연히 안정선은 없다
- path variable을 받을 수 있고, 데이터를 필터링하는 query parameter을 받을 수 있다
- Databody에는 내용을 넣지 않는다
@DeleteMapping(path = {
"/user/{userName}/delete",
"/user/{userName}/del"}) // path로 명시 하면 {}안에 여러 주소를 넣어줄 수 있다
public void delete(
@PathVariable("userName") String userName
){
log.info("user-name : {}",userName);
}path =?
- RequestMapping 시리즈에, controller가 담당할 주소를 적어주었다
- 이때 path 라는 파라미터를 사용하면 -> 여러개의 주소를 {}안에 적어줄 수 있다